Atoms and subatomic Particles
1/150
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
what is an atom
An atom is the basic unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus made of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. It is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms combine to form molecules, which make up all substances in the universe.
Atoms are the _________
building blocks of matter
Atoms are the _____ particles of an ______ that still have the elements properties
smallest, element
An atom is the _________ into which an element can be divided without losing its ________.
smallest particle, chemical properties
The word “Atom” comes from the Greek atomos and means _____
indivisible
Who was Democritus and what was his theory?
Democritus was a Greek philosopher who theorized that matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
What did Democritus reason would happen if a stone were continually cut into smaller and smaller pieces?
He reasoned that eventually, there would be a piece so small it could no longer be divided.
Who proposed the atomic theory in 1804?
John Dalton proposed the atomic theory in 1804.
What did Dalton's theory state about matter?
Dalton's theory stated that all matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms.
According to Dalton, what are atoms of a given element like?
Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. This has been proven false
What did Dalton's theory say about the divisibility of atoms?
Dalton's theory stated that atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. This has been proven false
What does Dalton's theory say about how atoms of different elements combine?
Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds.
According to Dalton, what happens during chemical reactions?
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
How has Dalton's atomic theory been modified over time?
Dalton's atomic theory has been largely accepted, but with three changes: atoms can be subdivided, not all atoms of an element are identical in mass, and atoms can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions.
What is true about the mass of atoms of a given element?
Not all atoms of a given element are identical in mass (due to isotopes).
Can atoms be created or destroyed?
Using nuclear fission and fusion techniques, atoms can be created or destroyed by changing them into other atoms.
Who discovered the first subatomic particle?
J.J. Thomson
What did J.J. Thomson realize about the accepted model of the atom?
It did not account for negatively or positively charged particles.
What particle did J.J. Thomson discover in 1897?
The electron, a negatively charged particle
What model of the atom did J.J. Thomson propose?
The plum pudding model.
What did J.J. Thomson's model fail to recognize?
It failed to recognize the positive charges in the atom as particles
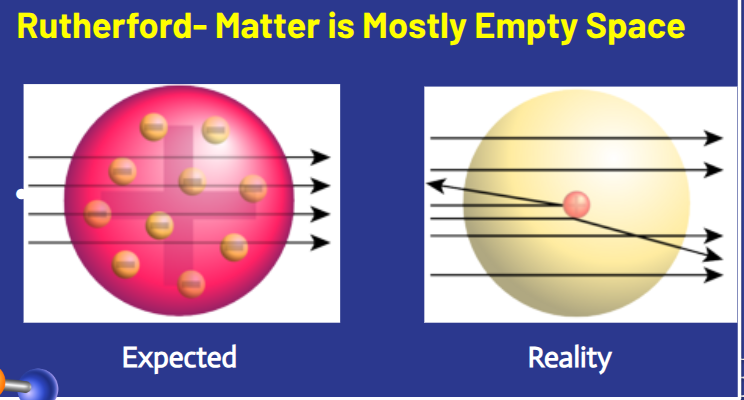
What experiment did Rutherford conduct?
The Gold Foil Experiment
What did Rutherford expect to happen when particles were fired at the gold foil?
He expected them to go straight through the foil
What actually happened when particles were fired at the gold foil in Rutherford’s gold foil experiment?
Most went straight through, but some bounced back.
What did Rutherford's experiment reveal about the structure of an atom?
Atoms have a dense, positive central core called the nucleus.
What did Rutherford discover about the space inside the atom?
Atoms are mostly empty space
In Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment, what was the expected outcome versus the actual result?"
The expected result was that all particles would go straight through the foil, but in reality, some particles bounced back, indicating a dense, positive nucleus at the center of the atom.
What is Bohr’s model of the atom also called?
The planetary model.
What did Bohr propose about the location of electrons in an atom?
Electrons are in orbitals around the positively charged nucleus.
State the model that first included electrons as subatomic particles.
J.J.Thomson
State one conclusion about the internal structure of the atom that resulted from the gold foil experiment.
Atoms have a dense, positive central core=nucleus
State one way in which the Bohr model agrees with the Thomson model.
Agrees about the presence of electrons.
Subatomic particles are particles that are _____ than the atom.
Smaller
____, ____, and _____ are the three main subatomic particles found in an atom.
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What are the three main Subatomic particles found in an atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What is an electron shell?
An electron shell (also known as an orbital) is a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found. Each shell can hold a certain number of electrons. Electrons in different shells have different energy levels.
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons. This gives it a positive or negative electrical charge. Ions are important in chemical reactions and electricity conduction.
What is the mass of an electron?
One electron has a mass of 0.000549 amu. This mass is extremely small compared to protons and neutrons. For most calculations, we consider the mass of an electron to be 0 amu because it is negligible.
What is the atomic mass unit (amu)?
The atomic mass unit is a unit of measurement used to describe the mass of atoms. It allows scientists to compare the mass of different atoms easily. The amu is defined based on the mass of protons and neutrons.
Fill in the blank: 1 proton = ___ amu
1 proton = 1 amu. Protons are one of the main components of an atom's nucleus. Their mass defines most of the atomic mass of an element.
Fill in the blank: 1 neutron = ___ amu
1 neutron = 1 amu. Neutrons are neutral particles in the nucleus of an atom. They have nearly the same mass as protons and contribute to the atomic mass but not the charge.
Why do we usually say 1 electron = 0 amu?
Because the electron's mass is extremely small compared to protons and neutrons, it is considered negligible. This simplifies atomic mass calculations. Even though it technically has a mass, it doesn’t significantly affect the total mass of an atom.
What is an atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. It determines the identity of the element. Each element has a unique atomic number.
What is an electron dot diagram?
An electron dot diagram shows only the valence electrons of an atom. Each dot represents one valence electron. It helps visualize how atoms form chemical bonds.
What is an energy level?
An energy level is a region around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. Electrons in different energy levels have different amounts of energy. Each energy level can hold a specific maximum number of electrons.
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons. This gives it a positive or negative charge. Ions are important in chemical reactions and electricity conduction.
What is an isotope?
An isotope is an alternative form of an element. Isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive.
What is mass number?
Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. It is represented by the letter A. Mass number helps distinguish isotopes of the same element.
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They determine how an atom interacts with other atoms. Valence electrons are key in forming chemical bonds.
What are some different substances that make up a pizza?
Pizza is made up of many substances such as cheese, tomato sauce, dough, and toppings. It is a mixture, not a pure substance. Each substance is made of different atoms or molecules.
What substances make up water?
Water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Each molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Water is a pure substance because it is made of only one type of molecule.
What substances make up an iron pot?
An iron pot is made of only iron atoms. It is an element because it contains only one type of atom.
Which particles are located in the nucleus?
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The nucleus is at the center of the atom. Electrons are not in the nucleus.
Which particles orbit around the nucleus?
Electrons orbit around the nucleus. They are much lighter than protons or neutrons. Electrons move in specific energy levels.
What causes the element to change?
The element changes when you change the number of protons. Protons determine the atomic number, which identifies the element.
Which number is equal to the number of protons in an atom?
The atomic number is equal to the number of protons. It identifies the element.
How can you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom?
Subtract the atomic number from the mass number. This gives the number of neutrons. Neutrons add mass but no charge to the atom.
What particles have an positive charge, negative charge, and no charge respectively?
Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus. Electrons orbit the nucleus.
How many electrons are in a neutral atom of lithium?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
A neutral lithium atom has 3 electrons. The number of electrons equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
How many neutrons are in an atom of Mg-25?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
Magnesium-25 has 12 protons. Subtracting 12 from the mass number 25 gives 13 neutrons.
What is the mass number of an atom with 5 protons and 7 neutrons?
The mass number is 12. Mass number = protons + neutrons = 5 + 7.
How many electrons are in O²⁻?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
O²⁻ has 8 protons and 10 electrons. It has gained 2 extra electrons to have a negative charge.
How many electrons are in Mg²⁺?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
Mg²⁺ has 12 protons but only 10 electrons. It has lost 2 electrons to have a positive charge.
How are electrons arranged around the nucleus of an atom?
Electrons are arranged in energy levels, which are like orbits around the nucleus. Each level can hold a certain maximum number of electrons. Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first.
How many electrons fit in the first energy level?
The first energy level can hold 2 electrons.
How many electrons fit in the second energy level?
The second energy level can hold 8 electrons.
How many valence electrons are in a neutral lithium atom?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
Lithium has 1 valence electron. Valence electrons are in the outermost energy level. They determine chemical bonding.
Notes: “Outermost energy layer” Doesnt refer to just the third energy level, it can be the secoND aswell.
What element has similar properties to lithium?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
Sodium, or any other element in that column, has similar properties to lithium. They are in the same column of the periodic table. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
What element has similar properties to beryllium?
![2025 Periodic Table Of Elements [Symbols, Atomic Numbers & More] - Commodity.com](https://commodity.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/periodic-table-2000-optimized.png)
Magnesium, or any other element in that column has similar properties to beryllium. They are in the same group with 2 valence electrons.
What do elements in the same column of the periodic table have in common?
Elements in the same column have the same number of valence electrons. This gives them similar chemical properties.
How is the periodic table organized?
The periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number. Elements with similar properties are in the same columns (groups). Rows (periods) correspond to energy levels of electrons.
What is an orbit, electron shell, or energy level in an atom?
An orbit, or electron shell, is a region around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. Each energy level can hold a limited number of electrons. Electrons fill the lower energy levels first before moving to higher ones.
What is a valence electron?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They determine how the atom interacts with other atoms in chemical reactions. Atoms with similar valence electrons often have similar chemical properties.
What is the relationship between matter, elements, and atoms?
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom. Atoms are the basic building blocks that make up elements.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a chart that organizes all known chemical elements. It arranges the elements by increasing atomic number and shows their symbols, atomic mass, and other properties. Elements in the same column (group) have similar chemical behavior.
How many elements are on the periodic table as of 2025?
There are 118 known elements on the periodic table as of 2025. Each element has a unique atomic number that identifies it. The elements are organized in rows and columns based on their properties.
How do we describe atoms of an element?
Atoms are described by the element they belong to. Atoms differ from one element to another. For example, a gold atom is chemically and physically different from an oxygen atom.
What is shorthand notation for an element?
Shorthand notation shows the element symbol, atomic number, and mass number. It is a compact way to represent atoms and their key properties

What is the atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. It acts like an ID number for the element. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
What is the mass number of an atom?
Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. It is usually rounded on the periodic table for simplicity. Mass number helps differentiate isotopes of the same element.
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a neutral sodium (Na) atom?

A neutral sodium atom has 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons. The protons define the element as sodium. The neutrons add mass but do not change the element’s identity.
What do the acronyms APE and MAN mean in atomic structure?
APE: Atomic number = Protons = Electrons. MAN: Mass number = Atomic number (protons) + Neutrons. They are useful to quickly determine numbers of subatomic particles in a neutral atom.
The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of…
The total number of protons in the nucleus. It does not count neutrons or electrons directly. The atomic number identifies the element.
How do you calculate the mass number of an atom with 21 protons and 24 neutrons?
Mass number = protons + neutrons. Here, 21 + 24 = 45. This number represents the approximate total mass of the atom.
How are elements ordered in the periodic table?
Elements are ordered by increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons. Atomic mass generally increases as you move across a period or down a group. Groups are columns, and periods are rows in the table.
What is a group or family in the periodic table?
A group is a vertical column of elements on the periodic table. Elements in a group have similar chemical and physical properties. Each element in the same group has the same number of electrons in its outer shell.
How many periods are there in the periodic table?
There are seven periods, which are horizontal rows. Period number indicates the number of energy levels (orbitals) the elements in that row have.
How do you read across a period and down a group?
Reading across a period means moving left to right across a row. Reading down a group means moving from top to bottom in a column. Properties often change gradually across a period but are similar within a group.
What happens if you increase the number of protons in an atom?
The atom becomes a different element because the number of protons defines the element. Its atomic number changes. Chemical properties change according to the new element.
What is the charge of an atom if it gains 2 electrons?
The atom becomes negatively charged. It now has more electrons than protons. The charge is -2.
Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of…
Valence electrons. Valence electrons determine how an atom reacts chemically. That is why elements in the same group have similar properties.
What is an ion and what types of ions exist?
An ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a charge. Positive ions (cations) form when electrons are lost, and negative ions (anions) form when electrons are gained. "Types" just refers to whether it is positively or negatively charged.
How does moving an electron to a higher energy shell affect an atom?
Moving an electron to a higher energy shell increases the atom’s energy. The atom becomes more reactive because electrons are farther from the nucleus. This can change how the atom bonds with others.
Cause: You add 1 proton to an atom. Effect?
The atom becomes a different element. Its atomic number increases by 1. Chemical properties change according to the new element.
Cause: You add 3 neutrons to an atom. Effect?
The mass number of the atom increases. The isotope of the element changes. Chemical behavior usually remains the same, but stability can be affected if it becomes radioactive.
Cause: An element loses 1 valence electron. Effect?
The atom forms a positive ion (cation). Its charge increases by +1. This changes its chemical reactivity because it now seeks to gain electrons to become stable.
Cause: An element has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Effect?
The element forms a +1 ion because it has one more proton than electrons. Its chemical reactivity changes because it seeks to gain an electron to balance its charge.
What are energy levels in an atom?
Energy levels are fixed distances from the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. Electrons in an atom are arranged in these energy levels. Each level can hold a specific number of electrons.
How does the positive charge of the nucleus affect the energy of electrons?
The positive charge of the nucleus attracts the negatively charged electrons. The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the stronger the attraction, and the lower its energy. Electrons farther from the nucleus have higher energy because the attraction is weaker.
How does the distance from the nucleus relate to an electron's energy?
The farther an electron is from the nucleus, the higher its energy. Electrons in higher energy levels are farther from the nucleus, and those in lower energy levels are closer.