Topic 1
0.0(0)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Last updated 6:23 PM on 4/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
**Anthropometric Data**
The aspect of ergonomics that deals with body measurements, particularly those of size, strength and physical capacity.
2
New cards
**Static** **(structural)** **data**
*Human body measurements when the subject is still.*
3
New cards
**Dynamic** **(functional)** **data**
*Human body measurements taken when the subject is in motion related to range and reach of various body movements. E.g. crawling height, overhead reach and the range of upper body movements.*
4
New cards
**Primary data**
Data collected by a user for a specific purpose.
5
New cards
**Secondary data**
Data collected by someone other than the user.
6
New cards
**Percentile range**
That proportion of a population with a dimension at or less than a given value.
7
New cards
**Clearance**
The physical space between two objects.
8
New cards
**Reach**
A range that a person can stretch to touch or grasp an object from a specified position.
9
New cards
***Adjustability***
The ability of a product to be changed in size, commonly used to increase the range of percentiles that a product is appropriate for.
10
New cards
**Range of sizes**
A selection of sizes a product is made in that caters for the majority of a market.
11
New cards
***Adjustability***
Consider how products can be adaptable for different markets or adjustable to cater for most.
12
New cards
**Psychological Factor Data**
Human factor data related to psychological interpretations caused by light, smell, sound, taste, temperature and texture.
13
New cards
**Nominal (Data) Scale**
Classification or division of objects into discrete groups. Each of which is identified with a name, e.g. category of cars, and the scale does not provide any measurement within or between categories.
14
New cards
**Ordinal (Data) Scale**
A statistical data type that exists on an arbitrary numerical scale where the exact numerical value has no significance other than to rank a set of data points. Deals with the order or position of items such as words, letters, symbols or numbers arranged in a hierarchical order. Quantitative assessment cannot be made.
15
New cards
**Interval (Data) Scale**
Based on numeric scales in which we know the order and the exact difference between the values. Organised into even divisions or intervals, and intervals are of equal size.
16
New cards
**Ratio (Data) Scale**
Allows *you to compare differences between numbers. For example, use a rating scale of 1-10 to evaluate user responses.*
17
New cards
**Qualitative Data**
Typically descriptive data used to find out in depth the way people think or feel – their perception. Useful for research at the individual or small (focus) group level.
* Taste, smell, temperature and texture.
* Qualitative data may be used in a design context relating to psychological factors, but individuals vary in their reaction to the data.
* Taste, smell, temperature and texture.
* Qualitative data may be used in a design context relating to psychological factors, but individuals vary in their reaction to the data.
18
New cards
**Quantitative Data**
Data that can be measured and recorded using numbers. Examples include height, shoe size, and fingernail length.
* Interval or Ratio Scale (Quantitative) – sound, temperature and light
* Interval or Ratio Scale (Quantitative) – sound, temperature and light
19
New cards
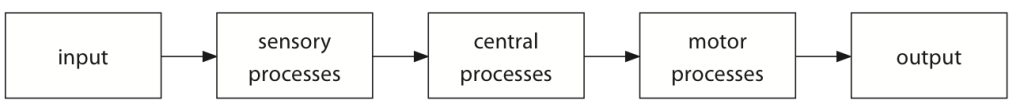
**Human information processing system**
*An automatic system that a person uses to interpret information and react. It is normally comprised of inputs, processes (which can be sensory, central and motor), and outputs.*
* The **input** would be the number to be called.
* The **sensory processes** would be the eyes, which would transmit information to the brain.
* The brain is the **central processing unit**, which examines the information and selects a response coded as a series of nerve impulses transmitted to the hand and muscles.
* These are the **motor processes**, which reconvert the instructions into actions, that is, outputs.
* The **input** would be the number to be called.
* The **sensory processes** would be the eyes, which would transmit information to the brain.
* The brain is the **central processing unit**, which examines the information and selects a response coded as a series of nerve impulses transmitted to the hand and muscles.
* These are the **motor processes**, which reconvert the instructions into actions, that is, outputs.
20
New cards
**Environmental factors**
*A set of psychological factors that can affect the performance of an individual that come from the environment that the individual is situated.*
* Environmental factors include, sound, temperature, lighting, air quality (pollutants) and smell.
* Environmental factors can affect different individuals in different ways. Individuals react differently to sensory stimuli.
* Efficiency and comfort are affected by such factors.
* Environmental factors include, sound, temperature, lighting, air quality (pollutants) and smell.
* Environmental factors can affect different individuals in different ways. Individuals react differently to sensory stimuli.
* Efficiency and comfort are affected by such factors.
21
New cards
**Perception**
The way in which something is regarded, understood or interpreted.
22
New cards
**Alertness**
The level of vigilance, readiness, or caution of an individual.
* Temperature
* Sound
* Lighting:
* Air quality
* Smell
* Temperature
* Sound
* Lighting:
* Air quality
* Smell
23
New cards
**Biomechanics**
The research and analysis of the mechanics of living organisms.
24
New cards
**Fatigue**
When people are put under physical or mental stress/activities for extended periods.
25
New cards
**Comfort**
This various between people. For instance, the type of bed that a person will choose is determined by the firmness of the mattress.