AQA GCSE Geography - The Changing Economic World
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
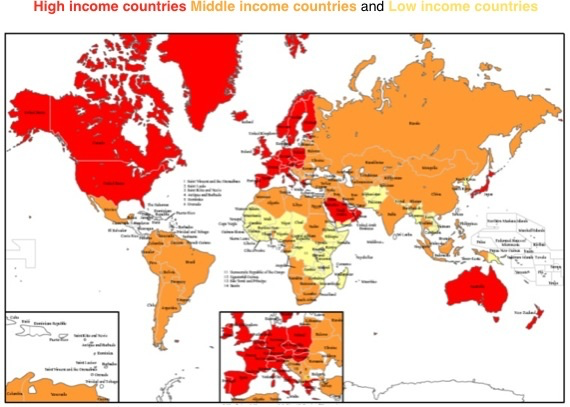
LIC (Low Income Country)
GNI per capita: <US$1,045
~30 countries
NEE (Newly Emerging Economy)
GNI per capita: US$1,045-12,736
~80 countries
HIC (High Income Country)
GNI per capita: >US$12,736
~80 countries
GNI per capita
The total value of goods and services produced by a country divided by its population
Birth rate
How many people are born in a country each year
Death rate
How many people die in a country each year
IMR (Infant Mortality Rate)
The number of deaths of children less than 1 year old per 1,000 births
Life expectancy
The average number of years a person can expect to live
People per doctor
The number of people who depend on a single doctor for healthcare needs
Literacy rate
The % of a country’s population that has basic reading/writing skills
Access to safe water
The percentage of people who have access to water that does not carry a health risk
HDI (Human Development Index)
Accounts for income, life expectancy and education. Combines these factors for a 0-1 variable signifying development
DTM stage 1
Very high, fluctuating birth/death rate, very low population
DTM stage 2
High birth rate, sharp fall in death rate, growing population
DTM stage 3
Birth rates fall, death rates plateau at a low level, population grows rapidly
DTM stage 4
Very low, fluctuating birth/death rates, population peaks
DTM stage 5
Birth rate stagnates, death rate rises slowly, population begins to slowly decline
Causes of uneven development - Physical
• Climate - too hot/dry, less water available, barren land
• Natural disasters - earthquakes, hurricanes destroy buildings
Causes of uneven development - Economic
• Varying levels of economic development - some countries rely on agriculture, manufacturing, services
Causes of uneven development - Historical
• LIC borrowing from HICs - to initially develop, LICs took out large loans, interest has to be repaid
• Colonialism - other countries have exploited valuable resources from countries and left underdeveloped infrastructure/unstable governance
Consequences of uneven development - Wealth
• For some groups in LICs/NEEs, QoL is not improving/is worsening
• Need for aid from other countries/NGOs
Consequences of uneven development - Health
• Some countries have very low life expectancies, high IMR/death rates
• People miss days of work/school from illness, thus economy is hindered
Consequences of uneven development - International migration
• LICs → HICs - seeking better opportunities/SoL
• e.g. channel boats France → UK
• Can lead to brain drain or a smaller labour force in LICs
Investment
TNCs invest money into LICs/NEEs
• Improves taxation (better SoL)
• Can impact lots of people (mostly urban)
Aid
Comes from charities, NGOs, governments
• Boosts growth
• Can lead to dependence - political influence
• Potential mismanagement although not always monetary aid
Intermediate technology
Technology such as water pumps that doesn’t require specialists to operate
• Local communities can operate
• Not expensive to maintain, can be fixed easily
• Not very impactful on closing development gap
Industrial development
Investing in an industry hoping it will take off
• Very risky strategy
• Can yield very large profits
• e.g. BRICS, MINT nations
Fair trade
Paying extra for local products from LICs/NEEs
• Multinational, large scale
• Accusations of violating the agreement
Micro-finance loans
Small loan banks → small businesses
• Helps locals to escape poverty
• Can allow ideas to become reality
• Low risk
Debt relief
Erasing debt for an obligation
• Lowers costs from interest
• Political influence issues
• Won’t close development gap
Tourism
Attracting tourists to a country for growth
• Provides jobs, higher paid
• Puts money into local economy
• Only works for a few countries
• e.g. Tunisia