week 3 block 4 FOME
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Basiliximab MOA
Binds IL-2R (CD25) → blocks T cell proliferation
Anaphylaxis affect on the cardiovascular system
hypotension
Example of Type III hypersensitivity?
Serum sickness (immune complex deposition)
Example of Type II hypersensitivity?
Transfusion reaction (IgM/IgG against cells)
What are the two phases of a Type I hypersensitivity reaction?
Immediate (minutes) and Late phase (hours)
What mediators are released during immediate Type I reaction?
Histamine, tryptase, leukotrienes
What causes the late-phase response in Type I hypersensitivity?
Leukotrienes attracting eosinophils, causing inflammation
What skin findings suggest anaphylaxis?
Flushing, pruritis, urticaria, angioedema
What defines refractory anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis not responsive to IM epinephrine
Why give H1/H2 blockers (antihistamines)?
For symptom relief of cutaneous symptoms only (e.g., itching)
What are the three diagnostic criteria for anaphylaxis?
Acute mucocutaneous symptoms + respiratory or hypotension
Two or more symptoms rapidly after allergen exposure
Hypotension after known allergen exposure
What does the T cell receptor recognize?
Peptide antigens that are bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules.
What does polymorphism of major histocompatibility complex molecules affect?
Binding and presentation of peptide antigens to T cells.
What type of antigen does major histocompatibility complex class I present?
Intracellular peptides from viruses or self-proteins.
What part of major histocompatibility complex class I binds to the cluster of differentiation 8 molecule?
The alpha-3 domain of the major histocompatibility complex class I alpha chain.
What is the role of transporter associated with antigen processing?
Transports peptides into the endoplasmic reticulum to load onto major histocompatibility complex class I molecules.
What type of antigen does major histocompatibility complex class II present?
Extracellular peptides from bacteria or soluble proteins.
What molecules strengthen adhesion between T cells and antigen-presenting cells?
Leukocyte function-associated antigen on T cells binds intercellular adhesion molecules on antigen-presenting cells.
What are the four steps of T cell activation?
Antigen recognition → Activation → Clonal expansion → Differentiation into effector and memory cells.
What is the mixed lymphocyte reaction?
Measures how much the recipient’s T cells proliferate in response to donor major histocompatibility complex molecules.
What is a cross-match test?
Tests if the recipient’s serum contains antibodies that bind to donor leukocytes.
What diseases are associated with a loss of tolerance?
Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, Graves disease, inflammatory bowel disease.
What causes autoimmunity related to major histocompatibility complex class I?
Loss of tolerance leads to activation of self-reactive cluster of differentiation 8 positive T cells by self-peptides.
How do superantigens activate T cells?
Bind outside of the normal peptide-major histocompatibility complex recognition site, causing massive nonspecific activation.
What happens if a T cell gets signal 1 without signal 2?
The T cell becomes anergic (nonresponsive).
What are the two signals needed to activate a naïve T cell?
Signal 1: T cell receptor binds peptide-major histocompatibility complex.
Signal 2: Cluster of differentiation 28 on the T cell binds B7 molecules on the antigen-presenting cell.
Where are major histocompatibility complex class II molecules found?
On professional antigen-presenting cells like dendritic cells, macrophages, and B lymphocytes.
What part of major histocompatibility complex class II binds to the cluster of differentiation 4 molecule?
The beta-2 domain of the major histocompatibility complex class II molecule.
Which T cells recognize major histocompatibility complex class II molecules?
Cluster of differentiation 4 positive helper T cells.
What are the two signals needed to activate a naïve T cell?
Signal 1: T cell receptor binds peptide-major histocompatibility complex.
Signal 2: Cluster of differentiation 28 on the T cell binds B7 molecules on the antigen-presenting cell.
What happens if a T cell gets signal 1 without signal 2?
The T cell becomes anergic (nonresponsive).
What causes autoimmunity related to major histocompatibility complex class I?
Loss of tolerance leads to activation of self-reactive cluster of differentiation 8 positive T cells by self-peptides.
What are the four steps of T cell activation?
Antigen recognition → Activation → Clonal expansion → Differentiation into effector and memory cells.
What molecules strengthen adhesion between T cells and antigen-presenting cells?
Leukocyte function-associated antigen on T cells binds intercellular adhesion molecules on antigen-presenting cells.
What is a cross-match test?
Test for preformed antibodies in transplant recipients to prevent hyperacute rejection.
What is the function of the CD3 and zeta chains on T cells?
Transmit activation signals from TCR to the inside of the T cell.
What is the role of TH1 cells?
Activate macrophages to kill intracellular microbes.
What is central T lymphocyte tolerance?
Negative selection in thymus → apoptosis of self-reactive T cells.
What is the role of FOXP3?
controls genes regulating Treg (regulatory T cell) function.
How do checkpoint inhibitors work?
Block molecules like CTLA-4 or PD-1 to boost T cell activation against tumors.
What is chronic rejection?
Months to years; fibrosis and gradual graft loss.
What is allo-reactive T cell?
T cell that reacts to non-self MHC from another individual.
Why are dendritic cells better than macrophages at activating naive T cells?
Dendritic cells are migratory and express high MHC II + co-stimulators.
What type of immune defect is associated with Histoplasmosis?
Th1 impairment → poor macrophage activation.
How do checkpoint inhibitors work?
Block molecules like CTLA-4 or PD-1 to boost T cell activation against tumors.
What is the function of the CD3 and zeta chains on T cells?
Transmit activation signals from TCR to the inside of the T cell.
What cytokines are associated with TH1 and TH2 cells?
TH1 = IFN-γ.
TH2 = IL-4, IL-5
Where are central memory T cells found?
Lymphoid organs → allow rapid clonal expansion after re-exposure.
What is central T lymphocyte tolerance?
Negative selection in thymus → apoptosis of self-reactive T cells
What is peripheral T lymphocyte tolerance?
Mature T cells become anergic, suppressed by Tregs, or undergo deletion.
How does CTLA-4 affect T cells?
Inhibits T cell activation by binding B7, blocking costimulation.
What is the role of FOXP3?
FOXP3 controls genes regulating Treg (regulatory T cell) function.
What is activation-induced cell death?
Self-antigen recognition triggers apoptosis via Fas/FasL.
What are the main transplantation antigens?
MHC (HLA) proteins.
What is direct vs indirect allorecognition in transplants?
Direct: Recipient T cells recognize donor MHC directly.
Indirect: Recipient APCs present donor peptides.
Alemtuzumab MOA
Binds CD52 on T/B cells → direct lysis
Glucocorticoids
Bind GR → translocate to nucleus → modulate gene transcription
Alemtuzumab black box warning
Life-threatening infusion reactions, autoimmune cytopenias, malignanc
rATG blackbox warning
Cytokine release, PTLD, serious infection
Glucocorticoids blackbox warning
Long-term use → serious metabolic & skeletal effects
Mycophenolate mofetil must not be given to
pregnant women
CD8 Role
targets intracellular pathogens & tumors
CD4 Role
regulator of adaptive IR
Preferred test for Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Dihydrorhodamine: DHR Flow Cytometry assay
Nitroblue Tetrazolium: NBT Works too
CD 19 and 20 are markers for
B cells
In DiGeorge and Severe immune deficiency disorder, patient lack a
Thymic shadow
IgE is a common type of —-
type 1 hypersensitivity
Wegner’s Granulomatosis Is
C-ANCA Mediated
CD 4 is mainly on
Helper and inducer T cells
CD8 is mainly on
Cytotoxic T cells and some NK cells
p-ANCA (perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies) is associated with
Microscopic polyangiitis
Decreased B lymphocytes:
X-linked Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia (commonly in male patients)
Tuberculin skin test:
Delayed (Type IV) hypersensitivity; requires antigen-presenting cells and cluster of differentiation 4 T lymphocytes
Interferon-gamma release assay:
Used to detect latent or active tuberculosis
Serum protein electrophoresis works by
Detects M protein spike in gamma region
Serum protein electrophoresis is used to diagnose
Multiple myeloma (usually immunoglobulin G or A)
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (typically immunoglobulin M)
Indirect Coombs: Detects
unbound antibodies in patient plasma
Positive result Of the Coombs test
Agglutination (clumping) due to cross-linking antibodies
Decreased immunoglobulin A is in
Celiac disease
Increased in all immunoglobulin classes Could indicate
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
LYMPHOCYTE ADHESION DEFECT that affects selectins
type 2
Type I
Defect in beta-2 integrin (cluster of differentiation 11/18)
Type II lymphocyte adhesion defects
Absence of fucose (defect in selectin binding)
Type III LYMPHOCYTE ADHESION
Defect in beta-1, beta-2, and beta-3 integrins
C5 through C9:
increased risk of Neisseria bacteremia
C3 and C4:
low levels in lupus nephritis (consumption)
C3:
low in post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (deposition)
preferred calcineurin inhibitor
Tacrolimus
What system responds in the first 12 hours to an infection
Innate immune system
Mast cells, NK cells and ILCs, dendritic cells, phagocytes, epithelial barriers,
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome Underlying cause
dysfunctional lysosomes
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome Symptoms
-Pale skin and unique eyes
-Cranial and peripheral neuropathies (muscle weakness,
ataxia, sensory loss)
-
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency Signs and symptoms
Delayed umbilical cord separation at birth
• Recurrent necrotic S. aureus infections without pus
Selective IgA Deficiency Can only be diagnosed after
4yo
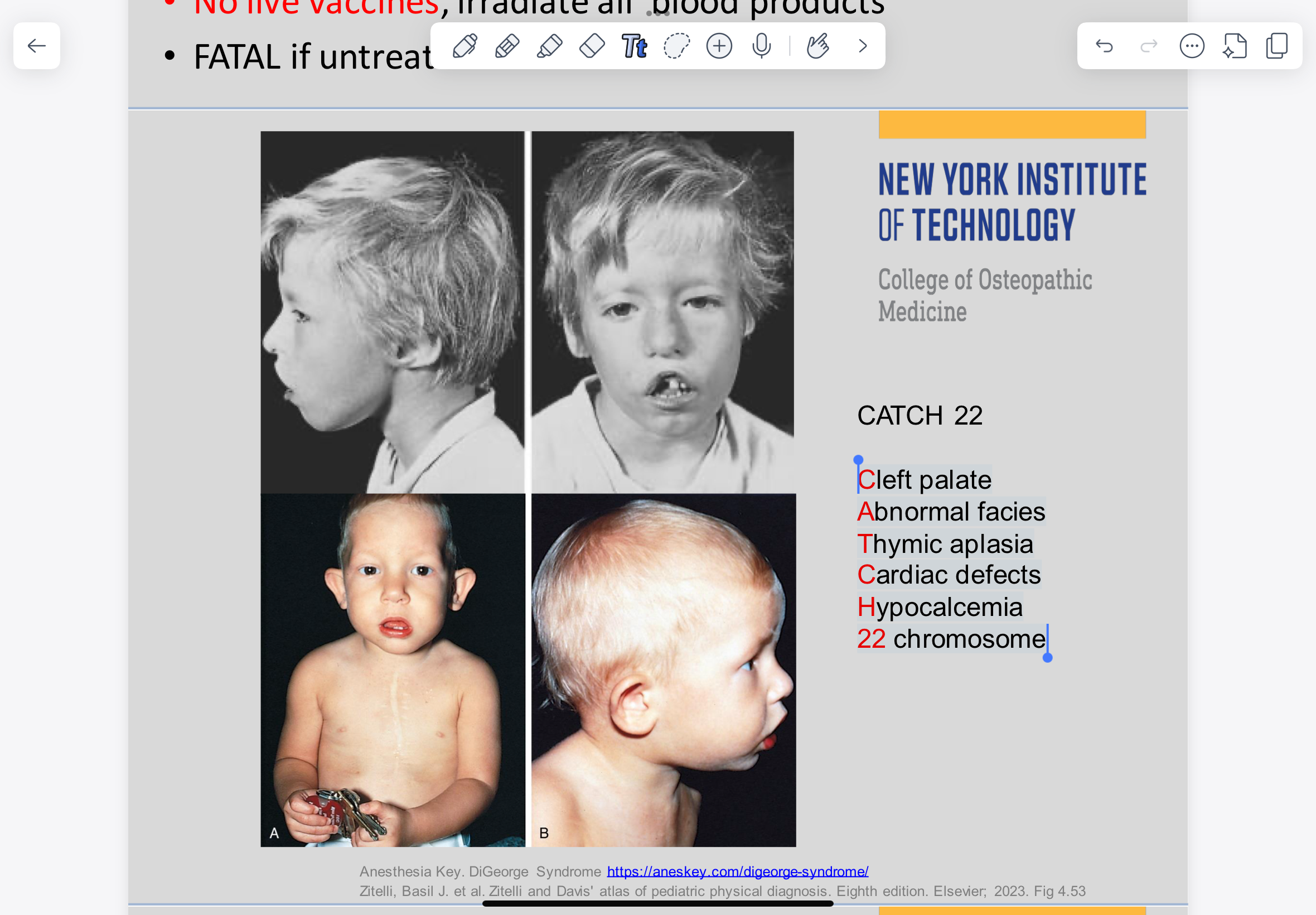
DiGeorge Syndrome Signs and symptoms
Cleft palate Abnormal facies Thymic aplasia Cardiac defects Hypocalcemia 22 chromosome
nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test diagnoses
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Chronic Granulomatous Disease Infected with
catalase + bacteria
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome is diagnosed by
peroxidase + lysosomal granules in neutrophils
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency Is caused by a mutation in the gene encoding for
CD18 adhesion molecule
Recurrent sinopulmonary and Mycoplasma
infections is common in
CVID (Common Variable Immunodeficiency)