Outer Ear Disorders
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
microtia
small pinna
anotia
absent pinna
atresia
absence or closure of ear canal opening
Can you do AC testing if there is no EAC?
No, should be able to do bone conduction.
Different types of microtia
Type I, II, III, IV
Could be an indicator of other malformations of the ear
Preauricular pits and tags
Auricular keloid
Large, round, flesh-colored ball. Common after piercing or trauma.
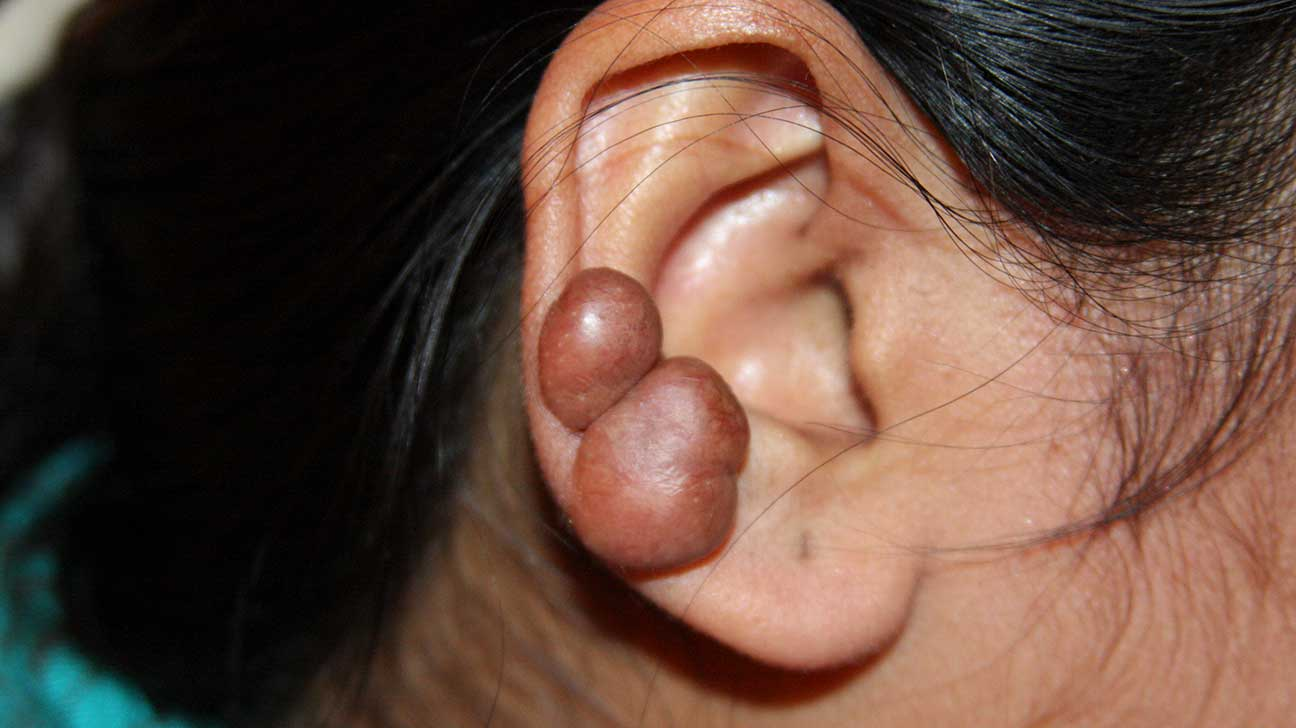
auricular keloid
auricular perichondritis
Swelling of the tissue surrounding the cartilage of the ear
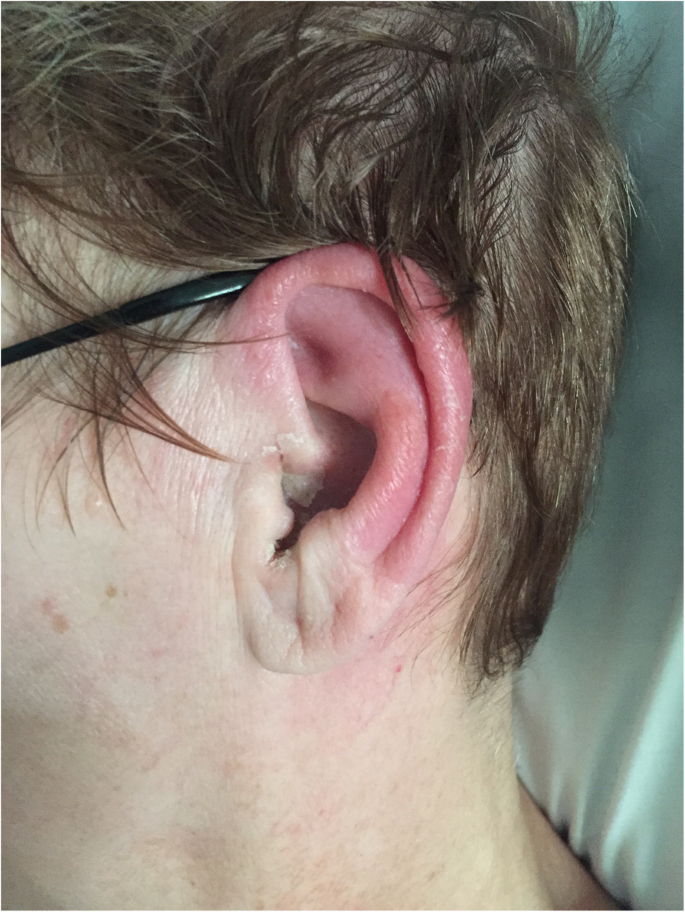
aricular perichondritis
auricular hematoma
accumulation of blood in the subperichondrial space as a result of trauma to the pinna
Cauliflower ear
result of untreated or poorly treated auricular hematoma. Bubbling appearance of the ear.
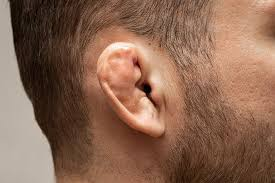
cauliflower ear
Auricular frostbite
Tissue necrosis after prolonged exposure to cold temperatures
basal cell carcinoma
Commonly caused by excessive sunlight exposure. Most common form of skin cancer
herpes Zoster Oticus
Rash or blisters on the skin of the ear canal. Ear pain, burning sensation, vertigo, tinnitus, facial weakness, ipsilateral hearing loss
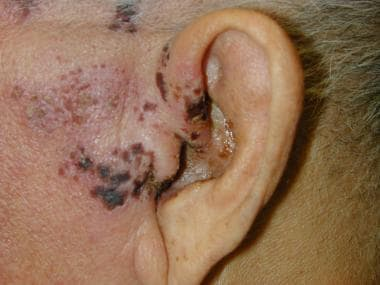
herpes zoster oticus
Exostosis
Benign bony growth in the medial portion of the ear canal (Surfer’s ear) due to cold weather. Usually multiple, bilateral, and painless.
Osteoma
Benign bony growth in the lateral portion of the ear canal. Usually singular.
Otitis Externa
Inflammatory or infection of the EAC. Redness, swelling, and thickening of the canal skin.
Otomycosis
Fungal ear infection of the EAC. Common in hot and humid areas.
Hematoma
Subepidermal collection of blood, result from direct physical trauma.
Causes of hematoma
q-tips
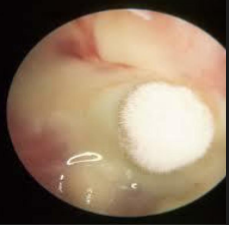
Otomycosis
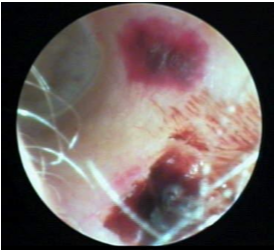
Hematoma
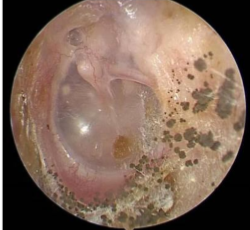
Otomycosis
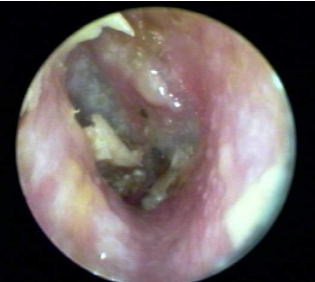
Otitis externa