Anova
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Measurement scale
DV: Metric
IV: Non-metric
ANOVA is a model to test if there are difference in the mean between a metric dependent variable (DV) and one or more non-metric independent variables (IV). These independent variables are called factors. ANOVA is a type of linear regression.
Test if there are differences in the mean of a metric (interval or ratio) dependent variable across different levels of one or more non-metric (nominal or ordinal) independent variables (factors). When there are 2 IVs, we call it a two-way ANOVA. If there is only 1 independent variable with only 2 levels, we can use a t-test. Examples:
2.Designing
Designing the ANOVA: When designing an ANOVA we have to think about the model. Defining the ANOVA consists of 2 main parts:
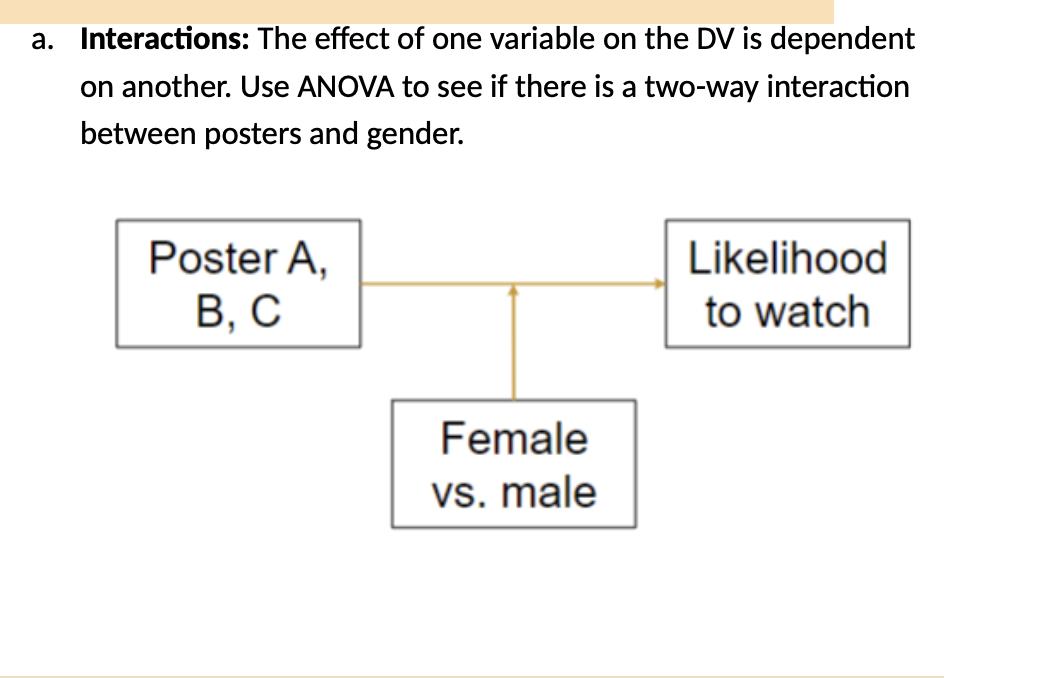
This is an example of a two-way ANOVA. Is there an effect per poster and does this difference depend on if someone is a male or female? 3 possibilities:
There are differences for everyone
There are no differences at all
There are differences between males and females
Interactions = Moderators
Coveriates = controls
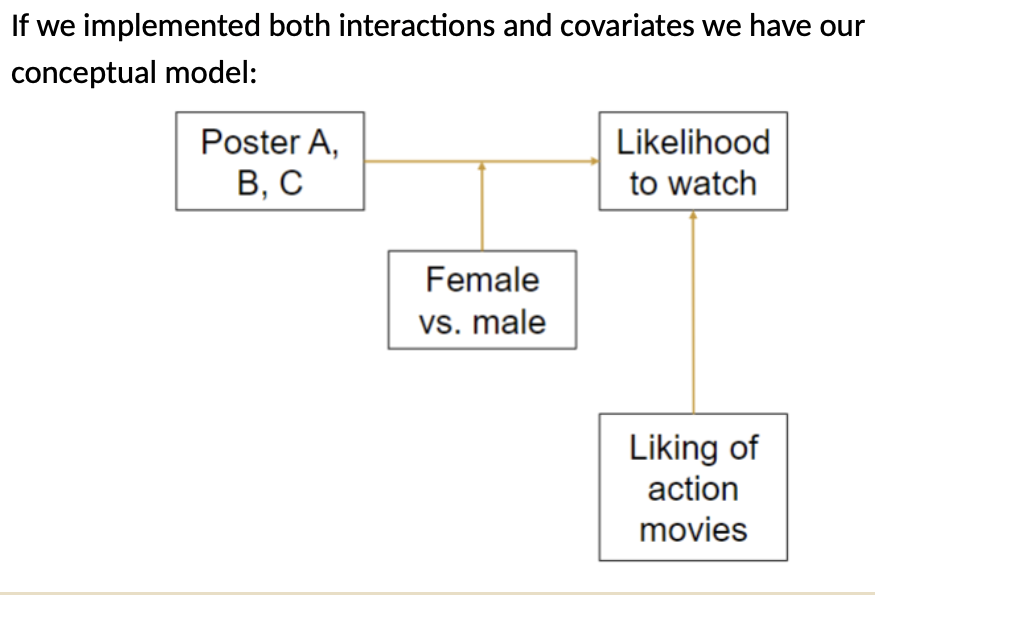
3. Checking Assumptions:


(A)
Independence of Observations (crucial!)
If observations aren’t independent → estimates & standard errors are wrong.
1. Between-Subjects Design
Each participant → only one condition (1 combo of IVs).
Outcomes are usually independent, but can be correlated if outside factors differ.
Control context: same day, mood, weather, etc.
2. Within-Subjects Design
Each participant → all treatments.
Outcomes correlated (same person).
Compare each person to themselves → removes random variation (“luck of draw”).
Counterbalance order (e.g., some see A first, others C).
Higher power: fewer subjects needed, but must adjust analysis for dependence.
In short:
Between = independence assumed, control conditions carefully.
Within = dependence expected, counterbalance & adjust analysis.
B
Equality of Variance (Homoscedasticity):
Is the variance equal across treatment groups? (Somewhat important). If variances are not equal, this could affect the standard errors. To check this:
Test:
Levene’s Test: Conduct a Levene’s test to check if the variances of all variables are the same. The null is that all variances are equal,
So we do not want to reject the null, and the p-value should be big.
If homoscedasticity is violated:
If the sample size is similar across treatment groups, then it is robust
If not, transform the dependent variable and redo the test
Add a covariate and redo the test
C
Normality: Are the residuals (approximately) normally distributed? (Least important). If the residuals are not normally distributed, this could affect the standard errors only when the sample is small. We can only check normality after the model is estimated, since it is about the normality of the residuals of the model. To check this:
Test:
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test/Shapiro-Wilk Test: Conduct a test to test the normality of the residuals.
The null is that the residuals are normally distributed, so we do not want to reject the null, and the p-value should be big enough.
If normality is violated:
If the sample size is large, then it is robust
If the sample size is small, transform the dependent variable to make the distribution more symmetric
Special cases

4.Estimating


F = MSSB/MSSW
5.Interpreting the Results:
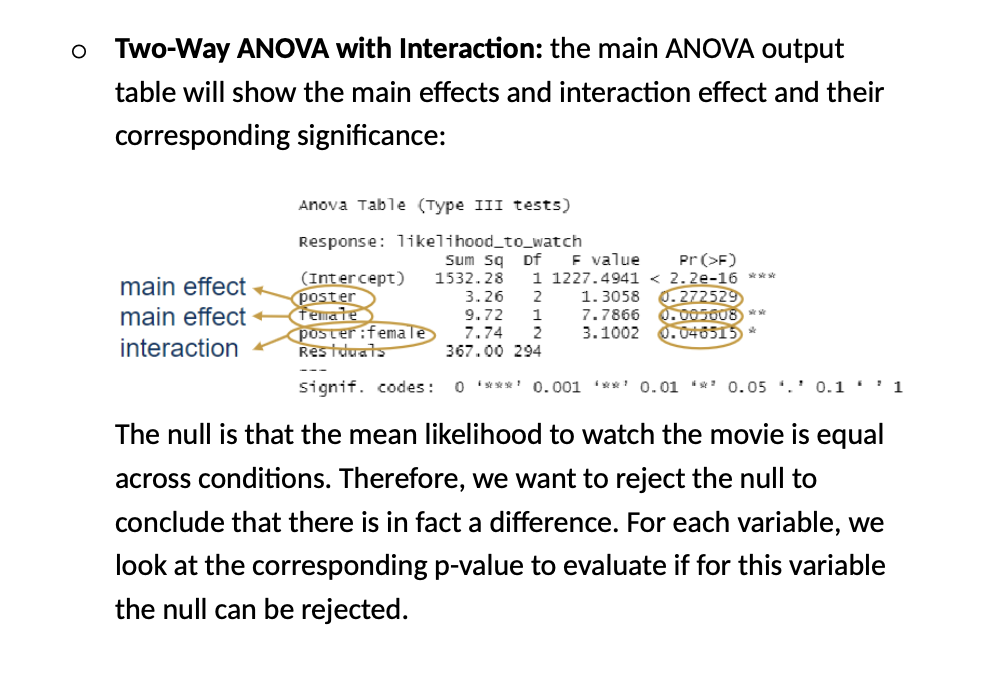



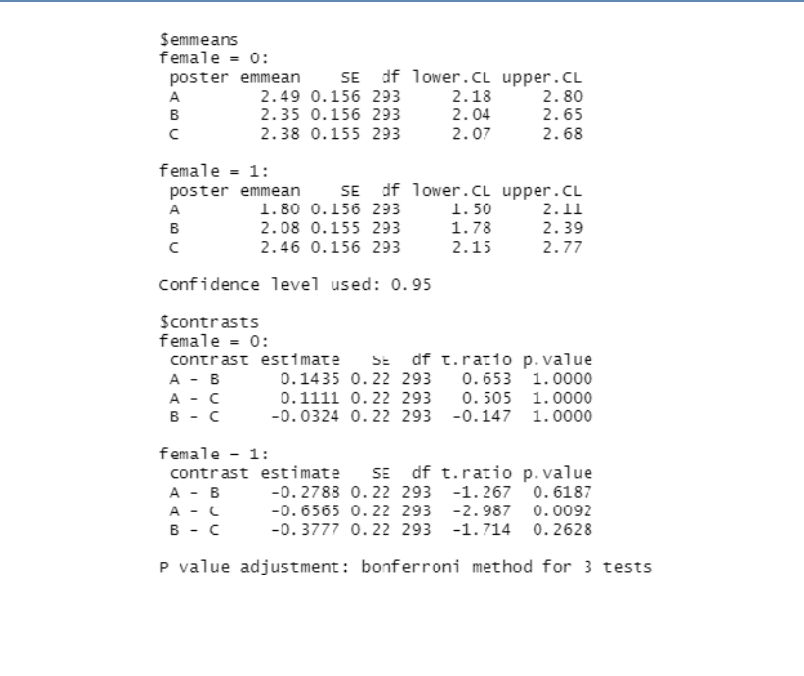
Validating outcomes
-Control through covariates
-Replicate study