CINE 100- Cinematography
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Cinematography
'writing in movment', art and technique of capturing images on film or digitally to tell a story visually.
Tonality
considering how light registers on film
Contrast
refers to the difference between the darkest and lightest areas of the frame
Exposure
regulates how much light passes through the camera lens
Tinting
accomplished by dipping the already developed film into a bath of dye. The dark areas remain black and gray, while the lighter areas pick up the color
Toning
Colors the darker areas of the film, leaving highlights mostly unchanged
Speed of Motion
how fast or slow movement appears on screen, which depends on the frame rate at which the film is shot and projected.
Normal motion
filmed and projected at the tandard frame rate (24 frames per second) → looks natural
Slow motion
filmed at a higher frame rate and projected at normal speed → movement appears slower and more dramatic
Fast motion
filmed at a lower frame rate and projected at normal speed → movement appears faster and sometimes comedic or frantic
Ramping
technique where the speed of motion changes within a single shot.
Time-lapse cinematography
permits us to see the sun set in seconds or a flower sprout bloom in a minute. For this, a very low shooting speed is required, perhaps one frame per minute, hour, or even day
High-speed cinematography
such as recording a bullet shattering glass, the camera may expose hundreds or thousands of frames per second
Wide-angle (short focal length)
captures a wide field of view, objects appear smaller and farther apart (less than 35mm)
Standard (middle focal length)
view similar to human vision, objects appear natural and proportionate
Telephoto (long focal length)
captures a narrow field of view, objects appear closer together and larger (around 100mm)
Zoom
adjusting the lens to magnify or shrink the subject in the frame without moving the camera
Depth of field
refers to the range of distance in a shot that appears acceptably sharp and in focus
Selective focus
Only one part of the shot is in sharp focus; the rest is blurred
Deep focus
Everything in the frame, from foreground to background, is in sharp focus
Racking/pulling focus
used to switch our attention between foreground and background making one plane blurred and another sharp
Superimposition
technique where two or more images are layered on top of each other in the same frame
Composite
combining multiple images into one seamless shot for visual storytelling or effects
Rear projection
pre-filmed footage is projected onto a screen behind the actors, creating the illusion that they are in a different location
Matte work
the art of blending filmed footage with painted or digital images to create scenes that don't exist in real life
Framing
how filmmakers choose to arrange people, objects, and space inside the camera's view to create meaning, mood, and focus for the audience
On-screen space
everything the audience can see inside the frame, includes characters, objects, settings, and actions that are visible (ex: a character walking across a room that the camera shows)
Off-screen space
everything that exists outside the frame, but the audience knows (or senses) it's there. Filmmakers suggest off-screen space through sound, character reactions, or camera movement. (ex: A character looks to the side and reacts to someone we don't see but know is there)
Angle
The direction from which the camera views the subject
Level
Refers to the horizontal alignment of the camera relative to the subject.
Canted (dutch) angle
Camera is tilted sideways so the horizon isn't level creating disorientation/uneasy effects
Height
refers to how high or low the camera is placed. Even with the same angle, changing height alters composition
Camera Distance
How close or far the subject appears in the frame
Extreme long shot (ELS)
subject tiny, background dominates
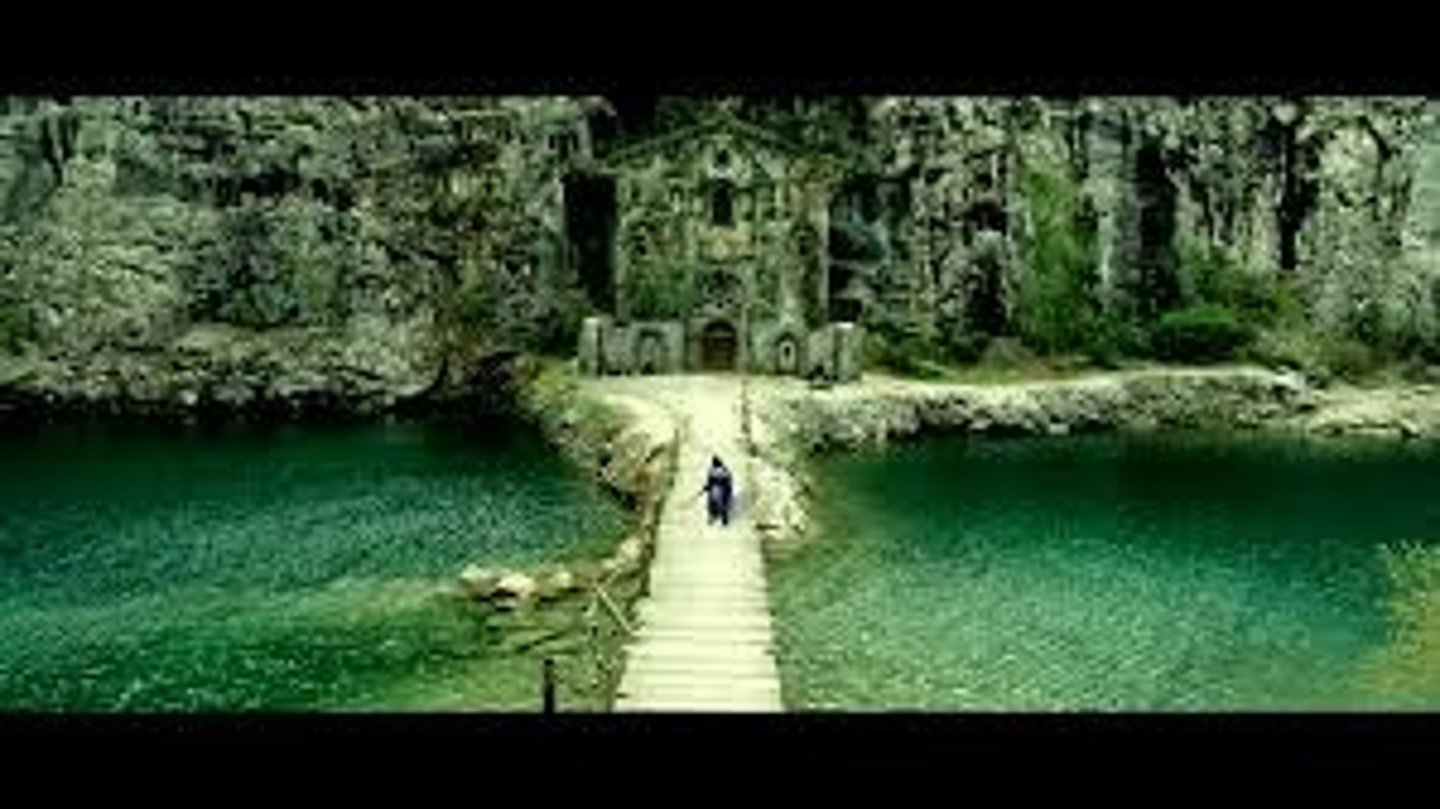

Long shot (LS)
full-body view of the subject plus surrounding space
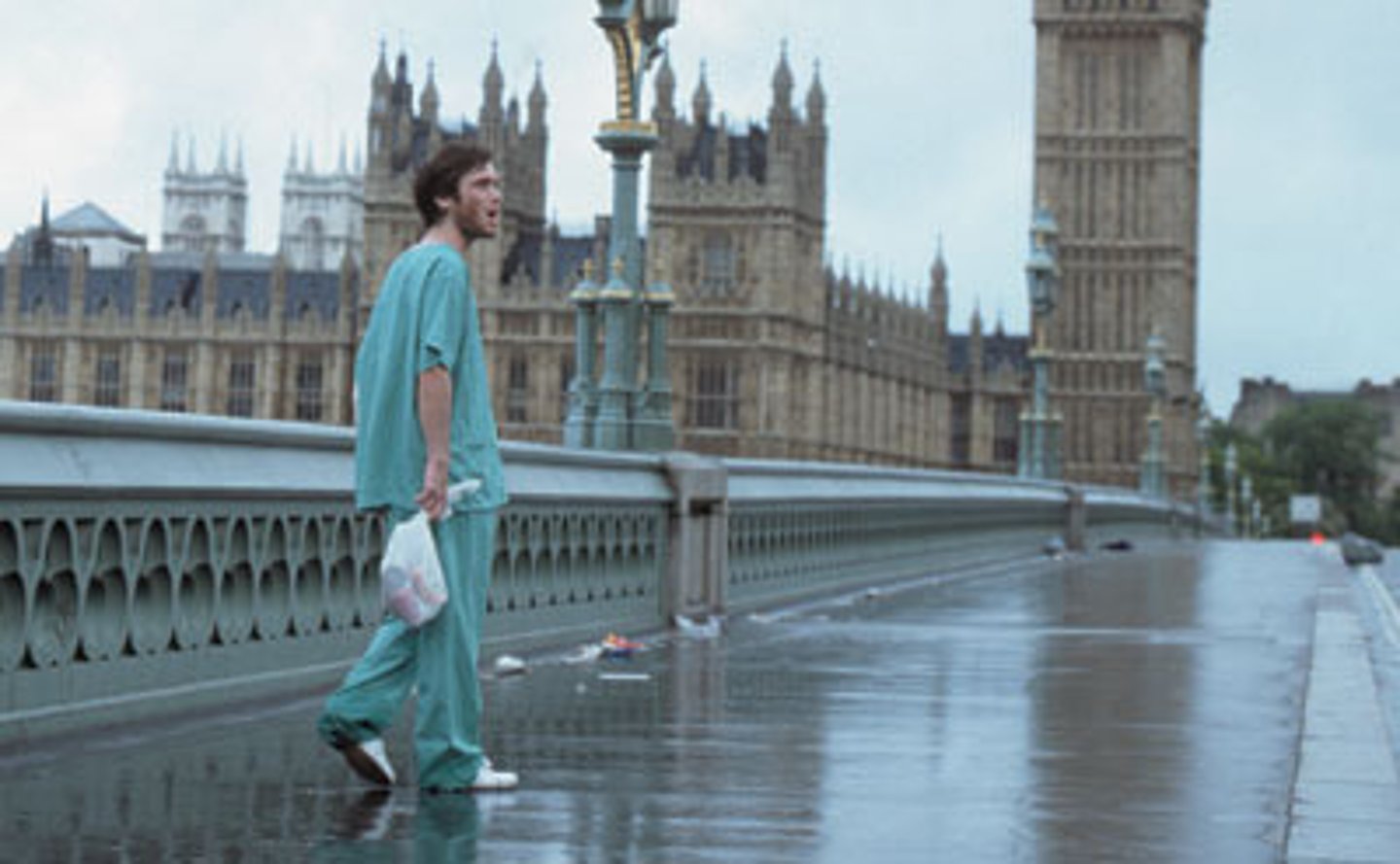

Medium long shot (MLS)
knees up; balances figure + surroundings
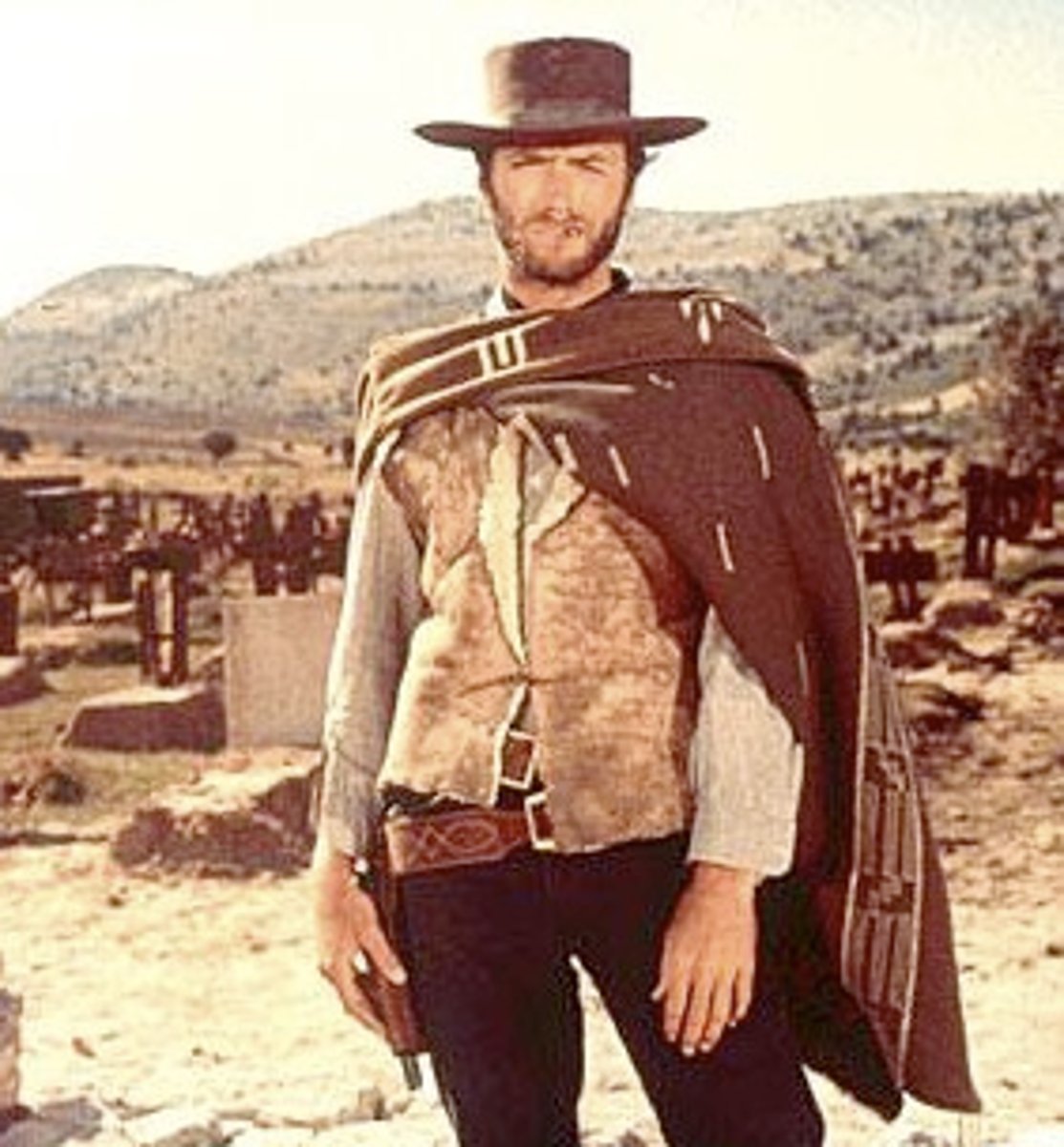

Medium shot (MS)
waist up; shows gestures & expressions

Medium close up (MCU)
chest up
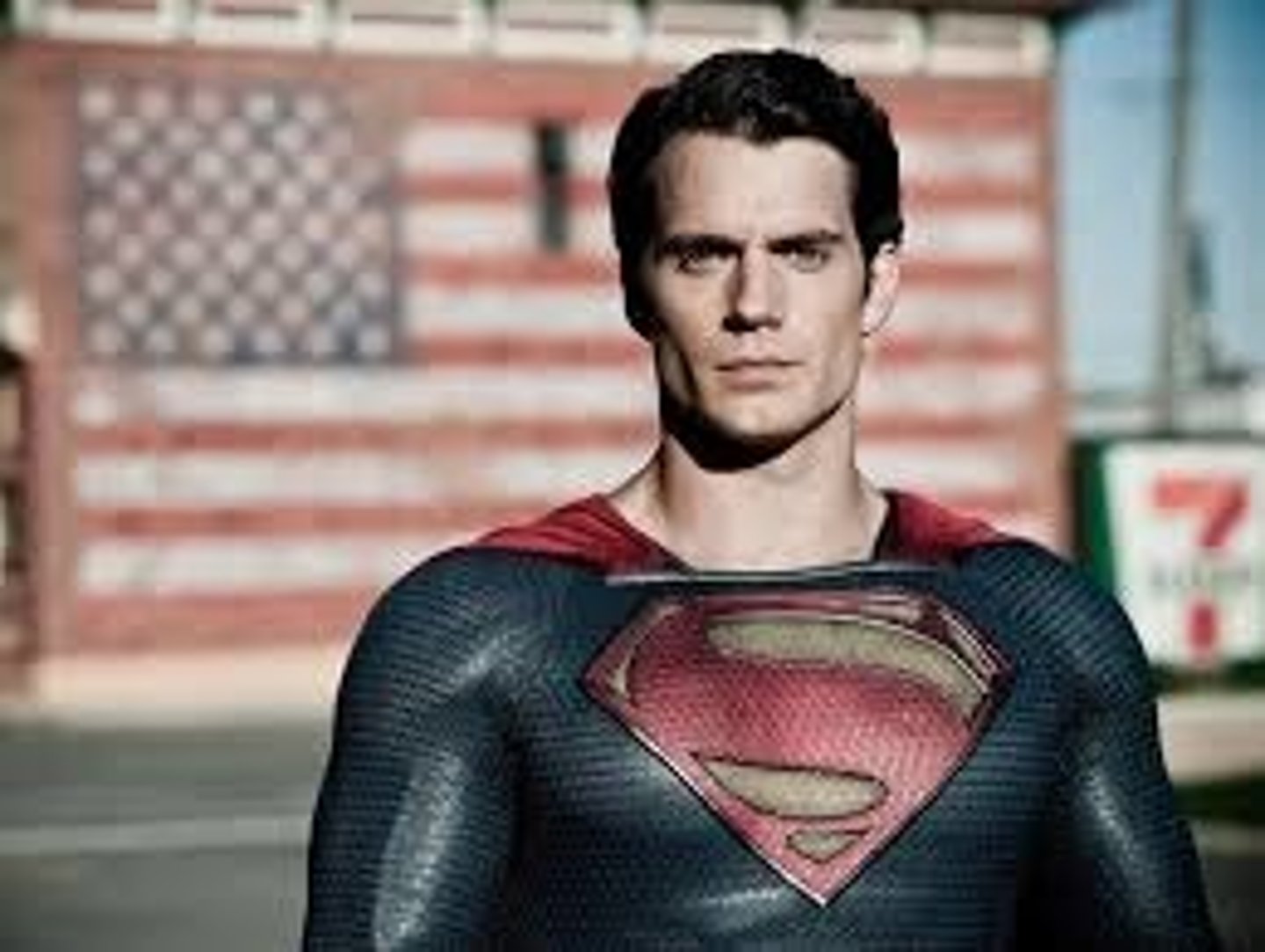

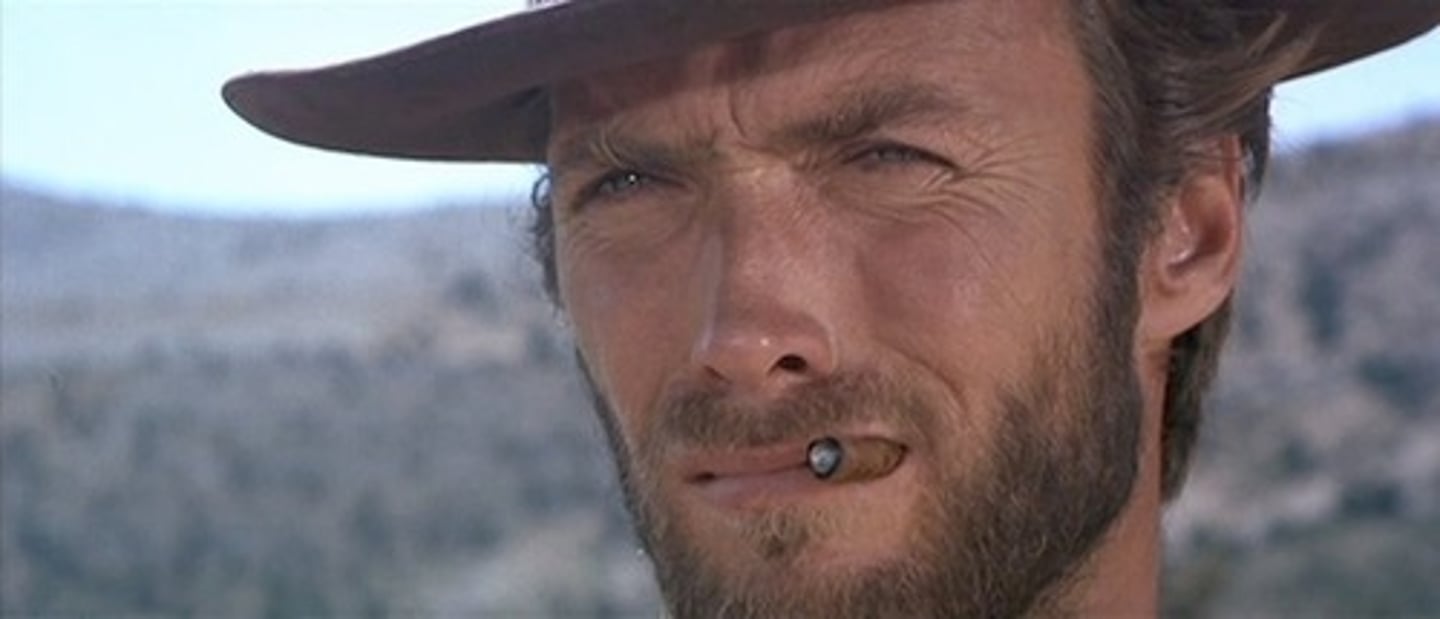
Close up (CU)
face, hands, objects, emphasizes detail & emotion

Extreme close up (ECU)
magnifies a small part (eye, object)
Mobile framing
changing the composition of the shot by moving the camera during filming
Pan
Rotating the camera horizontally from a fixed position → scans the scene left or right
Tilt
Rotating the camera vertically from a fixed position → looks up or down.
Track
Moving the camera alongside or following a subject, usually on tracks → follows action smoothly
Dolly
Camera mounted on a wheeled platform that moves toward or away from the subject → creates push-in or pull-back effect
Crane
Camera mounted on a crane or jib → moves up, down, or across large spaces → gives sweeping, dramatic shots
Aspect ratio
the ratio of the frame widthto the frame height
shot scale
refers to how much of a subject or scene is visible in the frame
Long take
a single shot thatruns for a long period of time