Module 1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Active Ingredient
the component of a drug which produces the intended beneficial effect
Adverse drug reaction
(ADR)
any adverse reaction either within the therapeutic range (side effects) or as the result of toxic accumulation of drug
Black box warning
Warning that contains adverse effects that have a significant risk for severe or life-threatening effects
-strongest warning from FDA
Nonproprietary name
(Generic Name)
the official generic name assigned to a drug that is no longer subject to trademark rights
Over the counter
(OTC)
drugs that don't require a prescription from a veterinarian
Proprietary name
(Trade name/Brand name)
Unique name given to drug by manufacturers
-identified by (R) or TM symbols
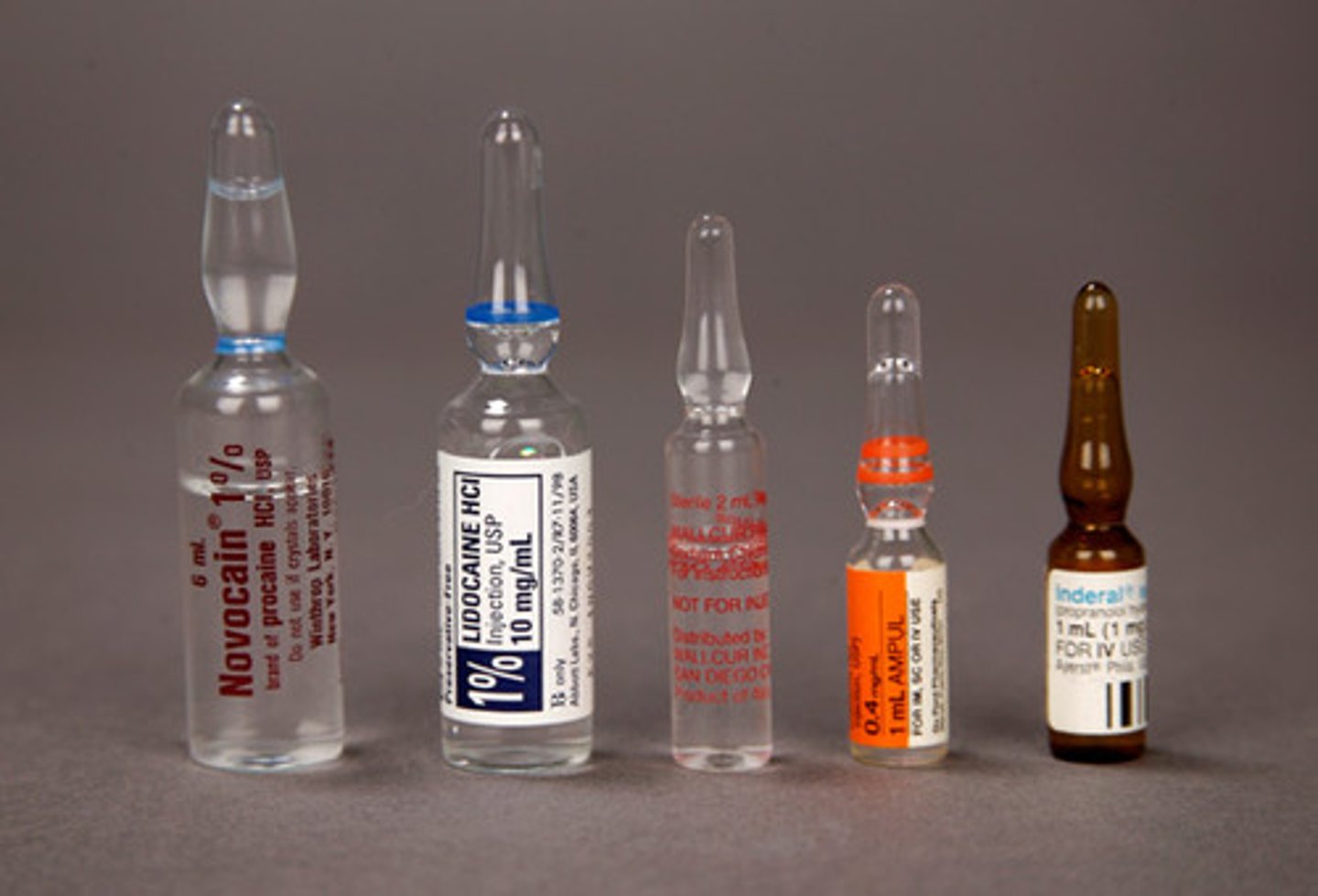
Ampules
Dosage form in which the drug is contained within a small, airtight, thin class bottle that is opened by snapping the narrow neck of the ampule bottle
Aqueous solution
A water medium i which the drug has been dissolved
Caplet
A solid dosage form that is elongated to facilitate easy swallowing
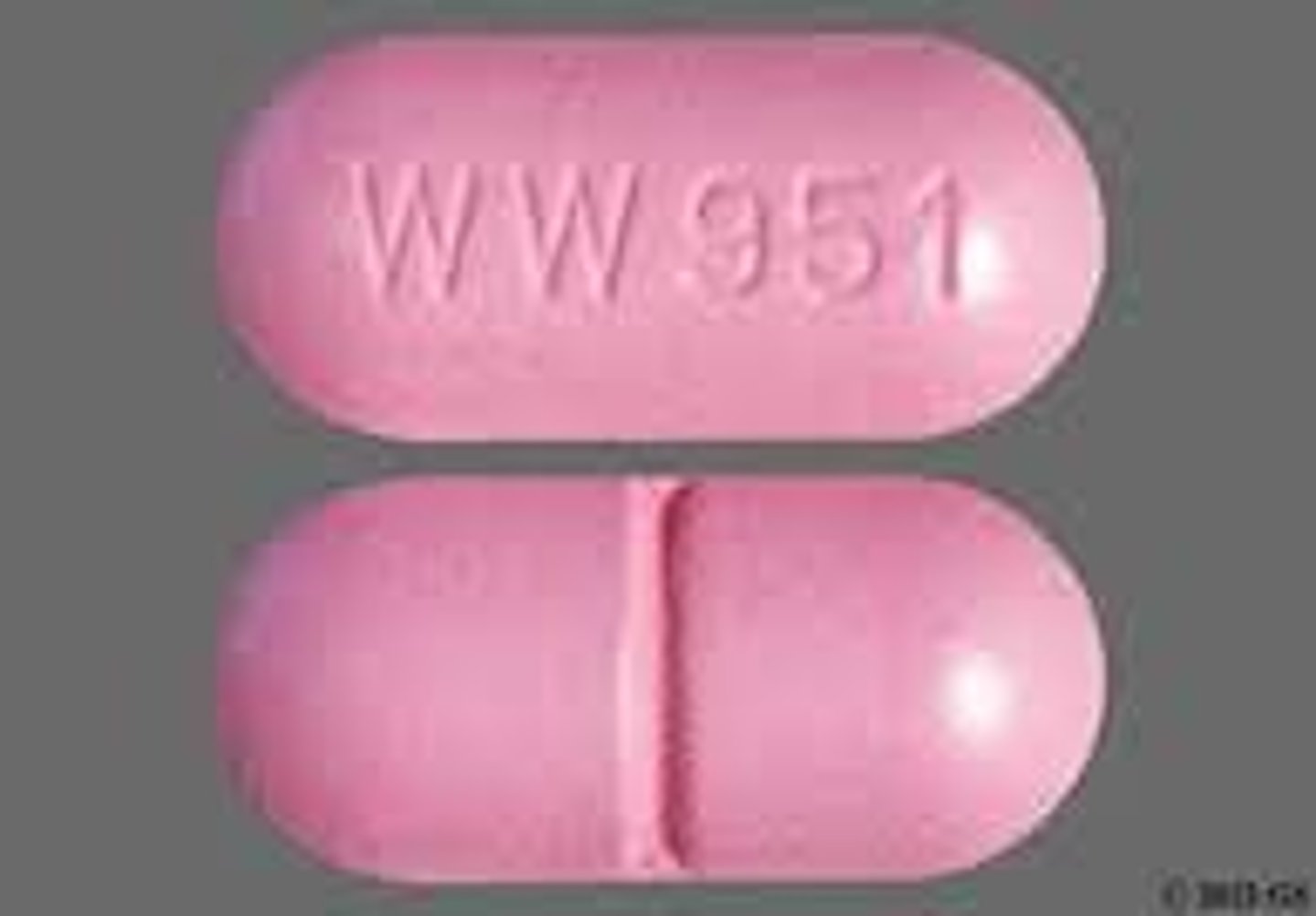

Capsules
Powdered drug surrounded by a capsule made of gelatin, modified starch, or cellulose
Elixir
Alcohol based solutions used for oral or topical application
Emulsion
Liquid suspension composed of two liquids that do not readily mix together
Enteric coating
Coating designed to protect the active ingredient from the harsh acidic environment of the stomach by not allowing the tablet to dissolve until it reached the more alkaline environment of the small intestine
Extract
A therapeutic agent composed of prepared plant or animal parts rather than synthesized chemicals in a lab
Gel caps
Powdered drug surrounded by a capsule made of gelatin
Liniments
An oily liquid preparation to be used on the skin
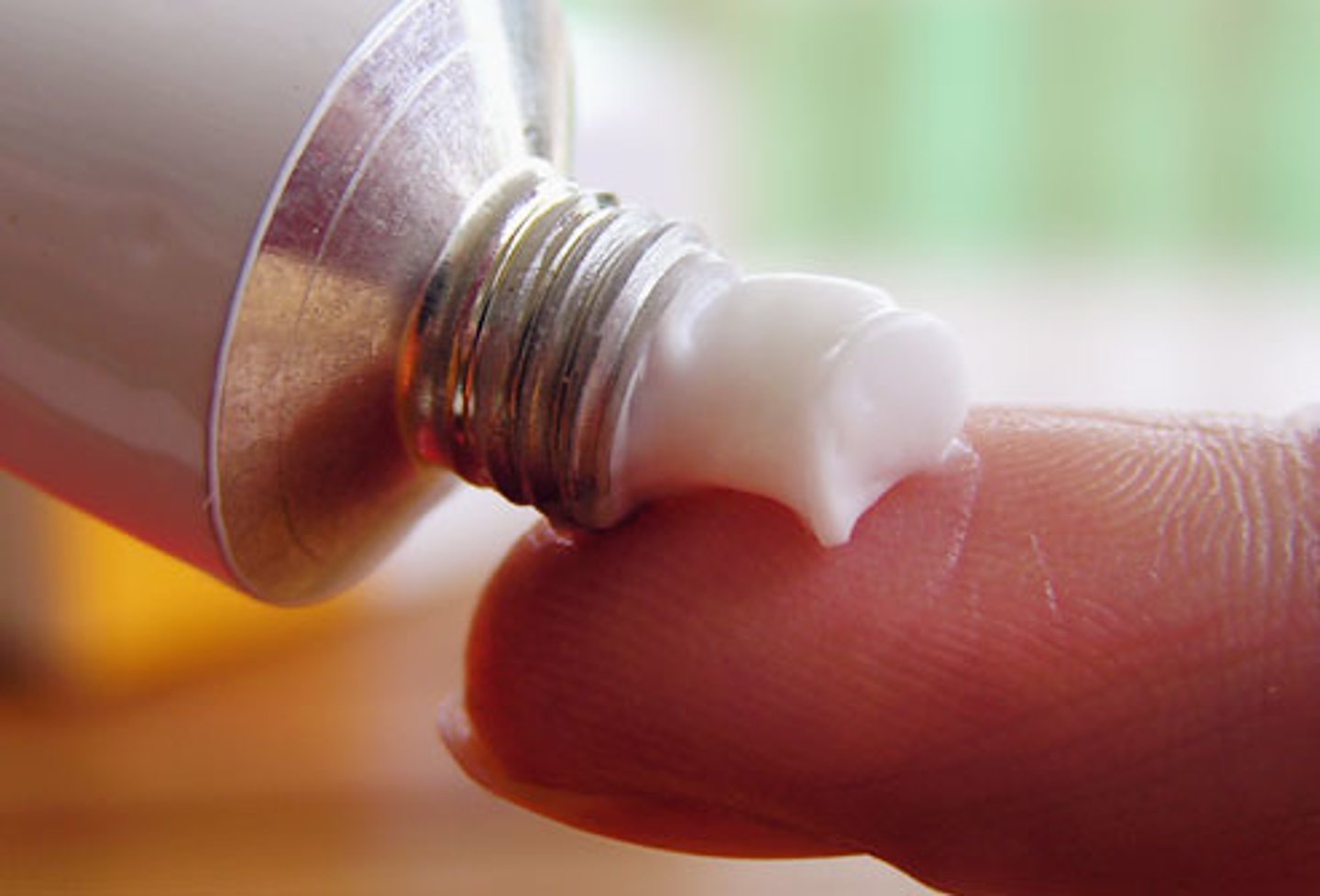
Ointment
A semisoild preparation for external application to the skin or mucous membranes
-suspensions or solutions that liquefy at body temperatures (creams/gels)
Pastes
A semisolid preparation containing one or more drug substances for topical application
-fatty pastes: thick, stiff ointments that do not flow at body temp
-gel: made form a single phase aqueous gel
Suppositories
Dosage form designed to be placed in the rectum
Suspension
A liquid preparation consisting of solid particles dispersed throughout a liquid medium in which they are not soluble
Sustained release drugs
Controlled release, coated drugs
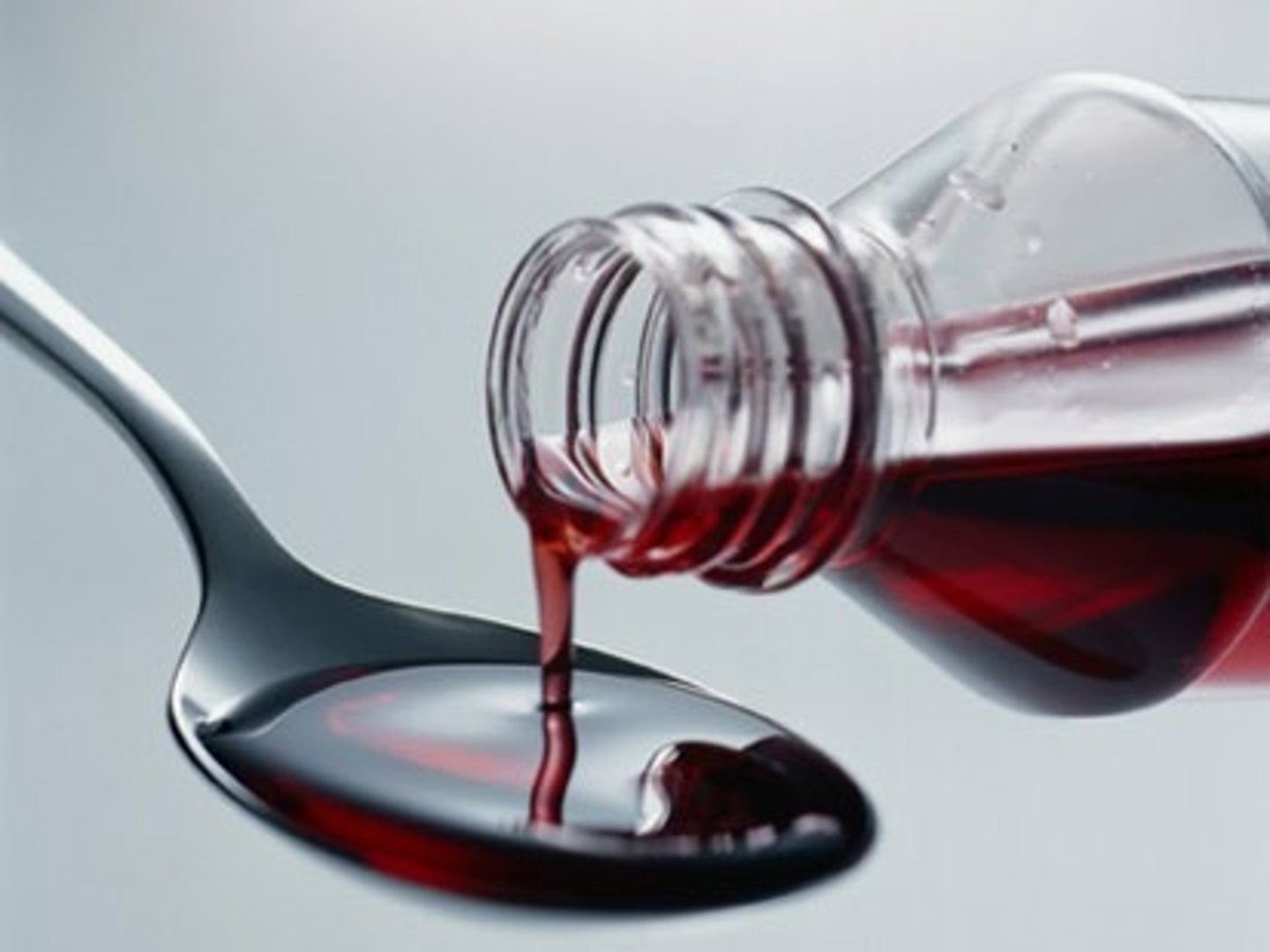
Syrups
Drugs dissolved in a liquid sugar solution

Tablets
Solid dosage form of a medicinal substances, of varying weight, size, and shape, which may be molded or compressed
Tinctures
An alcoholic or hydroalcoholic solution prepared from vegetable materials or from chemical substances
Pharmacology
the study of how drugs behave in the body
Pharmacokinetics
Study of how drugs move through the body (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion)
Pharmacodynamics
what a drug does to the body
Applied Pharmacology
applying pharmacology to specific treatments
Clinical pharmacology
applying how drugs behave in the body to a specific patient for a specific disease/treatment
Food and Drug Administration
(FDA)
The federal agency responsible for protecting public health by controlling and supervising safety standards for food, drugs, and cosmetic products
Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA)
Federal agency dedicated to protecting human health and the environment
Label use
Use of a drug in an animal in a manner that is in accordance with the approved labeling
Extra label
(Off-label)
Use of a drug in an animal in a manner that is not in accordance with the approved labeling
Package insert
Contains info mandated by FDA regulations for veterinary drugs
-will only contain information for which the manufacturer has done the mandated testing or otherwise documented in compliance with FDA requirements

Precaution
A protective measure taken in advance
-includes ADRs
Rx symbol
Symbol indication a prescription

Side effects
reactions to medicine other than the one intended
Therapeutics
The branch of medical science concerned with the treatment of disease
TM
Indicates that the name is a registered trademark owned by the company and cannot be used by other manufacturers

VCPR
Veterinary client patient relationship
-The veterinarian has examined or has adequate medical knowledge of the patient and has agreed to assume responsibility for veterinary care of the patient
Warning
More serious or frequent side effects than those found in the precautions sections
-adverse drug effects that could potentially do significant harm to the patient
Withdrawal time
Time between last dose and when the animal can be slaughtered for meat or food products
Xylitol
Artificial sweetener that causes massive release of insulin, causing hypoglycemia and liver necrosis in dogs
Contraindication
Circumstances/conditions in which a drug should not be used
Drug formularies
A collection of recipes, formulas, and prescriptions
Generic equivalent
Drugs produced or marketed by companies other than the original "brand" developer
Generic name
(Nonproprietary name)
A more concise name given to the specific chemical compound
Dosage form
Description of a drug's physical appearance
-included in the package insert/drug label
-solid, liquid, semisolid, injectable
Injectable dosage forms
Drugs administered by a needle and syringe (ampules, multidose vial, single dose vial)
Indications
specific signs or circumstances under which it is appropriate to administer a drug to a patient
Legend drugs
Drugs limited to being dispensed by a licensed prescriber (veterinarian)
-contain ingredients that have toxic effects, potential to be abused, potential to harm the patient/handler of the drug
Liquid dosage forms
drugs that are in a liquid form (syrups, suspensions, liniments, tinctures, elixirs, emulsion)
Multidose vials
Vials in which multiple doses can be withdrawn over time
Semisolid dosage forms
Drugs that are neither liquid nor solid (gels, ointments, creams, pastes)

Single dose vials
Vial in which all the drug is used at once
Solid dosage forms
Drugs that are in a solid form (tablets, capsules, caplet, suppositories)
4 Rules of safe drug usage
1. All drugs are poisons (have potential to cause harm)
2. No drug is a silver bullet (no drug will magically cure a disease)
3. All doses are guesses
4. Complacency kills
Chemical name
Describes the chemical composition or molecular structure of a drug
-used by chemists, pharmacologists