Bootcamp Spinal Nerves and Muscle Stretch Reflexes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the CNS?
brain and spinal cord (central nervous system)
What is the PNS?
Everything else, all nerves ( not brain or spinal cord )
What are the basic parts of a neuron ( neuron anatomy) ?
1. Dendrite
2. Nucleus
3. Soma
4. Schwann Cell
5. Nodes of Ranvier
6. Myelin
7. Axon
8. Axon Terminal
9. Cell Body
10. Axon Hillock
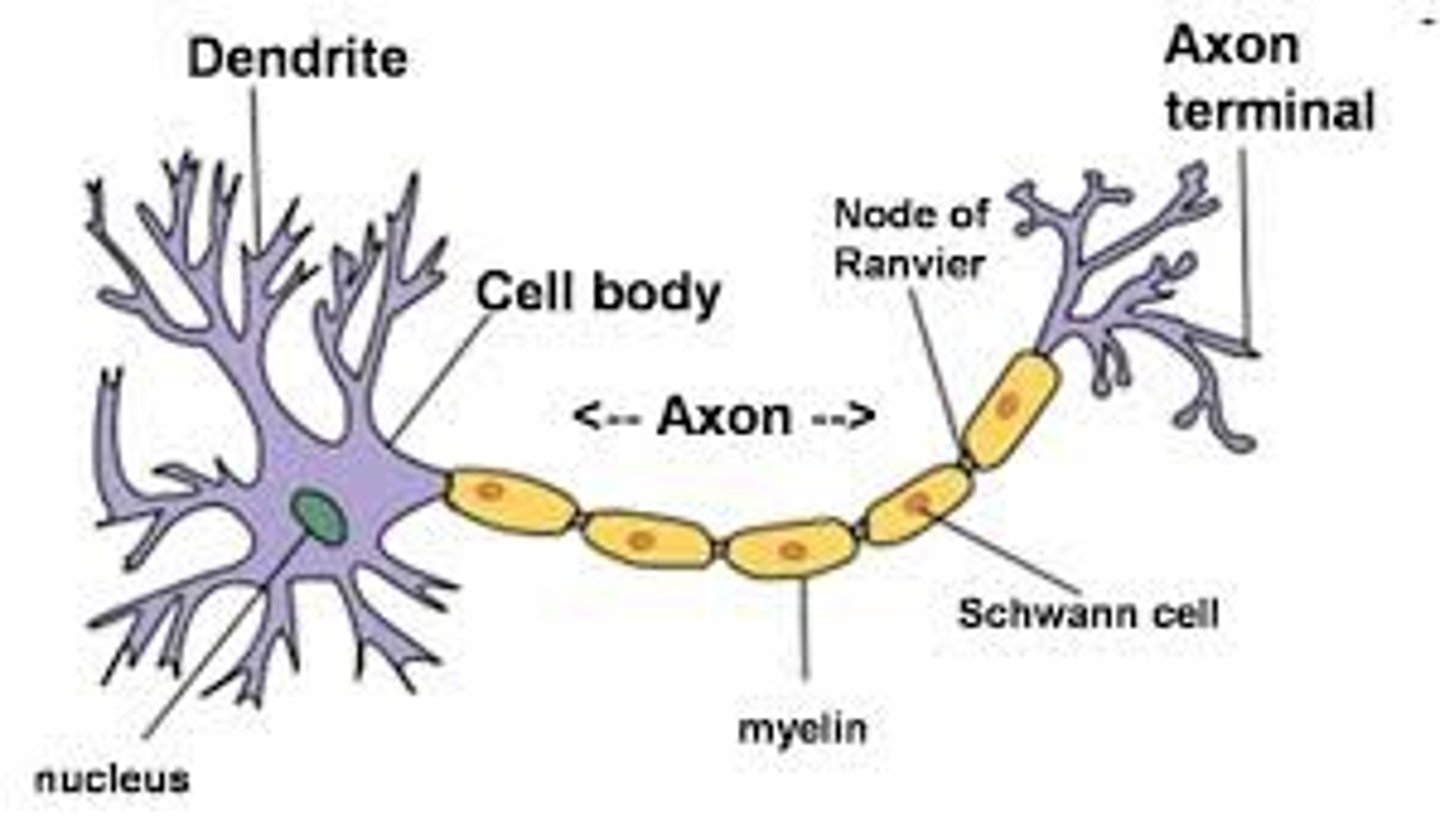
What is a synapse?
special junction where neuron communicates with another cell / creates an action potential that goes from the terminal down and moves along the information ( relay information : two cells communicate)
What are the different types of neurons ?
A. Multipolar
B. Pseudounipolar
C. BiPolar
Multipolar
Lots of dendrites coming out( two or more )
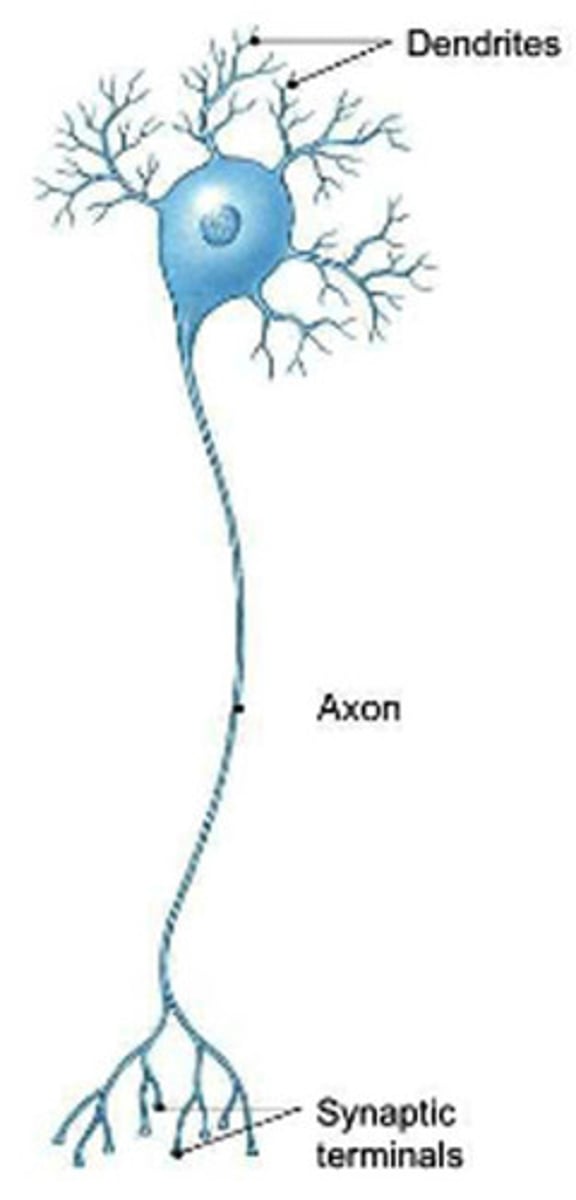
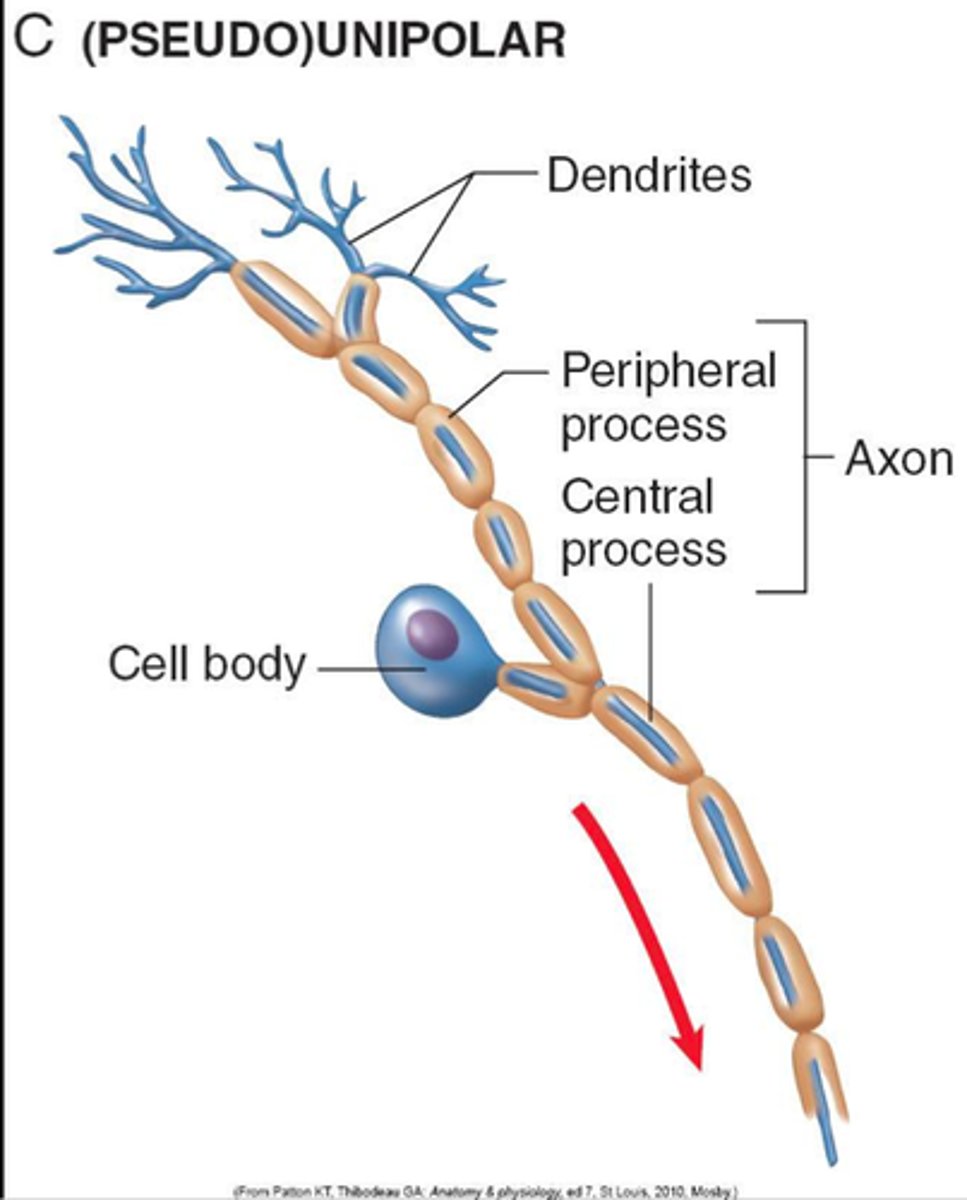
Pseudounipolar
One axon splits and one goes to CNS
bipolar neuron
One axon and one dendrite can find them in special senses
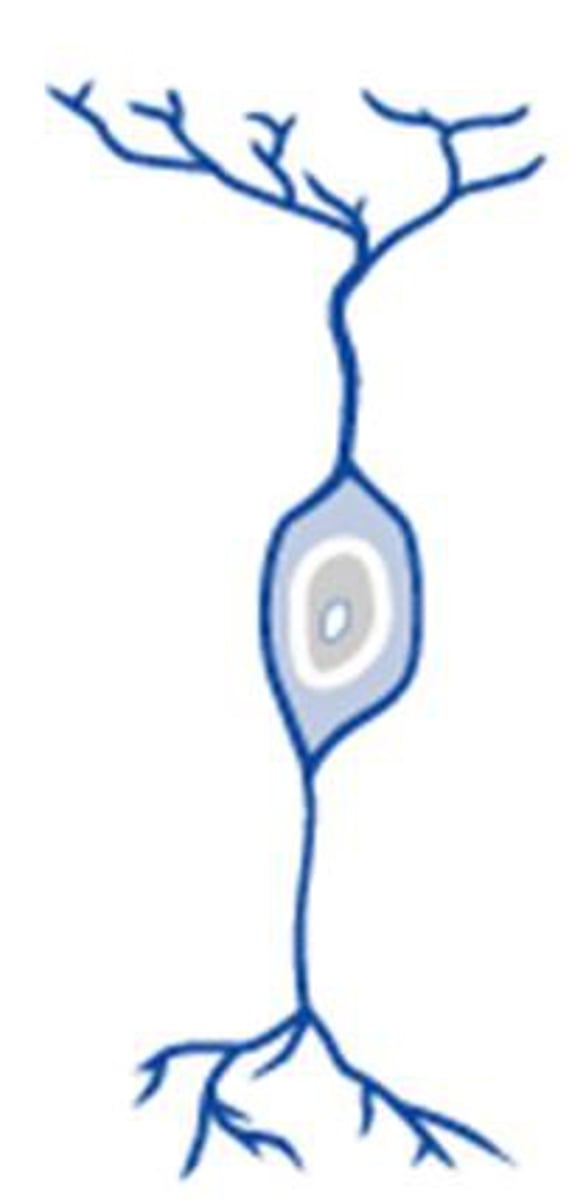
quick note :
dendrite : receives info
axon : transmit info out
What is grey matter
collection of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS
What is white matter
bundles of myelinated axons ( remember grey is nonmyelinated ) important for cns and pns
PNS
roots, rami, and nerves
what is afferent?
sensory/ arriving ( when the action potentials are directed towards the CNS)
What is efferent?
motor, exit
action potentials are directed toward the periphery
Functional components of the PNS : special
special sensory - taste, smell, touch, hearing, etc
Functional components of the PNS: general
pain , pressure, touch, temperature, vibratory senses
Functional components of PNS : somatic
everything else
functional components of PNS: Visceral
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands ( epithelium) * only three things
Efferent
out exiting
afferent
In- Arriving
Basic Functional types of axons:
General Somatic Efferent -
Only skeletal muscle
Basic Functional types of axons:
General Visceral Efferent -
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands ( epithelium) efferent ( exiting) . General visceral efferent (GVE) fibers are nerve fibers that carry motor impulses from the central nervous system to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
General Somatic Afferent
an sensory neuron that carries impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints. t has to do with pain, temperature, MSK golgi Tendon, and muscle spindles ( musculoskeletal to cns)
General Somatic Efferent
General visceral efferent (GVE) fibers are nerve fibers that carry motor impulses from the central nervous system to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
General Visceral Afferent
sensory neurons that convey information from internal organs (viscera) to the central nervous system (CNS)