DNA/RNA/Protein synthesis - notes -
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the 4 nitrogen bases of DNA
Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
What is the macromolecule of DNA
nucleotides
Each nucleotide in DNA contains…
a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen containing base (ATGC)
What holds together two complementary chains of polynucleotides
Hydrogen bonds
Whats DNA replication
Process in which DNA is replicated
When does Dna replication occur
the eukaryotic cell cycle
1st step of DNA replication
when an enzyme (Dna helicase) breaks the bonds between bases in DNA
2nd step of DNA replication
The DNA is exposed so they can be “read” by another enzyme, (polymerase)
3rd step of DNA replication
1 strand (original) is used to build two new DNA strands with complementary
Dna replication is a …… process
semi conservative because half of the parent DNA molecule is conserved in each of the two daughter DNA molecules.
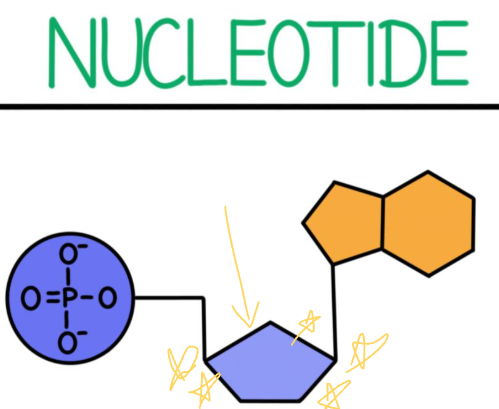
What part of the nucleotide is this?
The sugar (deoxyribose)
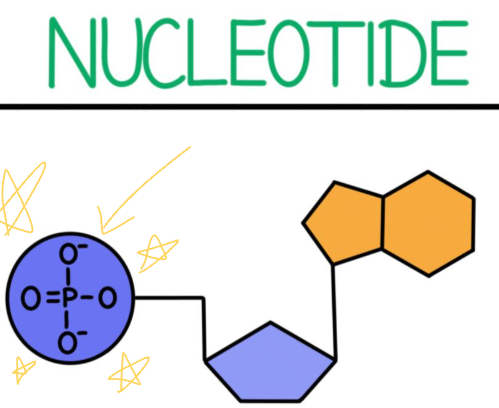
What part of the nucleotide is this?
Phosphate group
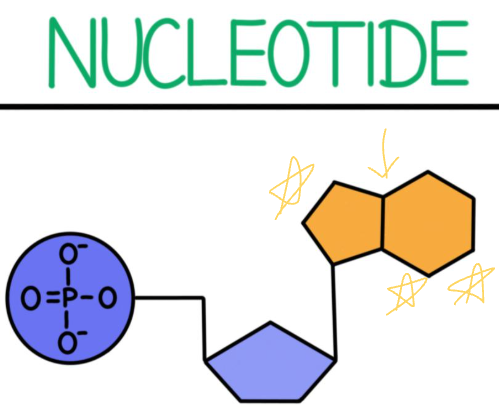
What part of the nucleotide is this?
Nitrogen containing base
What type of biological molecule is DNA helicase
An enzyme
What type is DNA replication, where two different DNA strands are created each with half of the original DNA
Semi-conservative replication
4 stages of the cell cycle
G1, S, G2, and M
In the cell cycle what cycles are called “interspace”
The first three stages
This is the cell's main growth phase. The cell is getting bigger and doing its normal everyday work (like a skin cell protecting your body, or a liver cell filtering blood).
At the end of G1, if you could see the DNA, you'd see the homologous chromosomes (the two versions of each chromosome, one from each parent) visible.
G1 (gap 1)
Who was the first person to actually isolate DNA from cells
Friedrich Miescher
This is the most important part of preparation: the cell copies all of its DNA (chromosomes). This is called DNA replication.
After this stage, every chromosome is now doubled, ready to be split evenly between two new cells.
S (Synthesis)
The cell continues to grow and makes any last-minute proteins and organelles it needs to complete division. It's double-checking everything before the big event.
At the beginning of the next stage (M), the duplicated chromosomes condense (coil up tightly) and you can clearly see the "X" shape, where the two identical copies (sister chromatids) are joined at the center (centromere).
G2 (Gap 2)
This is the stage where the cell actually divides. It first separates the duplicated DNA (mitosis) and then splits the rest of the cell contents (cytokinesis) to form two identical daughter cells.
The two new cells then go back to the beginning of the G1 phase to start the cycle all over again!
M (Mitosis): Cell Division
1st step of protein synthesis
Transcription
3 differences between DNA and RNA
They have different sugars. They have different bases. Different structure
What sugar does DNA and RNA have
DNA- deoxyribose RNA- ribose
What is the difference in the bases of DNA and RNA
DNA has a-t-c-g and RNA has a-U- c-g (a pairs with u)
Transcription occurs in the……. of eukaryotic cells
Nucleus - because Dna is stored in nucleus but too large to pass through the pores in the nuclear membrane
Step 1 of Transcription
Dna unwinds/unzips at a specific gene
step 2 of transcription
free floating RNA nucleotides match with COMPLEMENTARY DNA bases
step 3 of transcription
when the mRNA transcript is completed it leaves the nucelus
step 4 of transcription
DNA molecule zips back up and winds back up
DNA alone cannot ‘‘tell’’ your cells how to make proteins. It needs the help of RNA
DNA alone cannot ‘‘tell’’ your cells how to make proteins. It needs the help of RNA
what are the 3 types of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)