P1 Motion, forces and energy
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
How is length measured? + units
ruler, tape measure, micrometer
km, cm, mm
How is volume measured? + units
measure cylinder
cm3 m3
What is time intervals measured by?
clocks (both analogue and digital), timers
How to find average value for distance?
1)measure distance multiple times
2)find average by adding values and dividing by number of measurements
How to find average value for period of oscillation of a pendulum?
1)measure multiple cycles (swings)
2)record total time
3)divide by number of swings for average of one swing
formula = time/oscillation
What does have scalar quantity have?
magnitude
Examples of scalar quantities
distance, speed, time, mass, energy, temperature
What does have vector quantity have?
has magnitude and direction
Examples of vector quantities
force, weight, velocity, acceleration, gravitational field strength
What is speed?
distance travelled per unit time
Speed formula
s=d/t
s=speed (m/s)
s=distance travelled (m)
t=time taken (s)
Average speed formula
v=s/t
v=average speed (m/s)
s=total distance travelled (m)
t=total time taken (s)
What is velocity?
speed in a given direction
Velocity formula
velocity=displacement/time
displacement is change is position
What is acceleration?
rate of change in velocity per unit time
Acceleration formula
a=(v-u)/t
a=acceleration (m/s2)
v=final velocity (m/s)
u=inital velocity (m/s)
t=time taken for change (s)
Axis for distance-time graph
x-axis=time
y-axis=distance
Axis for speed-time graph
x-axis=time
y-axis=speed
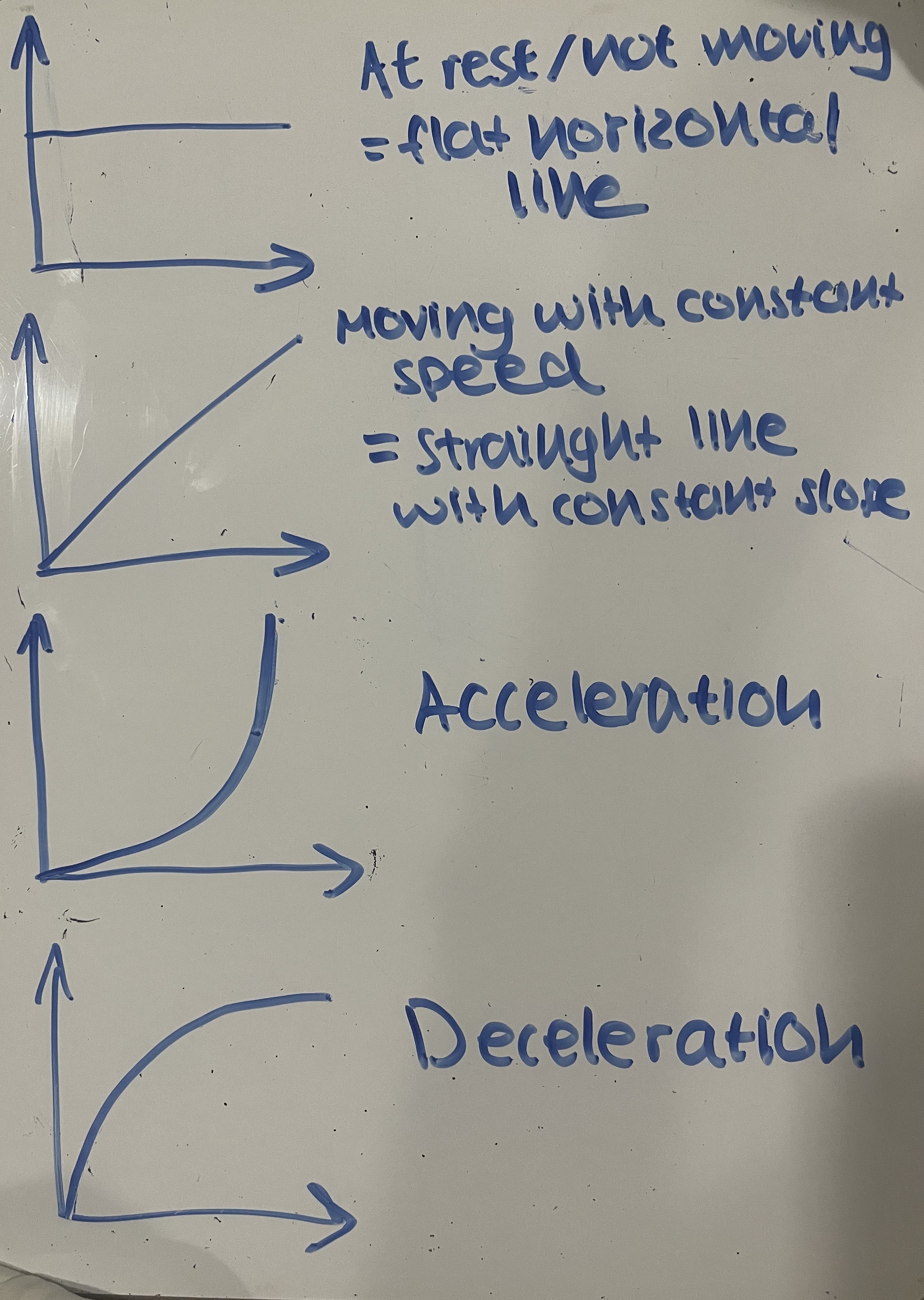
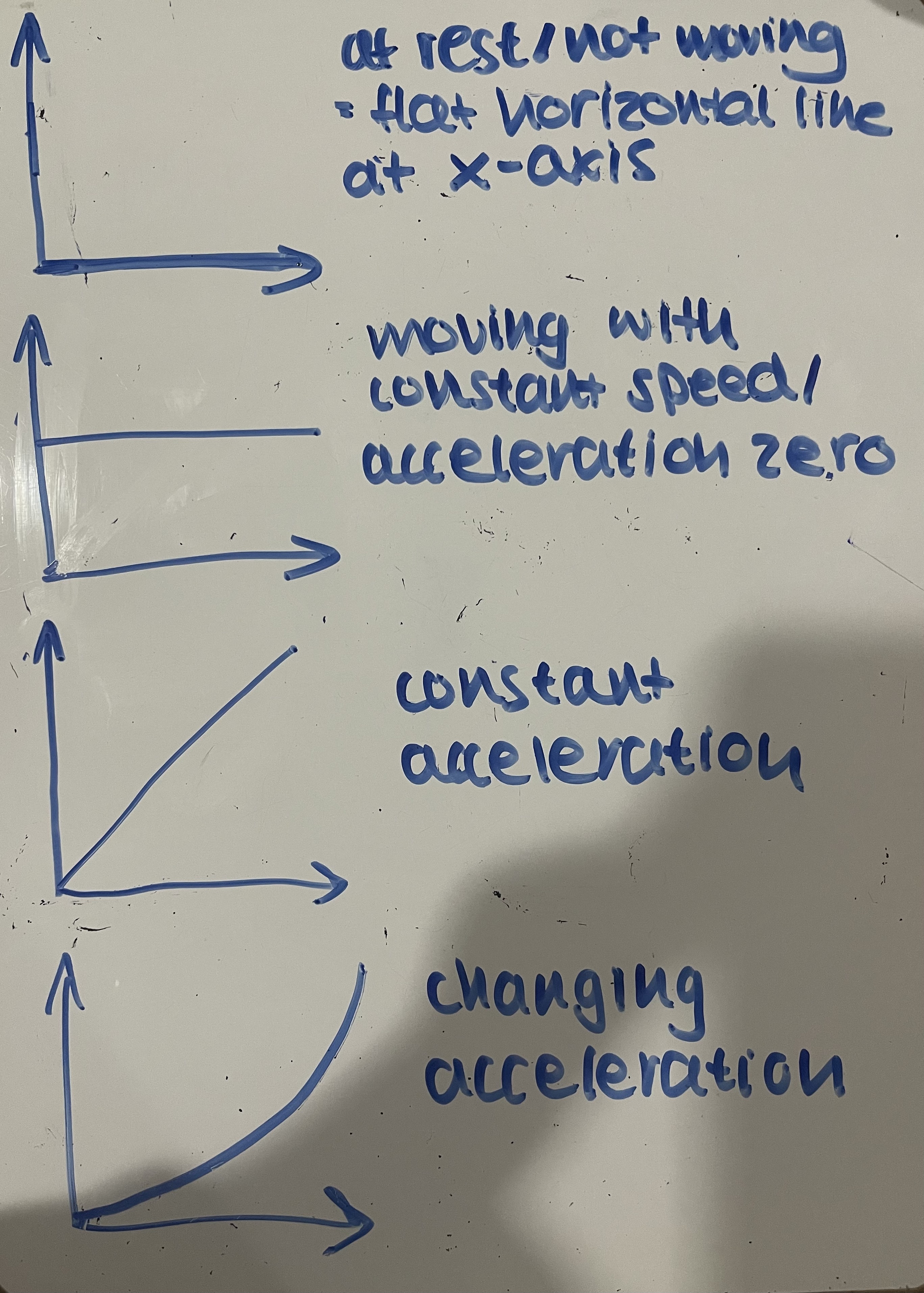
What is accelerating?
object moving with increasing speed
What is decelerating?
object moving with decreasing speed (it is a negative in calculations)

What do the shapes of these distance-time graph mean?

What do the shapes of these speed-time graph mean?
How to calculate speed from a distance-time graph?
by finding the gradient (by drawing a tangent if it is not a straight-line section)
How to calculate distance travelled from a speed-time graph?
finding the area underneath the graph
What is the acceleration of free fall g for an object near to the surface of the earth?
9.8 m/s2
What is mass?
a measure of the quantity of matter in an object
-measured in kg
-not determined by gravity
-stays the same wherever you are
-not a force
What is weight?
the gravitational force on an object that has mass
-measured in newtons (N)
-determined by gravity
-changes wherever you are
-is a force
What is gravitational field strength?
the gravitational force per unit mass
Gravitational field strength formula
g=w/m
g=gravitational field strength (N/kg)
w=weight (N)
m=mass (kg)
What is the gravitational field strength near to the surface of the Earth?
9.8N/kg
What is gravitational field strength is equivalent to?
the acceleration of free fall
What is weight in the concept of the gravitational field?
weight is the effect of a gravitational field on a mass
What is density?
mass per unit volume
Density formula
p=m/v
p=density (g/cm3 or kg/m3)
m=mass (g ot kg)
v=volume (cm3 or m3)
How to determine the density of a liquid?
1)Find mass using scale
2)Find volume using measuring cylinder (1cm3=1ml)
3)Plug into formula
How to determine the density of a regular shaped solid?
1)Find mass using scale
2)Find volume by measuring dimensions and using the formula for volume for specific shape
3)Plug into formula
How to determine the density of a irregular shaped solid?
1)Find mass using scale
2)Find volume using displacement method:
-fill measuring cylinder with known amount of water
-dunk in object
-measure rise in water
-solid’s volume = water’s volume in cylinder with object - water’s volume in cylinder without object
3)Plug into formula
How to determine if an object will float or sink?
an object will float if it is less dense than the liquid it is placed in and sink if it is more dense than the liquid it is placed in
What is the density of water?
1 g/cm3
-objects with density greater than this sink in water
-those with a density less than this floats
What is a force and what can it do to an object?
it is a push or pull. it can cause an object to change size, shape, speed and direction of motion.
-measured in newtons
What is friction?
the force between two surfaces that may impede relative motion and produce heating
What does friction act on?
friction/drag acts on an object moving through liquid (upthrust) and a gas (air resistance)
What factors increase friciton experienced?
friction increases with speed and surface area
What is a resultant force?
a single force that describes the combined action of all forces acting on an object
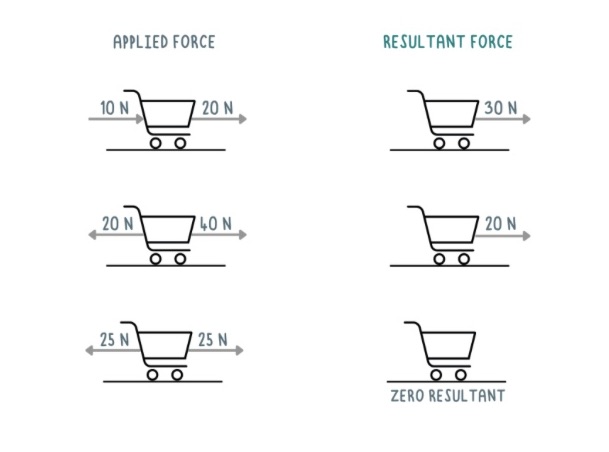
How to find the resultant of forces acting along the same straight line?
if forces act in the same direction, add them together
if forces act in opposite direction, subtract to find difference between them
Find the resultant force for these diagrams
What will an object do without a resultant force?
remains at rest or continues in a straight line at constant speed
What will an object do with a resultant force?
an object's velocity will change (acceleration) either by changing speed or direction of motion.
Force formula
f=ma
f=force (newtons, N)
m=mass (kg)
a=acceleration (m/s2)
Draw and label a load-extension graph
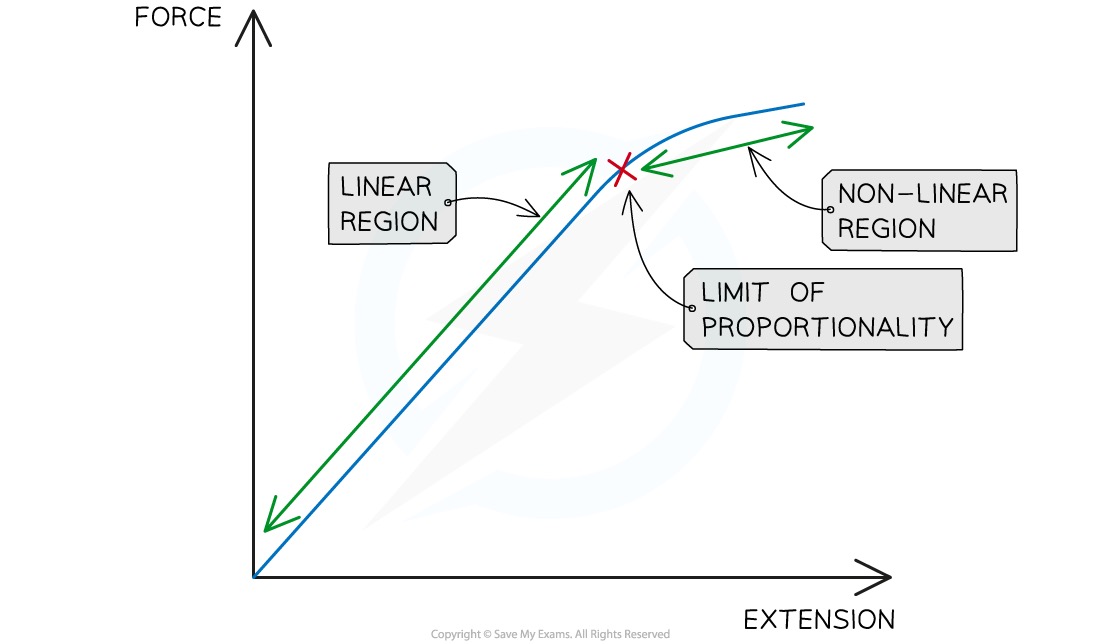
Explain the elastic region/straight line/linear part of graph
-at the start, the graph is a straight line passing through
-this proves Hooke’s law that the extension is proportional to the force over this range
-the material behaves elastically and will return to original length after load is removed
Explain the limit of proportionality
-this is the point where the straight line begins to curve/becomes non-linear which shows that from this point onwards, the material will no longer follow Hooke’s law
Explain the plastic region/curve line/non-linear part of the graph
-after passing the limit of proportionality, further loading less to a non-linear curve
-this means that the material no longer behaves elastically and won’t return to original position (plastic deformation)
What is the spring constant?
force per unit extension
Spring constant formula
k=F/x
k=spring constant (N/m or N/cm)
F=force (N)
x=extension (m or cm)
What is the moment of a force?
a measure of its turning effect
What does the size of a moment depend on?
-size of the force (bigger force, bigger moment)
-distance of the force from the pivot (centre of rotation) (bigger distance from pivot, bigger force)
2 examples of moments in everyday life
-a bike pedal, when riding a bike, pressing your foot down on the pedal causes a moment about the pivot, turning the pedal arms
-a see-saw, when sat on a see-saw, the weight of each person causes a moment. The person that creates a larger moment, is lowered to the floor. If both people create equal moments, the see-saw is balanced.
Moment of a force formula
moment = force x perpendicular distance from the pivot
moment (Nm, newton meters)
force (N)
perpendicular distance from the pivot (m)
When there is a force on either side of the pivot, which way will the object rotate?
in the direction of the force that creates a greater moment (either clockwise or anticlockwise).
When is the object in equilibrium?
when there is no resultant force and no resultant moment
-the clockwise moment equals the anticlockwise moment
How to balance a beam using this diagram?
-the weights must be moved so that the clockwise turning effects equal the anticlockwise turning effect and the net movement is zero, equilibrium
-if the beam tends to swing clockwise m1 can be moved further away from the pivot to increases its moment
-if the beam tends to swing anticlockwise m2 can be moved closer to the pivot to decrease its moment
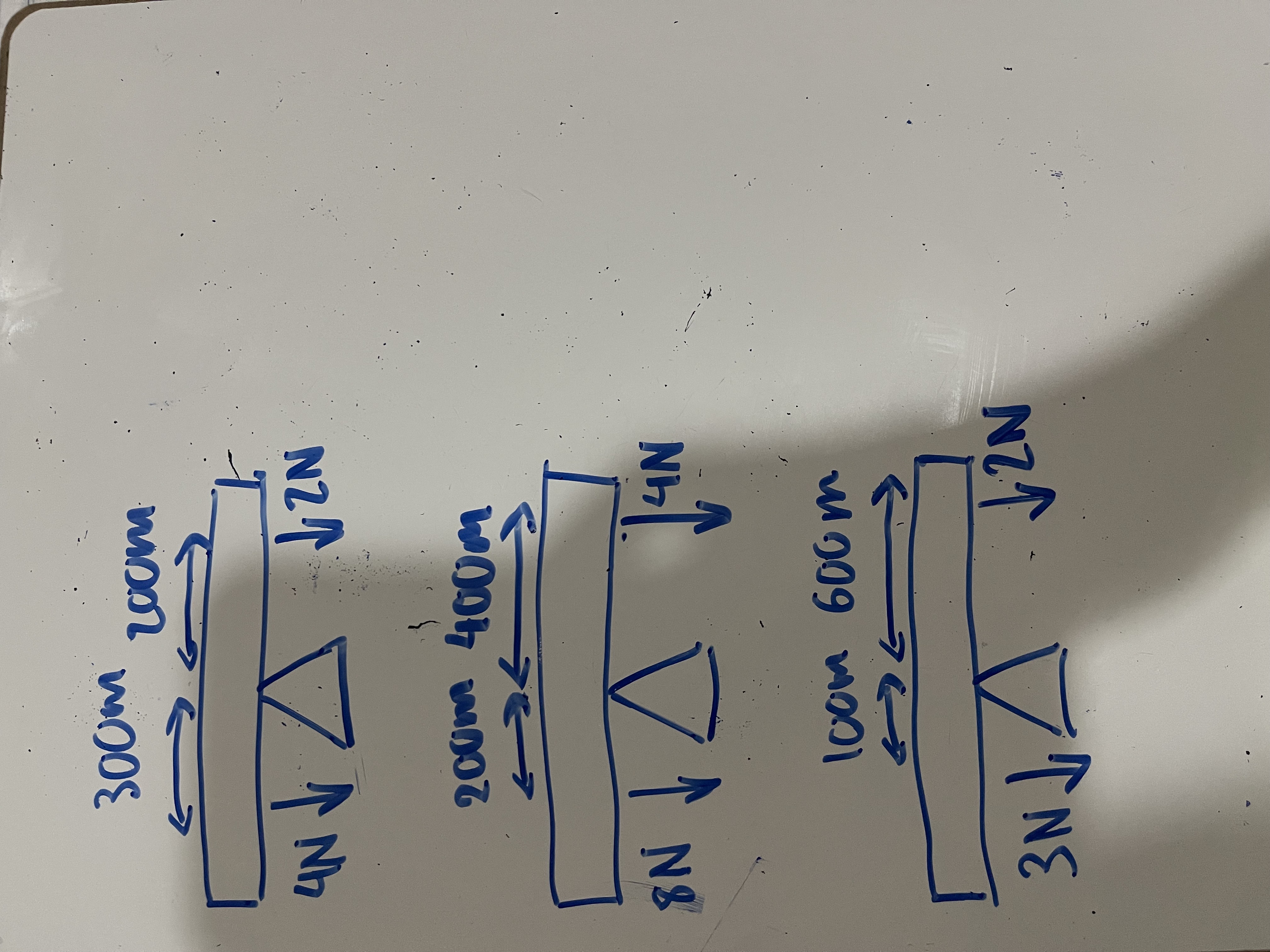
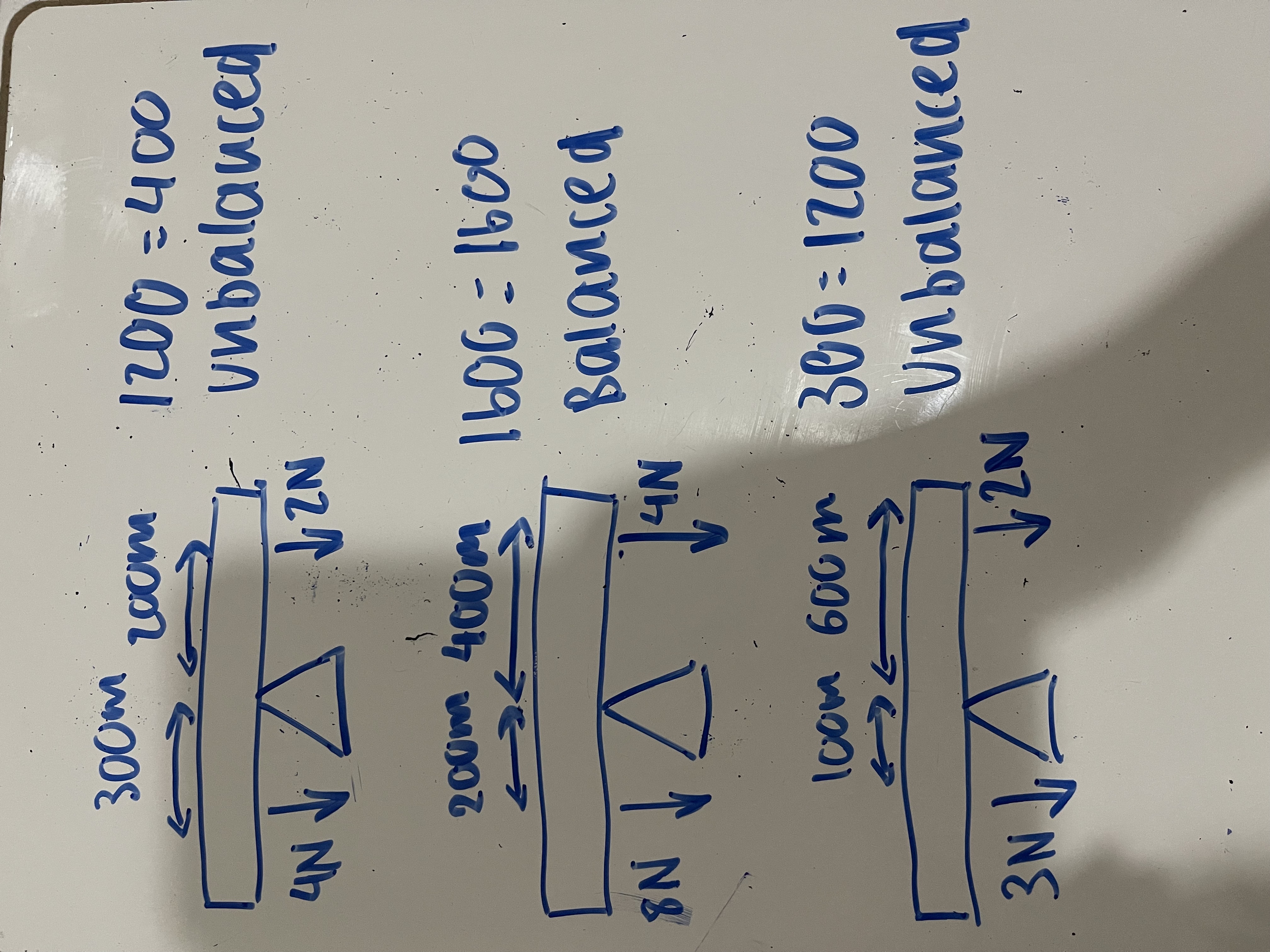
Calculate the moments for these diagrams + state if they are equilibrium
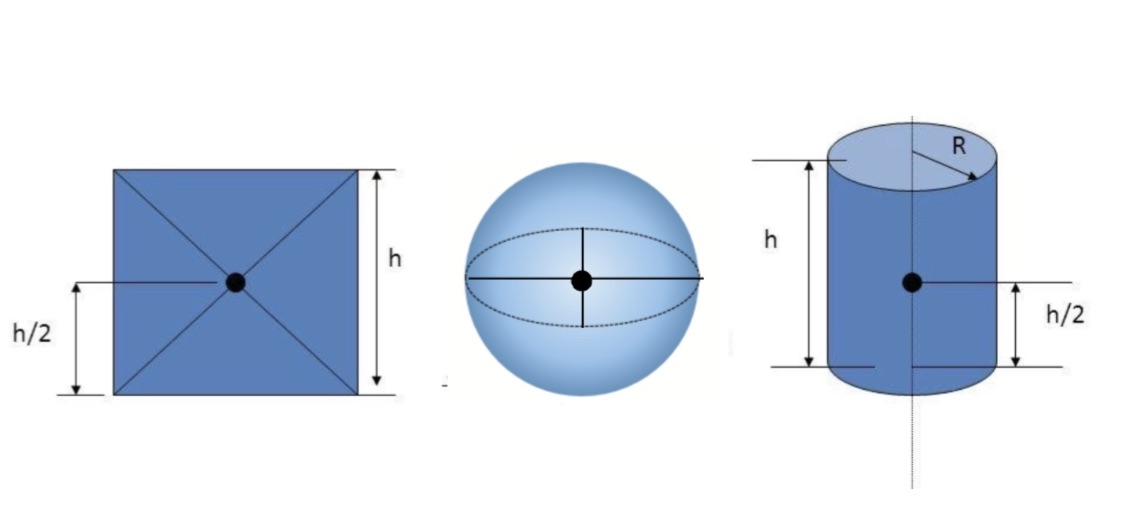
What is the centre of gravity?
the point at which all of an object’s weight can be considered to act
Identify the position of the centre of gravity for rectangular blocks, spheres and cylinders?
How to determine the position of the centre of gravity of an irregularly shaped plane lamina?
Hang the lamina from different points, draw a line along the plumb line from each suspension point, and the intersection of these lines will be the center of gravity.
When will an object be in stable equilibrium? +example
if the centre of mass is below the point of suspension of an object like a hanging plant pot
When will an object be in unstable equilibrium? +example
if the centre of mass is above the point of suspension of an object like a pencil placed on its sharp end
What causes an object to topple?
if the line of action of the object’s weight moves outside the base, there will be a resultant moment and it will topple
How to increase object’s stability?
lowering its centre of gravity, increasing the area of its base
What can energy be stored as?
kinetic, gravitational potential, chemical, elastic (strain), nuclear, electrostatic and internal (thermal)
What is kinetic energy?
the energy of a moving object
What is gravitational potential energy?
the energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field/position above earth/height above the ground
What is chemical energy?
the energy stored chemical bonds, released/absorbed during chemical reactions
What is elastic energy?
the energy stored when an object is stretched or squashed, energy is released when object returns to original shape
What is nuclear energy?
the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom, energy is released/transferred in nuclear reactions (fusion or fission)
What is electrostatic energy?
the energy stored when repelling charges have been moved closer together or when attracting charges have been pulled further apart.
What is thermal/internal energy?
the energy the object has due to its temperature (the total kinetic and potential energy), transferred by convection, conduction or radiation
Kinetic energy formula
Ek = 1/2 mv2
Ek=kinetic energy (J)
m=mass (kg)
v=velocity (m/s)
Change in gravitational potential energy formula
ΔEp = mgΔh
ΔEp=change in gravitational potential energy (J)
m=mass (kg)
g=gravity (N/kg)
Δh=change in height (m)
When is energy transferred between different forms?
during events and processes
Name the ways energy can be transferred
transfer by forces (mechanical work done), electrical currents (electrical work done), heating and waves (electromagnetic and sound)
How is energy transferred by forces/mechanical work done? + example
energy transferred by an action of a force and displacement
exp.when gravity accelerates an object downwards and gives it kinetic energy
How is energy transferred by electric currents/electrical work done? + example
electric current carries energy to be transmitted over distances
exp.when a current passes through a lamp and it emits light and heat.
How is energy transferred by heating? + example
energy transferred by conduction, convection and radiation
exp.when a fire is used to heat up an object
How is energy transferred by waves (electromagnetic/sound) ? + example
electromagnetic waves- transfer energy across various distances and mediums
sound waves- transfer energy through vibrations
exp.vibrations cause waves to travel through air as sound
What happens to the energy during transfers?
energy is always conserved. the total energy before is equal to the total energy after.
-energy can not be created or destroyed, its only transferred form one store to another
What do all energy transfers result in?
the surroundings being heated
-the lost energy is transferred into non-useful thermal energy
What is the general structure for drawing a flow diagram?
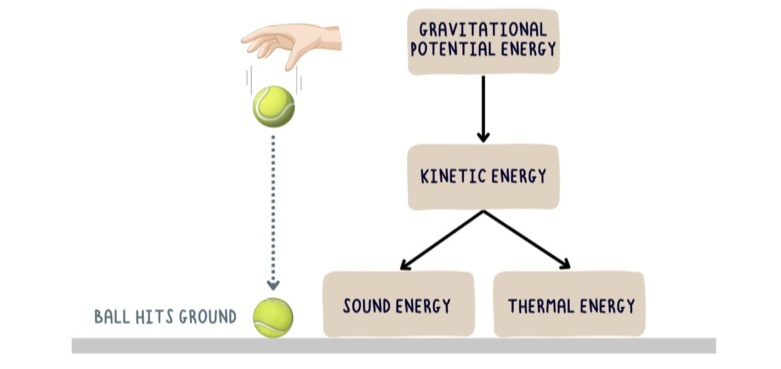
Draw a flow diagram for dropping a ball
When a ball is dropped, gravitational potential energy becomes kinetic energy as it accelerates downwards. Upon impact with the floor, this kinetic energy will become thermal energy and sound energy. The energy never ceases, it is transferred between forms.
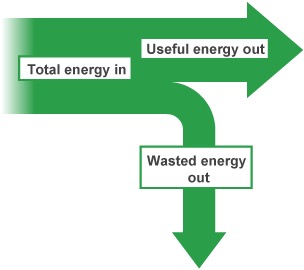
What is the general structure for drawing a sankey diagram?
What is work done?
a measure of the amount of energy transferred
What is the (mechanical or electrical) work done equal to?
the energy transferred
Mechanical work done formula
W = Fd = ΔE
W=work done (J)
F=force (N)
d=distance moved in direction of force
ΔE=energy transferred
Name all the ways useful energy can be obtained?
fossil fuels, biofuels, water (including waves, tides, and hydroelectric dams), geothermal resources, nuclear fission, light from the Sun (solar cells), infrared and other electromagnetic waves from the Sun to heat water (solar thermal collectors), wind (wind turbines)
What is the main source of energy for all our energy resources except geothermal, nuclear and tidal?
radiation from the sun
What are fossil fuels? includes, formed from, stored as
-includes coal, oil and natural gas
-formed from remains of plants and animals that lived million of years ago
-stored as chemical energy
How is fossil fuels used to generate electrical power?
1)fossil fuels are burned in a boiler producing heat
chemical energy → kinetic energy
2)the heat boils water to produce steam which drives a turbine
thermal energy → kinetic energy
3)the turbine is connected to a generator which generates electrical power
kinetic energy → electrical energy
Advantages of fossil fuels
-readily available
-reliable
-large scale
Disadvantages of fossil fuels
-non-renewable
-releases greenhouse gases that cause global warming