Overview of the Peripheral Nervous System
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Sensory Receptors
Respond to information from the environment- stimuli. Sensation & perception occur in the brain.
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to touch, vibration, stretch (force).
Thermoreceptors
Respond to temperature change.
Photoreceptors
Respond to light (retina).
Chemoreceptors
Respond to chemical changes (blood).
Nociceptors
Respond to damaging stimuli causing pain.
Exteroceptors
Stimuli outside the body.
Interoceptors
Stimuli inside the body.
Proprioceptors
Stimuli inside the body.
Perceptual detection
Ability to detect that stimulus has occurred.
Magnitude estimation
Ability to detect how intense the stimulus is.
Spatial discrimination
Ability to detect the site or pattern of stimulation.
Feature abstraction
Neurons tuned into one feature of a stimulus over all others.
Quality discrimination
Ability to differentiate the sub-modalities.
Pattern recognition
Ability to differentiate patterns in our world.
Pain receptors
Activated by histamine, ATP, acids, K+, etc.
Referred Pain
Visceral pain afferents along the same pathways as somatic pain.
Nerves
Bundles of axons.
Nerve Classification
Mixed- sensory & motor fibres. Conduct impulses both to and from CNS.
Afferent neuron cells
Contained in dorsal root ganglia.
Endoneurium
Connective tissue wrapping around individual axons.
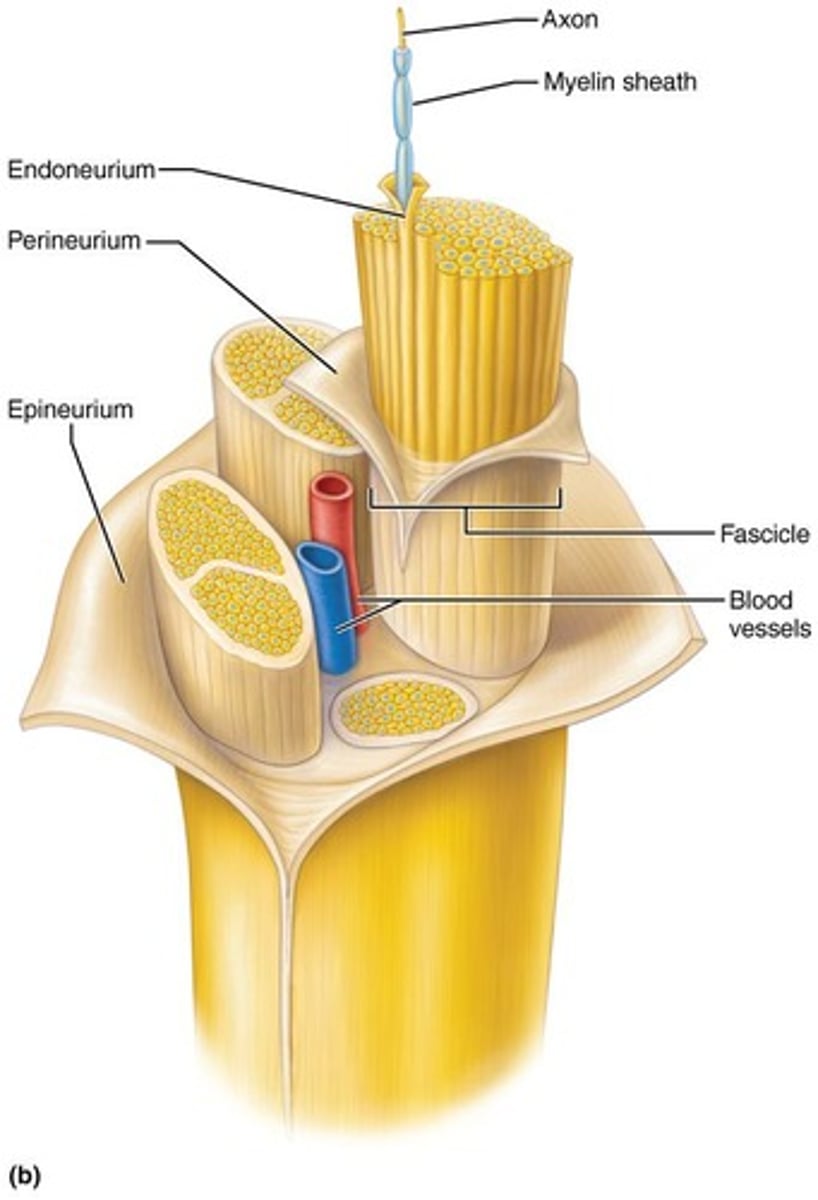
Perineurium
Connective tissue wrapping around a bundle of axons.
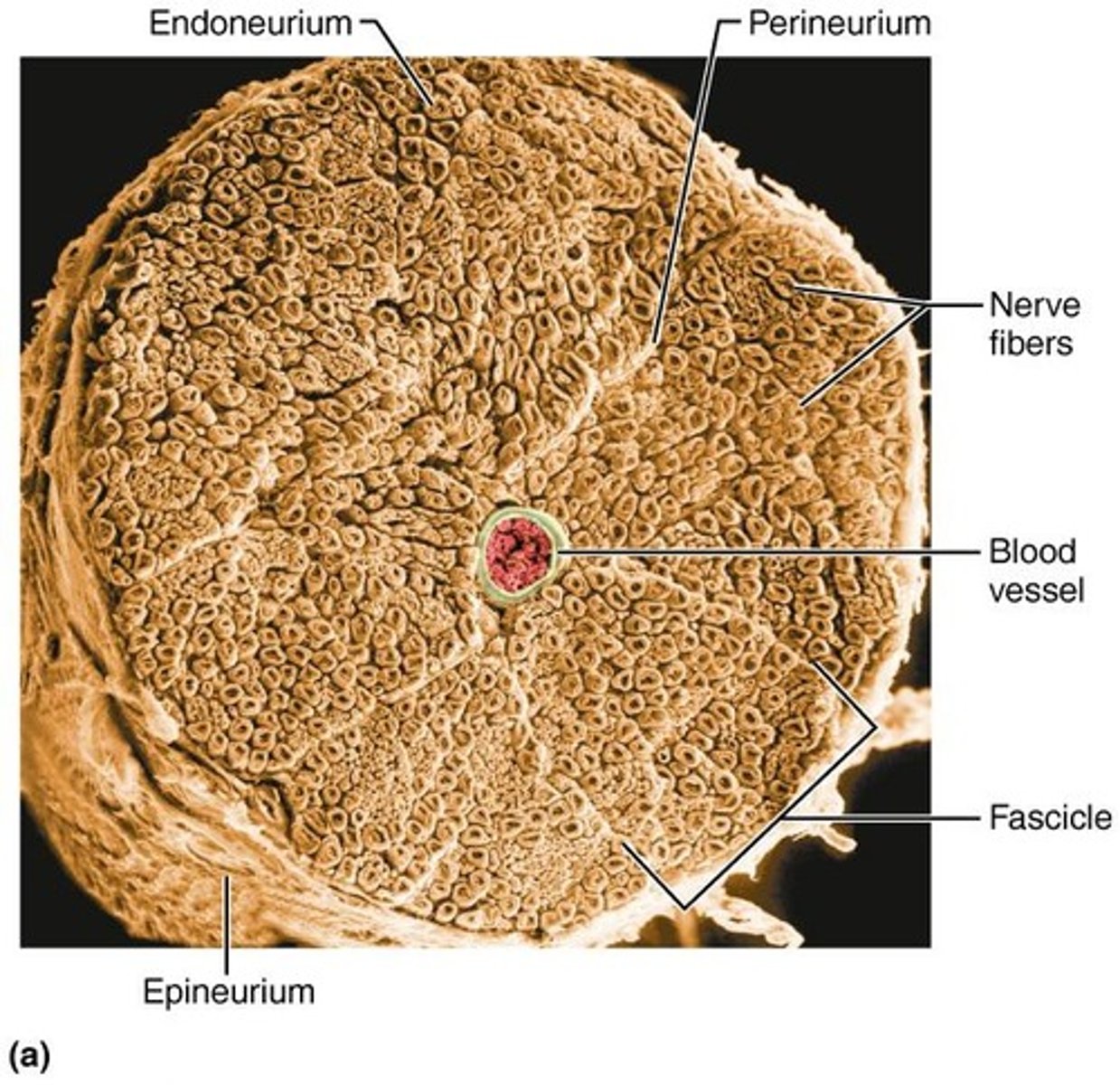
Epineurium
Connective tissue wrapping around the entire nerve.
Afferent neuron
Neuron cells contained in dorsal root ganglia.
Autonomic motor neurons
Efferent neurons located in the ventral root.
Nerve Repair
Mature neurons do not generally repair; PNS axons may repair under right circumstances, while CNS axons are viewed as irreparable.
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of cranial nerves are associated with the brain, with two attaching to the forebrain and the rest to the brain stem.
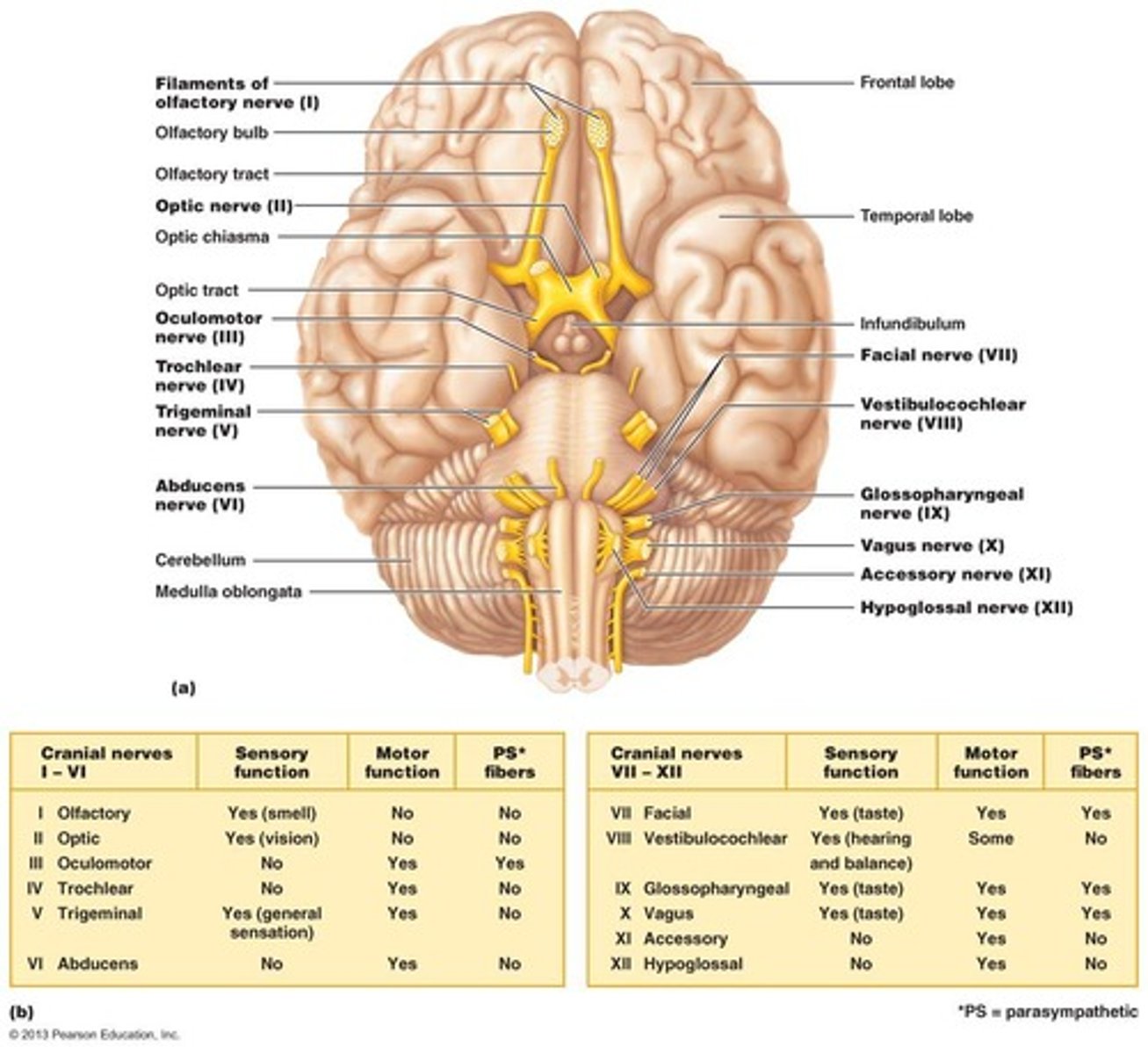
Cranial Nerves numbering
Each cranial nerve is numbered (I through XII) and named from rostral to caudal.
Cranial Nerves sensory vs motor
Most cranial nerves are mixed nerves, but two pairs are purely sensory.
Cranial Nerves mnemonic
Mnemonic: 'On occasion, our trusty truck acts funny—very good vehicle anyhow.'
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves exist, including 8 pairs of cervical nerves, 12 pairs of thoracic nerves, 5 pairs of lumbar nerves, 5 pairs of sacral nerves, and 1 pair of coccygeal nerves.
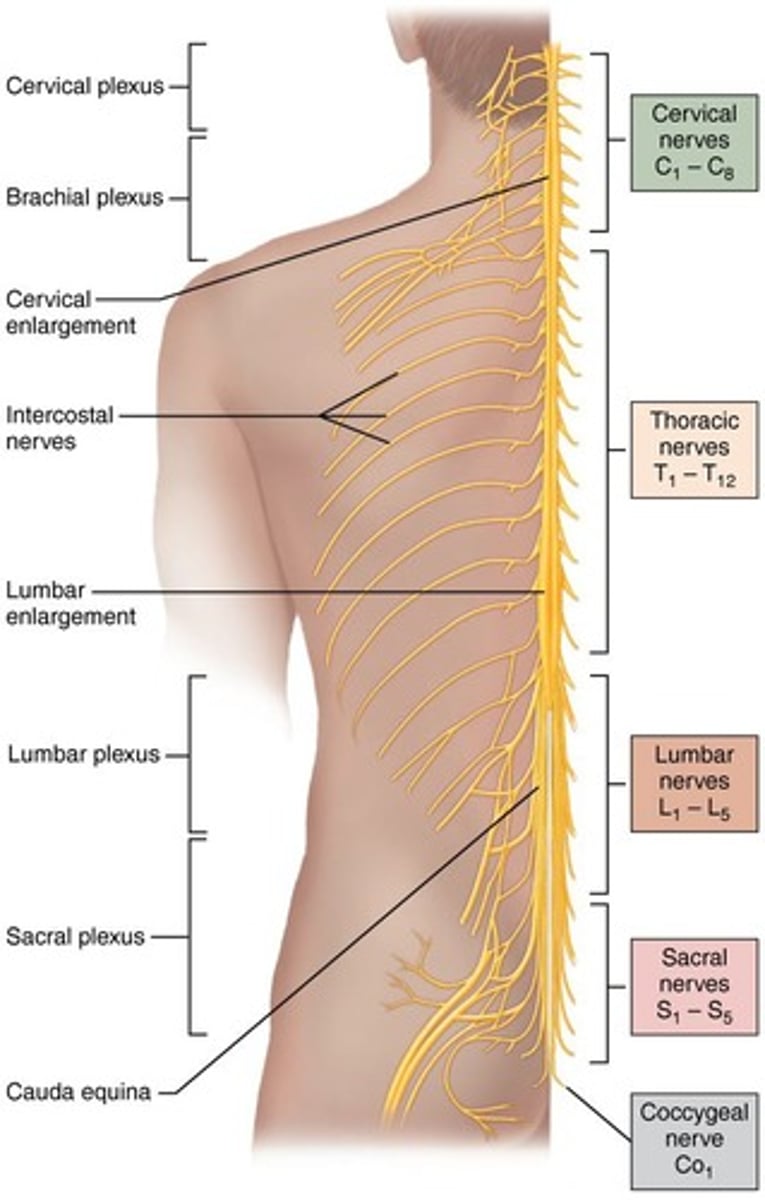
Spinal Nerves connection
Spinal nerves connect to the spinal cord via dorsal/ventral roots.
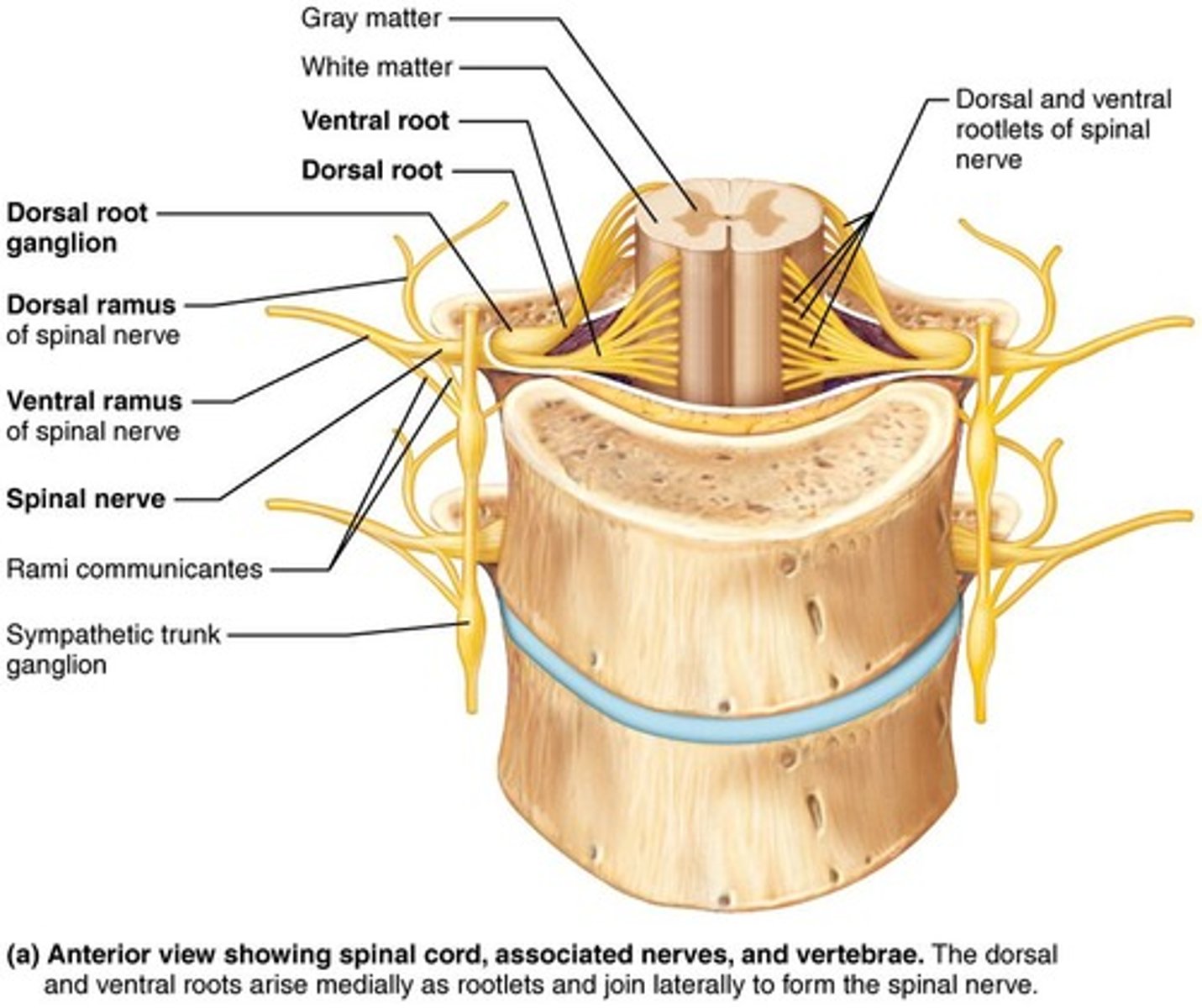
Ventral roots
Ventral roots contain motor fibers that innervate skeletal muscles and autonomic functions.
Dorsal roots
Dorsal roots contain sensory fibers from dorsal root ganglia.
Nerve plexuses
All ventral rami join to form nerve networks called nerve plexuses, which occur in cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions.
Cervical Plexus
Located under the sternocleidomastoid muscle, contains nerves from C1-C4, with the phrenic nerve being the most important.
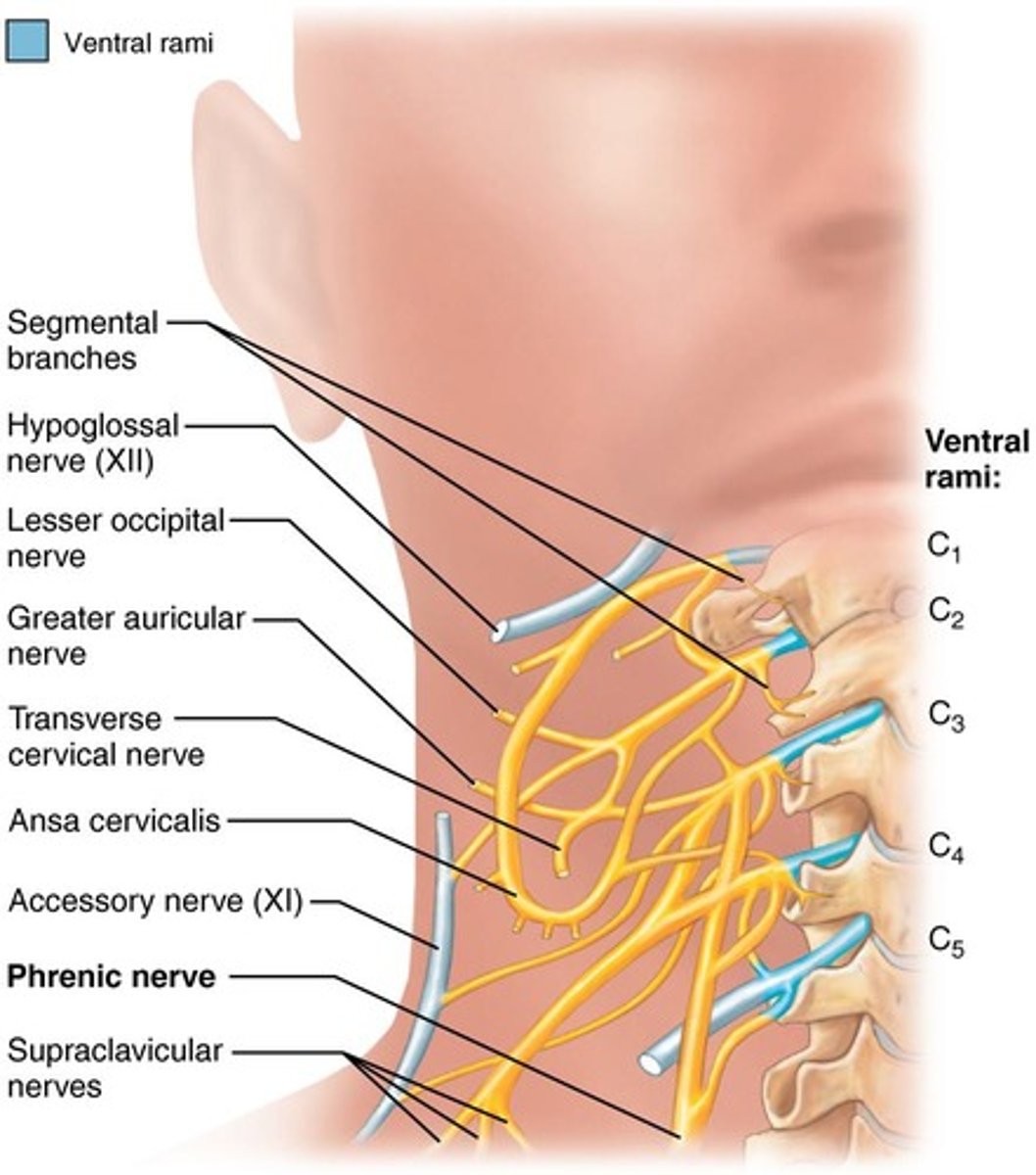
Phrenic nerve
Arises from C3-C5 and innervates the diaphragm.
Brachial Plexus
Situated in the neck and axilla, contains nerves from C5-C8 and T1.
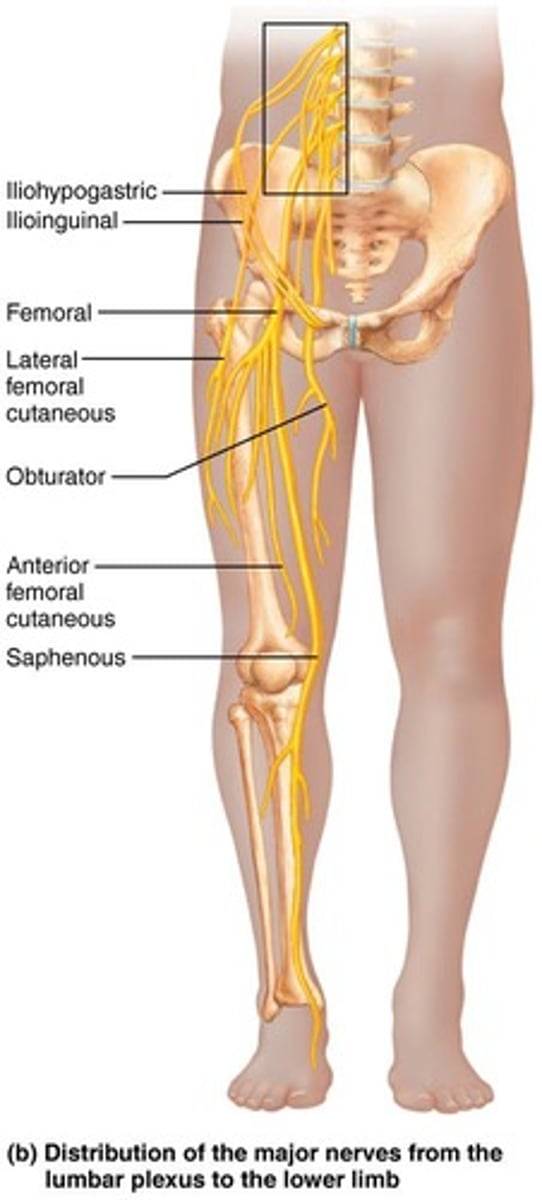
Lumbar Plexus
Overlaps with the sacral plexus and arises from nerves L1-L4.
Femoral nerve
Innervates the quadriceps group (motor) and the skin of the anterior thigh and medial leg from knee to foot.
Sacral Plexus
Arises from nerves L4-S4 and innervates the buttock, lower limb, pelvis, and perineum.
Sciatic nerve
The thickest and longest nerve, supplies the entire lower limb except for the anteromedial upper leg, and divides into tibial and common fibular nerves.
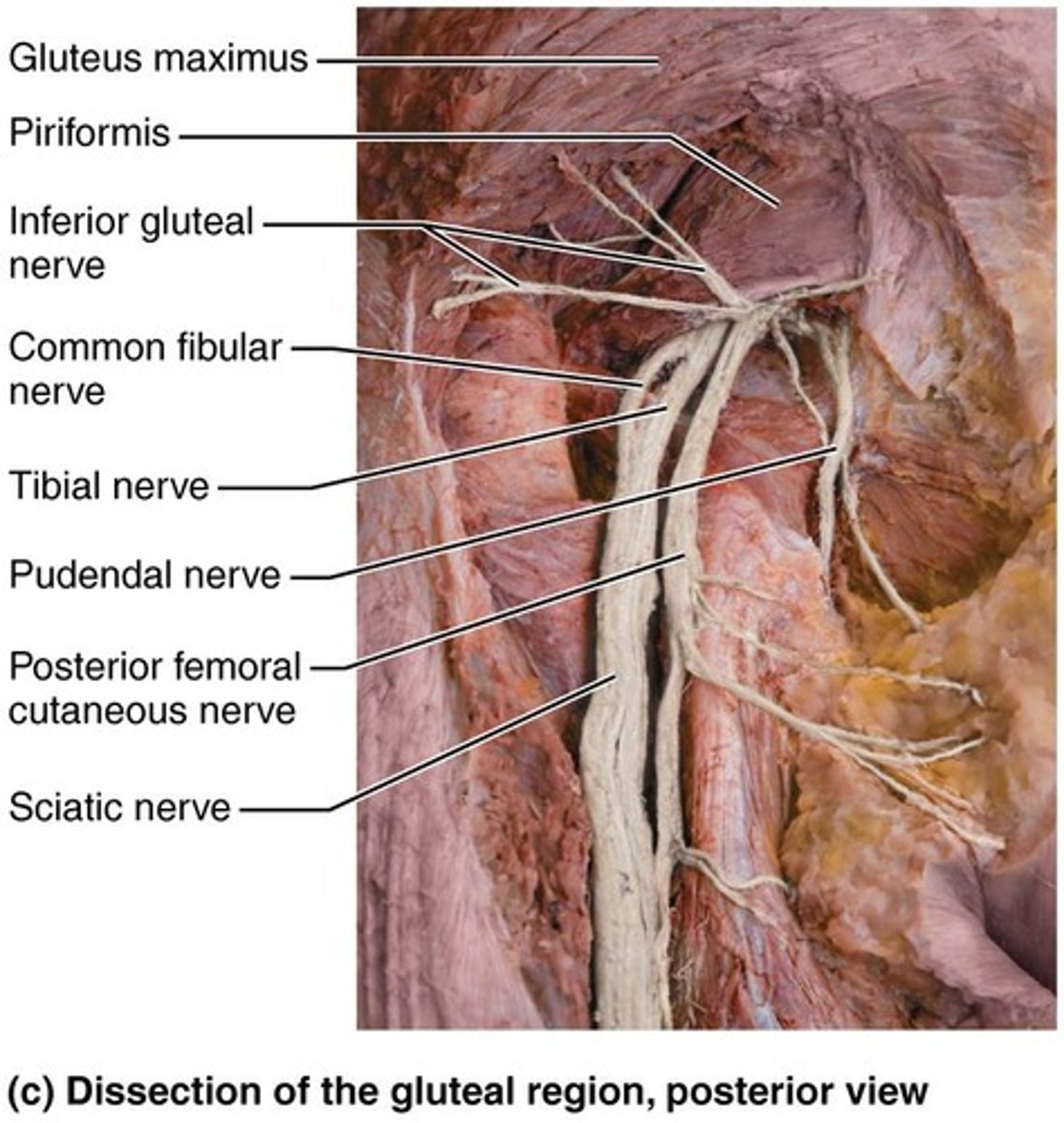
Tibial Nerve
Supplies posterior leg muscles and skin of the posterior calf and sole of the foot.
Common Fibular Nerve
Divided into superficial and deep branches. Innervates knee joint. Innervates skin of anterior and lateral leg. Innervates dorsum of foot.
Dermatomes
Represents area innervated by single spinal nerve. Mapping dermatome allows clinician to determine exact nerve injury.
Reflex Classification - Intrinsic
Automatic. Pulling arm back from burning stove. Provides protection.
Reflex Classification - Acquired
Learned. Driving a car. Comes from practice and repetition.
Reflex Classification - Somatic
Activate skeletal muscle.
Reflex Classification - Visceral
Activate smooth/cardiac muscle or glands.
Stretch Reflex
Purpose: to aid NS in coordinating activity of skeletal muscles. Obtains information about muscle from muscle proprioceptors.
Autonomic Nervous System
Stabilizes internal environment via a system of motor neurons that innervate smooth and cardiac muscles as well as glands.
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
Responsible for exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS)
Responsible for digestion, diuresis, and defecation.
Key Differences - Sympathetic
Nerve fibres originate in thoracic/lumbar regions of spinal cord. Short preganglion. Long postganglion. Ganglia are close to spinal cord. Long lasting and widespread effect.
Key Differences - Parasympathetic
Nerve fibres originate in brain/sacral region of spinal cord. Long preganglion. Short postganglion. Ganglia are close to effector sites. Localized and short lived effect.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Released by all ANS preganglionic axons and all Parasympathetic ANS postganglionic axons (at synapses with their effectors).
Cholinergic Fibers
ACh-releasing fibers.
Norepinephrine (NE)
Released by sympathetic postganglionic axons. Classed as adrenergic fibers.
Adrenergic Fibers
Fibers that release norepinephrine.
Hypothalamus
Gives order to lower CNS structures for regulation (i.e. medulla oblongata). Regulates heart activity, blood pressure, body temperature, water balance, endocrine activity, and fear (with limbic system).
Dual Innervation
PSNS & SNS serve same organs but generally have opposite effects.