macromolecules
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what breaks down carbohydrates/.starches into maltose(disaccharide)
amylase
what breaks down proteins
pepsin
what breaks down lipids
lipace
what is an essential amino acid
one that the body can’t make on it’s own
what does the oral cavity do
-contains salivary amylase which breaks down starches
-food is also mechanically broekn down my teeth
extra: digestion starts here
what does the esophagus do
food moves down here into the stomach via peristalsis
what does the stomach do
-pepsin breaks down proteins
-the stomach secretes HCL to create the acidic enviro for protein breakdown
what does the small intestine do
-contains the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
-contains pancreatic amylase + lipase which digests carbohydrates + lipids
-bile emulsifies fats + lipid breakdown
what does the large intestine do
-Absorbs water and forms feces
-what is the path of food throughout the body
Mouth
esophagus
stomach
small intestine(duodenum, jejunum, and ileum)
large intestine
rectum
anus
what does lipase do specifically with breaking down lipids
-catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides into fatty acids + monoglycerides
-they are then absorbed by the small intestine
what do bile salts do
they mif large fat droplets into smaller ones, increasing the surface area for lipase action, aiidng in fat breakdown
what does the stomach do
breaks down proteins using pepsin
into smaller peptides
HCL=also here for protein breakdown
what is the optimal condition for pepsin activity
pH of 1.5-2.0
explain the difference with biuret reagants reacting with peptide bonds that are whole peptides, and short peptides
whole proteins: the solution turns purple because the reagant reacts wiht long-chain polypeptides
short peptides: the solution may appear light purple or slightly pink because the reagent reacts wiht fewer peptide bonds

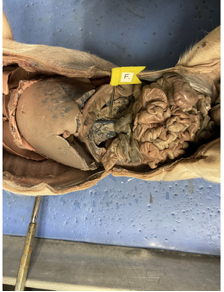
what is this
esophagus
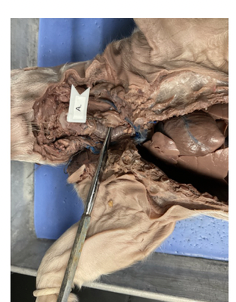
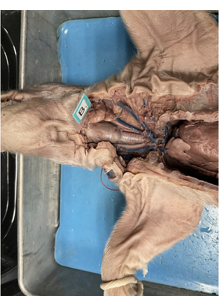
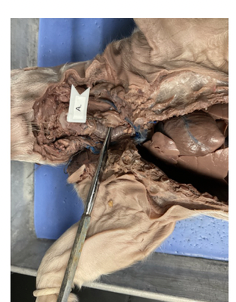
what is this
salivary gland
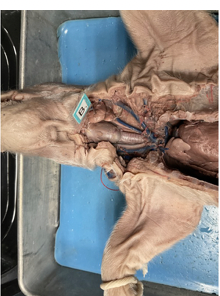
what is this
cecum
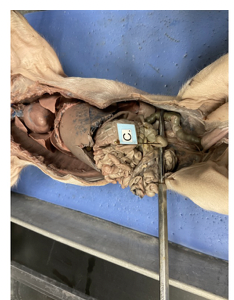
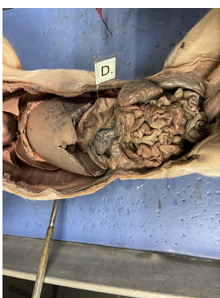
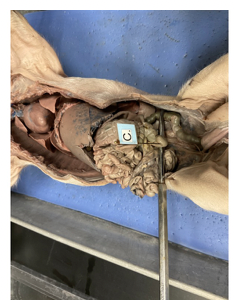
what is this
stomach
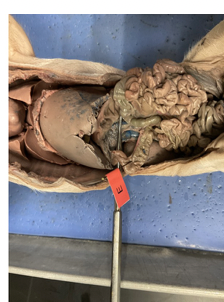
what is this
the duodenum
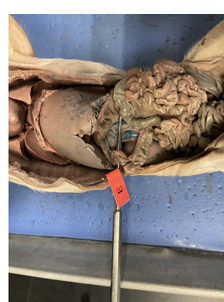
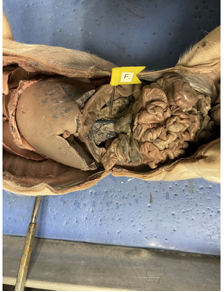
what is this
pancreas