Biochemistry
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what are atoms?
single unit made of neutrons, protons, and electrons
what are molecules?
groups of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bonds due to electron interactions
what are macromolecules?
large molecules (polymers) formed from the bonding of smaller molecules (monomers)
what are ionic bonds?
transfer of electron from one atom to another atom of very differing electronegativity (typically done to help fill valence shells)
what are covalent bonds?
sharing of electrons between atoms of similar electronegativities
what are the two types of covalent bonds? how are they different?
nonpolar and polar
nonpolar: equal electron sharing
polar: unequal electron sharing that results in the formation of a dipole
what are hydrogen bonds?
hydrogen bonds are weak bonds between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom (N,O,F)
how are macromolecules formed?
dehydration reaction: links monomers to form polymers, and forms water in the process
how are macromolecules broken down?
hydrolysis: water is used as an input to break polymers into monomers
what are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
what is the polymer of a protein called?
peptide chain
what type of bond links proteins?
peptide bonds
what is the function of proteins?
structural help, transportation, defense, storage, enzymes
what are the 4 structures of proteins?
primary, secondary, tertiary, quarternary
what is a primary protein?
linear chain sequence of amino acids
what is a secondary protein?
local folding of amino acid chain into alpha helices and beta sheets via hydrogen bonding between amino and coarboxyl groups of the adjacent amino acids
what is a tertiary protein?
3D shapes of proteins formed due to noncovalent interactions between the R groups of proteins
which covalent bond is the exception in tertiary protein formation?
disulfide bonds
what is a quaternary protein?
3D protein shape consisting of 2+ separate peptide chains
how many polypeptide chains are in a teritary protein?
1
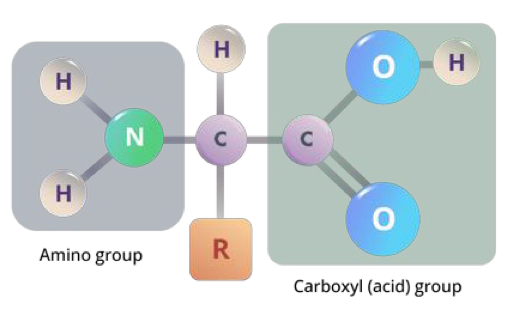
what is the structure of an amino acid?
4 components attached to a central carbon:
amino (NH2) group
carboxyl (COOH) group
R group
Hydrogen
what is the polarity and water affinity of lipid molecules?
nonpolar and hydrophobic molecules
what is a monomer of lipids?
hydrocarbon
what is a polymer of lipids?
hydrocarbon chain
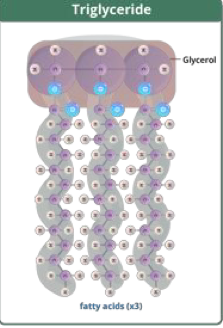
what are triglycerides?
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
saturated (single bonds, straight chain)
unsaturated (double bonds, branched chain)
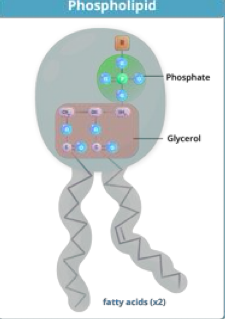
what are phospholipids?
2 fatty acids + phosphate group atatched to a glycerol backbone
amphipathic with a polar head and nonpolar tail
form phospholipid membrane bilayer
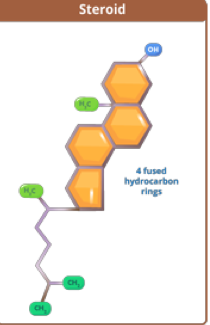
what are steroids?
3 6-membered rings + 1 5-membered ring
Examples include hormones and cholesterol
what are the 3 types of lipids?
triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
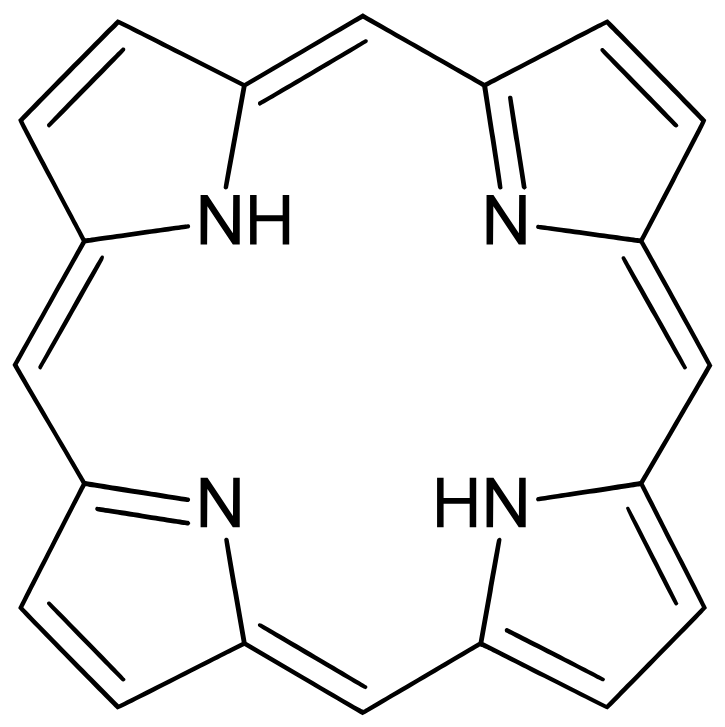
what are porphyrins?
4 joined pyrrole rings with a metal center atom
examples include chorphyll and hemoglobin
non-lipids but are commonly asscoiated with the lipid membrane
what are the monomers of nucleic acids?
nucelotides
what are the polymers of nucleic acids?
nucleic acids themselves!
ex: DNA or RNA
what is the bond linkage between nucleotides?
phosphodiester bonds
what is the function of nucleic acids?
encode, express, and store genetic information
what is the function of carbohydrates?
to store energy
what is the function of lipids?
insulation, energy storage, endocrine signaling, cell structure
what is the linkage type between lipids?
covalent carbon-carbon bonds
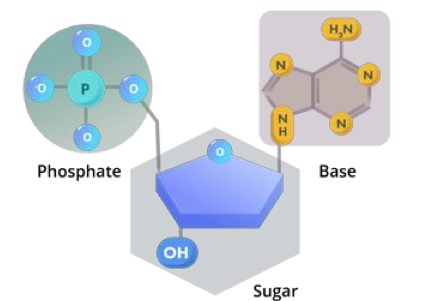
what is the structure of a nucleotide?
nitrogenous base
phosphate group
sugar
what sugar does DNA contain and what is attached to that sugar?
deoxyribose and is has an H attached to the 2’ carbon of the sugar
what sugar does RNA contain and what is attached to that sugar?
ribose and is has an OH attached to the 2’ carbon of the sugar
what are two important factors of DNA?
DNA strands run antiparallel and they are complimentary to one another
what kind of nitrogenous bases are A and G? how many rings do they have?
purines; 2 rings
what kind of nitrogenous bases are T and C? how many rings do they have?
pyrimidines; 1 ring
how many hydrogen bonds form between A and T?
2
how many hydrogen bonds form between C and G?
3
what does C and G having more H bonds than A and T indicate for the strand?
DNA strand will require a higher temperture to dentaure the C and G bonds versus the A and T bonds
is RNA single or double stranded?
RNA is single stranded
what is chargaff’s rule?
A & T are always present in equal amounts and G & C are always present in equal amounts
what are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides (single sugar molecule)
ex: glucose
what are the polymers of carbohydrates?
polysaccharides (polymer of sugar molecules)
ex: glycogen, cellulose, chitin
what is the linkage type between carbohydrates?
glycosidic bonds
what are 2 joined sugar molecules called?
disaccharides
ex: sucrose = glucose + fructose