Market Structures and Monopoly: Key Concepts and Strategies
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Monopoly
a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes
-price maker
-arises due to barriers to entry, other firms cant enter the market to compete.
Barriers to Entry
monopoly resources, government regulation, production process: natural monopoly
Competitive Firm Demand Curve
Horizontal (perfectly elastic)
The firm can increase Q without lowering P
MR=P
Monopolist demand curve
to sell a larger Q, the firm must reduce P. Thus, MR ≠ P
profit maximizing price
MR=MC
Marginal Revenue
the change in total revenue from an additional unit sold
Average Revenue
TR/Q
profit
(P-ATC) x Q
Has a supply curve that shows how its Q depends on P
competitive firm
Q and P are jointly determined by MC, MR, and the demand curve
Hence, no supply curve for ______
monopoly
deadweight loss
the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium
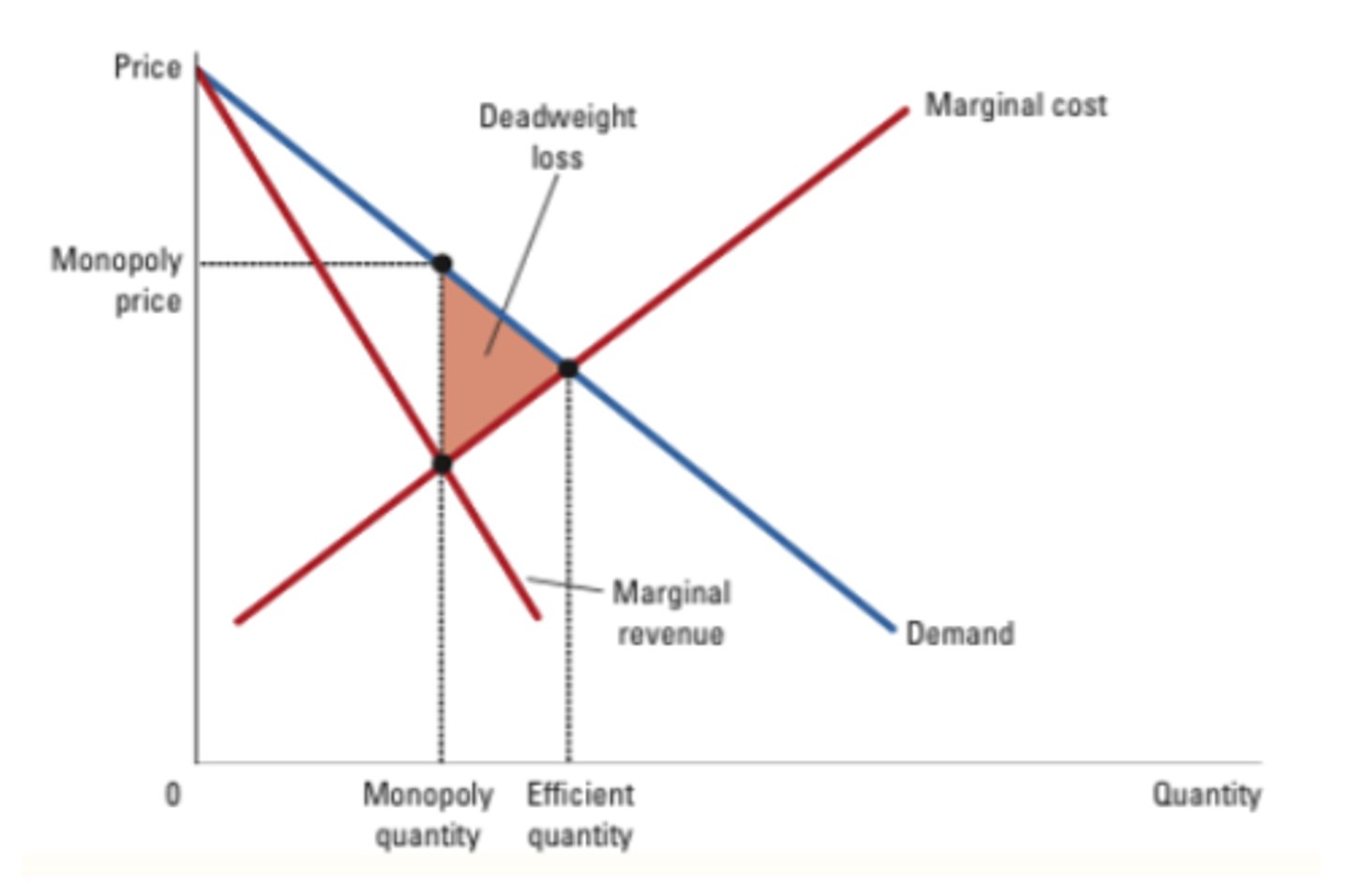
Monopolys can be inefficient because
-Monopoly produces Q < efficient quantity
-Deadweight loss
Price discrimination (price customization)
- Sell the same good at different prices to different customers
- A firm can increase profit by charging a higher price to buyers with higher willingness to pay
- Requires the ability to separate customers according to their willingness to pay
- Can raise economic welfare
price discrimination formula
tr 1 + tr2 (q2-q1 * p ) - tc
perfect competition
p=mc
monopoly
p > mc
oligopoly
A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market
monopolistic competition
a market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but not identical
Concentration ratio
the percentage of the market's total output supplied by its four largest firms
-less than 50% for most markets
short-run profits
•New firms enter the market
•More product variety available
•Demand for each firm decreases
•Prices fall and profits decline to zero
short-run losses
•Some firms exit the market
•Remaining firms face higher demand
•Prices rise
long run
•Price = Average Total Cost = zero economic profit
•Firms charge a markup over marginal cost
•Firms do not produce at minimum ATC = not fully efficient
When oligopoly's are making decisions they take int o account
P or Q can affect other firms and cause them to react
Game theory
the study of how people behave in strategic situations
Oligopolist make the most profit when they...
cooperate and together act like one big monopolist
duopoly
a market with only 2 sellers
simplest type of oligopoly

collusion
agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce or prices to charge
cartel
a group of firms acting in unison