FAR - Chapter 13 - Analysis and interpretation of financial and non-financial information
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What’s the formula for gross profit margin?
Gross profit/ Revenue * 100%
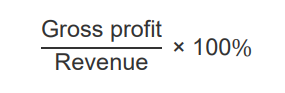
What are 4 changes in revenue that affect gross profit margin?
Sales price changes – without a corresponding change in the cost of goods or services sold.
Sales mix – a shift between selling high margin and low-margin products (Differentiation v. Cost leadership).
New products – launching new products with different margins compared to existing products
Currency effects – for exporters, sales price in £ is affected by movements in exchange rates.
What are 5 changes in cost of sales that affect gross profit margin?
Purchase costs – a change in the cost of raw materials without a corresponding change in the sales price.
Production costs – changes in labour costs or the amount of labour required (operational efficiency) per item impacts production costs.
Inventory obsolescence – if written down, cost of sales will increase relative to revenue.
Currency effects – for importers cost per unit in £ is affected by changes in exchange rates.
Economies of scale – buying in bulk may reduce cost/unit
Does a change in sales volume alone affect the gross profit margin?
No as it would equally affect both revenue and cost of sales.
However, if increased sales volumes result from offering discounts, the gross profit would decrease, leading to a lower gross profit margin.
What is the formula for operating profit margin?
Operating profit / Revenue * 100
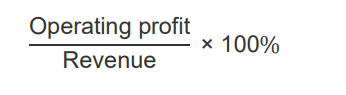
What are 4 additional factors that may affect operating profit margin?
Exceptional items – for example a significant doubtful debt expense.
Relocation or research costs – increases expenses.
Proportion of fixed and variable costs (operating gearing) – if a company has more fixed costs compared to variable costs, changes in revenue will have a more significant impact on the operating profit margin.
Operational efficiency – improving efficiency improves operating profit margin as it reduces costs (e.g. streamlining the credit control process).
What is the gearing ratio?
Debt/ Equity *100 (more common)
or
Debt/ Debt + equity *100
Debt is non-current liabilities that are interest-bearing, including bank loans, redeemable preference shares and lease liabilities.
Equity includes share capital, share premium, revaluation surplus and other reserves.
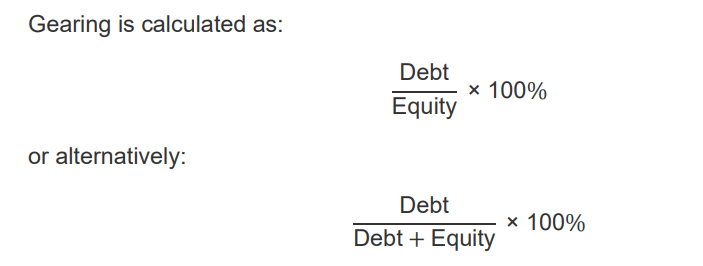
What does the gearing ratio show and what is it used for?
The gearing ratio shows the proportion of the company’s total finance which is in the form of debt relative to equity
It is used to assess solvency risk: High levels of debt generally indicate high risk, as interest and capital repayments on debt must still be paid, even if profits decrease.
Why may manageable levels of debt may be viewed as positive?
the returns that investors expect on debt are generally lower than equity and interest expenses typically attract tax relief
What are the 4 factors affecting the gearing ratio & how?
Issuing or buying back shares
Issuing ordinary shares increases equity, which decreases the gearing ratio.
Issuing redeemable preference shares qualify as debt, which increases the gearing ratio.
Buying back shares reduces equity, which increases the gearing ratio.
Debt management
Borrowing increases the gearing ratio.
Repaying debt decreases the gearing ratio.
Revaluation of non-current assets
The upwards revaluation of property, plant and equipment increases the revaluation surplus in equity and decreases the gearing ratio.
Profitability
Profits will increase equity and decrease the gearing ratio, whereas losses will decrease equity and increase the gearing ratio.
What’s the formula for asset turnover? & what does it measure?
Asset turnover measures how efficiently resources are used to generate revenue
Asset turnover = Revenue/ Capital employed
Capital employed is the total money a company has invested in its operations to generate profits.
It is calculated as either:
Capital employed = Equity + debt*
Capital employed = Total assets – current liabilities
*interest-bearing non-current liabilities only

What is non-current asset turnover & what does it measure?
Non-current asset turnover measures how much revenue is generated per £1 of non-current assets
NCA turnover= Revenue / Non-current assets
Higher asset turnover indicates assets are used efficiently to generate revenue.
Lower asset turnover suggests assets may not be being used efficiently to generate revenue.

What is inventory turnover & what does it measure?
Inventory turnover measures the efficiency of managing levels of inventory relative to demand
Inventory turnover is the number of times inventory is sold per year
Inventory turnover = Cost of sales/ Inventories
What is inventory days & what does it measure?
the number of days on average an item of inventory is held before it is sold
Inventories / Cost of sales *100
Why may a company have a higher number of inventory days compared to the previous year or industry average? (3 reasons)
Poor inventory management, leading to older items being held that need to be written down or written off.
Lower sales than forecasted.
Marketing issues preventing the sale of inventory as planned
What is the Trade receivables collection period formula and what does it measure?
the number of days it takes for credit customers to make payment.
Trade receivables / Revenue *365
*To avoid distorting the calculation, it is advisable to exclude cash sales from revenue as cash sales do not generate a receivables balance.
What is the Trade payables payment period formula and what does it measure?
measures the number of days it takes to pay credit suppliers
Trade payables / Credit purchases *365
*If the figure for credit purchases is not available, cost of sales should be used
What is the formula for return of capital employed & what does it measure?
Return on capital employed (ROCE) measures how effectively resources (capital employed) generate profits
Operating profit/ Capital employed * 100 (more common)
or
Operating profit margin * Asset turnover

What are 5 factors that influence the ROCE and how is the ROCE affected?
Revaluation of non-current assets - An upwards revaluation increases depreciation, which will decrease operating profit and increase capital employed. This lowers the ROCE.
Age of non-current assets - Older assets with a low carrying amount may generate a higher ROCE compared to newer assets with a higher carrying amount.
Leases - A new lease for a non-current asset increases liabilities and capital employed, which may reduce ROCE
Timing of an asset purchase - If a large investment in PPE is made at the year end, capital employed increases yet there may not be enough time for that asset to generate profits. ROCE would be expected to decrease
Industry type - Companies with large asset bases, such as manufacturing companies, usually have higher capital employed and therefore lower ROCE compared to tech or service companies
What may significant changes in ratios indicate?
Data errors or deliberate misstatements due to pressure to improve performance or meet loan covenants.
What are non-financial measures?
used to monitor operations and strategy, to provide an understanding of the performance of the company, its progress towards strategic objectives and alignment with the values it has set itself
What are 5 examples of what non-financial measures could be in relation to?
Customer satisfaction
Employee engagement
Operational efficiency
Innovation
Sustainability
What are 3 examples of Customer-related measures?
Net Promoter Score (NPS) – measures customer loyalty and satisfaction
Customer churn rate – the rate at which a business loses customers
Results from customer feedback surveys
What are 3 examples of employee -related measures?
Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) – similar to NPS but measures employee satisfaction
Employee retention rate
Gender pay gap
What are 5 examples of social measures?
Social measures:
Community contribution
Social Return on Investment (SROI) – calculates the social value a specific project or initiative generates
Occupational health and safety measures
Measures of labour conditions in the supply chain
Diversity and inclusion measures
What are 6 examples of environmental measures?
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions
Progress towards net zero targets
Habitat restoration metrics
Water usage
Energy usage
Recycled content
What are 4 examples of operational measures?
1.On-time delivery rate
Defect rate
Website bounce rate – the percentage of visitors who leave the website after viewing only one page
Website page views
What are 3 examples of innovation measures?
New product launches
Research and development costs in relation to revenue
Patent applications
What are 3 examples of cyber-security measures?
Data breaches
Average time to detect a threat and respond to a threat
Completion of security training by employees