benign and malignant tumors of the eyelids
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
where are the fine hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands
dermis
layers of the epidermis
basal
mitotic
melanocytes
spinosum
squamous cells
keratinocytes
granular
keratinized squamous
where do malignant eyelid lesions originate
deep to epidermis and infiltrates indward (towards blood and lymphatics)
what are the precancerous conditions
actinic keratosis
keratacanthoma
where do the benign eyelid lesions originate
epidermis and grows outwards
melanocytic nevus aka
moles
acquired
patho phys of melanocytic nevus
Clusters of Melanocytes derived from neural crest migrate to the skin during embryonic development and proliferates
clinical presentation of melanocytic nevus aqcuired
• Onset during childhood (5-15yo)
• Varies depending on age of patient and stage of nevus 3 stages:
Junctional (Childhood)
Compound (Young adult)
Intradermal (Later in life)
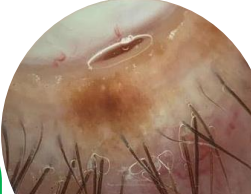
junctional melanocutic nevus
Flat and even colored
Limited to basal epidermis
Found in childhood
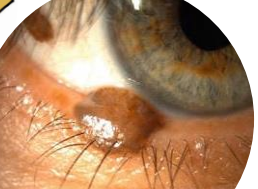
compound melanocytic nevus
Elevated and even colored
Level of Basal epidermis and dermis
Found in young adults
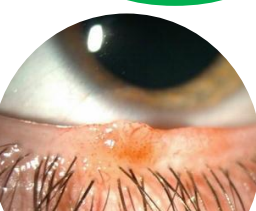
intradermal melanocytic nevus
Elevated and lightly colored or depigmented
Located in dermis
Found in older adults
melanocytic nevus management
monitor for change
send for ecision adn biopsy if sus
TAKE A PIC FOR COMPARISON
what are the congenital melanocytic nevus
congenital divided kissing nevus
Large Congenital periocular type
Congenital divided “Kissing” nevus
Develops before embryologic separation of eyelids, divides when eyelids separate

Large Congenital periocular type
• Deeply pigmented and larger than acquired nevus
• Elevated and has excess hairs
• Greater chance of malignant transformation to malignant melanoma up to 5%
• Greater risk with larger size

oculodermal melanocytosis aka
nevus of ota
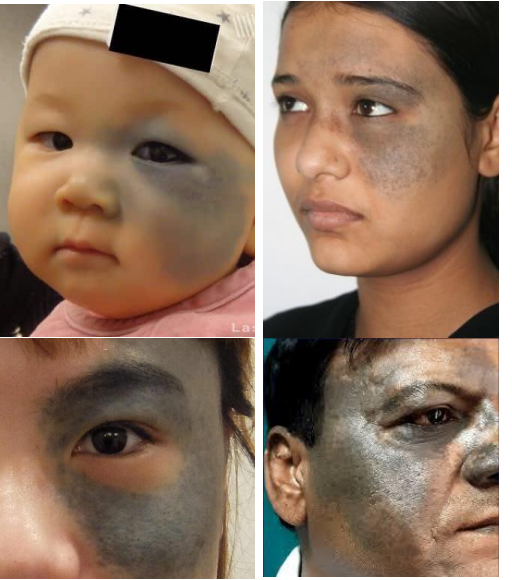
oculodermal melanocytosis cause
Congenital pigmentation of periocular skin, uveal tract, sometimes orbits, meninges, and palate.
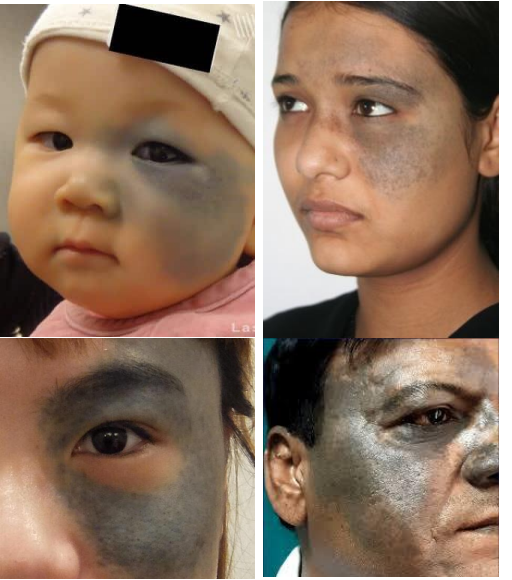
epi of oculodermal melanocytosis
1 Present at birth or during 1st year of life
• More common in Asians, particularly Japanese population and African descent
• HOWEVER, Higher risk of malignant uveal melanomas in whites 1:400
• Females > Male
pathophys of oculodermal melanocytosis
Excess melanocytes from neural crest origin become entrapped in the dermis during embryologic development
clinical presentation of nevus of ota
Flat, blue-grayish pigmentation of face, periocular skin, conjunctiva and sclera •
Tends to follow CN 5 V1 & V2 distribution
• Can have iris mammillations —> bumps on iris
• Often Unilateral, bilateral in only10% cases
• Risk of congenital glaucoma
• Infiltration of Melanocytes in drainage angle can lead to reduced outflow and increased intraocular pressure
• Risk of Uveal melanoma
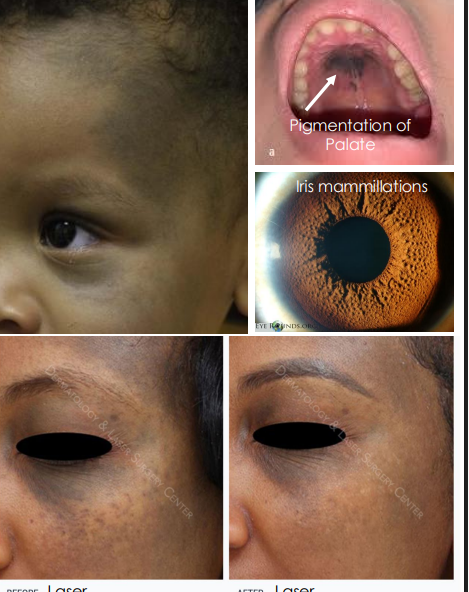
management of oculodermal melanocytosis
Routinely evaluate to detect early uveal melanoma with dilated fundus examination
• Routinely evaluate with comprehensive eye exam to detect glaucoma
• May be removed with laser therapy for cosmesis
• Refer to dermatologist or oculoplastics
squamous papilloma aka
skin tag
squamous papilloma cauase
idiopathic
benign squamous cell/keratinocyte proliferation
whats the most common benign eyelid lesion
Squamous Papilloma
patho phys of Squamous Papilloma
Benign hyperplasia of the squamous epithelium
clinical presentation of Squamous Papilloma
Can be sessile/Immobile and broad with smooth surface
• Can be pedunculated/stalked, elevated, with rough surface
• Can be solitary or multiple
• Flesh colored or pigmented
• Gradual onset and progress slowly
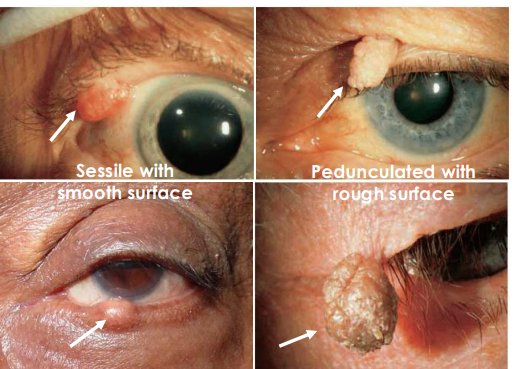
management of Squamous Papilloma
Observation or excision for cosmesis
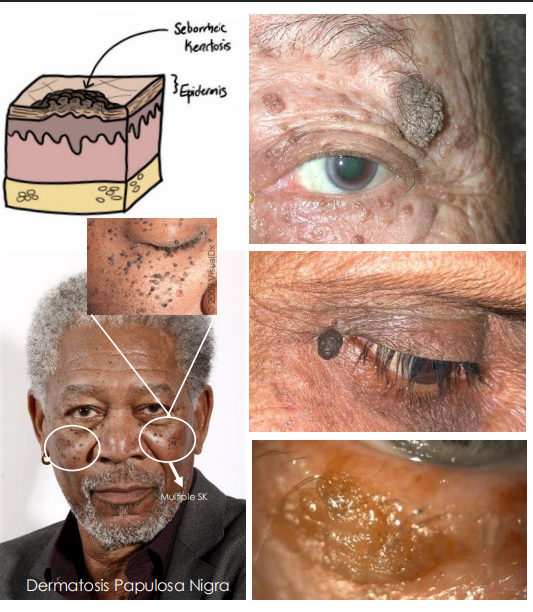
seborrheic keratosis cause
Benign proliferation of immature keratinocytes
seborrheic keratosis epi
• Common, middle to older age, no gender predilection•
seborrheic keratosis patho phys
hyperkeratosis and proliferation of keratinocytes with keratin-filled cysts, pigmented due to transfer of melanin from melanocytes
clinical presentation of seborrheic keratosis
Solitary, elevated, hyperpigmented (Brown, black, tan), waxy and scaly plaque
• Characteristic “Stuck-on” appearance
• Gradual growth
• Variant: Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra (DPN) in Asians and blacks
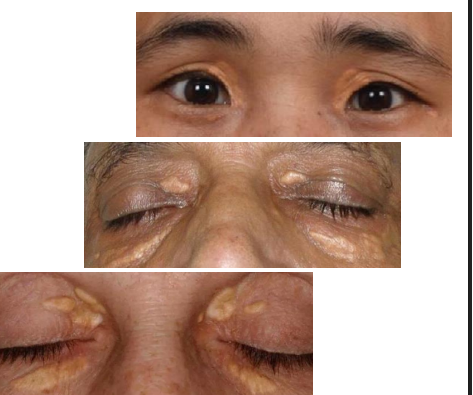
xanthelasma cause
Accumulation of cholesterol rich material in skin
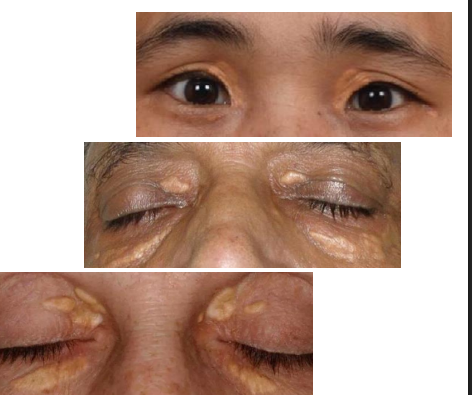
epi of xanthelasma
Common
• Middle to older age
• Females>males
• ~50% correlation to lipid disorder
patho phys of Xanthelasma
Form of lipoma that consist of infiltration of the dermis by foam cells (macrophages transformed by lipid)
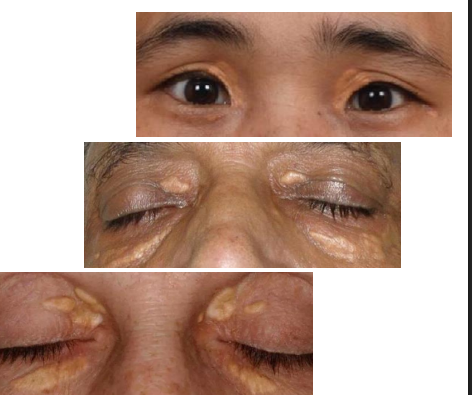
clinical presentation of xanthelasma
One or more flat, minimally elevated, creamyyellow, plaque-like lesions
• Often found medial aspect of eyelids
• Often bilateral and symmetric
management of xanthelasma
lipid disorder eval w PCP
observation or excision for comesis
milia aka
milk spots
milia cause
Congenital
• Acquired
• Primary spontaneous eruption
• Secondary to trauma, radiation, UV exposure, herpes zoster ophthalmicus
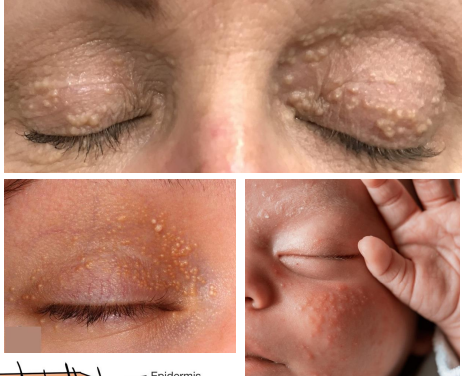
epi of milia
• Congenital form seen in newborns due to maturing of glands
• Any age, and persons
pathophys of milia
Sub-epidermally trapped keratin cysts/blockages of the pilosebaceous unit
clinical presentation of milia
Multiple, umbilicated, well-circumscribed, pinhead sized white nodules
epidermal inclusion cysts aka
epidermoid cysts
epidermal inclusion cyyst epi
• Male>Female
• Multiple lesions seen in patients with Gardner syndrome or Muir -Torre syndrome which has increased risk of colorectal cancer
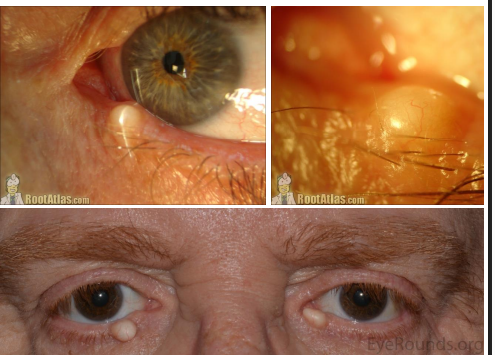
pathophys of epidermal inclusion cyst
Cyst lined by keratinized epithelium of epidermis and filled with liberated keratin often associated with a hair follicle
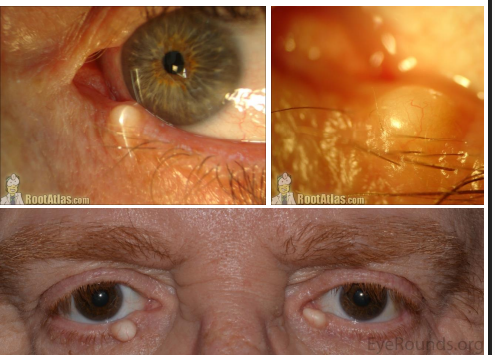
clinica presentatino of epidermal inclusion cysts
• Smooth, soft, white -yellow, round and movable lesion
• Smaller version is called milia
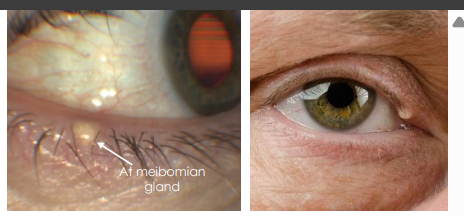
sebaceous cyst epi
elderly
sebaceous cyst pathophys
Secondary to occlusion of the duct of a sebaceous gland, filled with sebaceous material.
• Can occur in eyelid and adjacent tissue, most commonly affecting meibomian gland, less often Zeis glands
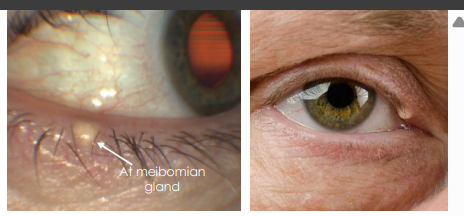
sebaceous cyst clinical presentation
Meibomian gland cysts are small, focal, subcutaneous nodule with minimal to no inflammation
• Extrameibomian gland cyst (Zeis) grow larger, smooth, yellow, opaque, “cheesy”, freely movable, and can rupture causing inflammation.
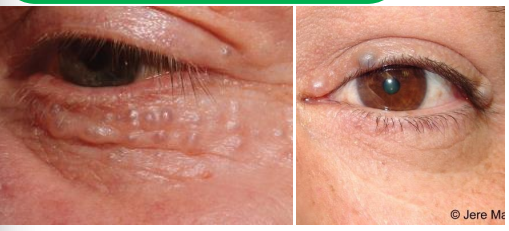
hidrocystoma types
eccrine
apocrine
eccrine hidrocystoma - retention cyst cause
Retention of sweat worsened by heat, humidity, and perspiration
eccrine hidrocystoma - retention cyst epi
• More common around eyelids but can occur anyway on the body
• Increases in number and size during summer and decrease in winter
• More common in adult women
eccrine hidrocystoma - retention cyst pathophys
Blocked sweat duct leading to retention of sweat within eccrine sweat gland and subsequent dilation forming a cyst.
apocrine hidrocystoma - sudiferous cyst cause
Benign tumor formation within Gland of Moll along eyelid margin
apocrine hidrocystoma - sudiferous cyst epi
• More common around medial canthus of eyes
• Typically found around hair follicles
• Not temperature dependent
• No gender predilection
• Adults >55 yo
apocrine hidrocystoma - sudiferous cyst pathophys
Abnormal proliferation (adenoma) of coil structure of apocrine secretory gland (Gland of Moll)
eccrine hydrocystoma clinical presentation
Clear, cystic, translucent lesion
• Sometimes appear bluish
• Can occur near but not at eyelid margin and around cheeks
• More likely to be multiple lesions
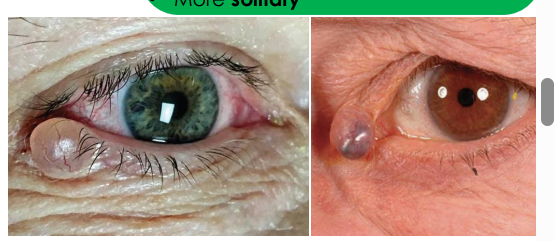
apocrine hydrocystoma clinical presentation
• Smooth, dome-shaped, translucent, larger and slow growing
• Often has a bluish-black color
• Occur near inner canthus, at eyelid margin and eyebrows •
More solitary
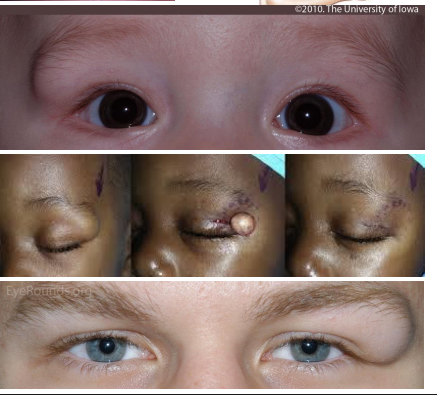
eyelid dermoid cysts cause
Congenital cystic lesion that can affect eyelid, orbit or both
whats the most common orbital tumor in kids
eyelid dermoid cyst
pathophys of eyelid dermoid cyst
• Entrapped ectoderm at a site of embryologic bony fusion therefore, occurs around bony orbital rim
• Composed of hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands
clinical presentatino of eyelid dermoid cysts
Smooth, subcutaneous mass, firm and not movable due to attachment to underlying periosteum
• Located superior-temporally at the site of the zygomaticofrontal suture
congenital capillary hemangioma aka
strawberry hemangioma
Congenital Capillary Hemangioma cause
Congenital, ”birth mark”
Congenital Capillary Hemangioma epi
• More common in preterm infants with low birth weight
• Most common infantile vascular tumor
• Females>males
Congenital Capillary Hemangioma pahtophys
Benign vascular tumor apparent at birth due to overgrowth of blood vessels that do not form properly during pregnancy
Congenital Capillary Hemangioma clinical presentation
Superficial Form: red, flat, lesion that enlarges then completely regresses by age 5
• Deep Form: Subcutaneous and under epidermis, blue-gray color, soft and palpable, IF deep in orbits, can cause proptosis
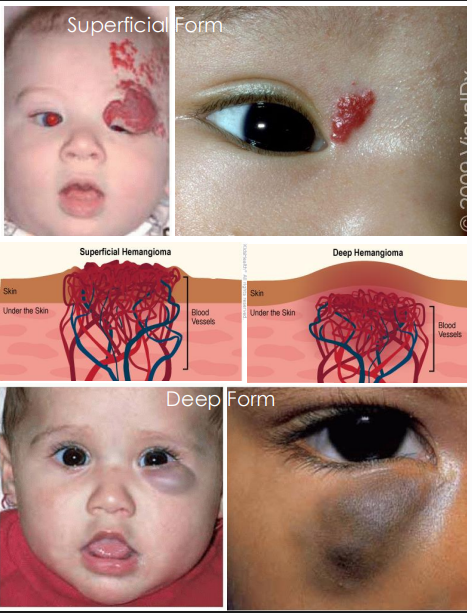
Congenital Capillary Hemangioma management
Most regress spontaneously, observation recommended unless sight threatening if affecting orbits
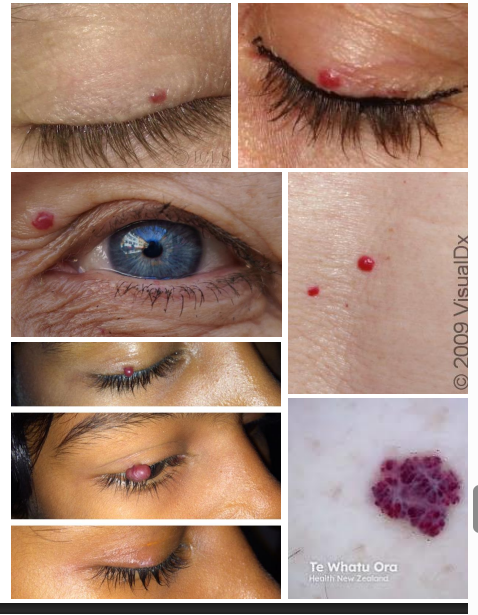
Acquired Capillary Hemangioma aka
cherry hemangioma
acquired capillary hemangioma cause
Related to aging,
some genetic predisposition,
hormonal changes such as pregnancy
Acquired Capillary Hemangioma epi
Middle aged and older adults
• Very common, can occur anywhere on the body
• Affects anyone, no gender, race predilection
pathophys of Acquired Capillary Hemangioma
Overgrowth of capillary vessels that become dilated
Clinical Presentation Acquired Capillary Hemangioma
• Solitary, distinct, elevated and movable
• Small lesions are red
• Larger lesions are red-blue
nevus flammeus aka
port wine stain
nevus flammeus cause
Congenital vascular malformation
• Can be isolated finding but can be associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome
epi of envus flammeus
• Present at birth, ~0.5% of newborns
• No gender predilection
pathophys of nevus flammeus
Congenital low flow vascular malformations of dermal capillaries that grows larger over time and does not regress
clinical presentation of nevus flammeus
Red to purple lesions around eyelids and periorbital region
• Often Unilateral but sometimes crosses midline
• Flat at birth but can become nodular with age
• Growth parallels growth of individual
• Follows the CN 5 (Trigeminal nerve) distribution
• Sturge-Weber Syndrome (SWS)
• Neurocutaneous disorder with abnormal blood vessel growth in brain, skin and eye
• Ocular complications:
• Episcleral telangiectasia, Congenital glaucoma, Choroidal hemangioma and retinal detachment
• Upper eyelid involvement highly associated with glaucoma
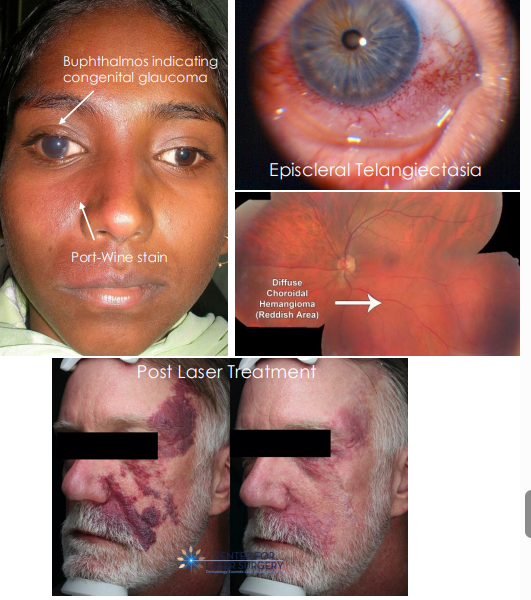
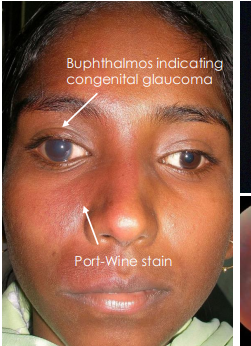
what indicates congenital glaucoma
bulphthalmos
management of nevus flammeus
• Laser photocoagulation or other forms of lasers to permanently close dilated vessels to improve cosmetic appearance.
• Treat ocular complications associated with SWS.
• Glaucoma, RD
actinic keratosis aka
solar keratosis
cause of actinic keratosis
Aging change in skin, and secondary to gradual damage from lifelong exposure to ultraviolet light
epi of actinic keratosis
• Fair skinned individuals
• Individuals exposed to prolonged and excessive sunlight
• Older aged individuals
• Males > Females
pathophys of actnic keratosis
Excessive and cumulative UV exposure induces DNA damage in keratinocytes leading to abnormal cell proliferation and growth within epidermis
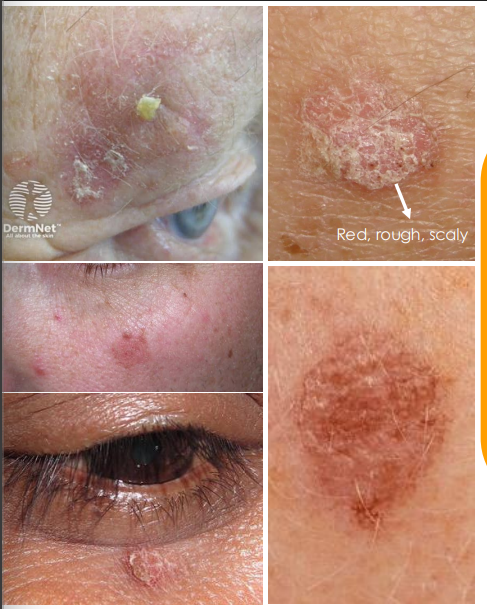
actinic keratosis clinical presentatino
• Multiple, red to pink, rough and scaly patches of skin
• Dry, Flat, Immobile, plaques, that can become nodular
• Affected skin may have ”sandpaper” texture
• Maybe itchy
• Precursor to Squamous Cell Carcinoma
management for actinic keratosis
• Larger lesions should be excised and biopsied by Oculoplastic or dermatologist
• Topical Chemotherapeutics
• Topical Immunomodulator
keratoacanthoma cause
Exact unknown, possibly related to UV radiation and chemical carcinogen
Keratoacanthoma epi
Older age >50
• Males>Females,
• Sun-exposure
Keratoacanthoma pathophys
Hyperkeratosis within a pilosebaceous unit with three phases:
1. Proliferation 2. Maturation 3. Involution.
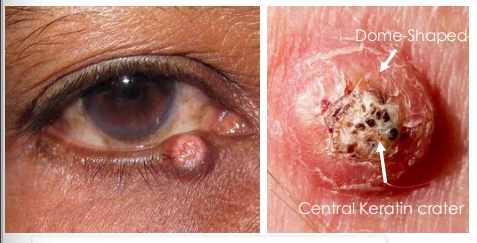
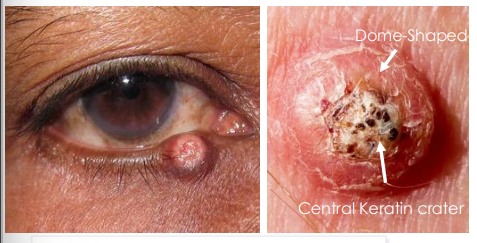
keratoacanthoma clinical presentation
• Dome-shaped with keratin filled central crater
• Rapid onset and grows over weeks and may spontaneously regress over months leaving a scar
• Considered as a low-grade form of Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) or precursor to SCC
basal cell carcinoma cause
Gradual damage from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light, prior irradiation, immunosuppression and indoor tanning
whats the most common malignant tumor of the eyelid
basal cell carcinoma
epi of basal cell carcinoma
Most common malignant tumor of eyelid
• Fair skinned individuals
• Older age >50 yo
• Males>Females
• Often found in sun exposed areas of body
• Lower eyelid most common
pathophys of basal cell carcinoma
DNA mutations of basal cells within epidermis cause uncontrolled cell growth, proliferation, tumor formation, tissue infiltration and invasion
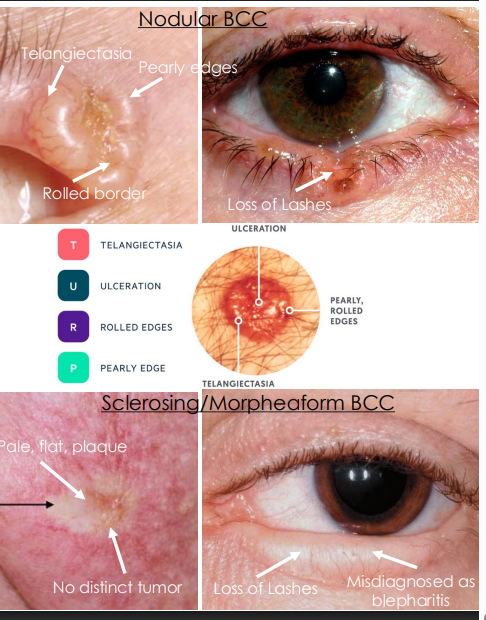
clinical presentation of basal cell carcinoma
. Nodular and Noduloulcerative (Rodent Ulcer) 80% of Eyelid BCC
• Pearly, waxy, translucent tumor with rolled borders with telangiectasia (feeder vessels)
• Loss of hair or lashes, become bleeding ulcer
2. Sclerosing/ Morpheaform <2% of Eyelid BCC
• Pale, flat, ill-defined margins, hardened plaque
• No distinct tumor, difficult to diagnose, invasive
managemetn of basal cell carcinoma
Refer to oculoplastic, dermatology, ocular oncology Excisional biopsy, Mohs microsurgery, Eyelid reconstruction as needed
squamous cell carcinoma cause
• Gradual damage from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light, prior irradiation and immunosuppression
• May arise from premalignant lesions such as Actinic Keratosis or Keratoacanthoma.
squamous cell carcinoma epi
• Fair skinned individuals >50 yo
• Males>Females
• <10% of eyelid malignancies, less common than BCC
pathophys of squamous cell carcinoma
DNA mutations of Squamous cell/ keratinocytes within epidermis cause uncontrolled cell growth, proliferation, tumor formation, tissue infiltration and invasion
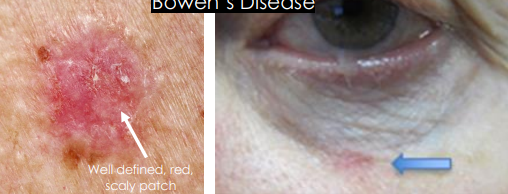
bowens disease SCC aka
Superficial SCC in situ)
in situ - in its place
Bowen’s Disease SCC clinical prseentation
• Pre-cancerous, Non-invasive but can convert to Invasive SCC
• Well defined, red, crusted, keratotic, scaly lesion, similar to actinic keratosis
• May resemble psoriasis or eczema