Psych-Soc Class 5 - Psychological Disorders and Consciousness
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
How common are psychological disorders?
¼ of US population
What are psychological disorders?
Behavior/psychological symptoms that are not in line with cultural norms and severe enough to cause significant personal distress and impairment to social, occupational, or personal functioning
Diagnosable and treatable
Combo of biological, sociocultural, and psychological stuff
What are characteristics of anxiety disorders?
18% of US
3.83% of world
Excessive fear/anxiety
Avoidance behaviors
Panic attacks
Wha tare types of anxiety disorders?
Phobias, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder
What are characteristics of depressive disorders?
10% of US
3.77% of world
Sad, empty, and/or irritable mood
Not related to normal grief
What are specific depressive disorders?
Major depressive disorder (harder, faster)
Persistent depressive disorder (weaker, longer)
What are characteristics of bipolar disorders? Pervasiveness?
0.61% of world
Bridge between psychotic and depressive disorders
Involves episodes/oscillations (cycles)
What are types of bipolar disorders?
Bipolar I disorder (manic-depressive)
Bipolar II disorder (less severe)
What are characteristics of schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders?
2% of US
0.29% of world
Delusions, hallucinations, and/or disorganized speech
May involve “negative” symptoms
What are types of schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders?
Schizophreniform disorder (brief)
Schizophrenia (lifelong)
Schizoaffective disorder (psychotic and mood)
Delusional disorder
Brief psychotic disorder
What are characteristics of trauma and stressor related disorders?
Exposure to trauma/stressful event
Exhibit any of a wide range of symptoms
What are types of trauma and stressor related disorder?
PTSD (specific event, flashbacks)
Acute stress disorder (PTSD for only a few days/months)
Adjustment disorders
What are characteristics of personality disorders?
6% of US
Enduring (lifetime) pattern of socially deviant feelings/behaviors
Pattern is inflexible and occurs across range of settings/relationships
Begins in adolescence/early adulthood
Not diagnosed in children
Three clusters
What are types of personality disorders?
Cluster A (odd/eccentric): paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal personality disorder
Cluster B (dramatic/erratic): antisocial, borderline, histrionic, and narcissistic personality disorders → resistant to psychotherapy
Cluster C (anxious/fearful): avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders
What are characteristics of somatic symptom disorders?
3% of US
Excessive and/or medically unexplainable symptoms
Commonly encountered in primary care
What are types of somatic symptom disorders?
Somatic symptom disorder
Illness anxiety disorder
Conversion disorder
Factitious disorder
What are characteristics of dissociative disorders?
10% of US
Disruptions and/or discontinuities
Abnormal integration of consciousness, identity, emotion, etc.
What are types of dissociative disorders?
Dissociative identity disorder
Dissociative amnesia (lack of awareness of amnesia)
Depersonalization/derealization disorder (weird dreamlike feeling)
What percent of the population has eating disorders?
6% of US
0.14% of world
What are characteristics of obsessive-compulsive disorders?
Obsessions (thoughts, urges, intrusions0
Compulsions (repetitive behaviors)
What are types of obsessive-compulsive disorders?
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Body dysmorphic disorder
Hoarding disorder
Trichotillomania (hair pulling)
What are characteristics of neurodevelopmental disorders?
Manifest early in development
Appear as deficits
Difficult to treat
Intellectual disability, communication disorders
What are types of neurodevelopmental disorders?
ASD
ADHD
Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
Intellectual disability
Tourette’s syndrome
What are characteristics of ASD?
Range of disorders
1 in 88 children age 8
Males 4x more likely
What are characteristics of ADHD?
2-4% school aged children
Motor restlessness, difficulty paying attention, distractibility, impulsivity
Unknown cause
What characterizes neurocognitive disorders?
Cognitive decline from previous level (complex attention, executive function, learning, memory, language, perceptual-motor, social cognition)
Major greatly impact everyday life, mild do not
What are types of neurocognitive disorders?
Major or mild neurocognitive disorder due to Alzheimers
Major or mild neurocognitive disorder due to Parkinsons
Traumatic brain injury
Huntington’s disease
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Amyloid plaques: clumps of protein fragments outside cells
Neurofibrillary tangles: clumps of altered proteins inside cells
Causes destruction/death of nerve cells → symptoms
What is Parkinson’s disease?
Dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra of basal ganglia die off → hard to control movement
Dopamine levels drop progressively (involved in sending messages in brain areas controlling coordination/movement)
Lewy bodies: inside neurons, abnormal protein aggregates
What are characteristics of substance-related and addictive disorders?
10 classes of drugs
Involve brain’s reward system
Tolerance and withdrawal
What are types of substance-related and addictive disorders?
1.37% of world (alcohol)
0.85% of world (drug)
Substance use disorder
Alcohol related disorder
Caffeine, cannabis, hallucinogen, etc. related disorders
Gambling disorder
What are characteristics of disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders?
Problems in self-control and emotion
Behaviors violate rights of others and/or cause legal trouble
What are types of disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders?
Oppositional defiant disorder: diagnosed young, confusion over consequences, lack of control
Intermittent explosive disorder: recurring bursts of aggression not in line with situation, lack of control
Conduct disorder: most severe, pattern of behavior, lack of remorse frequently
Pyromania: impulsive fire starting
Kleptomania: impulsive thievery
Impulses may involve same rewards systems as substance-abuse, same lack of control felt, same withdrawal felt
What are characteristics of feeding/eating disorders?
Disturbed eating behavior
Consumption and or absorption of food may be affected
What are type of feeding/eating disorders?
Pica: consumption of non-foods like plastic
Anorexia nervosa: restriction of food intake, distorted view of body, fear of gaining weight
Bulimia nervosa: binge-eating then purging, laxatives, exercise, etc.
Binge-eating disorder: bulimia without purging, normal//overweight
What are the therapeutic methods of the psychoanalytic approach?
Assumed problem: unconscious forces and childhood
Therapy goal: reduce anxiety through insight
Methods/examples: analysis/interpretation (thoughts, dreams, feelings, etc.)
AKA talk therapy
What are the therapeutic methods of the humanistic approach?
Assumed problem: barriers to self-understanding and self-acceptance
Therapy goal: personal growth through self-insight
Methods/examples: active listening and unconditional positive regard
What are the therapeutic methods of the behavioral approach?
Assumed problem: learned maladaptive behaviors
Therapy goals: extinguish maladaptive behaviors/learn adaptive ones
Methods/examples: systematic desensitization, flooding, aversion therapy
What are the therapeutic methods of the cognitive-behavioral approach?
Assumed problem: maladaptive behaviors and/or self-defeating thoughts
Therapy goals: extinction of undesired thoughts/behaviors, learning adaptive thoughts/behaviors, healthier thinking and self-talk
Methods/examples: reconditioning, desensitization, reversal
What is consciousness?
Awareness of selves, internal state, and environment
Always needed to complete novel/complex tasks
States: alertness (awake), sleep
What is the reticular activating system?
Controls alertness and arousal (consciousness)
Nuclei in brainstem that project to cortex
What is the circadian rhythm?
Biological clock
Increase/decrease alertness in predictable ways
What are three indicators of circadian rhythms?
Melatonin released by pineal gland
Body temperature
Serum cortisol (controls metabolization of glucose)
What are the two types of sleep disorders?
Dyssomnias: abnormality in amount, quality, or timing of sleep
Parasomnias: abnormal behavior during sleep
What are the three types of dyssomnia?
Insomnia: inability to fall/remain asleep; persistent; can stem from chronic stress; most commonly reported
Narcolepsy: periodic, overwhelming sleepiness during waking periods; last less than 5 mins, but are dangerous
Sleep apnea: intermittent cessation of breathing during sleep, results in awakening after about a minute without air; can repeat hundreds of times per night → deep sleep deprivation
What are the two types of parasomnias?
Somnambulism: sleep-walking; usually during slow wave (stage 3) sleep in first third of night; common in children
Night terrors: occur during stage 3 sleep (as opposed to nightmares during REM); not remembered
What is polysomnography?
Measuring of sleep
Uses EEG (brain), EOG (eyes), EMG (muscles)
What is characteristic of stage 1 sleep?
Between sleep and awake
EEG: theta waves
EOG: slow rolling eye movement
EMG: moderate
Fleeting thoughts experienced, non-REM

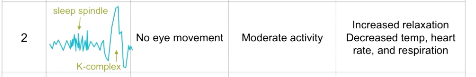
What are characteristics of stage 2 sleep?
EEG: sleep spindle and K complex
EOG: no movement
EMG: moderate
Increased relaxation
Decreased temp, heart rate, and respiration
What is characteristic of stage 3 and 4 sleep?
EEG: delta waves
EOG: no eye movement
EMG: moderate
Heart rate and digestion slow, growth hormones secreted
Deepest level of sleep

What is characteristic of REM sleep?
EEG: beta waves (awake kind), but more jagged
EOG: rapid eye movement
EMG: almost none
Where dreams occur

What are three classes of consciousness altering drugs?
Depressants, stimulants, hallucinogens
What are examples of depressants? Mechanisms of action? Effects?
Ex: alcohol, barbiturates, opiates
MoA: depresses CNS and stimulation of brain; upregulation of GABA or inhibition of glutamate
Effects: impaired motor control, eventual addiction, overdoses can lead to death
What are examples of stimulants? Mechanisms of action? Effects?
Examples: caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine
MoA: increased neurotransmitter release, inhibited reuptake of neurotransmitters, or both; increased norepinephrine or dopamine or acetylcholine agonist
Effects: increased alertness, euphoria, sped up body functions, pupil dilation, high followed by crash
What are examples of hallucinogens? Mechanisms of action? Effects?
Examples: LSD, THC
MoA: distorts perceptions in absence of sensory input (not well understood)
Effects: hallucinations, impaired judgement, slow reaction time
What is physical dependence? What is psychological dependence?
Physical: withdrawal symptoms when drug is not consumed; body adapts to the drug (tolerance); person depends on the drug to avoid withdrawal and function normally; only some drugs can cause this; can have this even without addiction
Psychological: drug is central to thoughts, emotions, behaviors, motivation; strong urge to use despite harmful effects; any drugs can lead to it and some non-drugs (ex: gambling)
What is addiction?
Compulsive drug use despite harmful consequences
Inability to stop using a drug and failure to meet work, family, or social obligations
Can include tolerance and withdrawal depending on the drug
Biologically based in pleasure centers of the brain (dopamine released in nucleus accumbens)