Gb1- Chapter 10
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
plants
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
photorespiration
hot, dry days cause the closing of stomata to conserve H2O but also decreases photosyntehsis.
decreased access to CO2 and builds up O2 concentration = wasteful
rubisco binds with O2 instead of CO2
costly because it consumes O2 and organic fuel without producing ATP or sugar
a key trade-off in balancing the needs
C3 plants
rubisco fixes carbon to RuBP and forms 3 phosphoglycerate
C4 plants
minimize the cost of photorespiration by incorporating CO2 into a four carbon compound as the first product of the Calvin Cycle.
ex) corn and sugarcane
in hot, dry weather, they partially close their somata to conserve water. this also decreases CO2
photosynthesis begins in mesophyll cells but is completed in bundle sheath cells that are arranged in tightly packed sheaths around the leaf veins
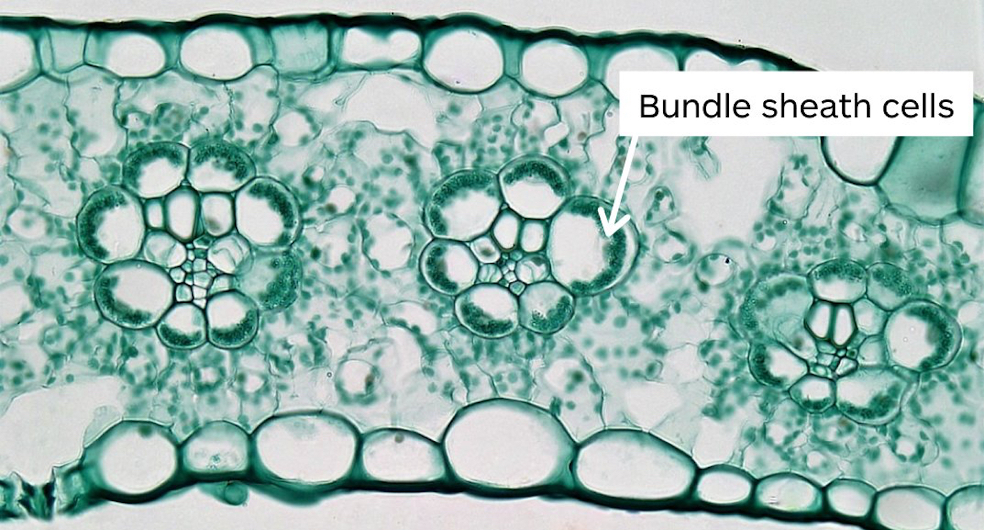
sugar production in C4 plants
In mesophyll cells, PEP carboxylase makes oxaloacetate using CO2
has higher CO2 affinity than Rubisco so it can fix Co2 even when the concentrations are low
Oxaloacetate is converted to malate and is exported to bundle sheath cells through plasmodesmata.
CO2 is released from four carbon compounds and used in the Calvin cycle. Pyruvate is transported back to the mesophyll cell where one ATP is used to convert it back to PEP. ATP comes from cyclic electron flow
C4 photosynthesis uses less water and resources than C3 photosynthesis
structural separation of Co2 from Calvin cycle
crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)
succulents conserve water by opening their somata at night to take in CO2 and close during the day. CO2 is for the calvin cycle used during the day
Temporal separation of CO2 from the calvin cycle