Prosth Midterm Study Set: Key Terms & Definitions
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
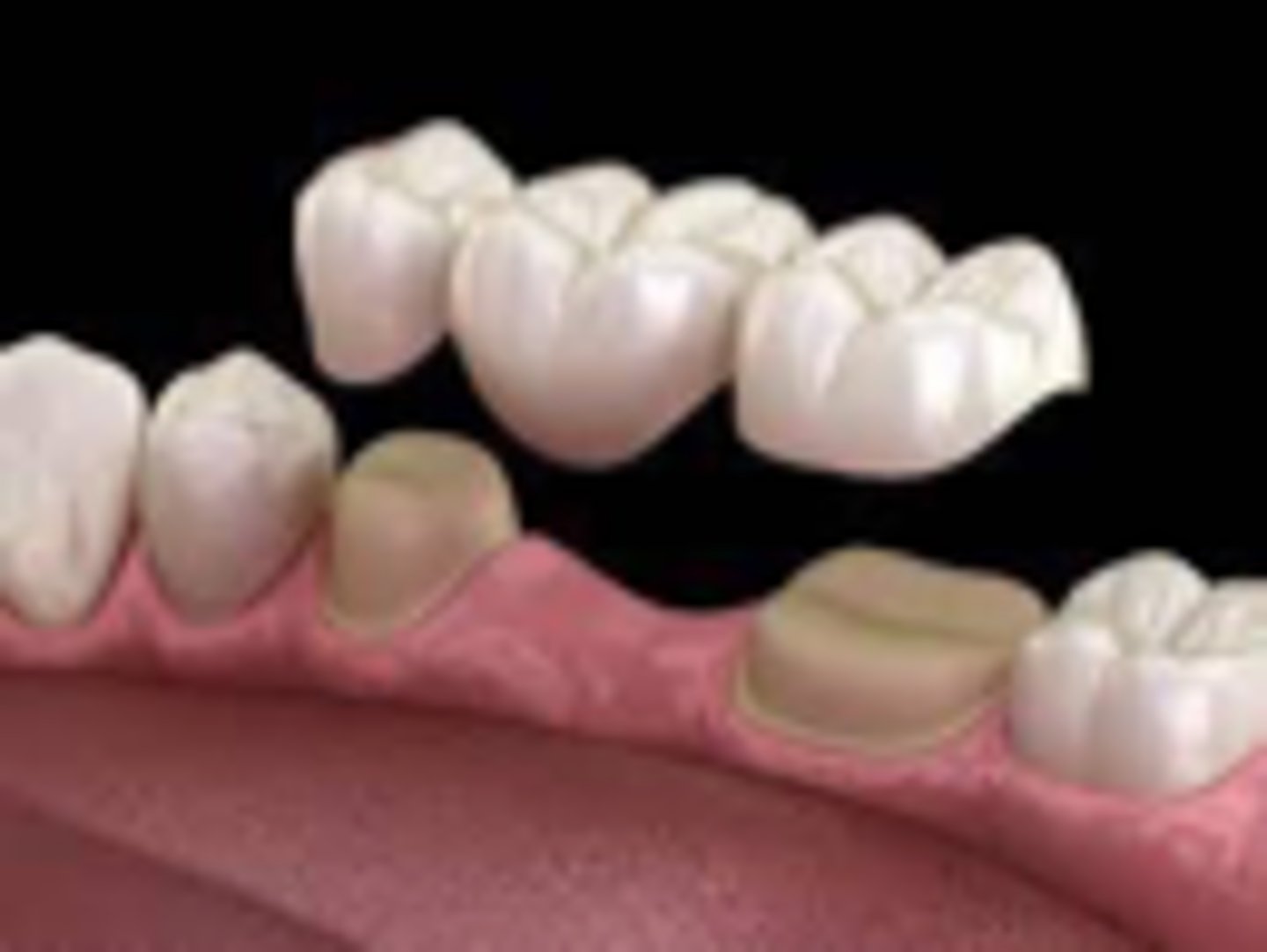
fixed prosthodontics
Cannot be removed from the mouth by the patient
Removable Prosthodontics
Can and should be removed from the mouth by the patient
Maxillofacial Prosthetics
Replaces anatomy of the head and neck beyond teeth and periodontium and/or helps aid in function due to lost anatomical structures
ex:
-Anaplasties (silicone)
-Obturator
-Speech Aid appliances
-Mandibular Resection Prosthesis
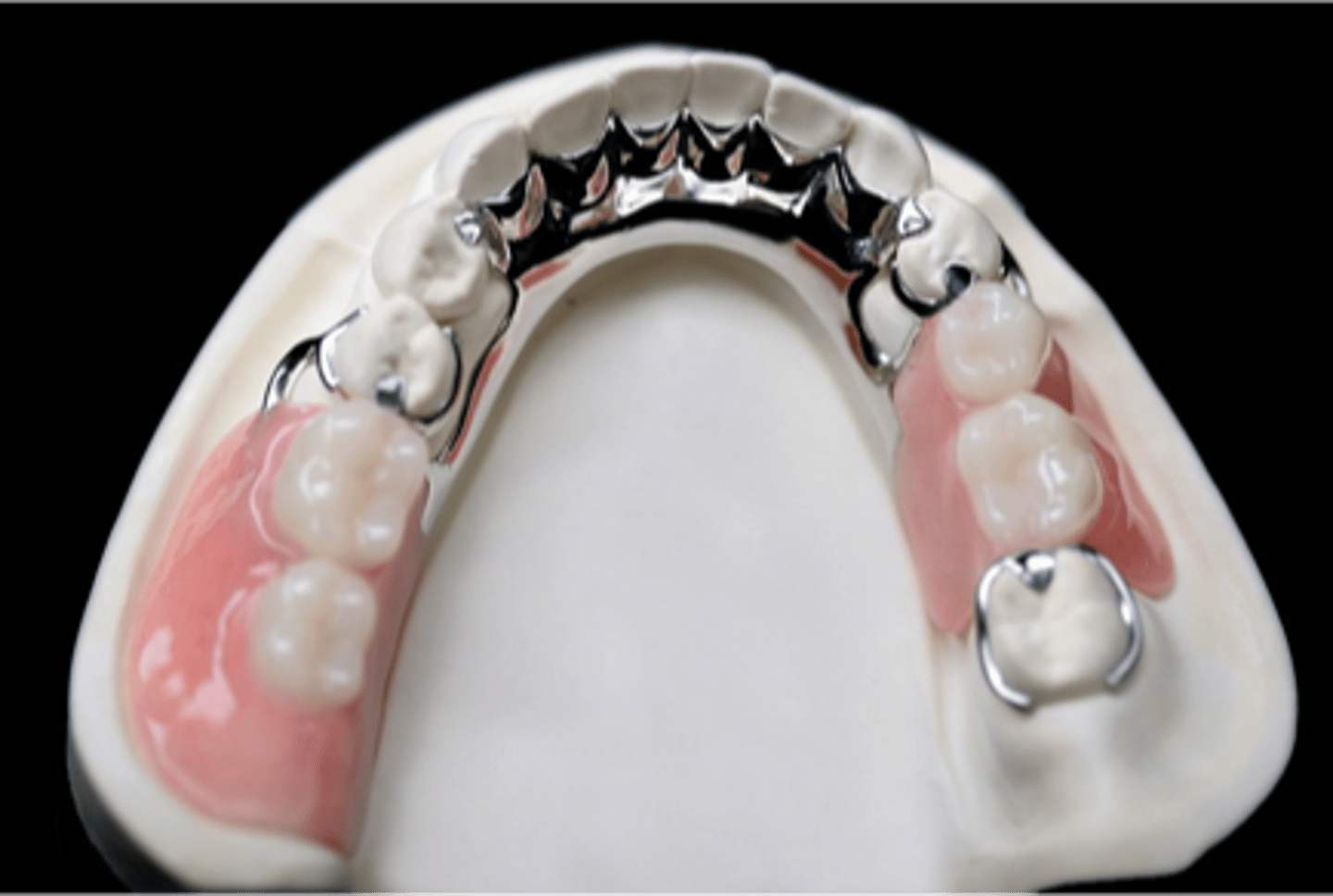
Removable Partial Denture
A prosthesis that replaces one or more missing teeth and contiguous tissues Is designed to be removed by the wearer Is supported and retained by teeth, implants, soft tissue or a combination
Abutment
any tooth or dental implant that supports a dental prosthesis

Retainer
the part of the prosthesis that attaches the prosthesis to an abutment
RPD
clasp assembly or attachment
FPD
crown abutment (floating tooth attached is a "pontic")
replace missing teeth, preserve teeth
RPD functions and requirements
Rests, Maxillary major connector, Denture Base
RPD Support Components- Resistance to force toward the tissues
Minor connectors, Proximal plates, Parts of clasps, Lingual plates, Rests, Denture Base
RPD Stability Components- Resistance to torsional and lateral forces
Direct retainers, Indirect retainers, Proximal plates
RPD Retention Components- Resistance to force directed away from the tissues (dislodging force)
RPD abutment
any tooth or crown that receives a direct or indirect retainer
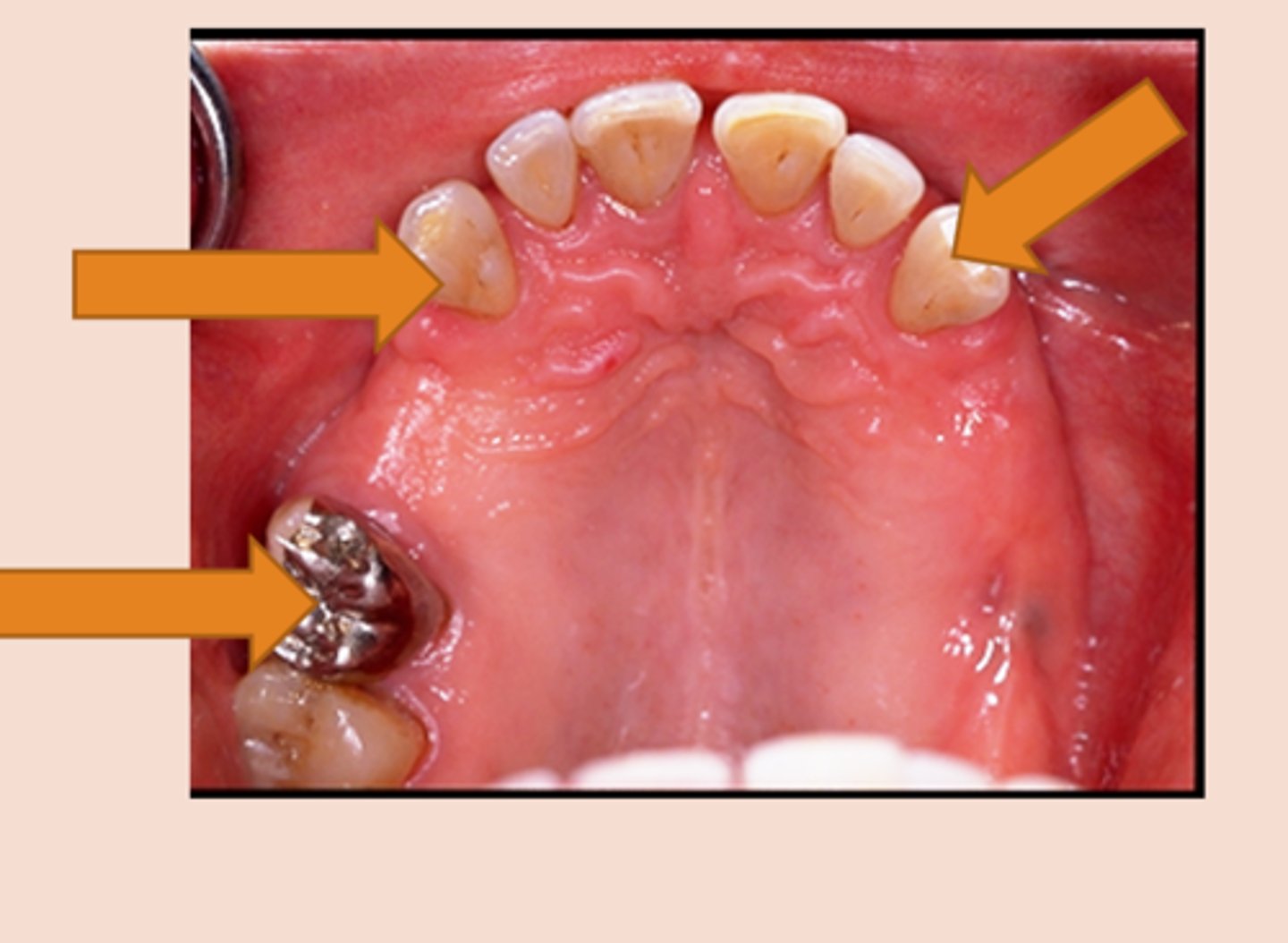
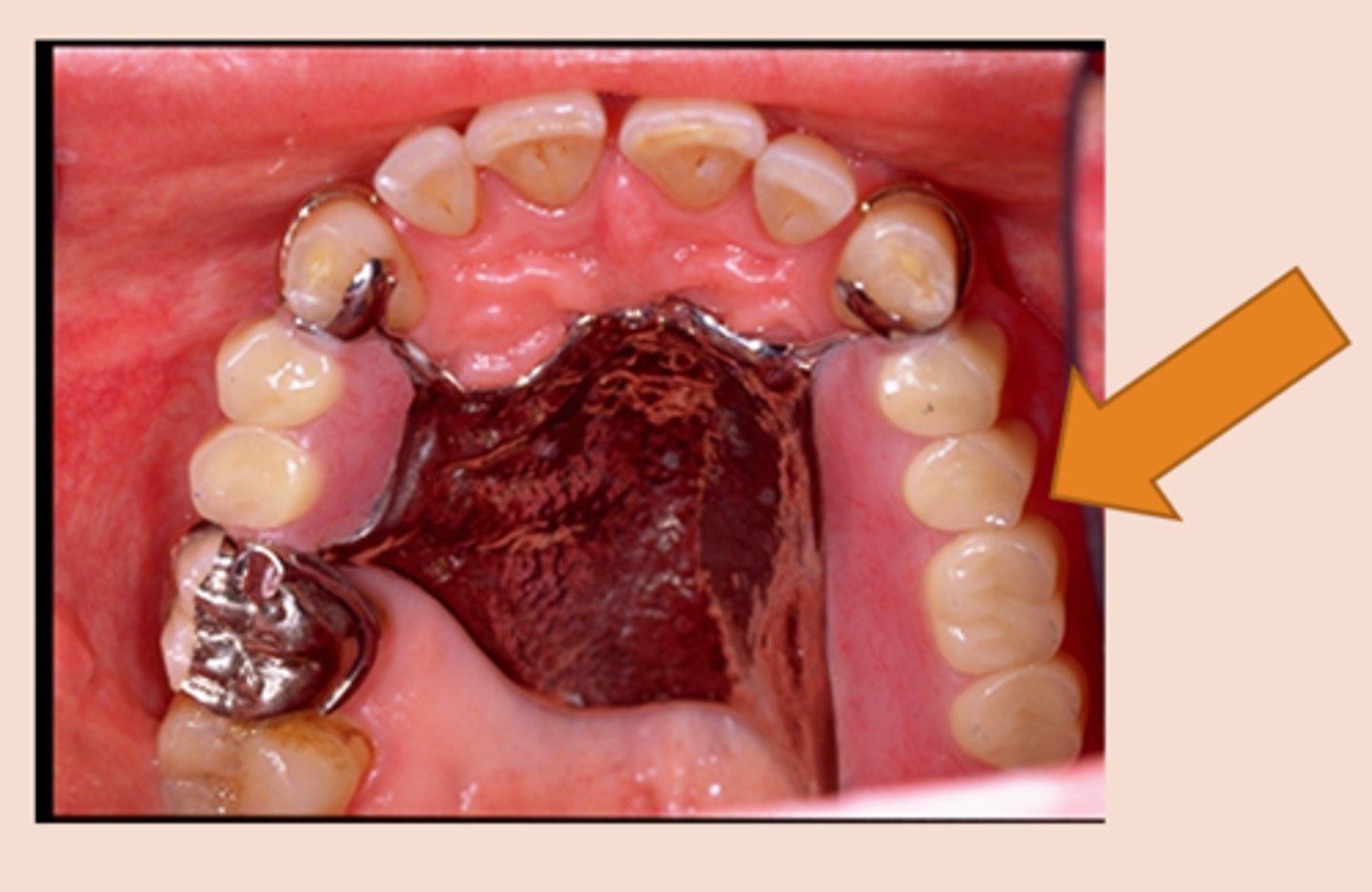
Distal extension
portion of the RPD which replaces teeth and has a mesial abutment only
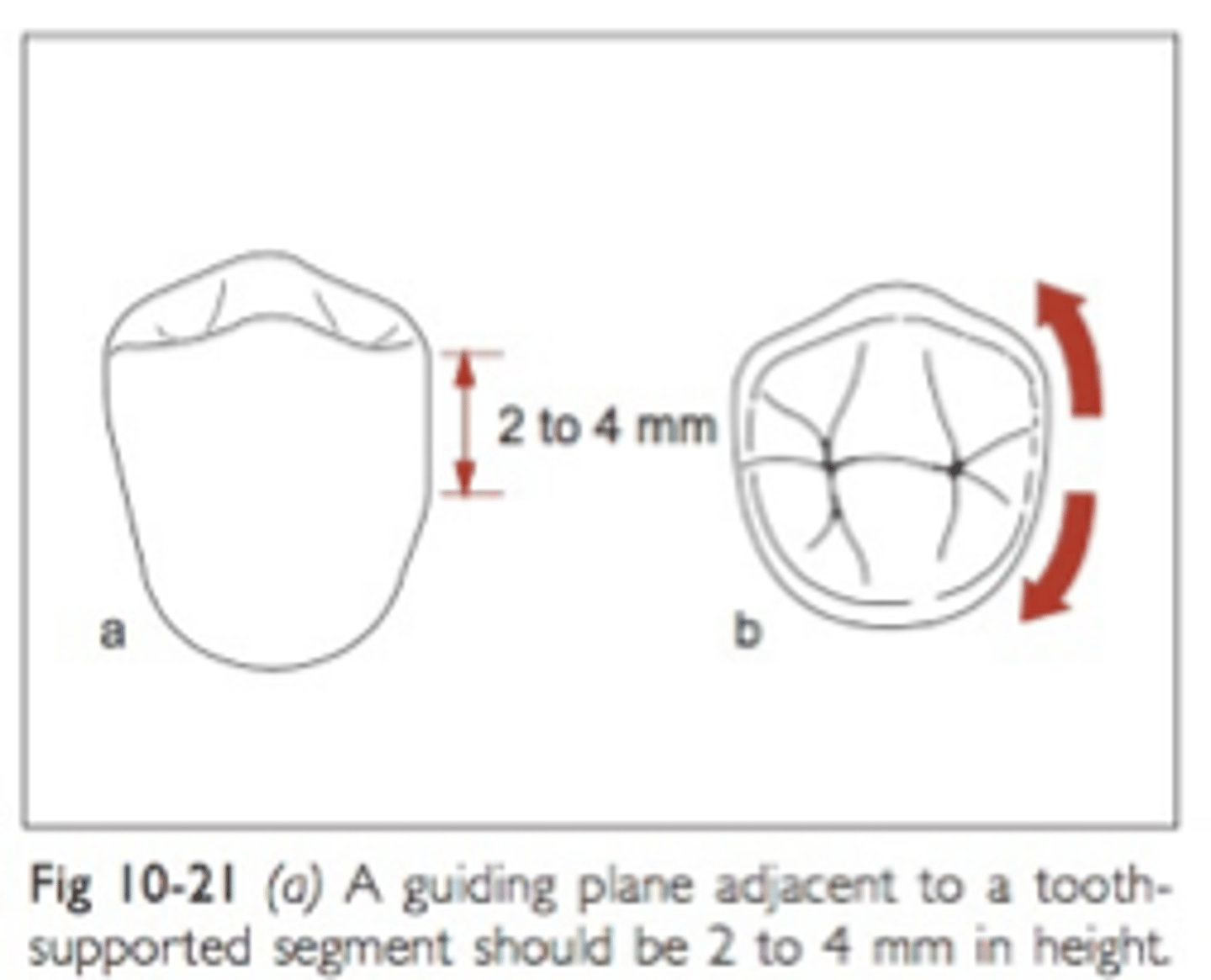
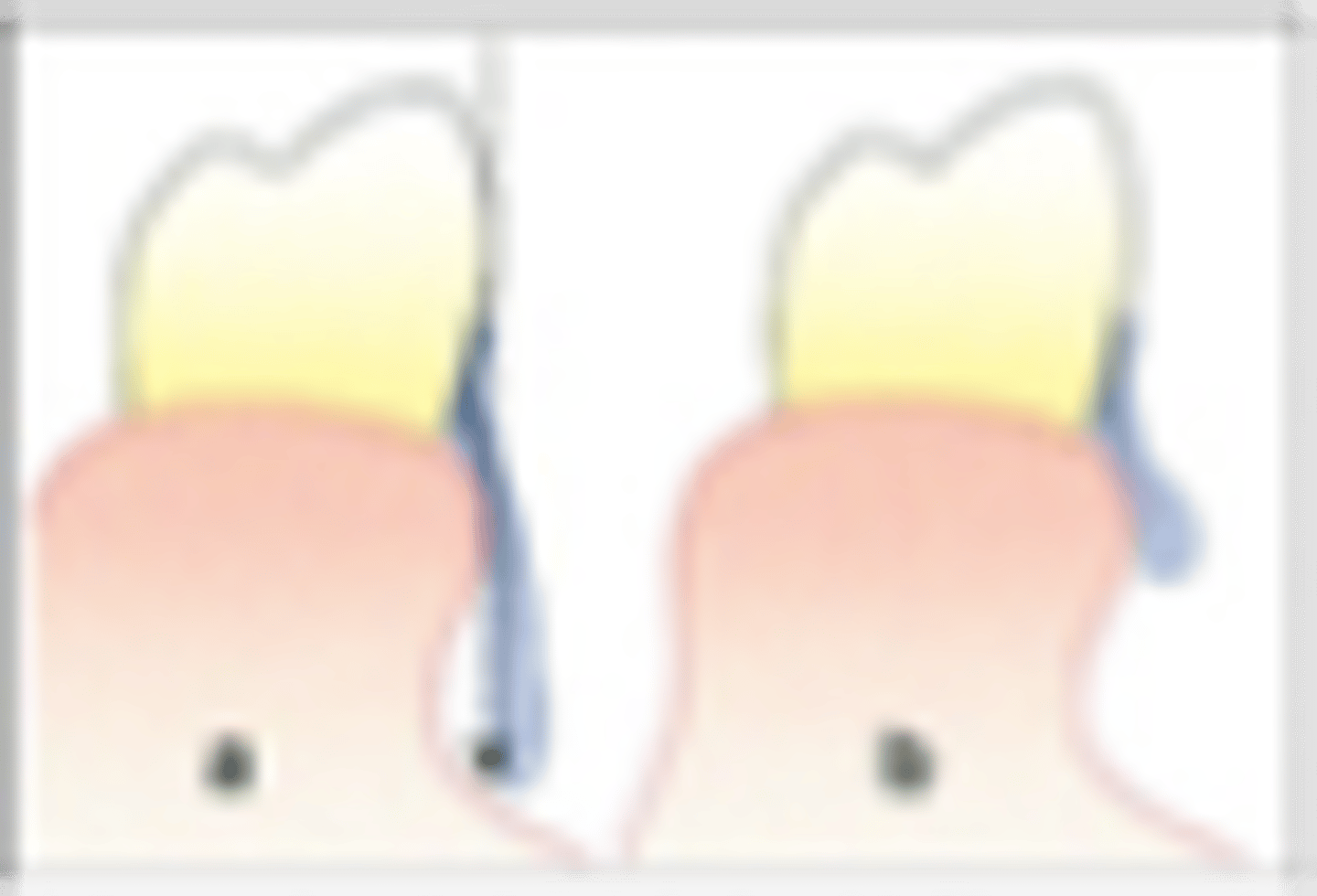
Guide planes
Are prepared (occasionally natural) axial surfaces of teeth against which the RPD glides during insertion and removal - defines the path of insertion
parallel
Guide planes must be ______ to each other and to the path of insertion
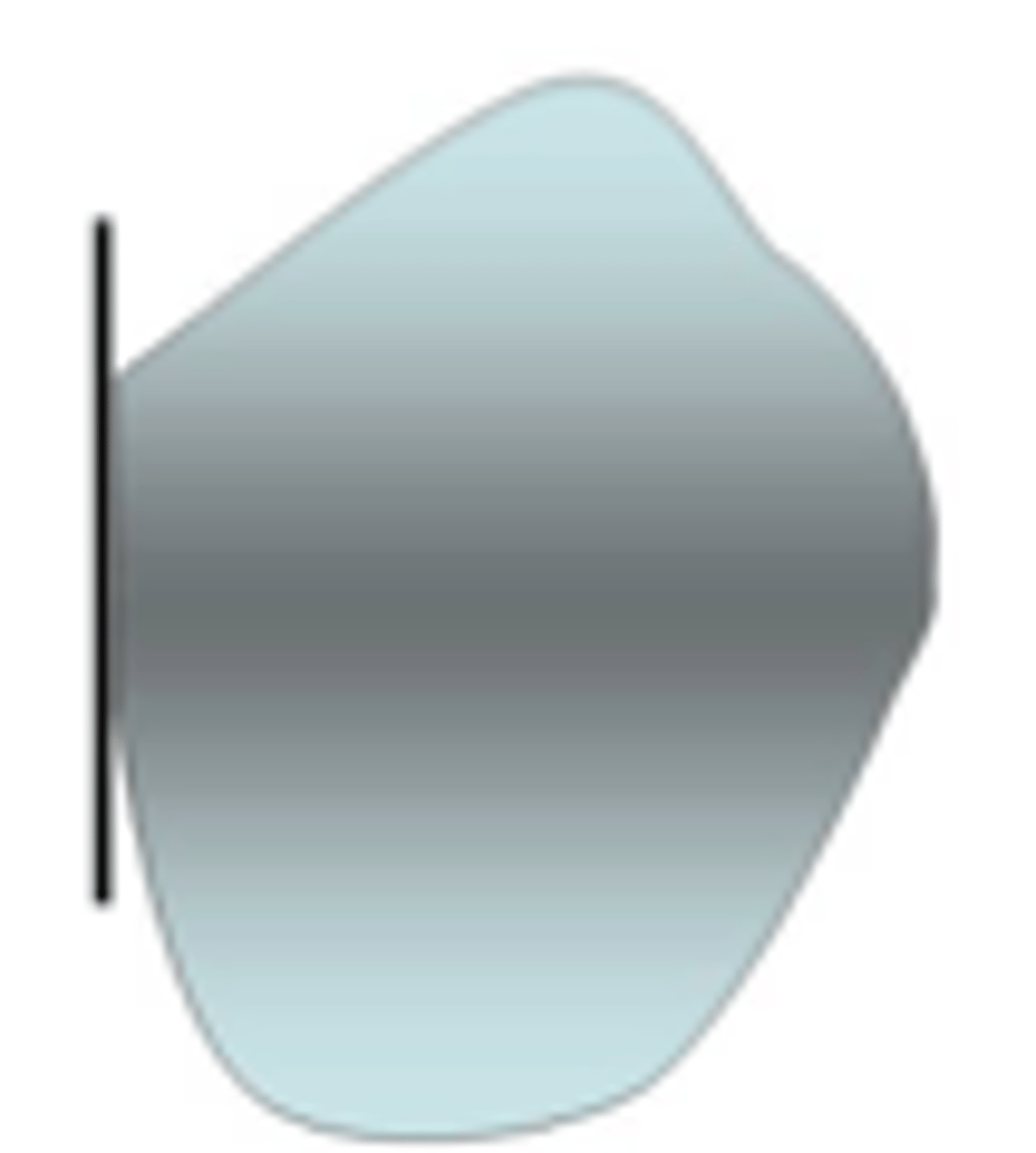
occlusal
Guide planes are Located in the _____ portion of the tooth (a proximal or lingual plate refers to the part of the RPD framework that is in contact with the guide plane)
natural curvature of the tooth buccolingually
Whether adjacent to tooth-borne or extension base segments, the prepared surface for RPD should not be a straight “slice” buccolingually, but should follow the ....
Major connector
The part of the removable partial denture that joins the components on one side of the arch to those on the opposite side, Aid in cross arch stabilization, transmitting functional loads from one side of the arch to the other
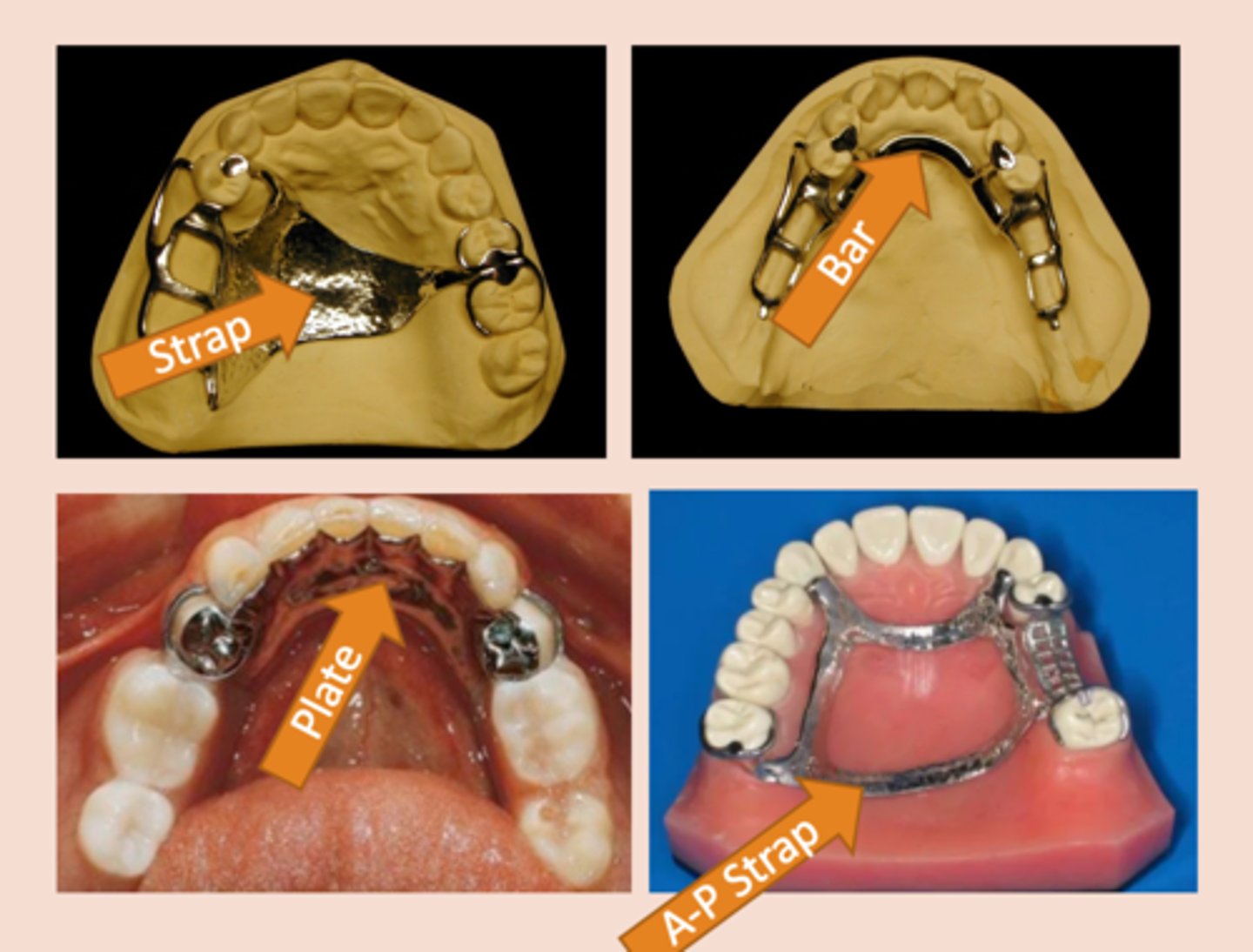
Full palatal plate (major connector)
indicated for maximum tissue support. Use in long distal extension cases or if anterior teeth are anticipated to be lost.
Indicated if the primary abutments are periodontally involved, or in cases with a shallow palatal vault or flabby tissues.

Open plate major connector
Coverage of palatal tori should be avoided if possible.
The tissue covering tori is thin and susceptible to irritation
6 mm
In the maxillary arch, borders of a major connector should be positioned at least _______from the free gingival margins. Otherwise the major connector should be carried onto the lingual surfaces of the teeth in the form of plating.
beading
Maxillary major connectors should have minor elevations at the borders that contact and place minor pressure on the palatal tissue; used to prevent food impaction under the partial

parallel
The borders of the major connector should run _______ to the free gingival margins of the remaining teeth
Lingual bar (Mn)
Most commonly used mandibular major connector.
7-8 mm or more
A lingual bar Requires the functional depth of the vestibule be ______; bar height is 4 to 5 mm. This permits the major connector to have a minimum height of 5 mm and allows 3 mm of space between the gingival margins and the superior border of the bar.
highest point of vestibule during function
when measuring vestibular depth, measure...
Lingual plate (Mn)
Major connector used when:
§ High lingual frenum or <8mm +/-
§ Excessive residual ridge resorption
§ Future anterior tooth replacement (perio, caries)
§ Lingual tori that would be impinged upon by a lingual bar
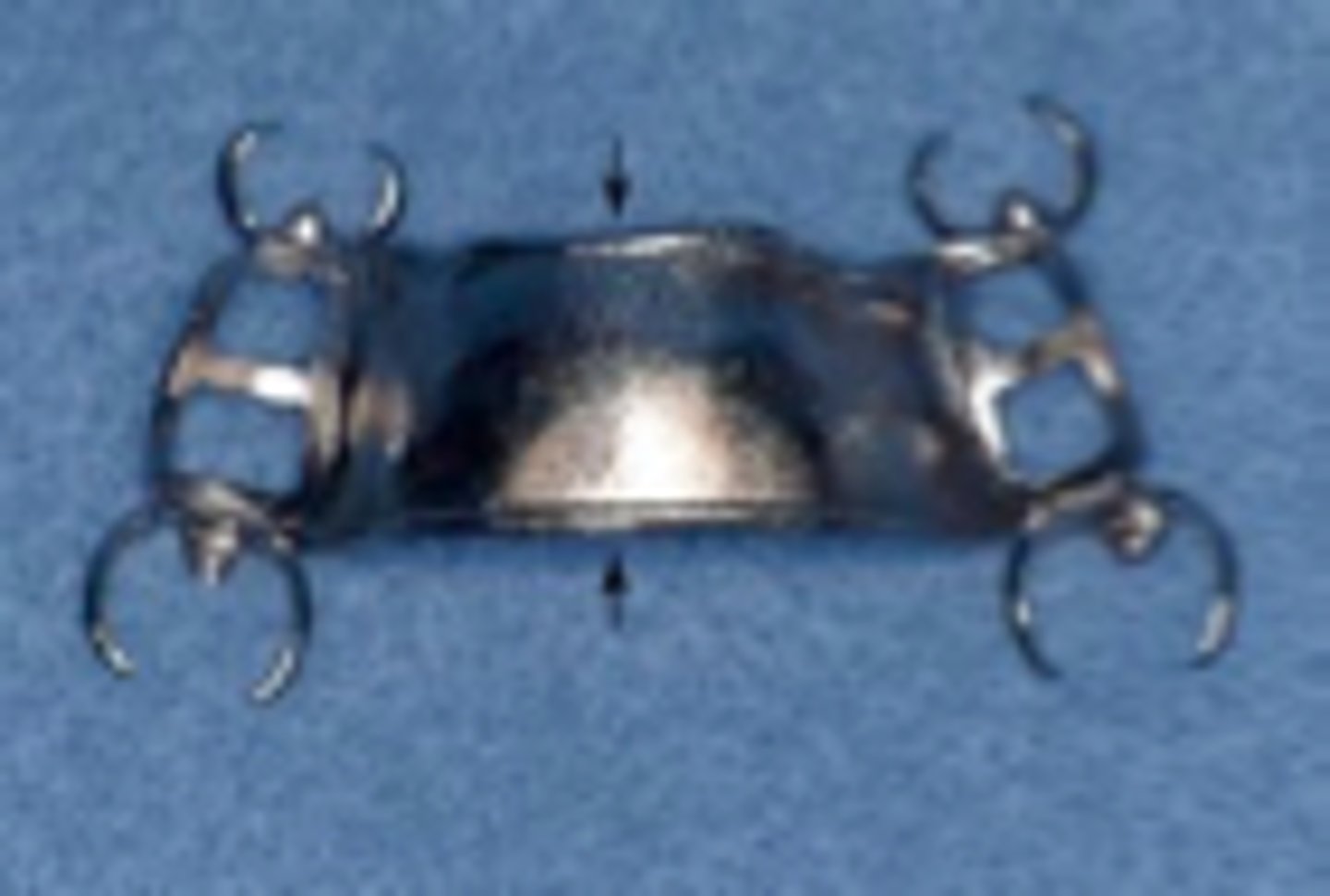
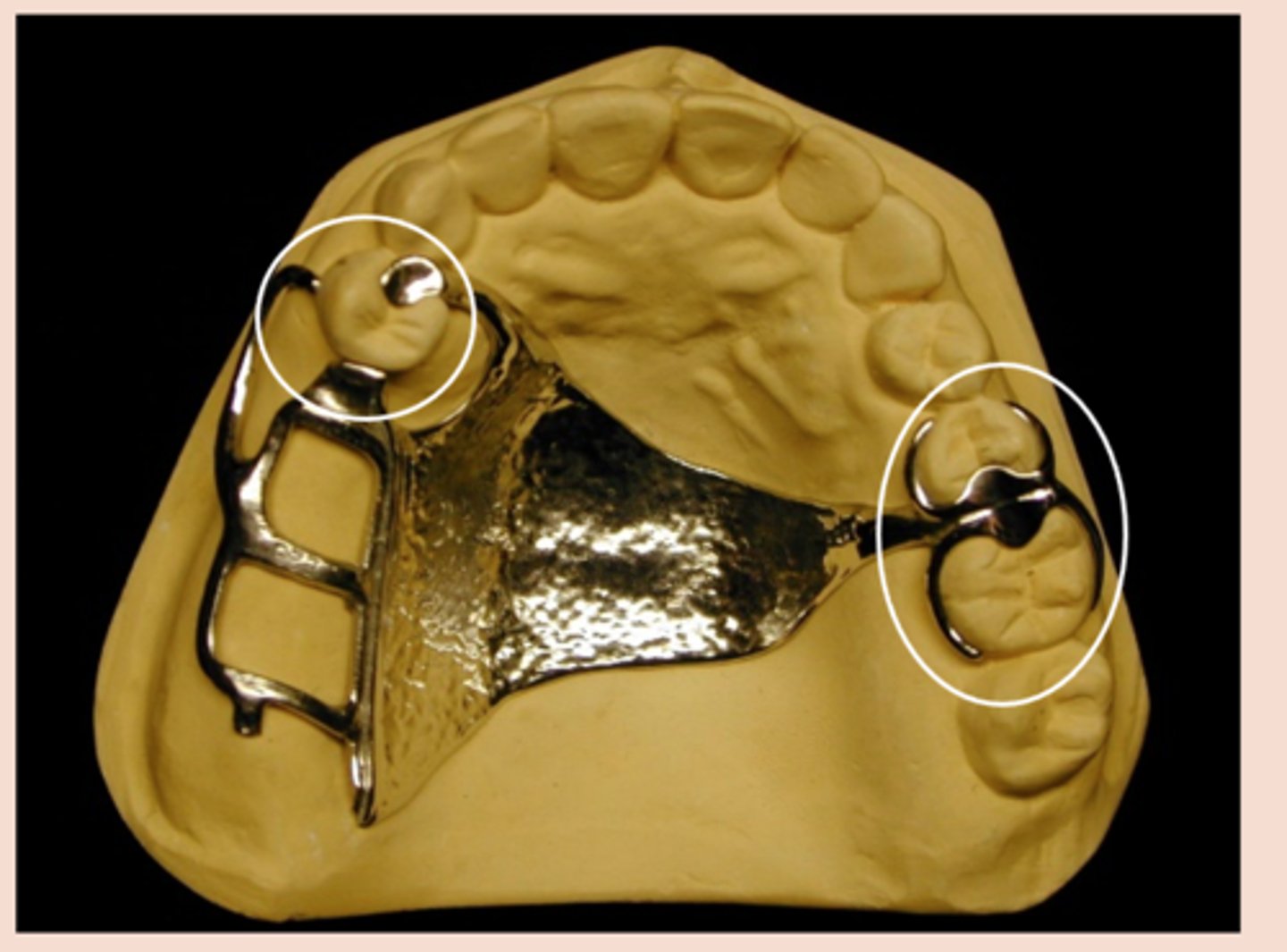
Direct Retainer
component of a removable partial denture that is used to retain and prevent dislodgement of the RPD and consists of a clasp assembly or attachment
Clasp Assembly
An extra coronal direct retainer that engages an abutment tooth for retention, stability and support of the partial denture
§Akers
§Embrasure
§RPI
§RPC
§Combination
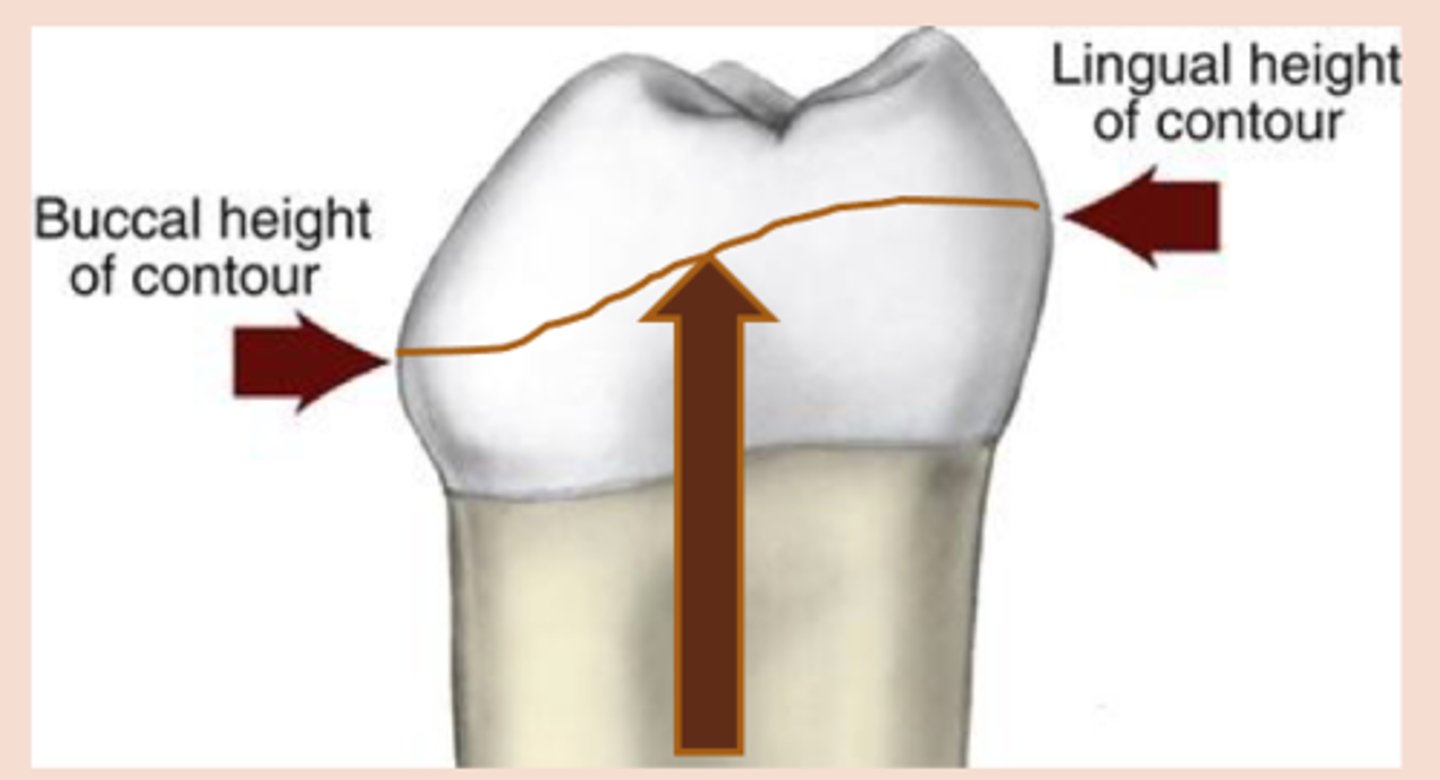
survey line
height of contour marked around the tooth
minor connector.
Clasp assembly is made up of a bracing/stabilizing or reciprocating element, a rest, and retentive element, and is connected to the major connector via a ...
(The clasp engages a portion of the tooth surface and either enters an undercut for retention or remains entirely above the height of contour to act as a reciprocating or bracing element)
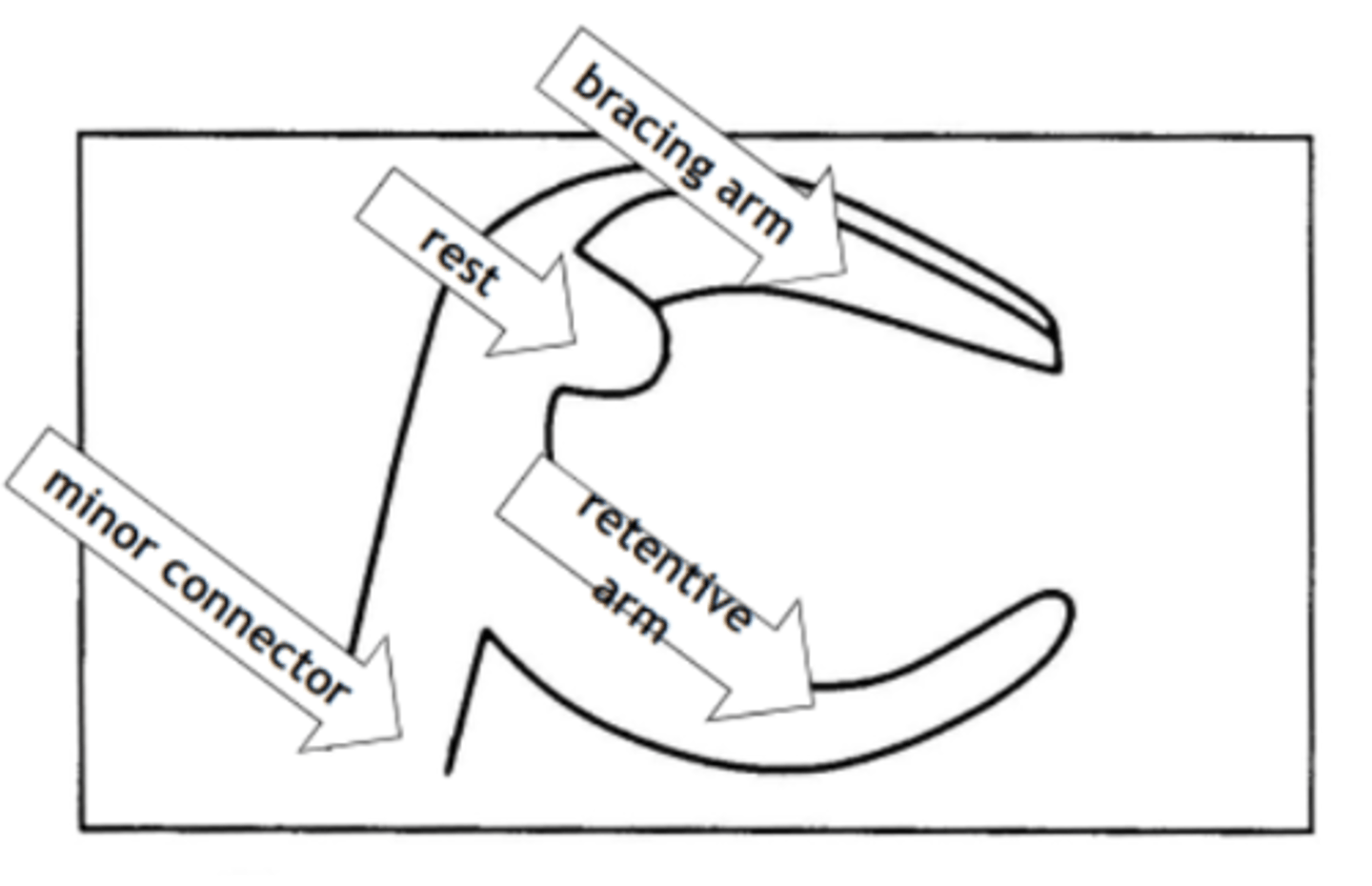
Minor connector
Connecting link between the major connector or base of the RPD and the other units of the prosthesis, such as the clasp assembly, indirect retainers or rests
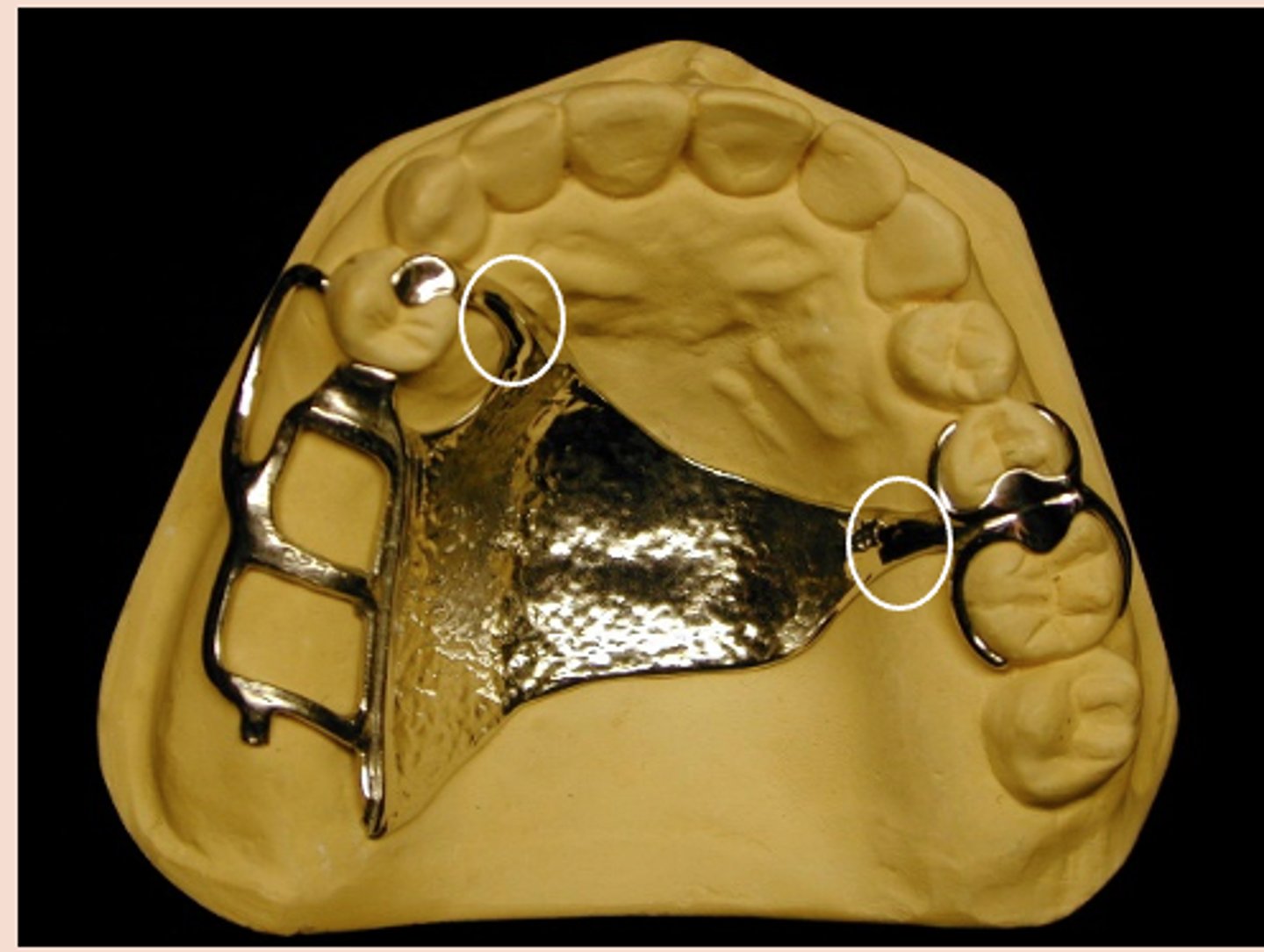
perpendicular
The borders of the minor connectors should run _______ to the free gingival margins of the remaining teeth.
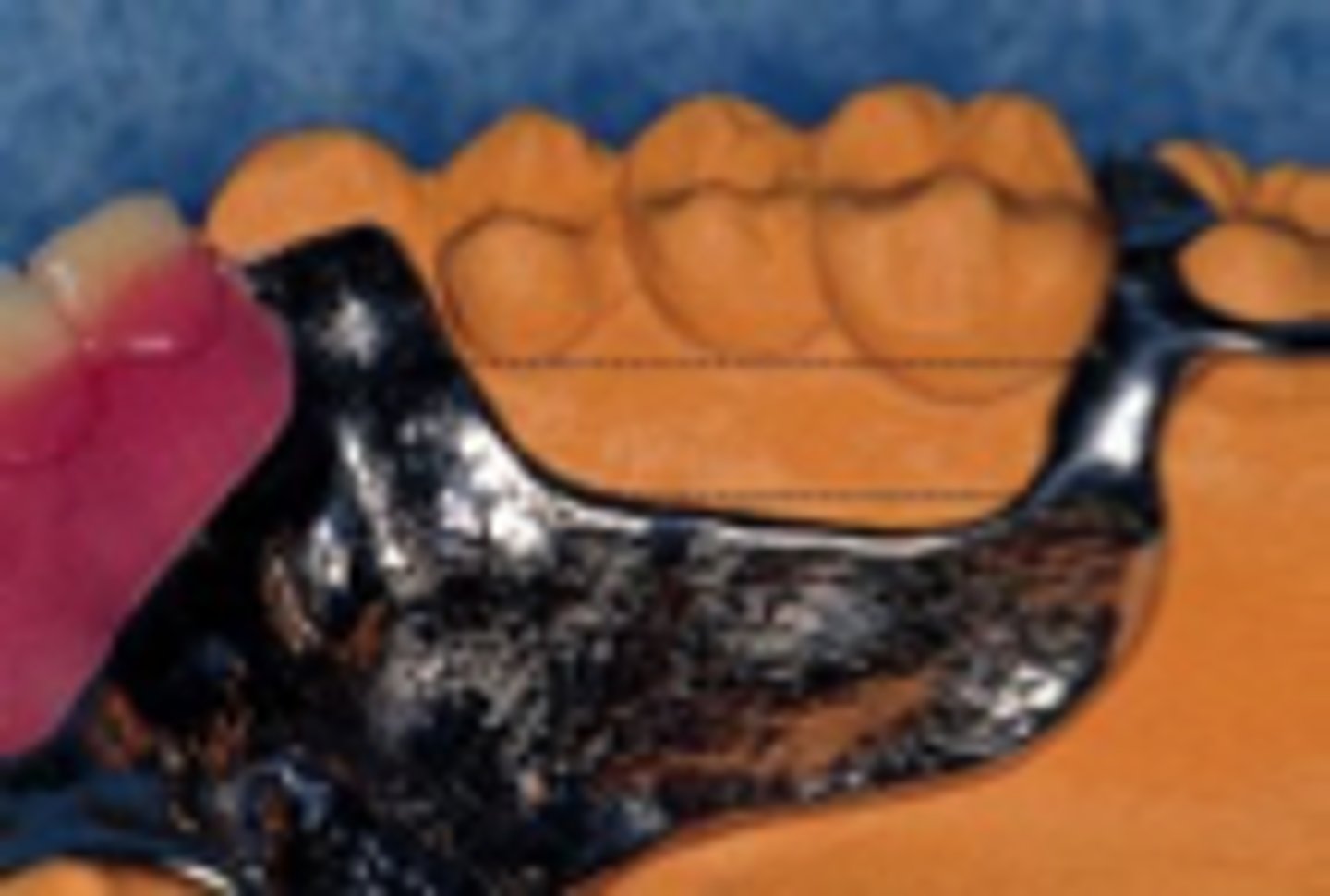
Acrylic Retention area
Since acrylic and metal do not bond, mechanical retention is required: Lattice, mesh, post, loop, beading
relief
mesh and lattice are made with ______ underneath to allow acrylic to wrap around metal completely
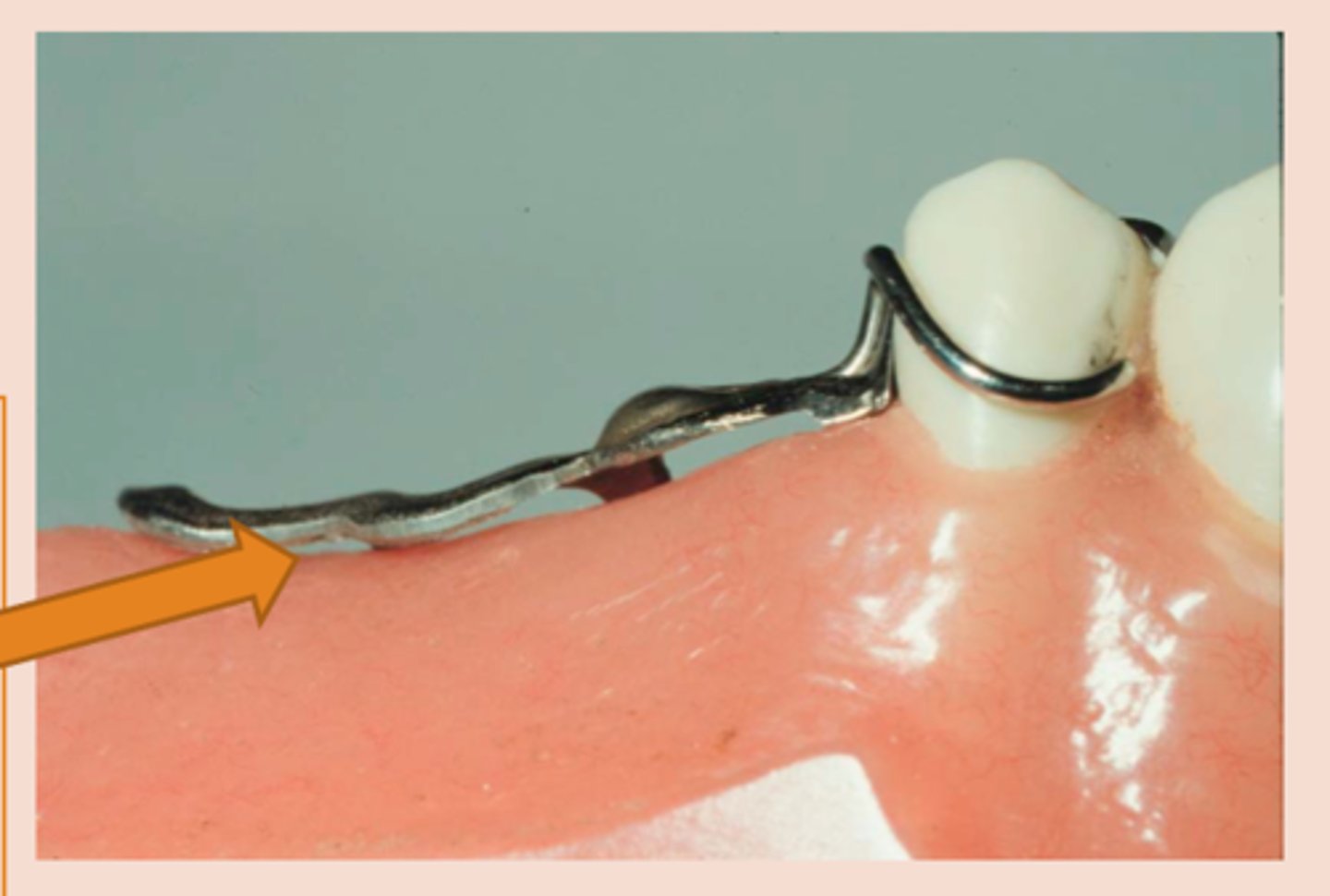
Beading and loops
hold denture tooth "veneer" (occluding surface is part of metal framework)
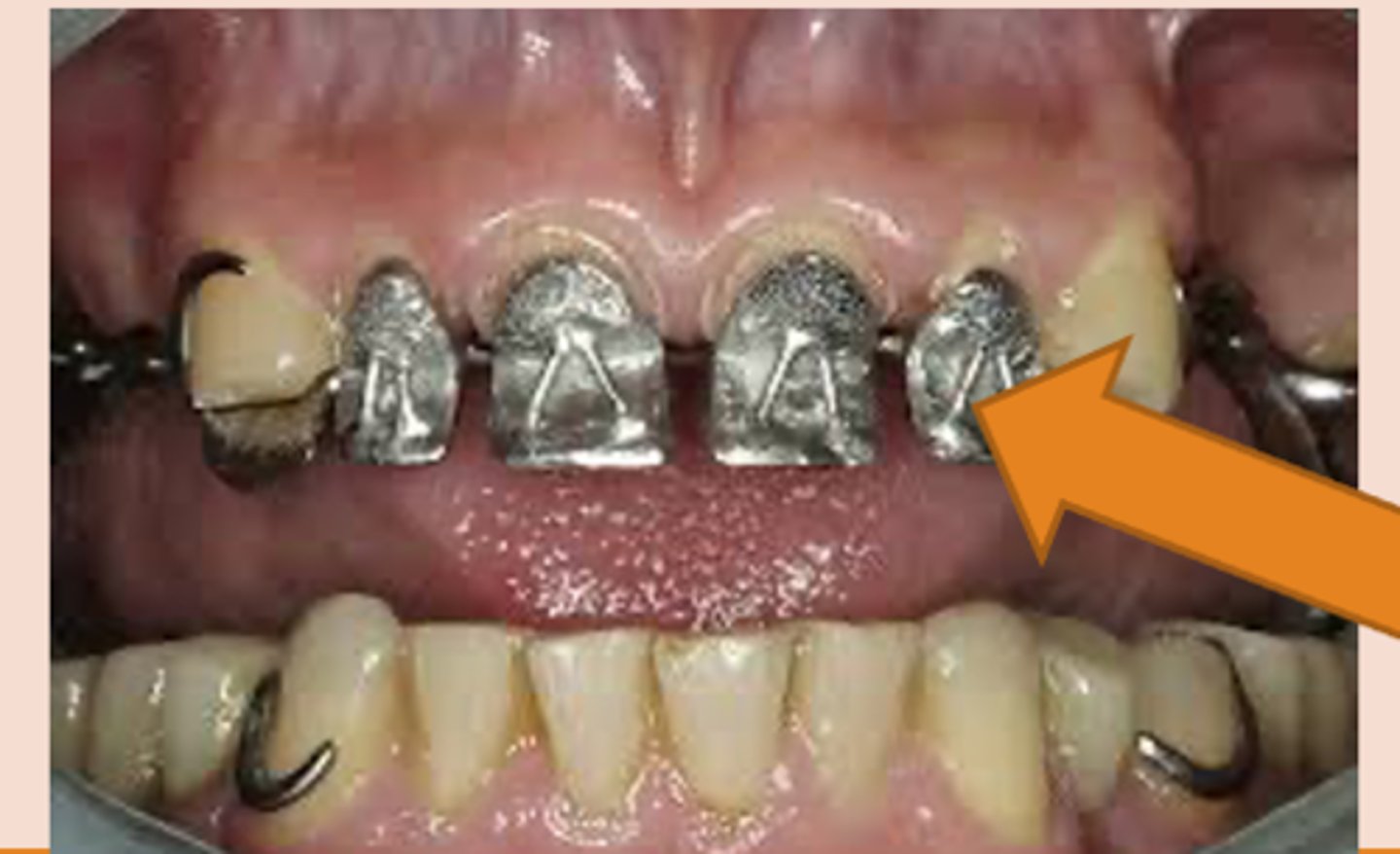
Tissue stop
small projection of metal at the distal end of an extension base framework that contacts the cast and prevents downward movement of the acrylic retention area during the processing of the RPD for delivery
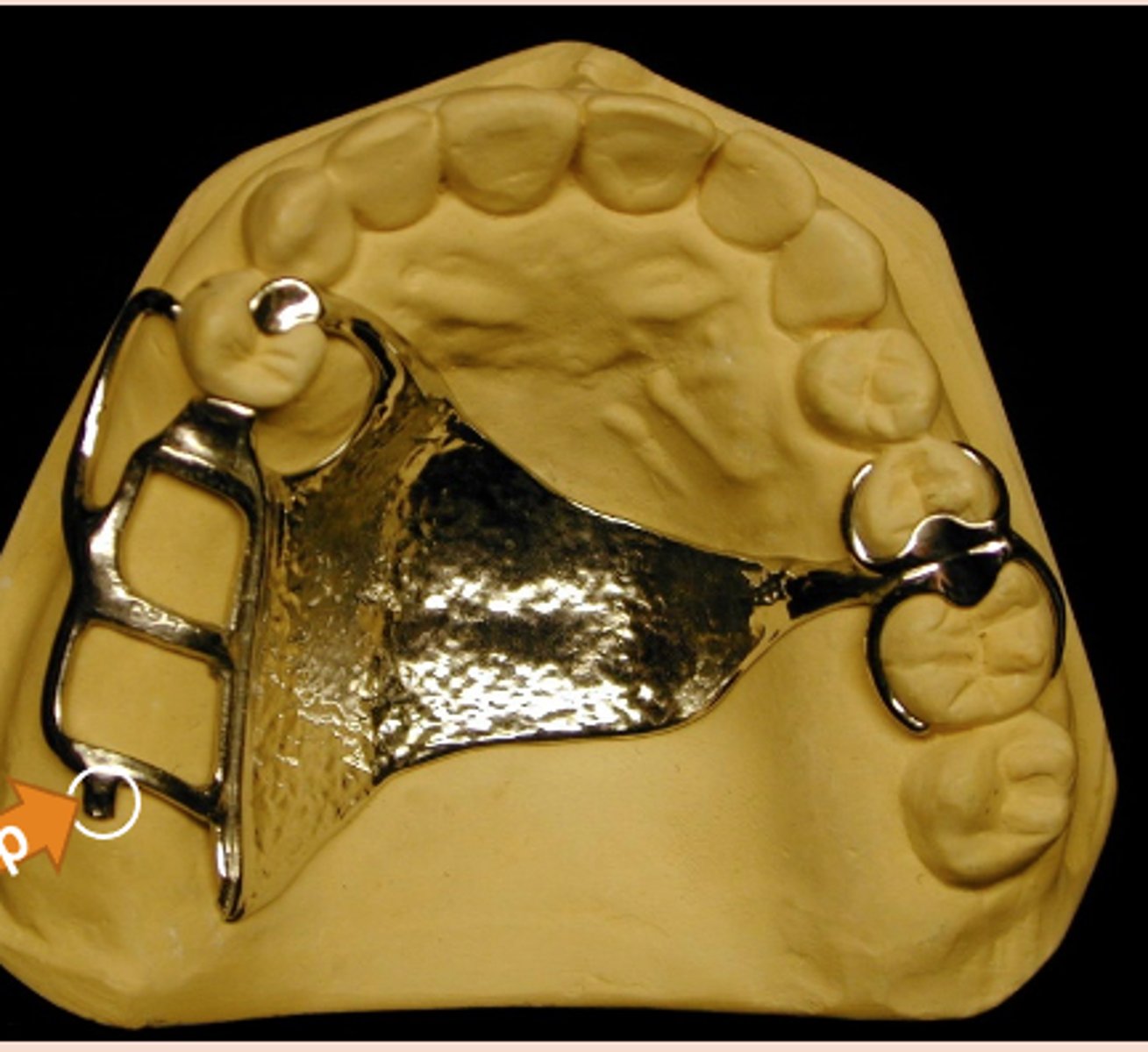
Denture Teeth
Fabricated from cross-linked PMMA (Acrylic). Can be modified with acrylic bur to fit edentulous space.
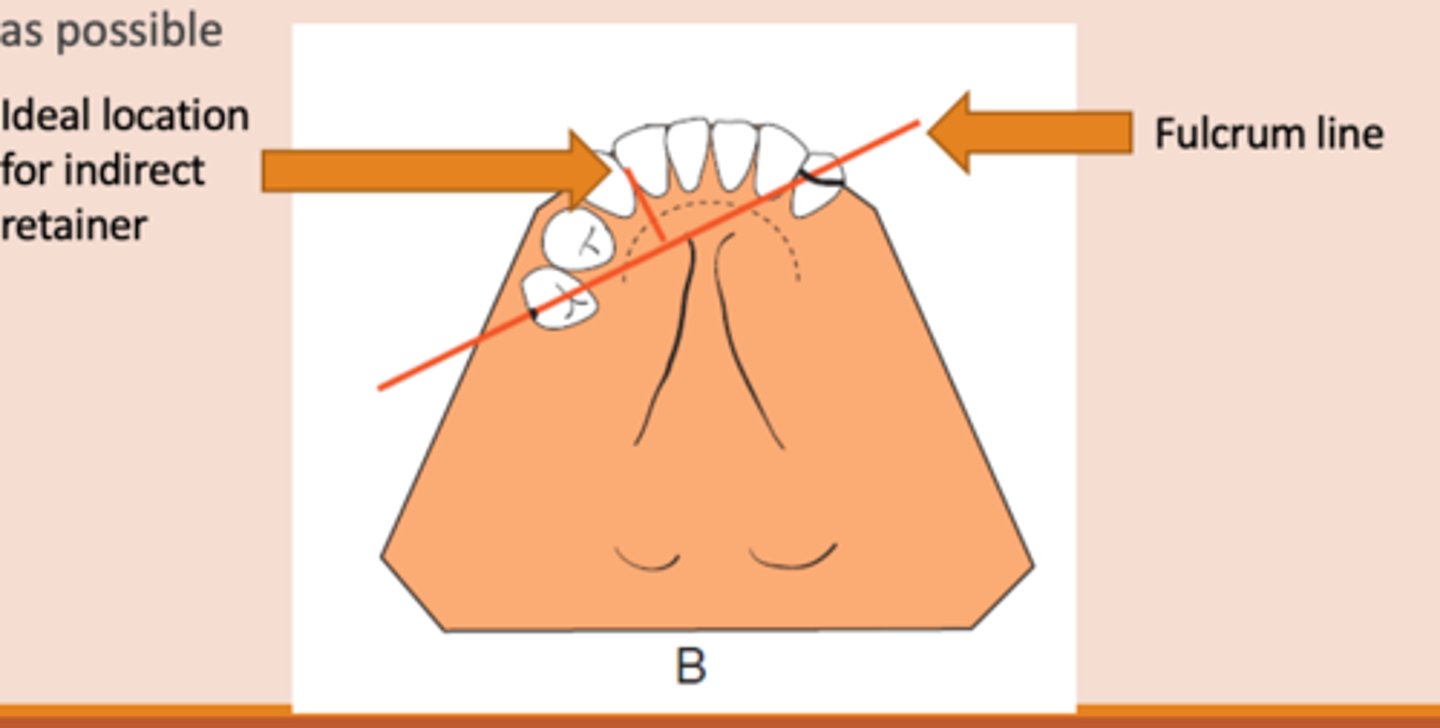
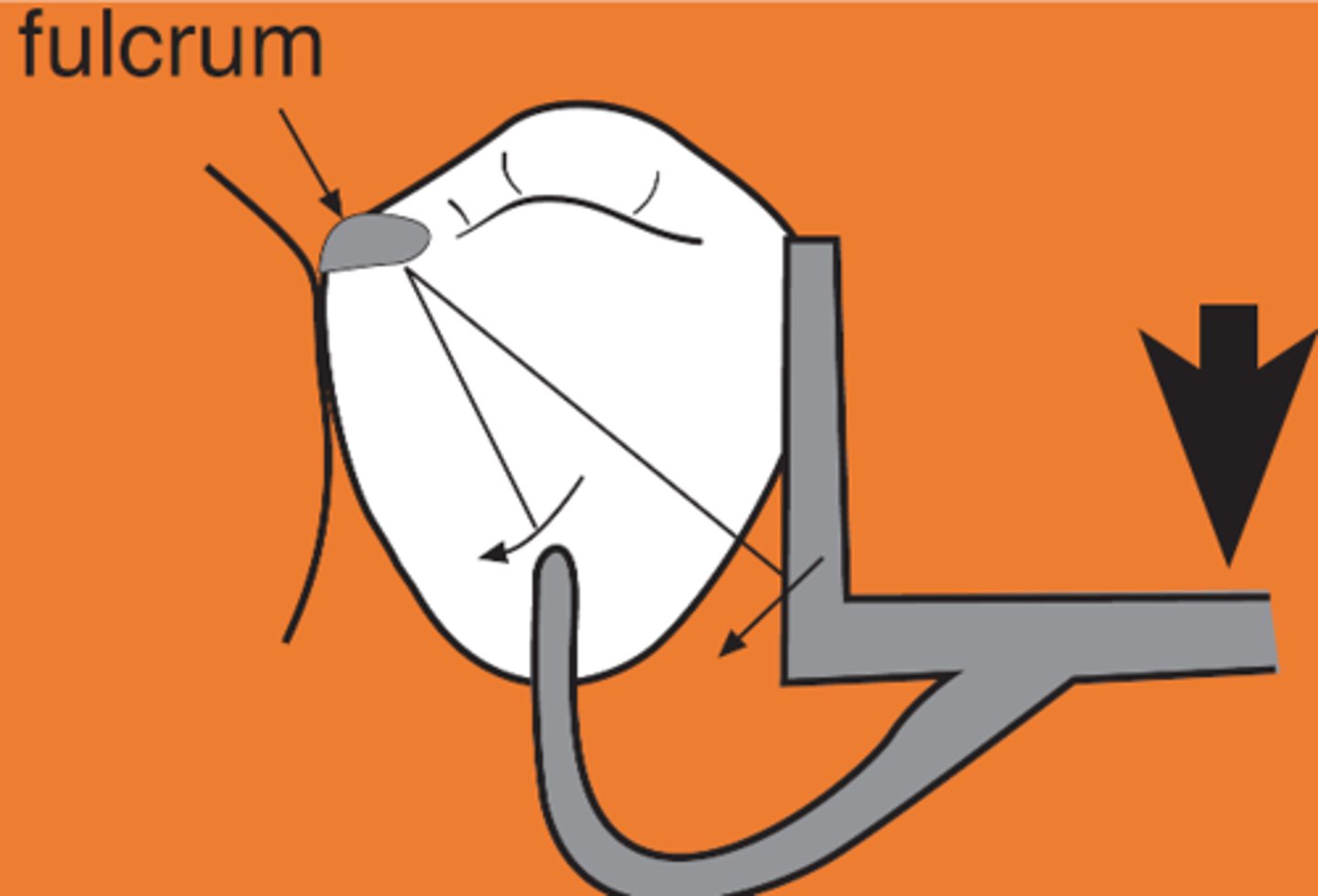
Indirect retainer
associated with extension base RPDs,
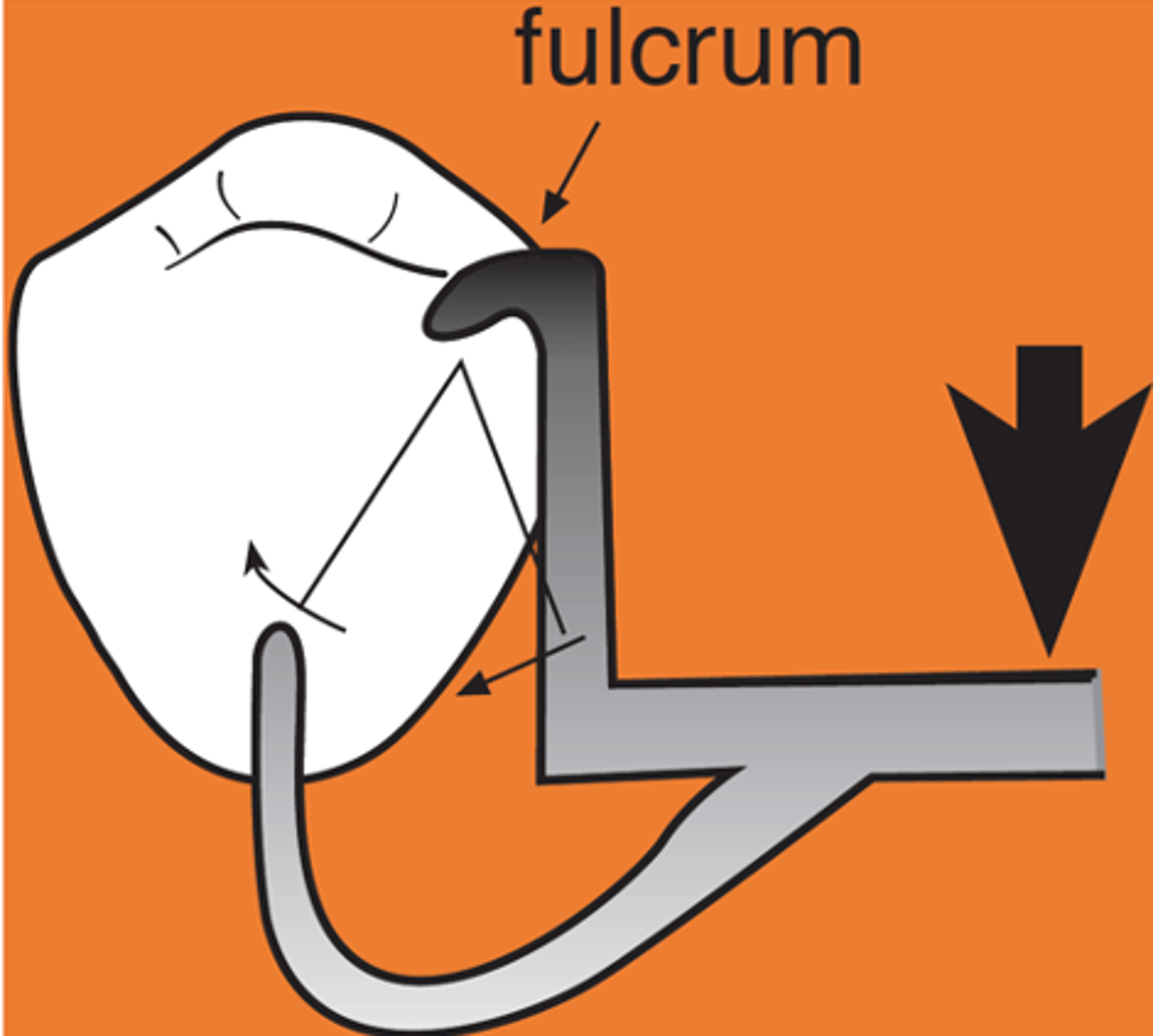
rotation occurs around rests: fulcrum line is through the most distal rest on each side, assist the direct retainers in preventing displacement through lever action on the opposite side of the fulcrum line when the denture base moves away from the tissues in rotation around the fulcrum line, prevents rotational displacement of denture from supporting soft tissues
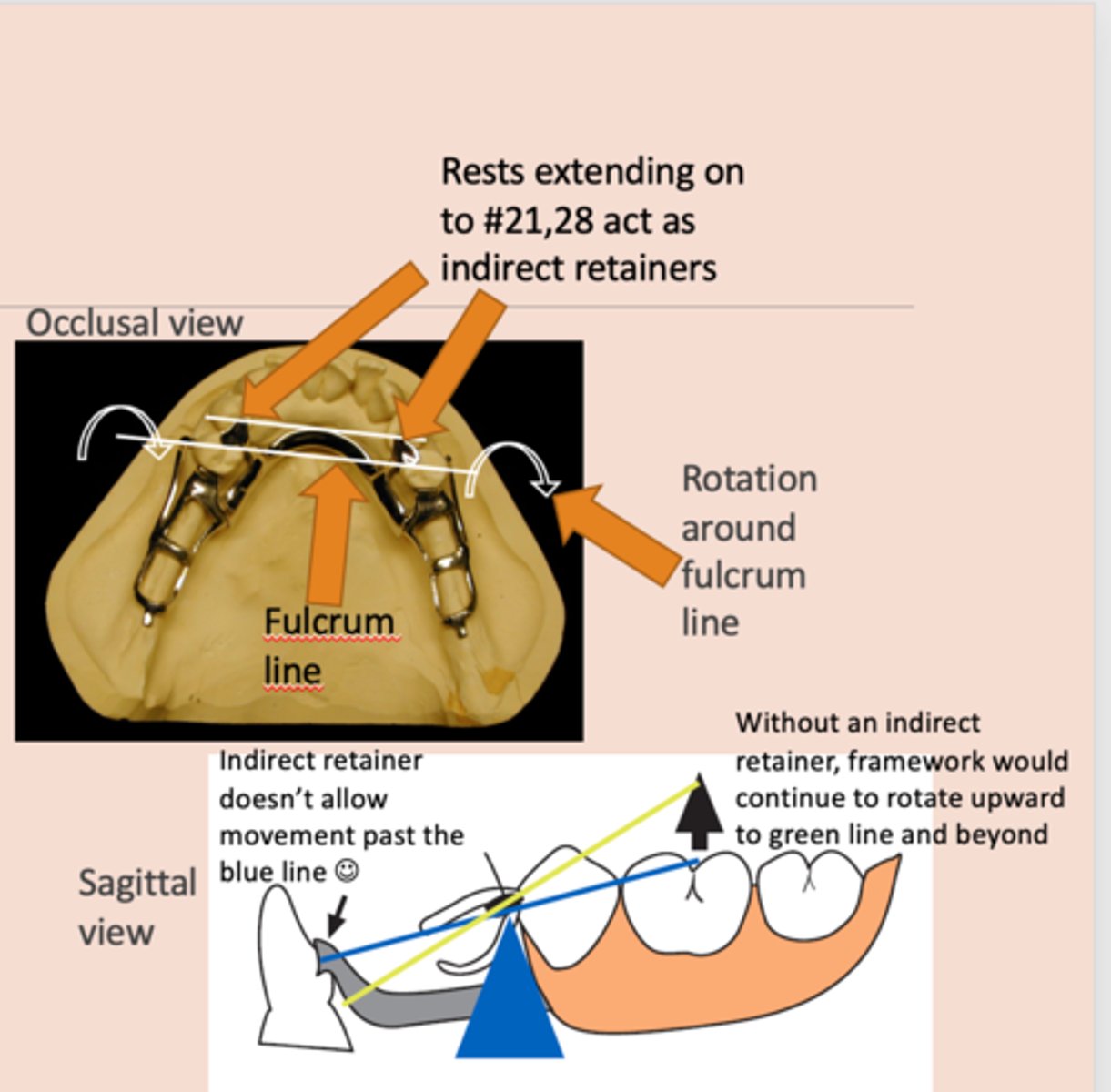
90°
An indirect retainer Ideally should be _______ from primary fulcrum line midway between the most distal rests, as far from fulcrum line as possible
Auxiliary occlusal rest
Indirect retainer type that is most commonly used
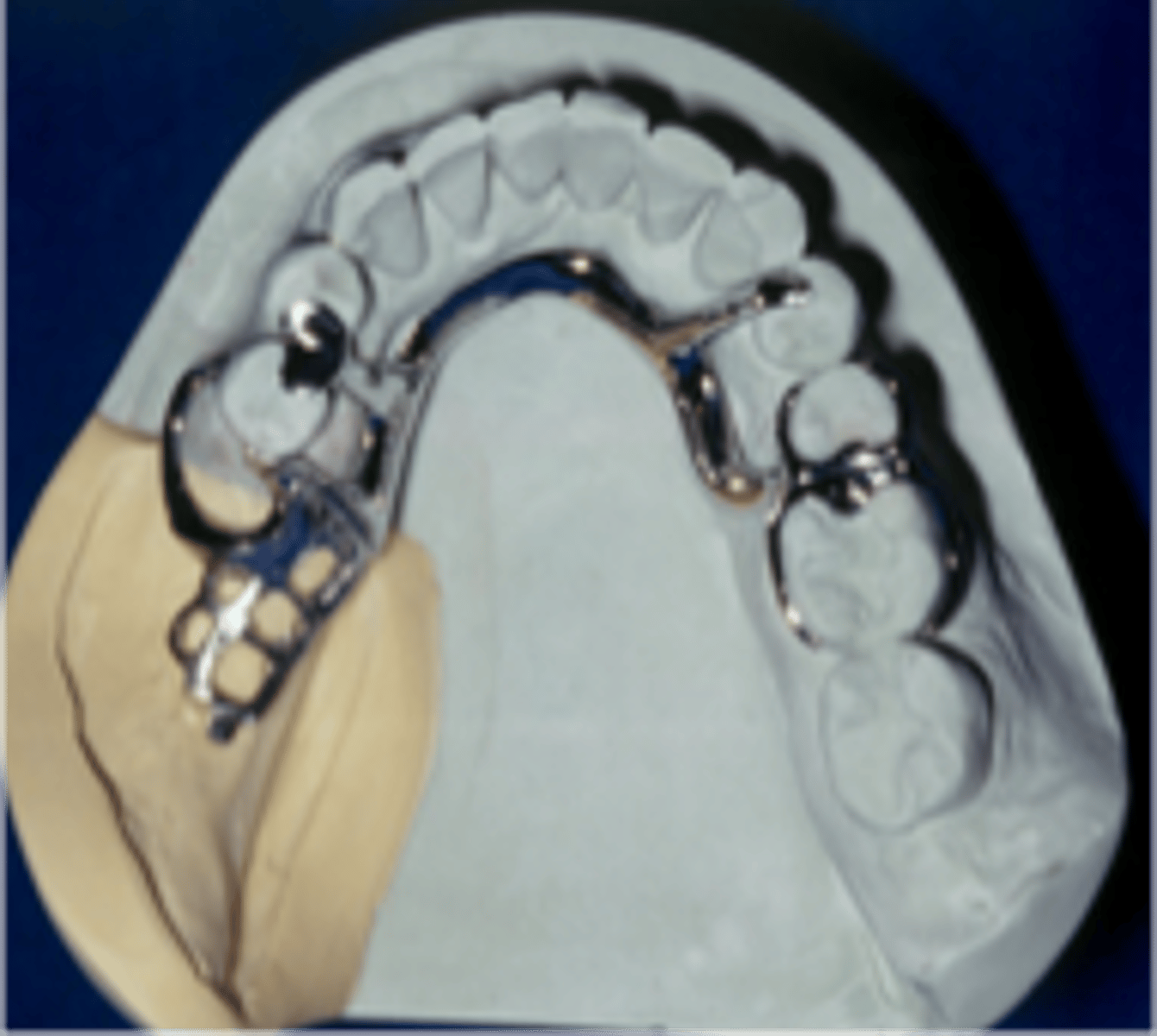
Rest on a canine
Indirect retainer type when premolars are unavailable or inappropriate)
• Cingulum rest on maxillary canines
• Incisal or cingulum rest on mandibular canines
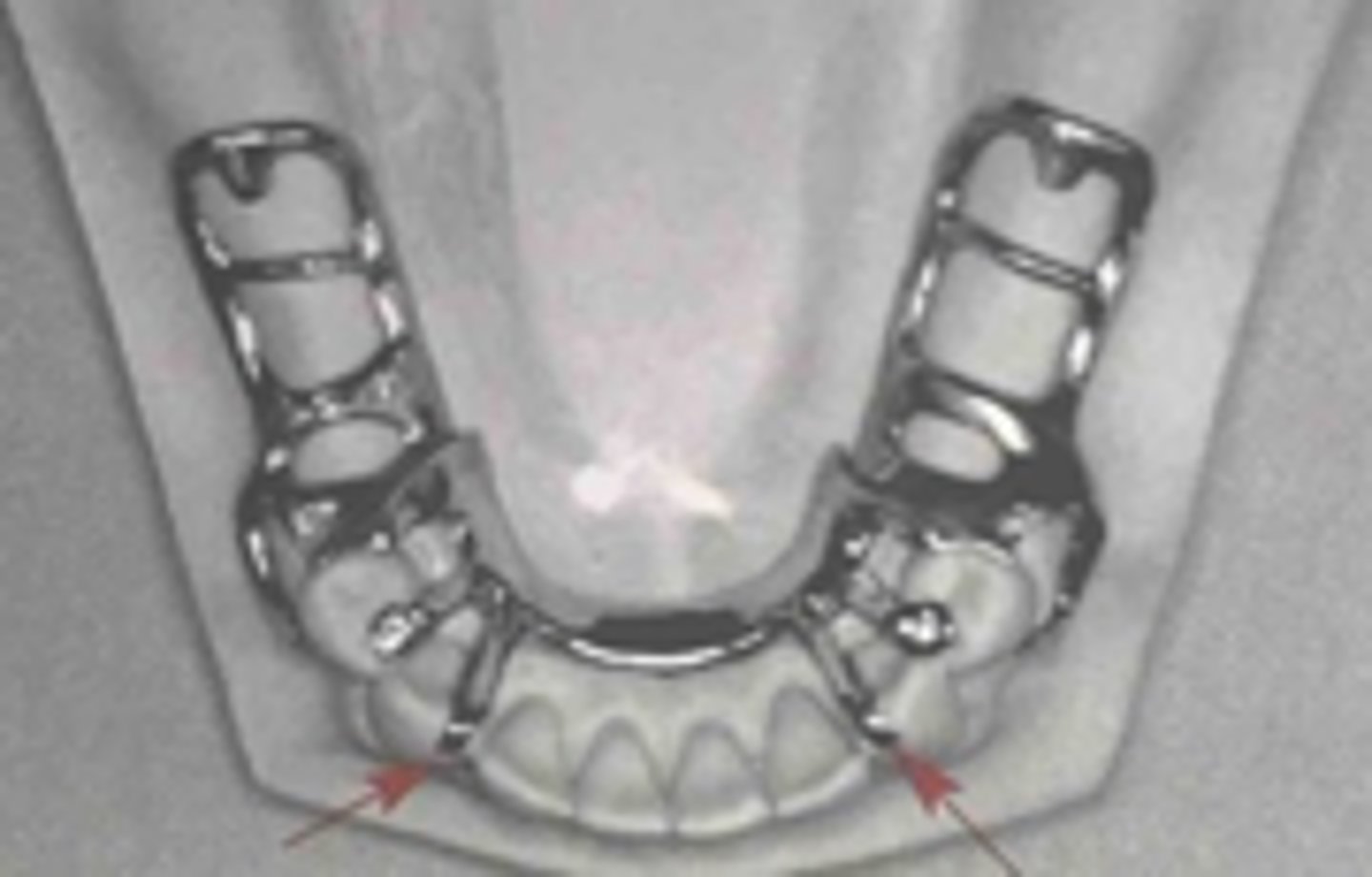
lingual plate
Indirect retainer that is a major connector, where rest seats should be present under plate, otherwise teeth will splay
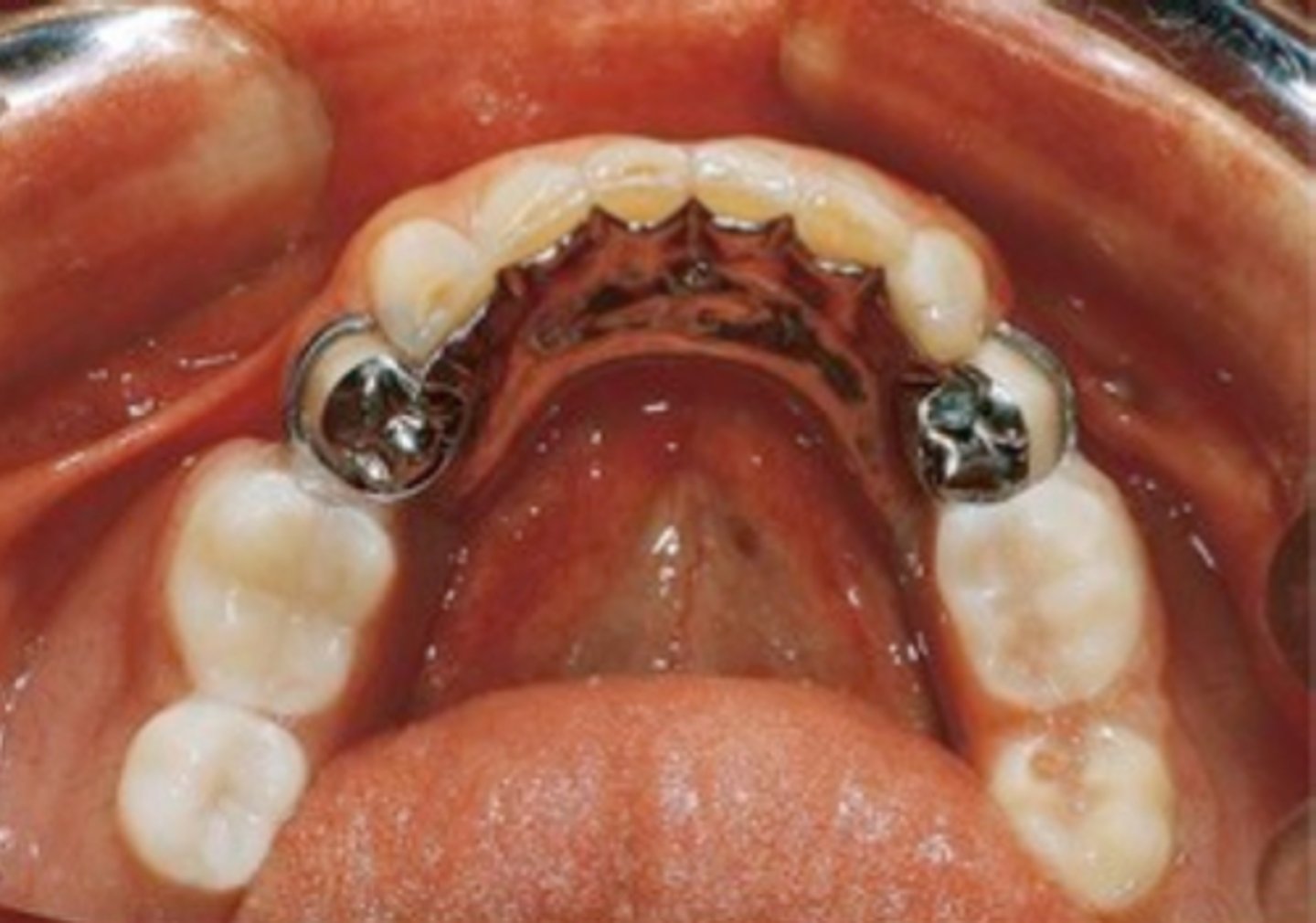
rests associated with clasp assemblies adjacent to modification areas
indirect retainer type
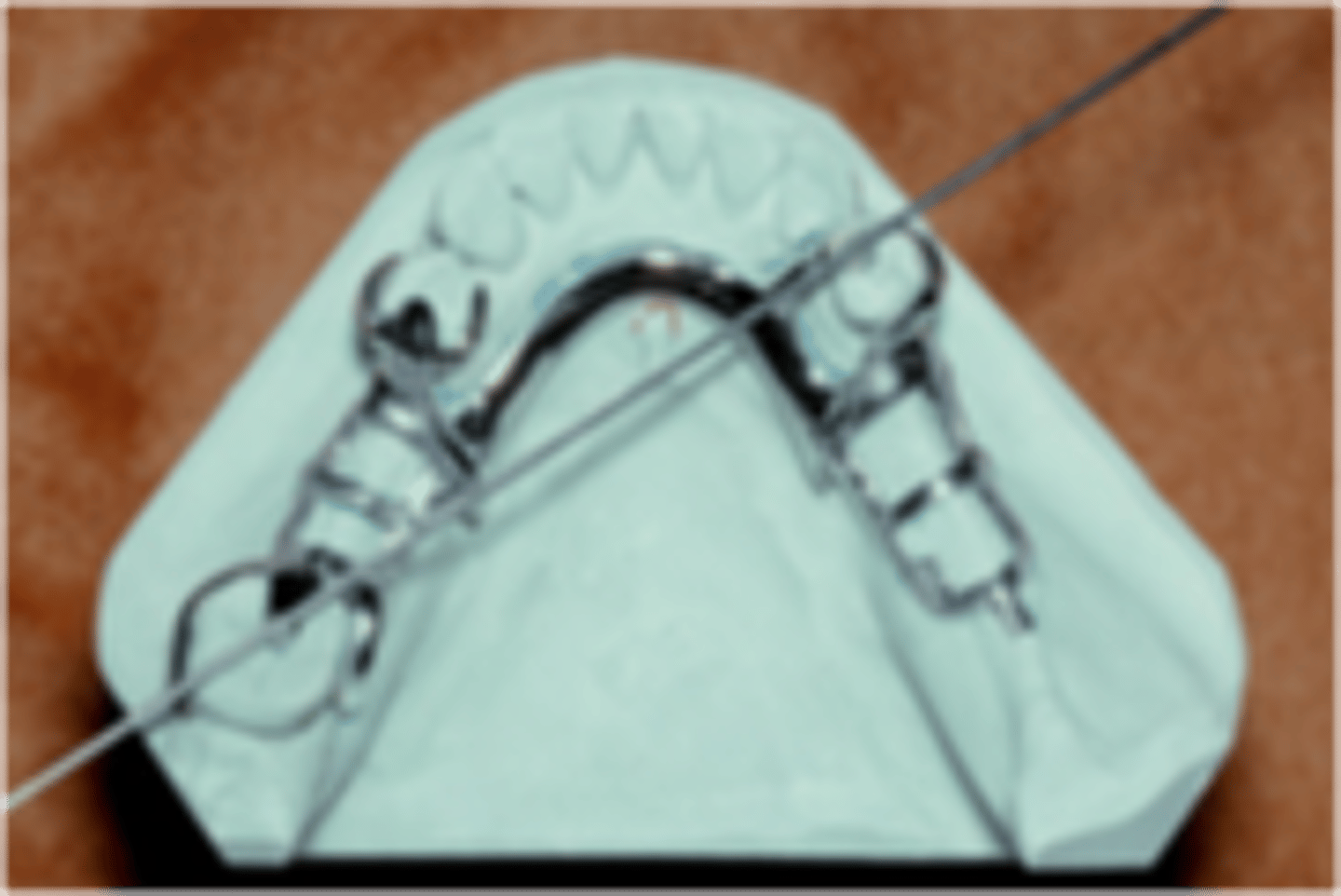
away from tissues
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
1) Retention: resistance to _______ force. Retentive arm (A) – only terminal 1/3 should be below survey line (height of
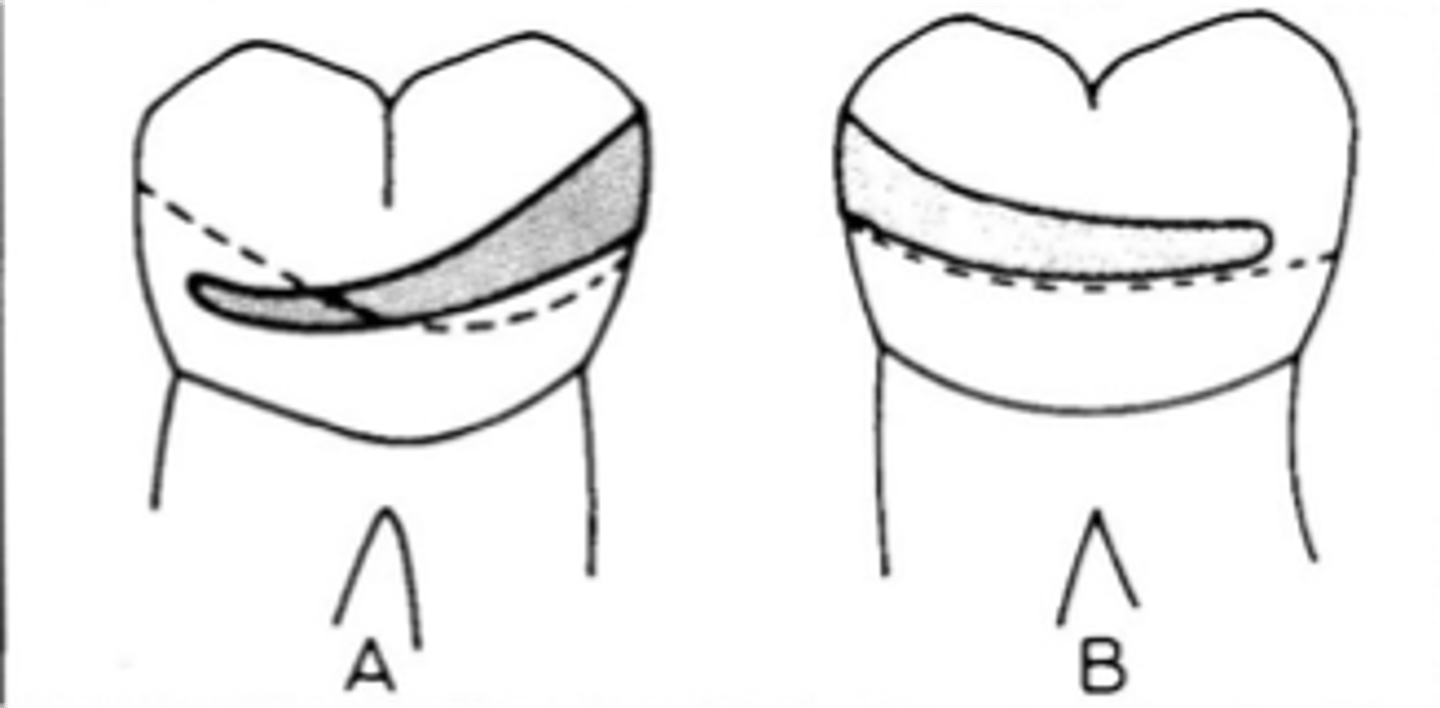
Bracing
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
2) the resistance to horizontal or torsional forces.
Bracing arm (B) – located entirely above the survey line
towards tissue
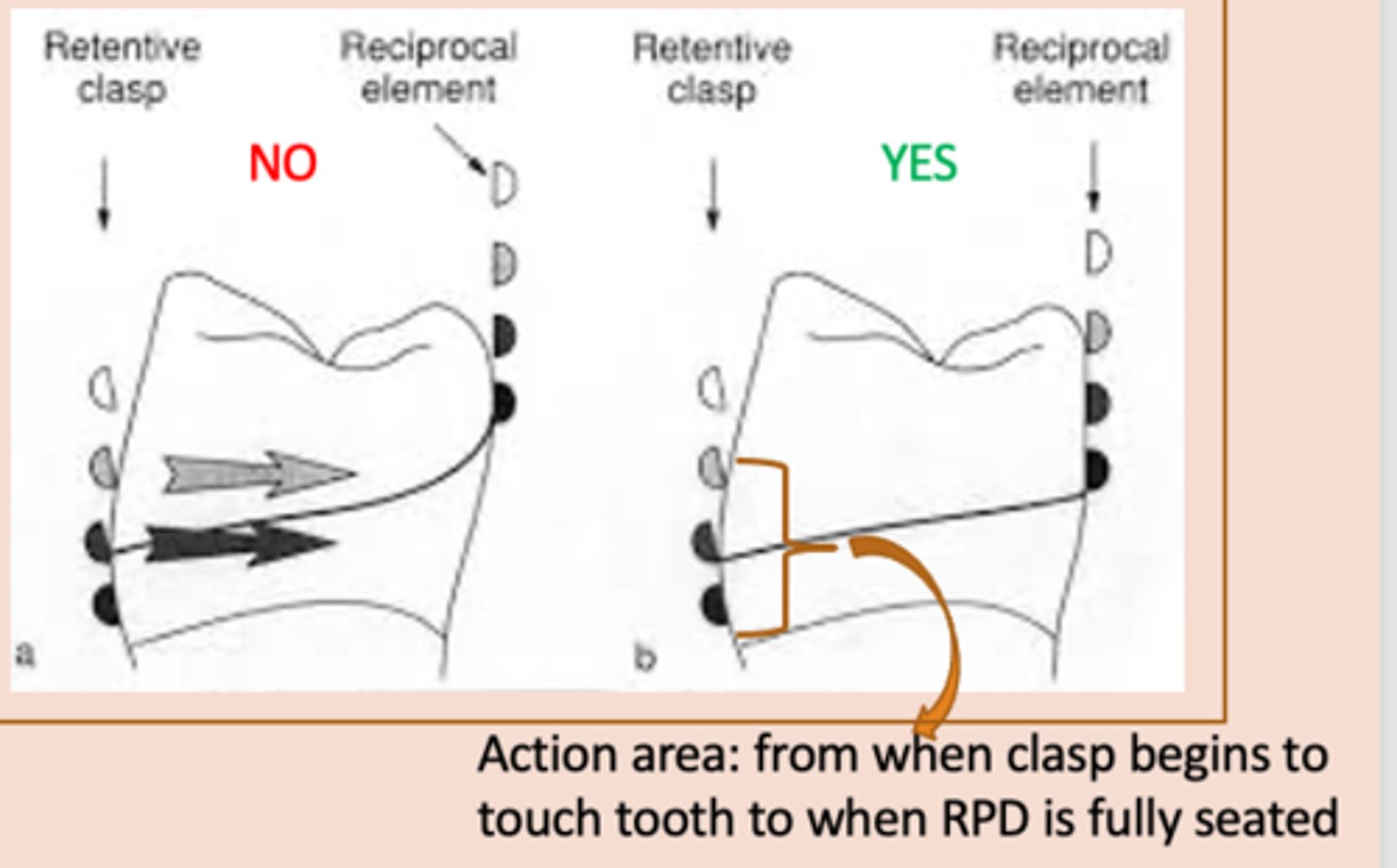
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
3) Support – resistance to _______ force.
Obtained from rests
Reciprocation
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
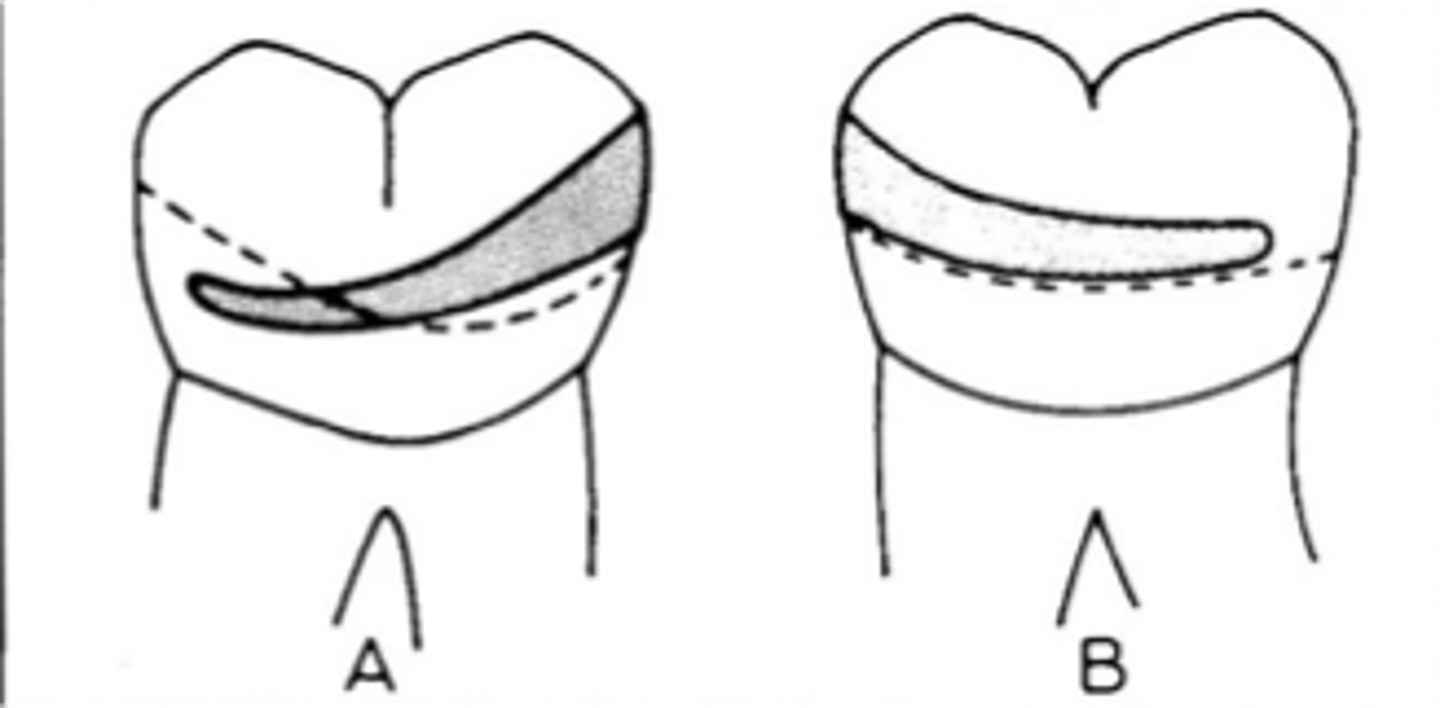
4) – the active form of bracing, resists transient horizontal forces on the tooth from the retentive clasp when a partial denture is being seated and unseated in the mouth. This clasp must begin to contact the tooth at the same time as the retentive clasp throughout the entire action area so that this horizontal force is counteracted, so the lingual contour of the tooth should be flattened or a crown with a milled lingual ledge should be planned.
Adequate encirclement
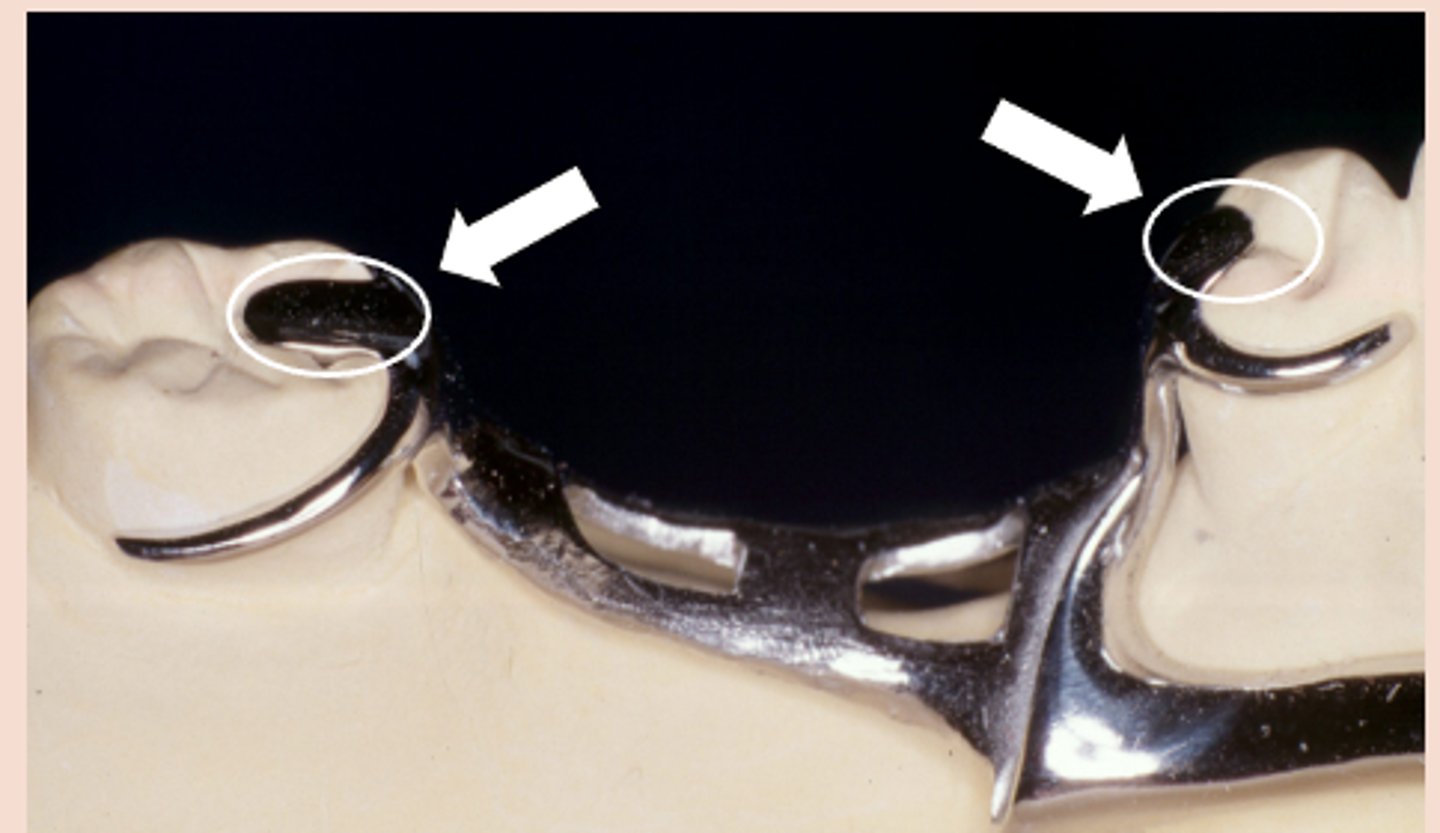
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
5) Clasp assembly must engage more than 180 degrees of the tooth to prevent migration of the tooth out of the clasp assembly
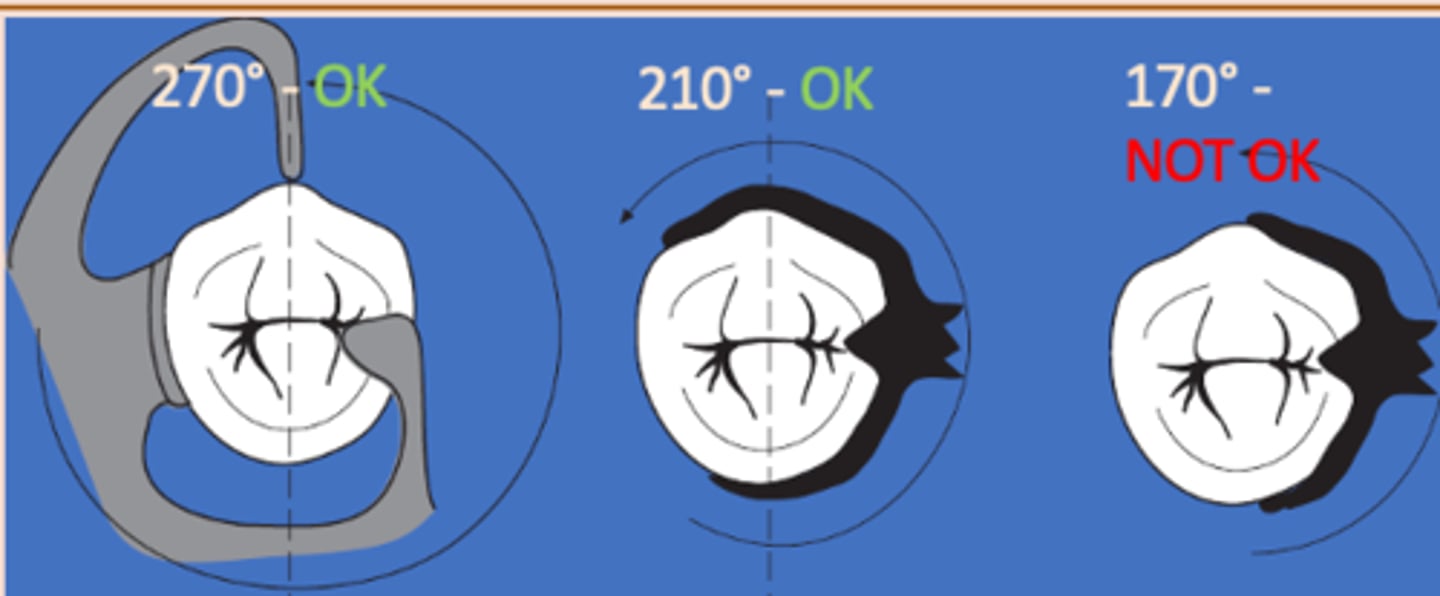
Passivity
Clasp Assembly six requirements:
6) No active force on the tooth when a clasp assembly is in place.
§Prevents discomfort and orthodontic tooth movement
§There should be forces acting during insertion and removal only
§No ________ = slow and uncomfortable extraction
survey crowns
This gold crown serves as an RPD abutment. The milled lingual ledge optimizes reciprocation and allows the bracing arm to restore normal lingual contour when the RPD is fully seated. The bracing arm would be less noticeable to the patient.
Rest
RPD Components - Clasp Assembly Components:
Fits into a rest seat, which is a planned preparation on an abutment tooth. May be part of a clasp assembly (direct retainer), or may serve as an indirect retainer
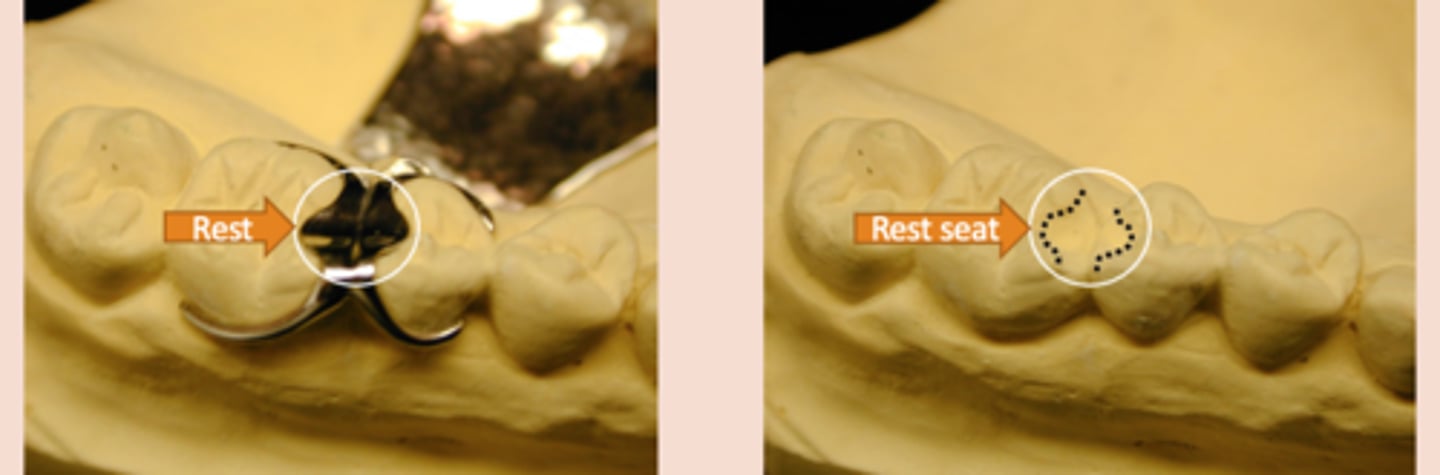

directs forces down to long axis of tooth, provides vertical stop (prevent tissue damage and proper position of RPD)
Rest functions
occlusal, cingulum, incisal (rarely used)
Rest types
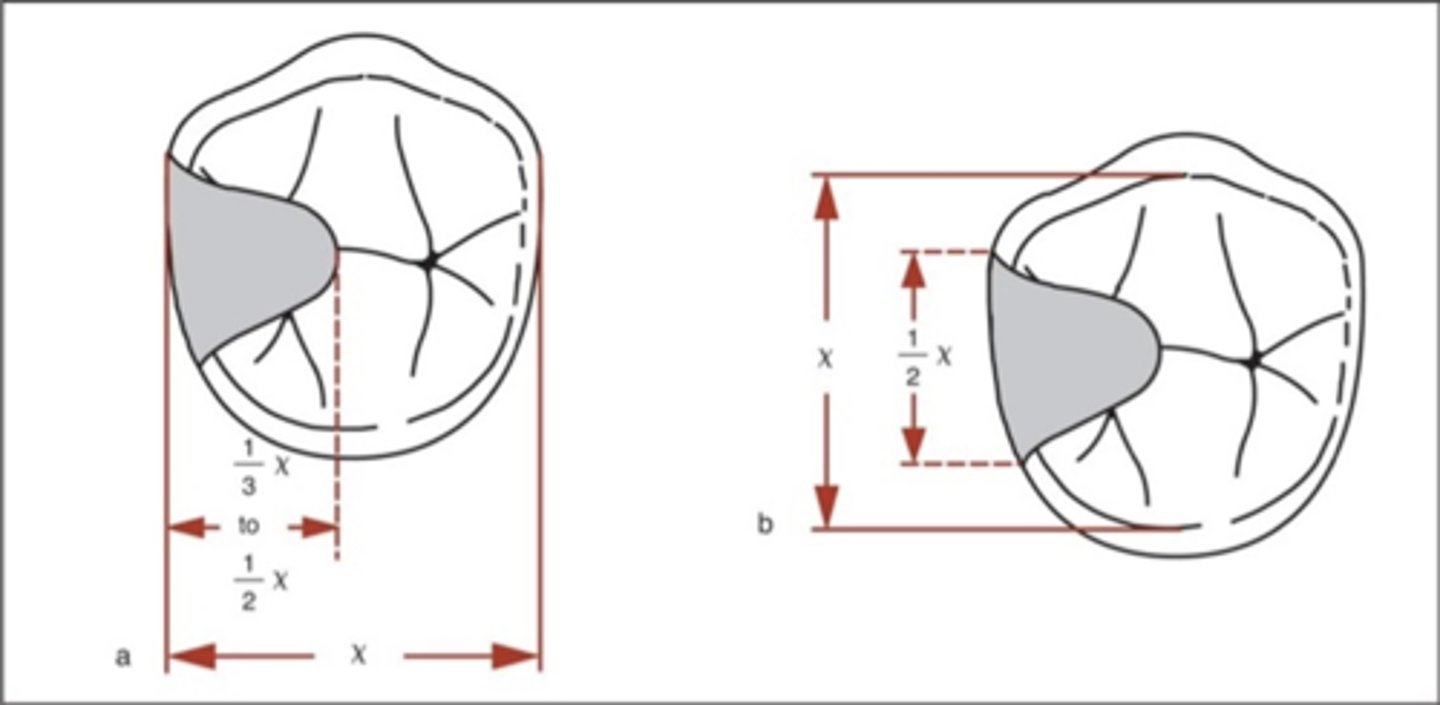
Occlusal rest
note: an extended occlusal rest is helpful when a molar abutment is mesially tipped, to enhance force down the long axis of the tooth (vs a more distally-directed force with a shorter mesial occlusal rest). If <1mm, the rest will break off!
inner
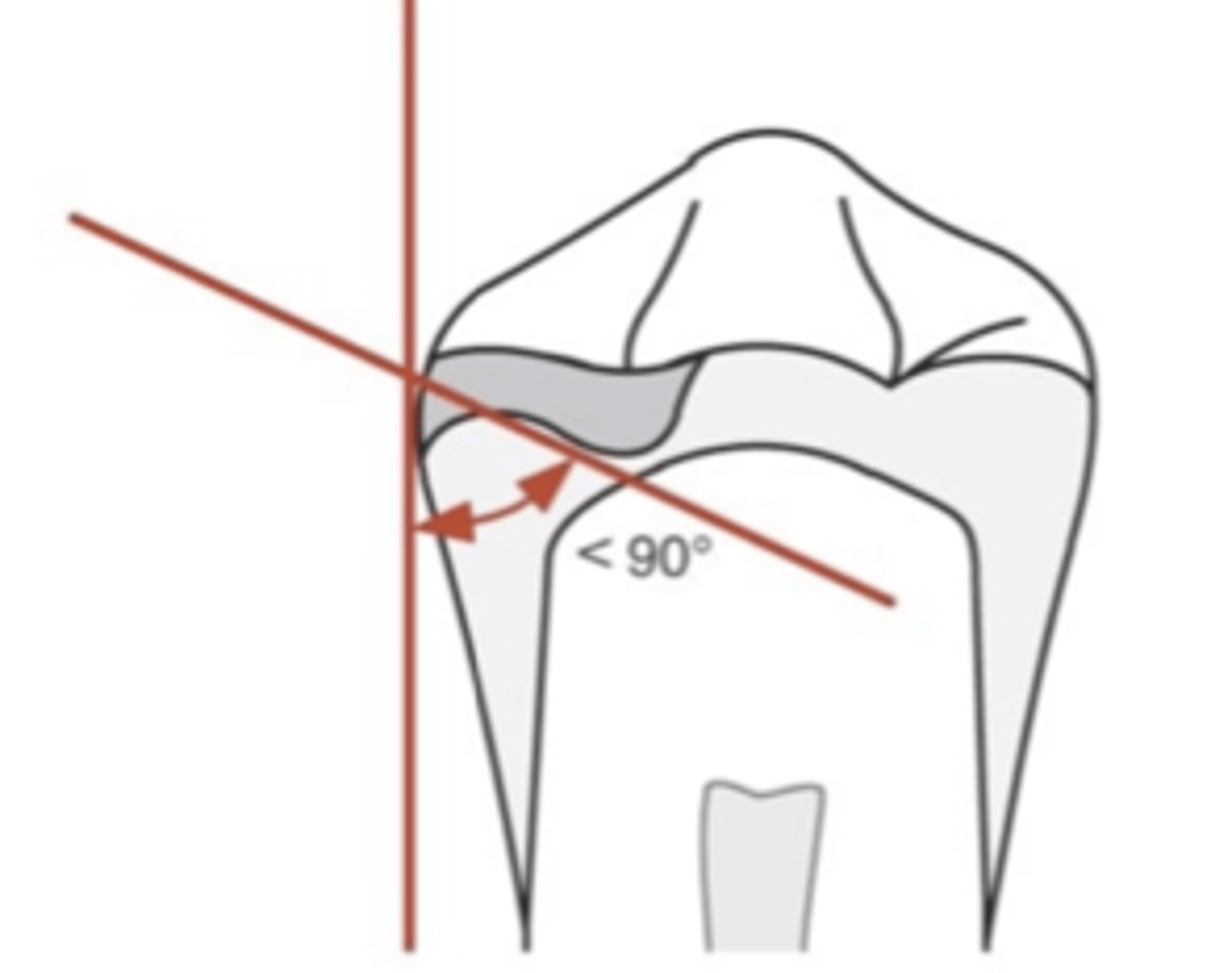
In an occlusal rest, the _______ portion must be located more apically than outer portion near marginal ridge (positivity). May or may not require tooth preparation. If the angle between minor connector and inner portion of rest is ≥90°, occlusal forces will act to slide the rest away from the tooth
Stress- releasing
Mesial occlusal rest on tooth adjacent to distal edentulous segment
• Rotation: retentive tip, proximal plate
• Move mostly down (and forward), releasing clasp from tooth
NOT stress releasing
Distal occlusal rest on tooth adjacent to distal edentulous segment
• Rotation: retentive tip, proximal plate
• Move mostly forward (tip rotates up)
• Toward height of contour (activate or bind)
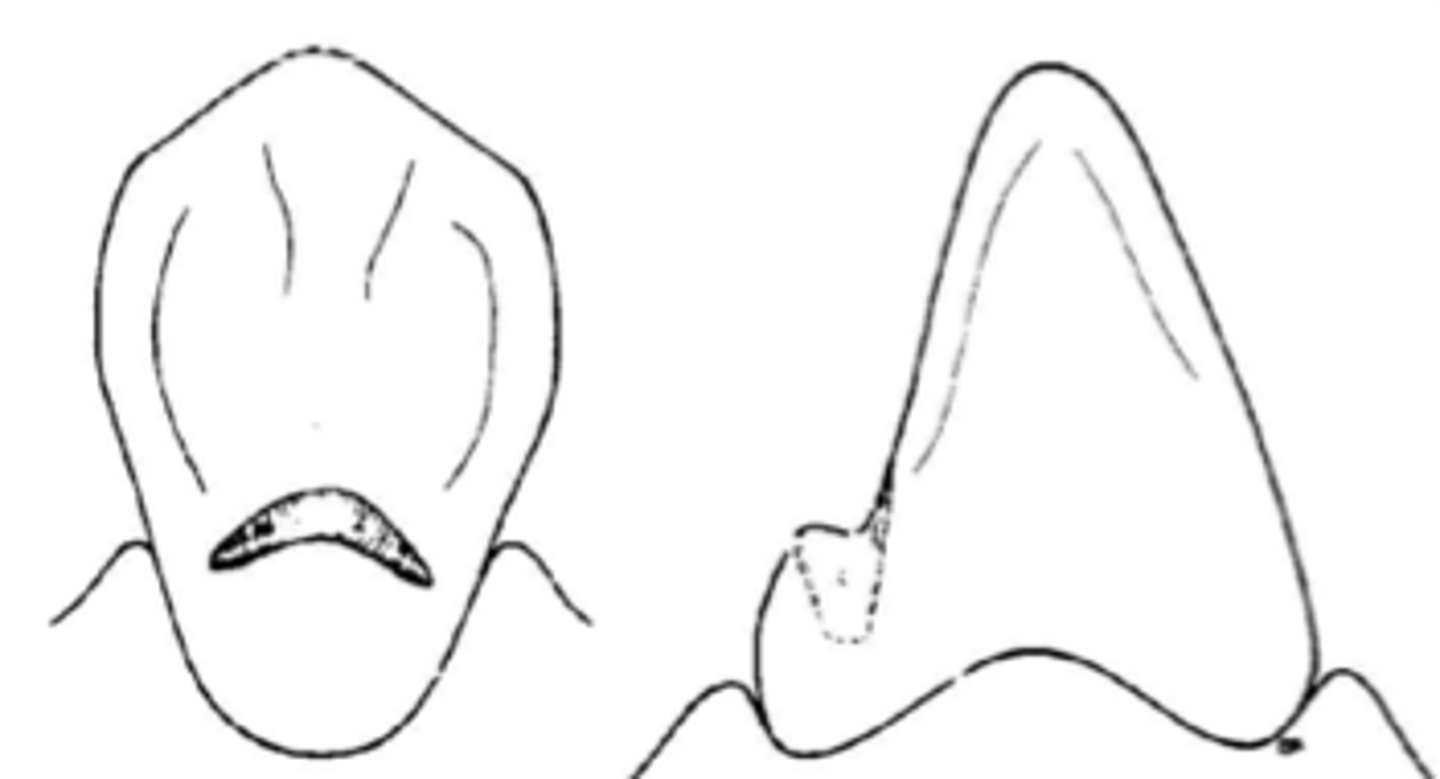
Cingulum rest
Similar to occlusal rests, the rest must be made at the correct angulation in reference to the tooth surface to prevent the rest from sliding away from the tooth.
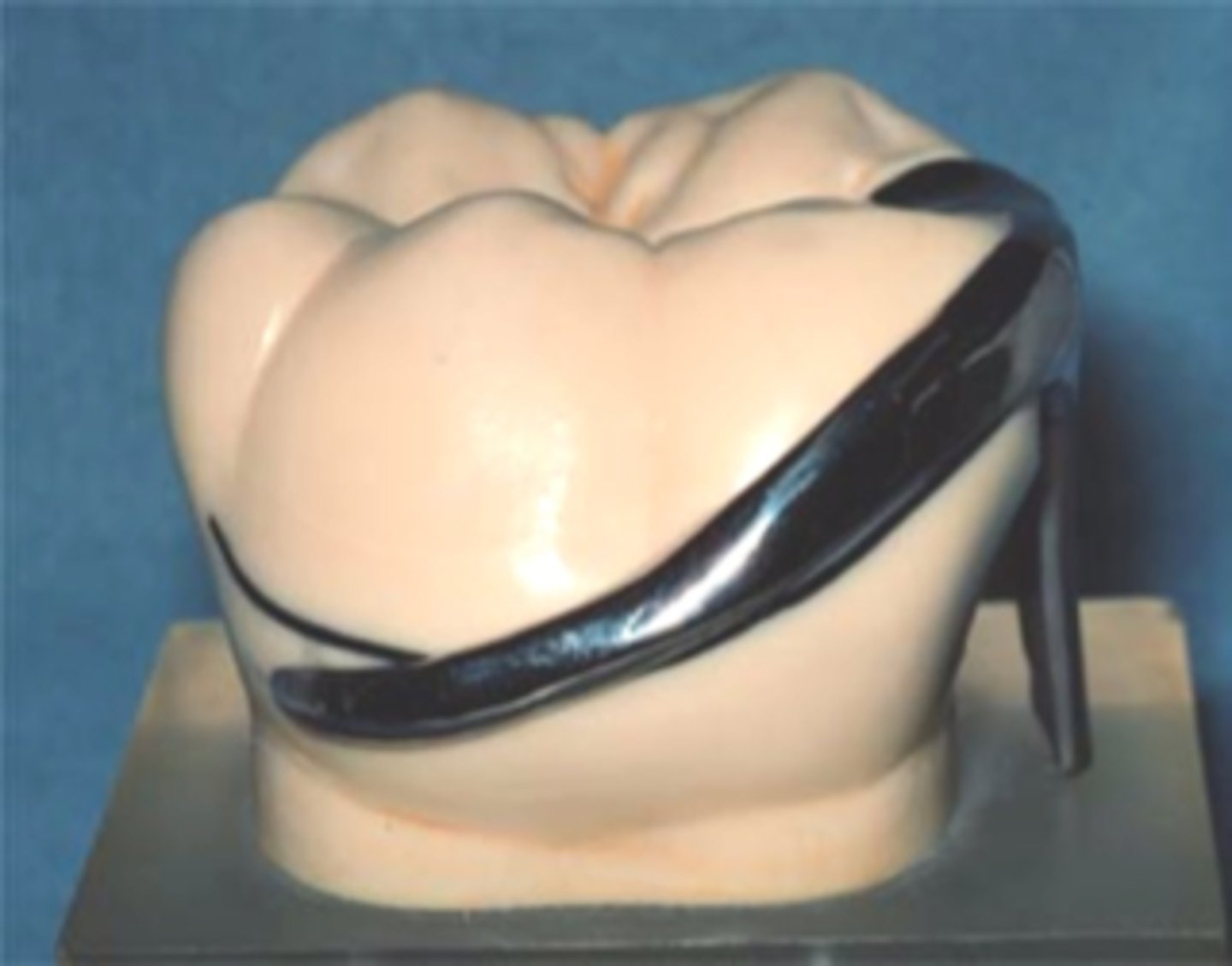
Suprabulge
clasp
• Begin above height of contour (rigid)
• Retentive tip in gingival 1/3 of tooth, below the survey line (flexible)
• Middle portion as low as possible but above survey line (*too close to occlusal surface à occlusal interference)
• In tooth-supported situations, stress release usually unnecessary, so Akers and embrasure clasp assemblies are ok to use
•Cast Circumferential clasp (Akers)
•Double embrasure clasp
•RPC (aka RPA) clasp (mesial rest, proximal plate, circumferental clasp). Due to the rest location, this clasp assembly provides stress release, but can be used when this is not necessary
Infrabulge (Bar) Clasps
clasp
• Retentive tip in gingival 1/3 of tooth
• More esthetic
• Less contact (Hygiene)
• Cast infrabulge clasps: Stress releasing design compensates for the difference in movement between teeth and mucosa – good for adjacent to distal extension areas, if an abutment is periodontally involved, if extensive edentulous space is present
---RPI clasp assembly (MESIAL rest, proximal plate, I bar)
---Other options: T bar, half T bar, etc
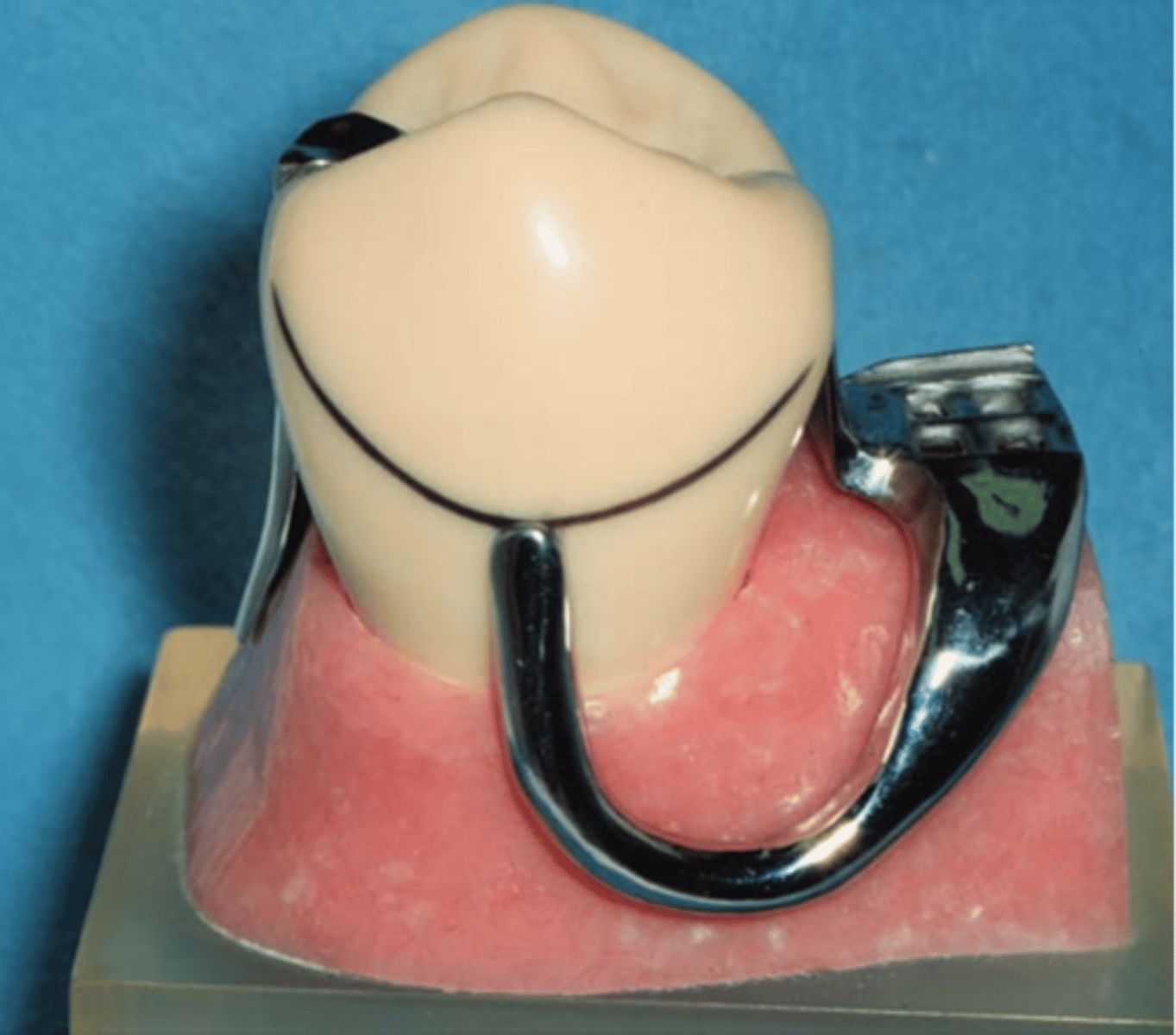
MESIAL rest, proximal plate, I bar
RPI stands for
insufficient vestibular depth, large soft tissue undercuts (a)
I Bar contraindications
Cast circumferential bracing/cast bar retentive arms
Combination Clasps:
suprabulge/infrabulge combo, Commonly used on tooth borne RPDs in esthetic areas.
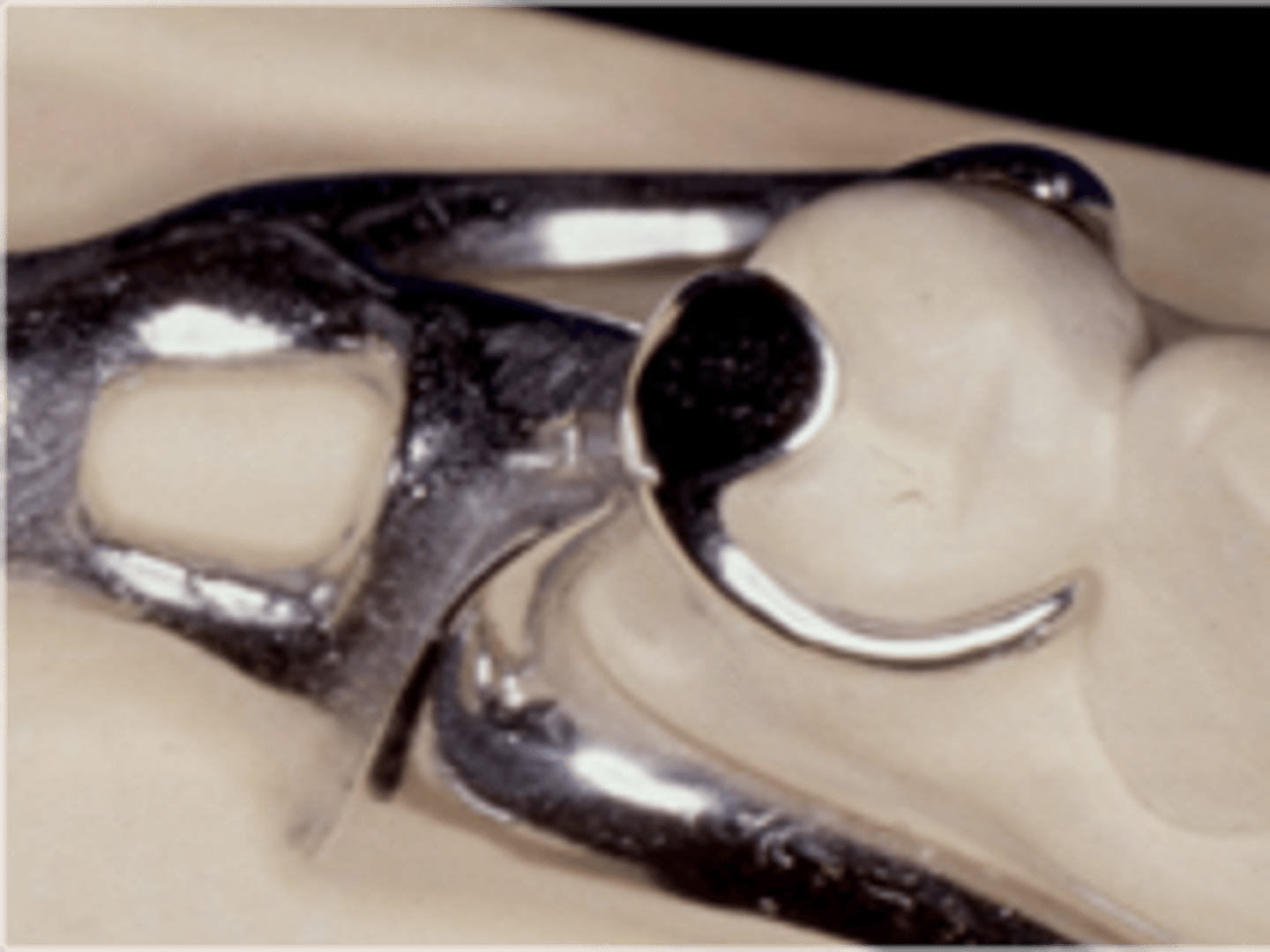
Cast circumferential bracing/wrought wire retentive arms
Suprabulge type clasp with a combination of two different metals (via soldering).
Stress-releasing clasp assembly (due to material), used on extension base RPD’s.
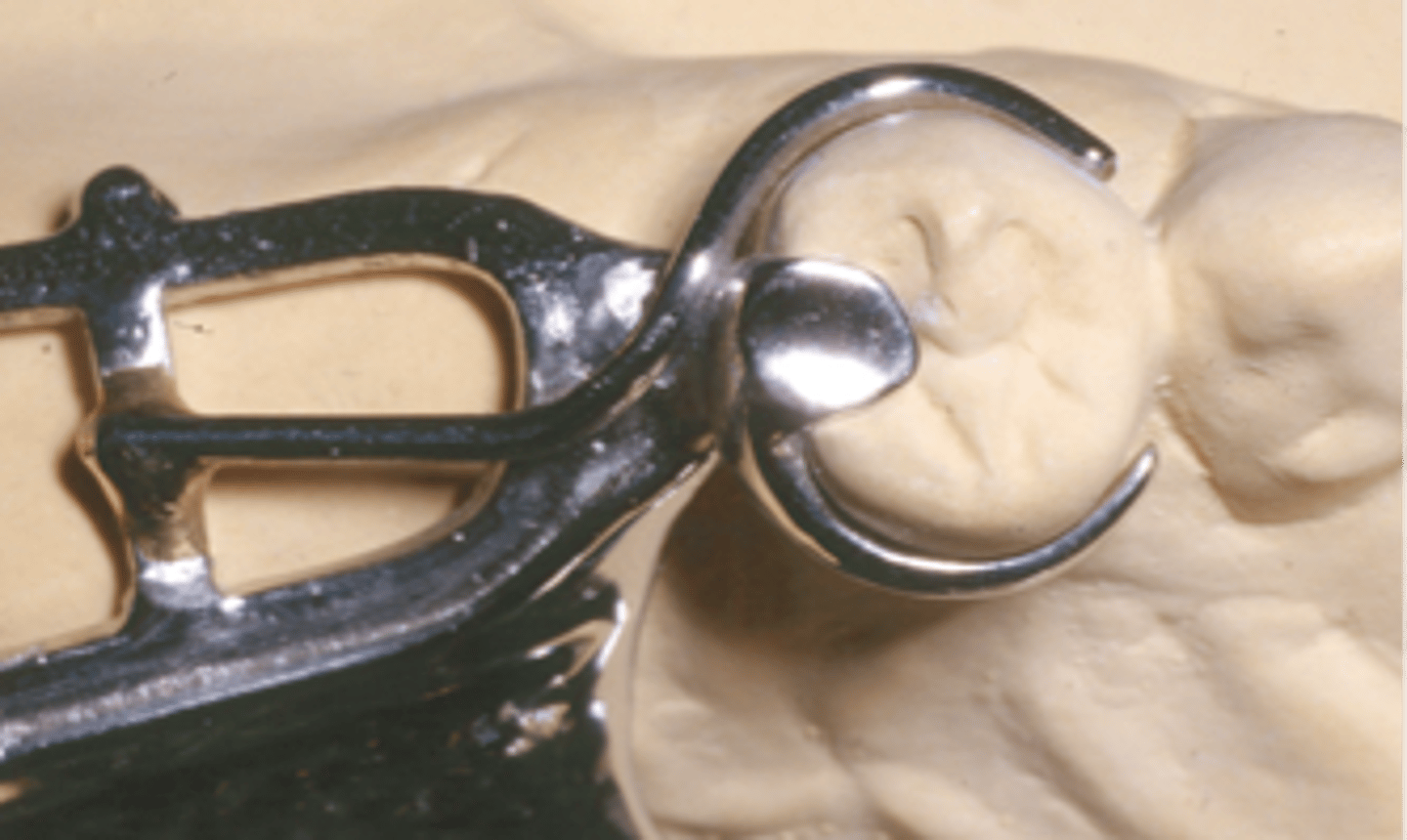

§ Type of Support (Nature of Supporting Tissue)
§ Minimal Tooth and Minimal Gingival Coverage
§ Location of the Survey Line
§ Bilateral Bracing
§ Contours of tissues adjacent to the abutment tooth
§ Anatomy of abutment tooth (including occlusion of opposing dentition)
§ Esthetics
§ Clasps on previous Removable Partial Denture
Choosing clasp assemblies
Location of the Survey Line, Anatomy of abutment tooth, Clasps on previous Removable Partial Denture
Factors in determining magnitude of retention
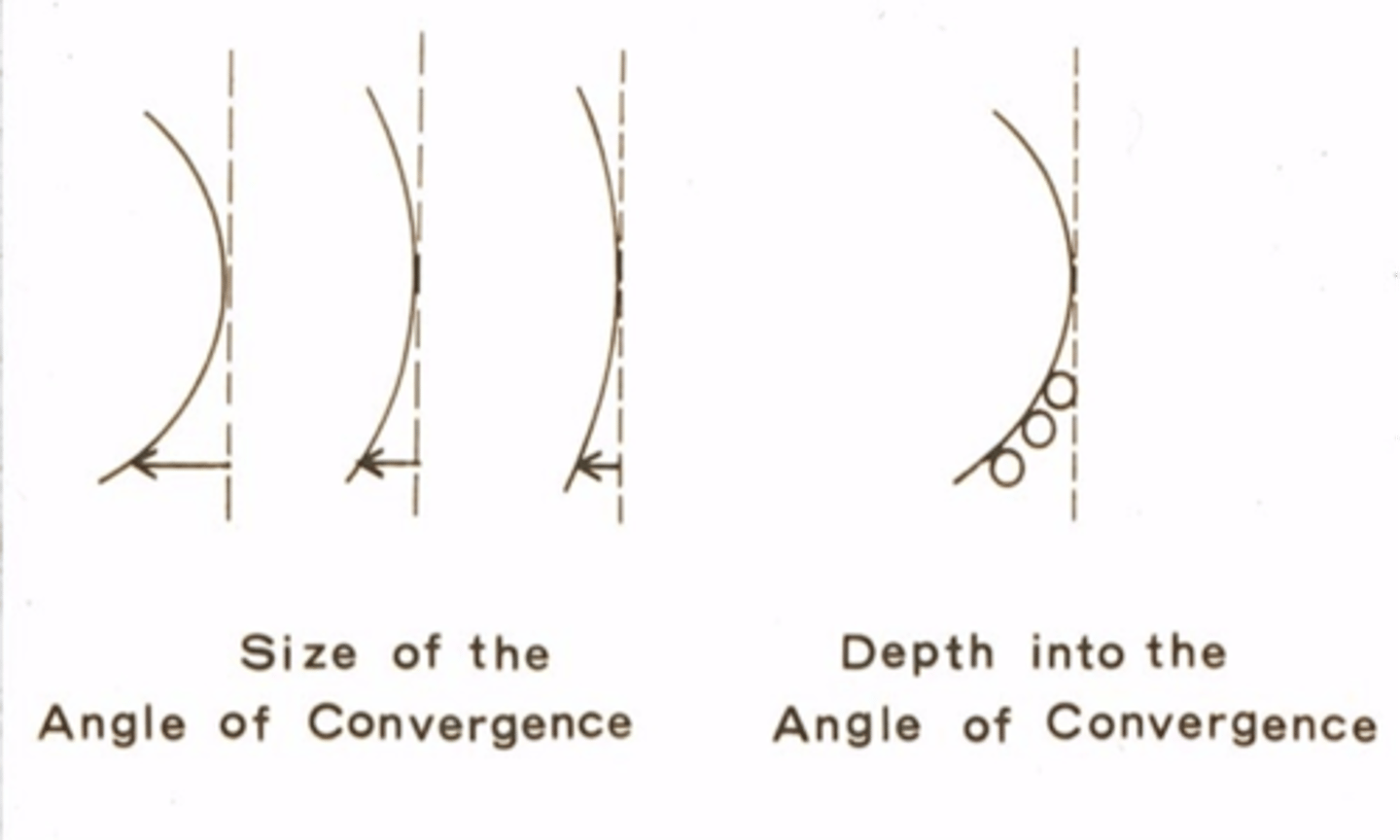
Angle of convergence
Determinants of Magnitude of Retention:
1) Size of angle
•Depth into angle (0.01” undercut vs 0.02” undercut)
•The more bulbous the tooth, the more retentive the clasp
•Ex: 0.01” undercut in a low convergence angle will not be as retentive as a 0.01” undercut in a high convergence angle
Clasp arm flexibility
Determinants of Magnitude of Retention:
2) Cross-sectional diameter of the arm
•Length of the arm: longer = more flexible
•Taper of the arm: more taper = more flexible
•Metal alloy used (wrought wire is more flexible than cast – greater tensile strength allows flexibility without fatigue)
Bar clasp, circumferential clasp
Determinants of Magnitude of Retention:
3) Push vs pull-type clasp
______: push type clasps – more retentive
________: pull type clasps – less retentive
Example: Think about pulling a stick along the ground behind you. The stick will offer very little resistance. If you push the stick in front of you the stick will shatter along the ground as friction increases. Push type clasps are thought to be very efficient due to “tripping action”.
Biomechanical
Classification type based on the nature of the supporting tissues
Kennedy
classification type based on location and number of edentulous areas
§Proposed in 1925
§Based on frequency of edentulous patterns in the population at the time
Tooth-borne
Biomechanical classification in which support comes from teeth
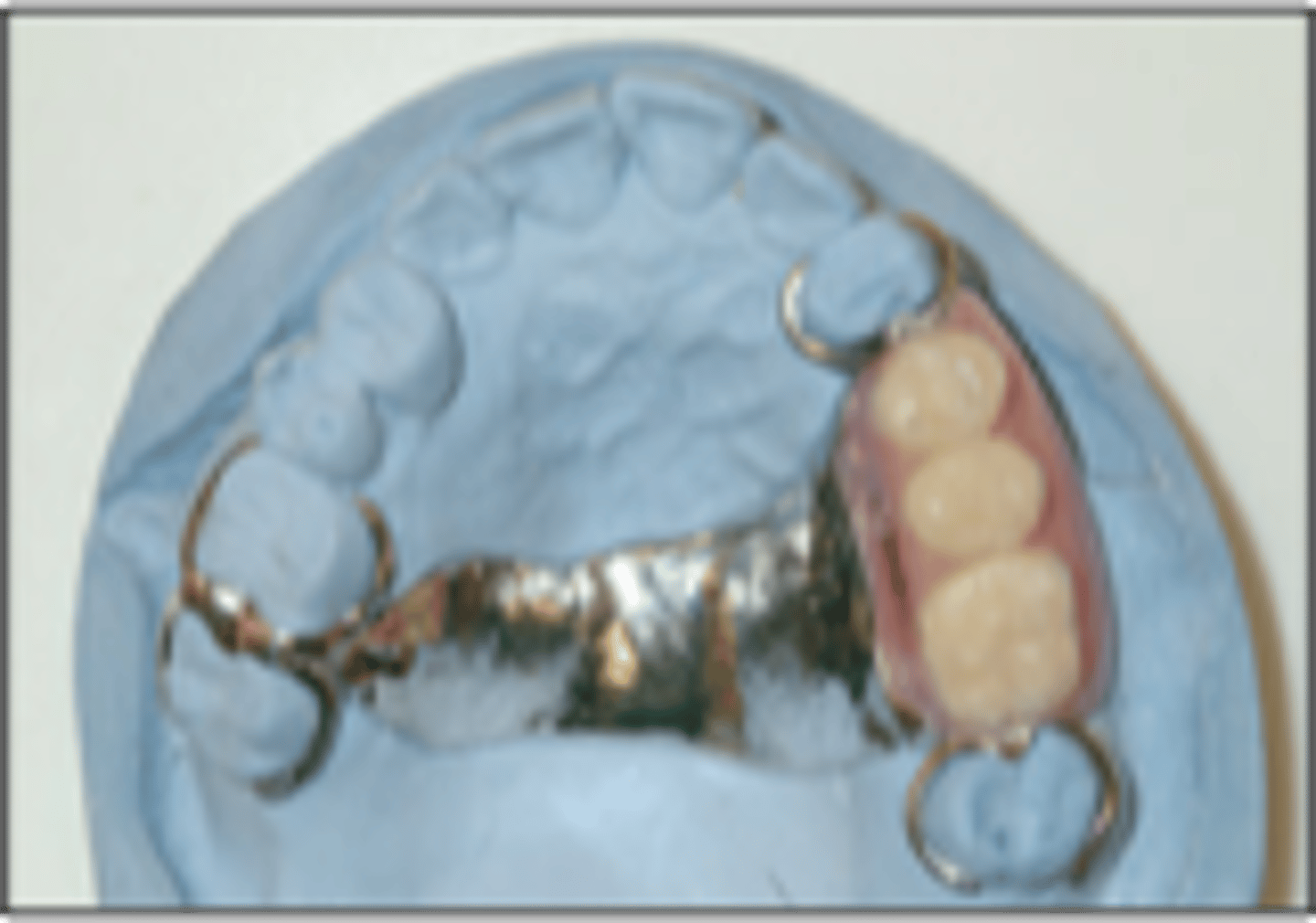
Tooth-soft tissue-borne
Biomechanical classification in which support comes from both teeth and soft tissue
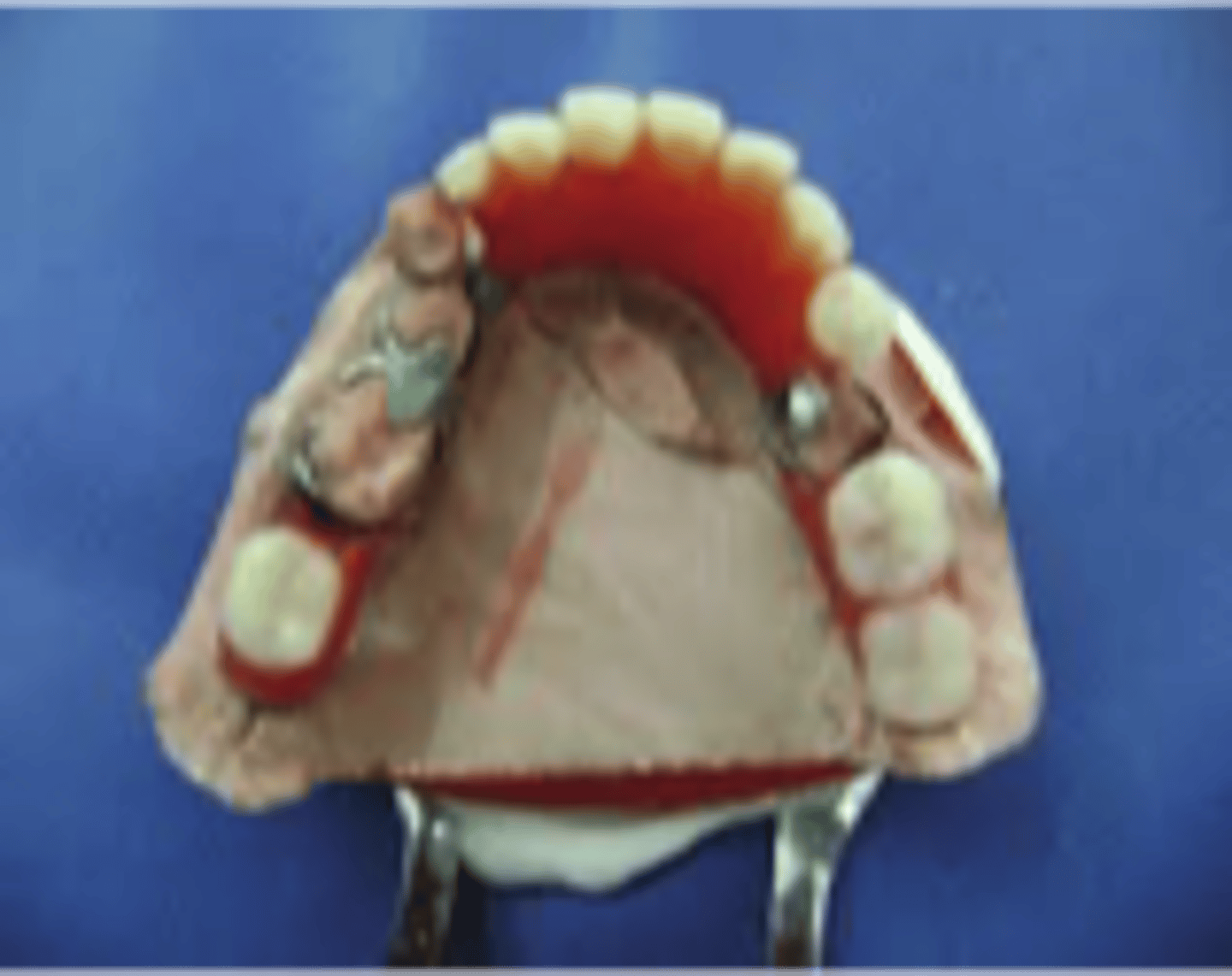
Soft-tissue borne
Biomechanical classification in which support comes from soft tissue onlysupport comes from soft tissue only
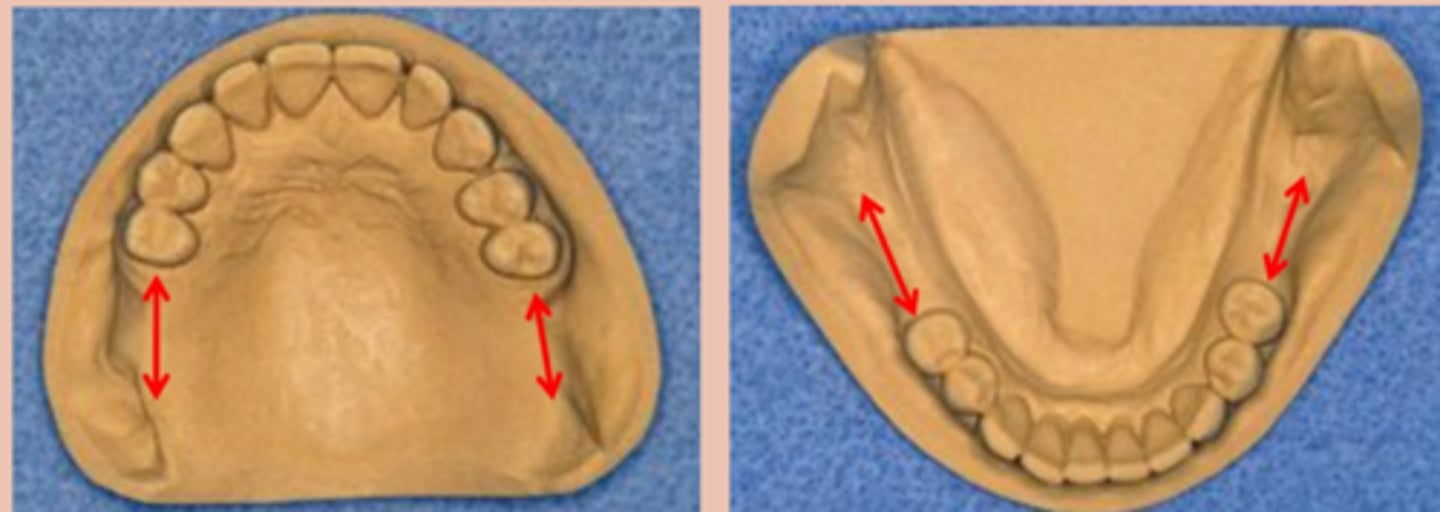
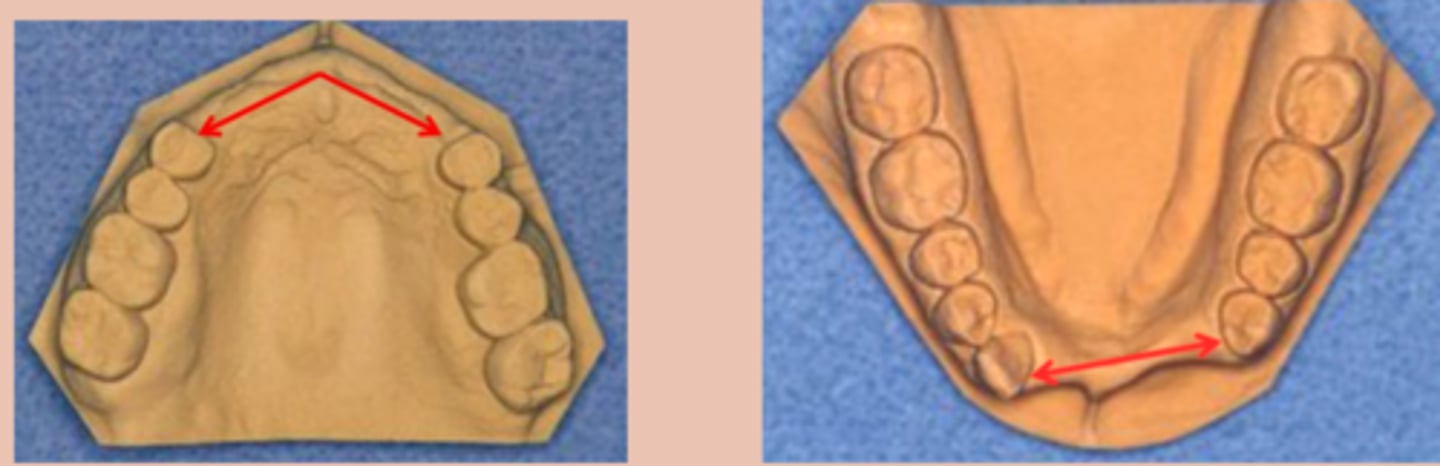
Kennedy Class I
Tooth and tissue supported:
bilateral edentulous area posterior to natural teeth
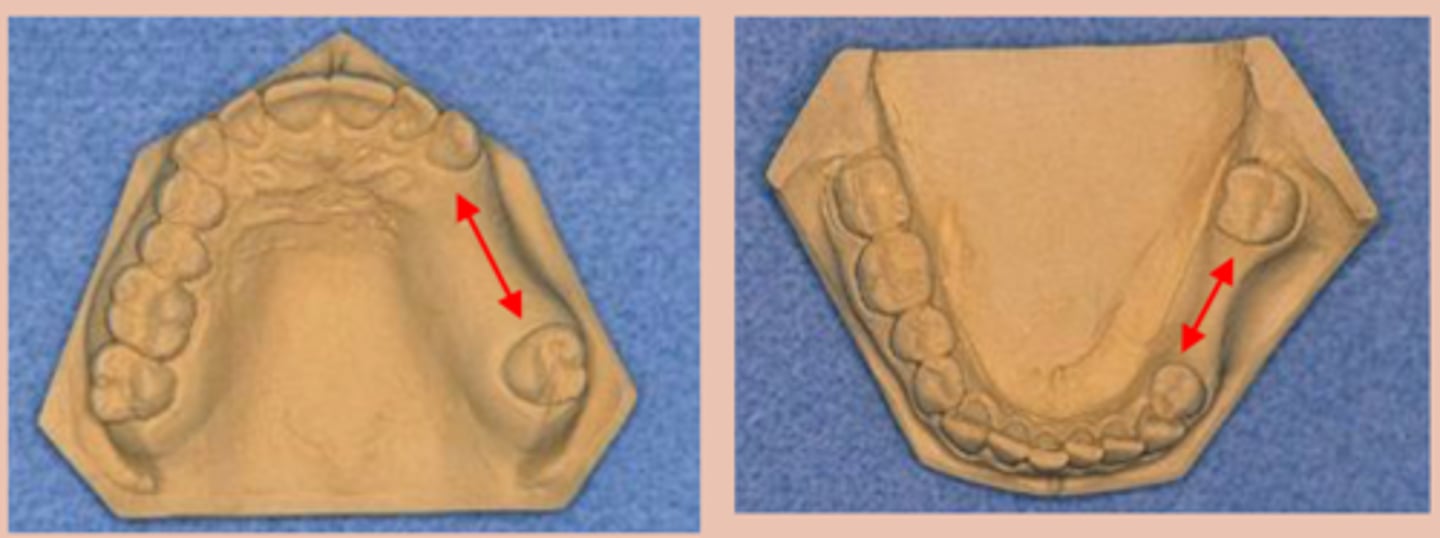
Kennedy Class II
Tooth and tissue supported:
unilateral edentulous area located posterior to the natural teeth

Kennedy Class III
Tooth supported:
A unilateral edentulous area with natural teeth both anterior and posterior to the area
Kennedy Class IV
Tooth and tissue supported, tooth supported:
A single but bilateral (crossing the midline) edentulous area located anterior to the remaining natural teeth
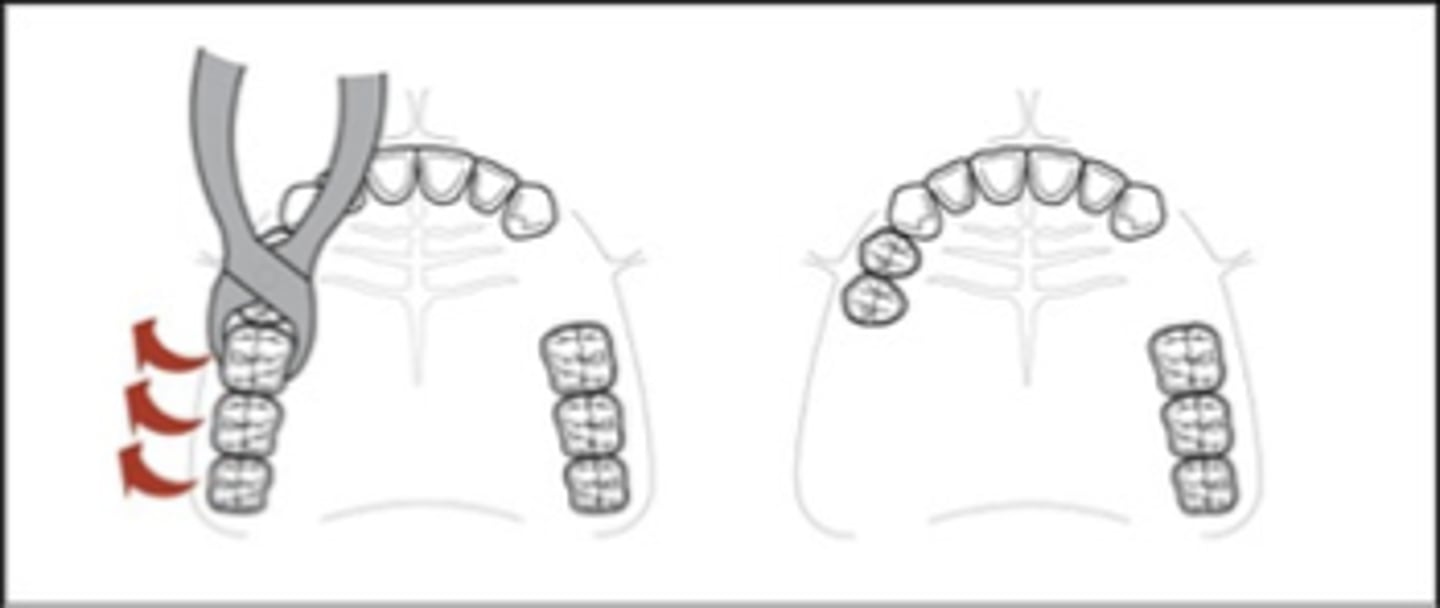
follow, extractions
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 1. Classification should ______ rather than precede any ______ of teeth that might alter the original classification
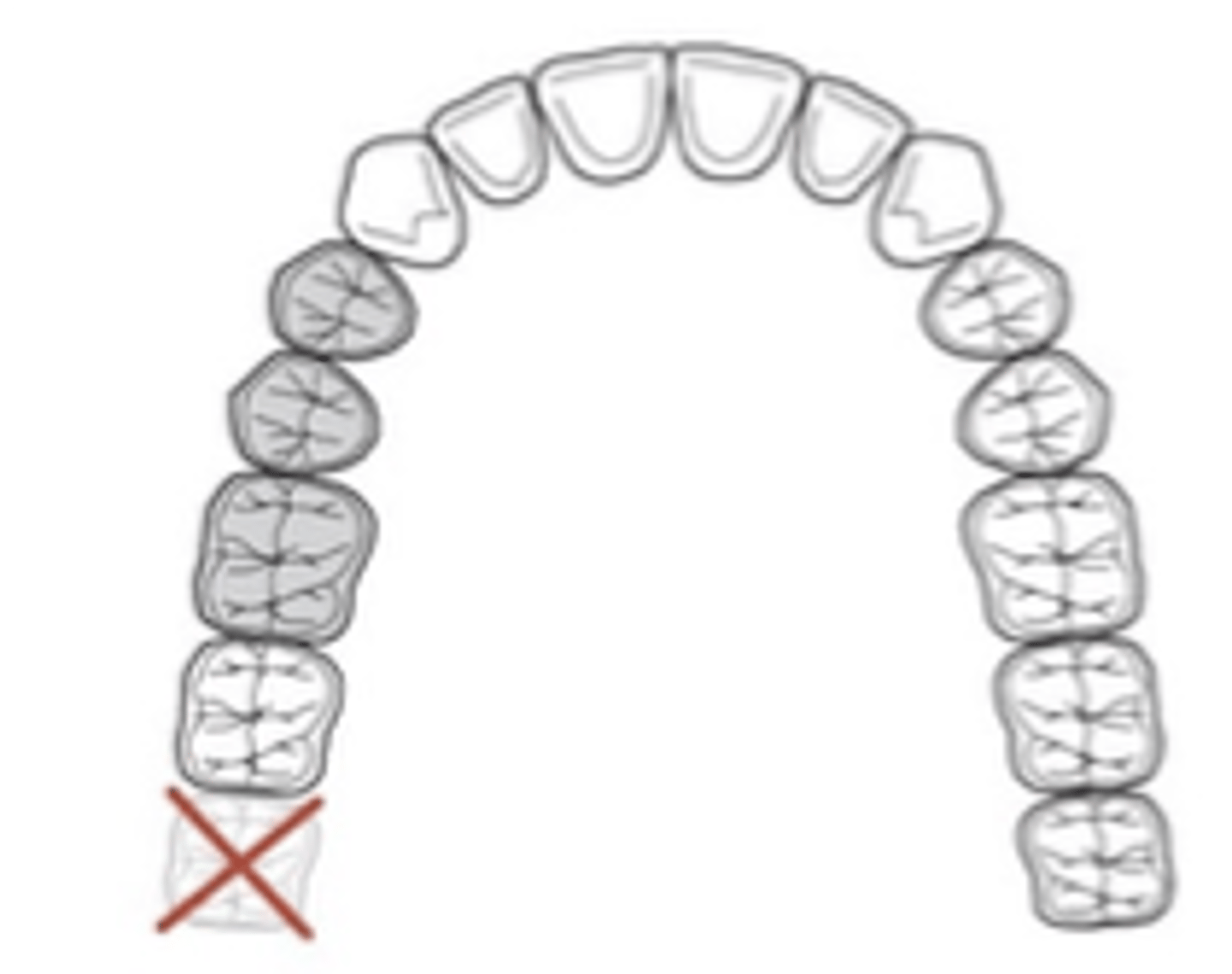
3rd, not considered
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 2. If a _____molar is missing and is not to be replaced, it is ______ in the classification
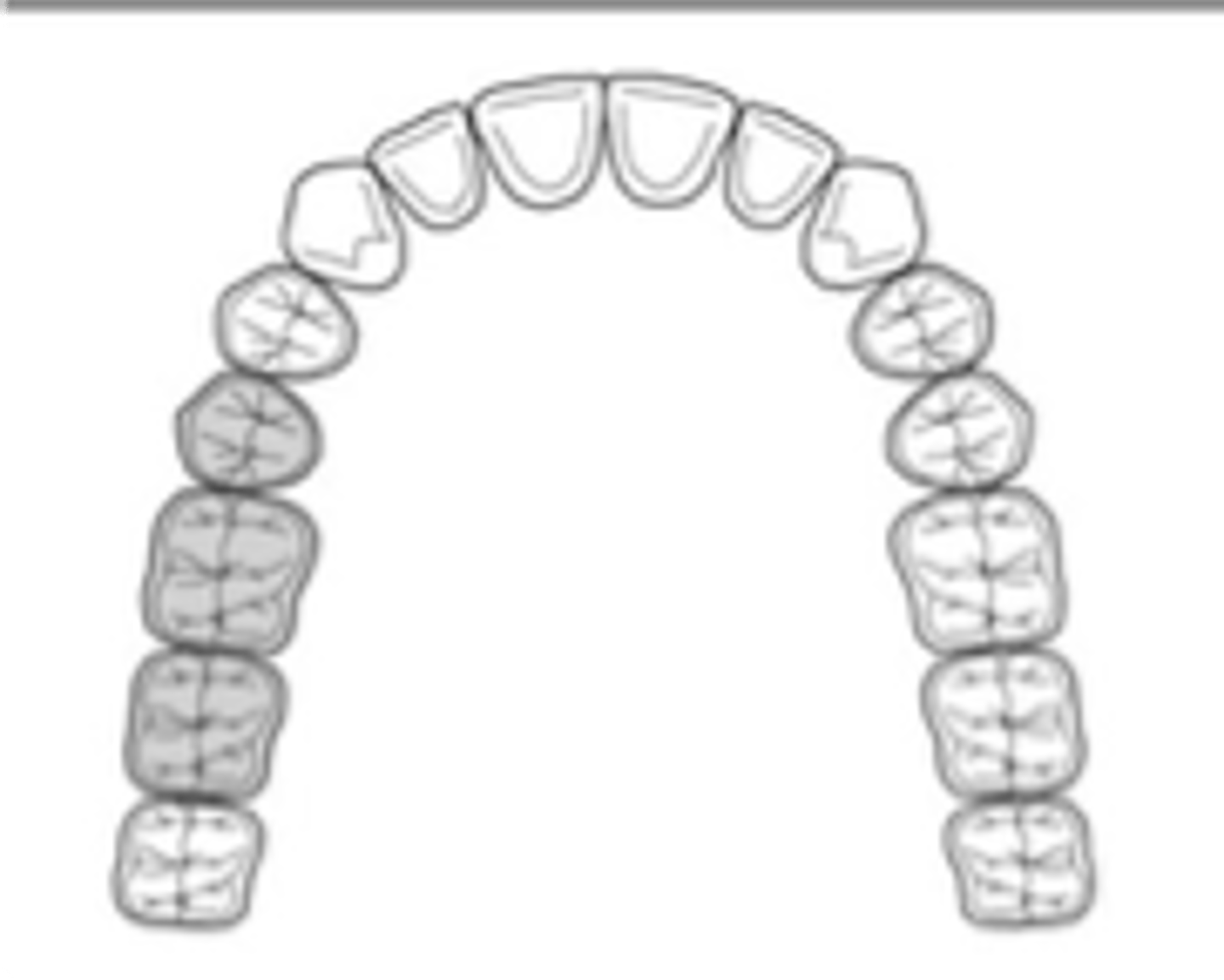
abutment
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 3. If a 3rd molar is present and is to be used as an ______, it is considered in the classification. (In other words, 3rd molars aren’t exempt from classification)
2nd
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 4. If a ______molar is missing and is not to be replaced, it is not considered in the classification (e.g., if the opposing second molar is likewise missing and is not to be replaced).
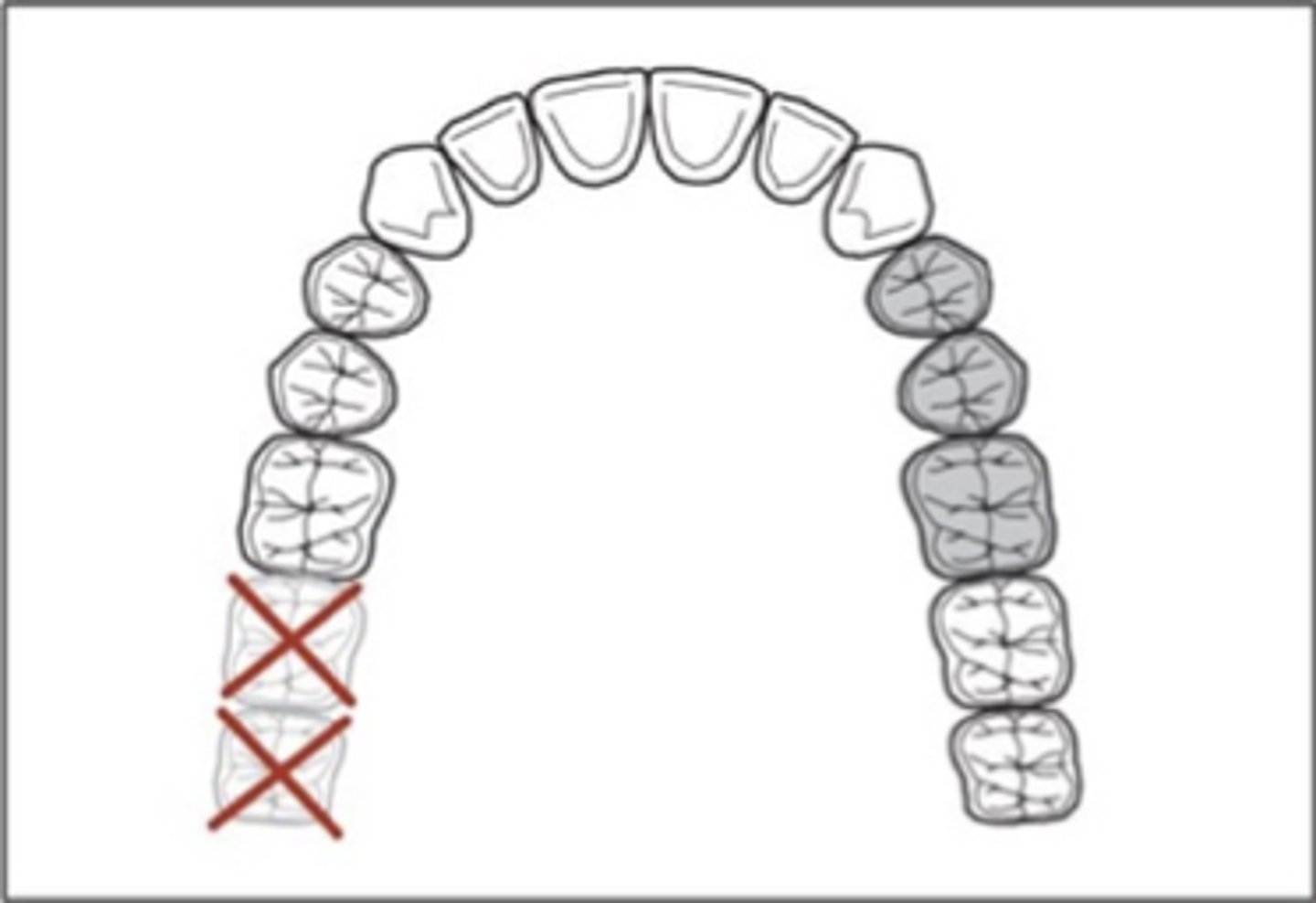
Class II
What would the classification be if the 2nd molar was being replaced? And if 2nd and 3rd molars were being replaced?
most posterior edentulous
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 5. As stated previously, the ______area (or areas) always determines the classification.
Rules 6, 7, and 8
pertain to modification spaces, which are designated with Arabic numerals. Allows further description of clinical situation, since many patients have more than one edentulous area that do not fit the Kennedy class I scenario
modification space (rule 6)
Each additional edentulous area (beyond those that determine classification) is a _______ - not each additional missing tooth (Rule 7).

Class IV
Applegate’s Rules:
Rule 8. No modification areas can be included in _______ arches (due to the most posterior edentulous area determining the Kennedy class)
Class IV
which Kennedy Class?
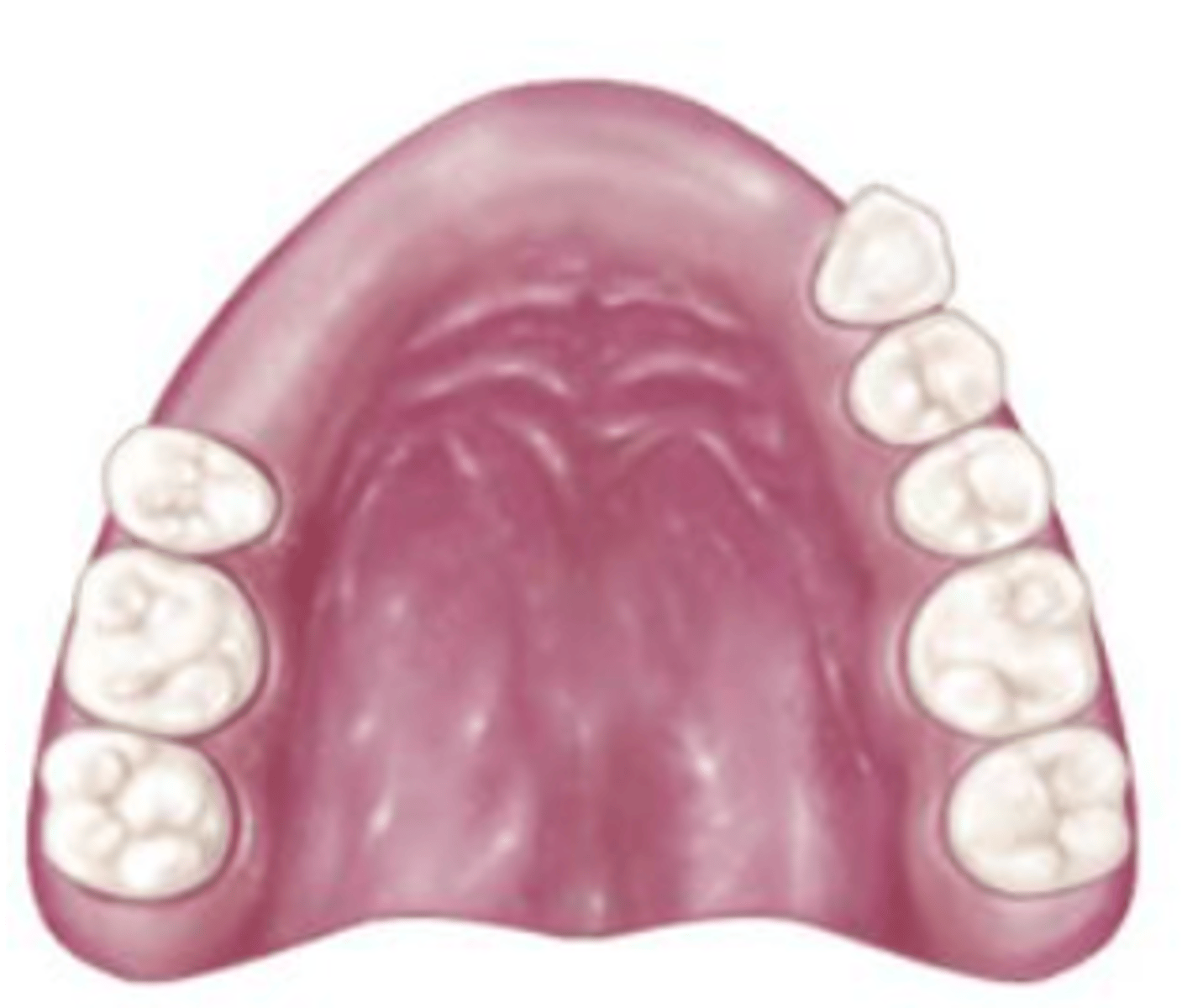
Class II Mod 2
which Kennedy Class?
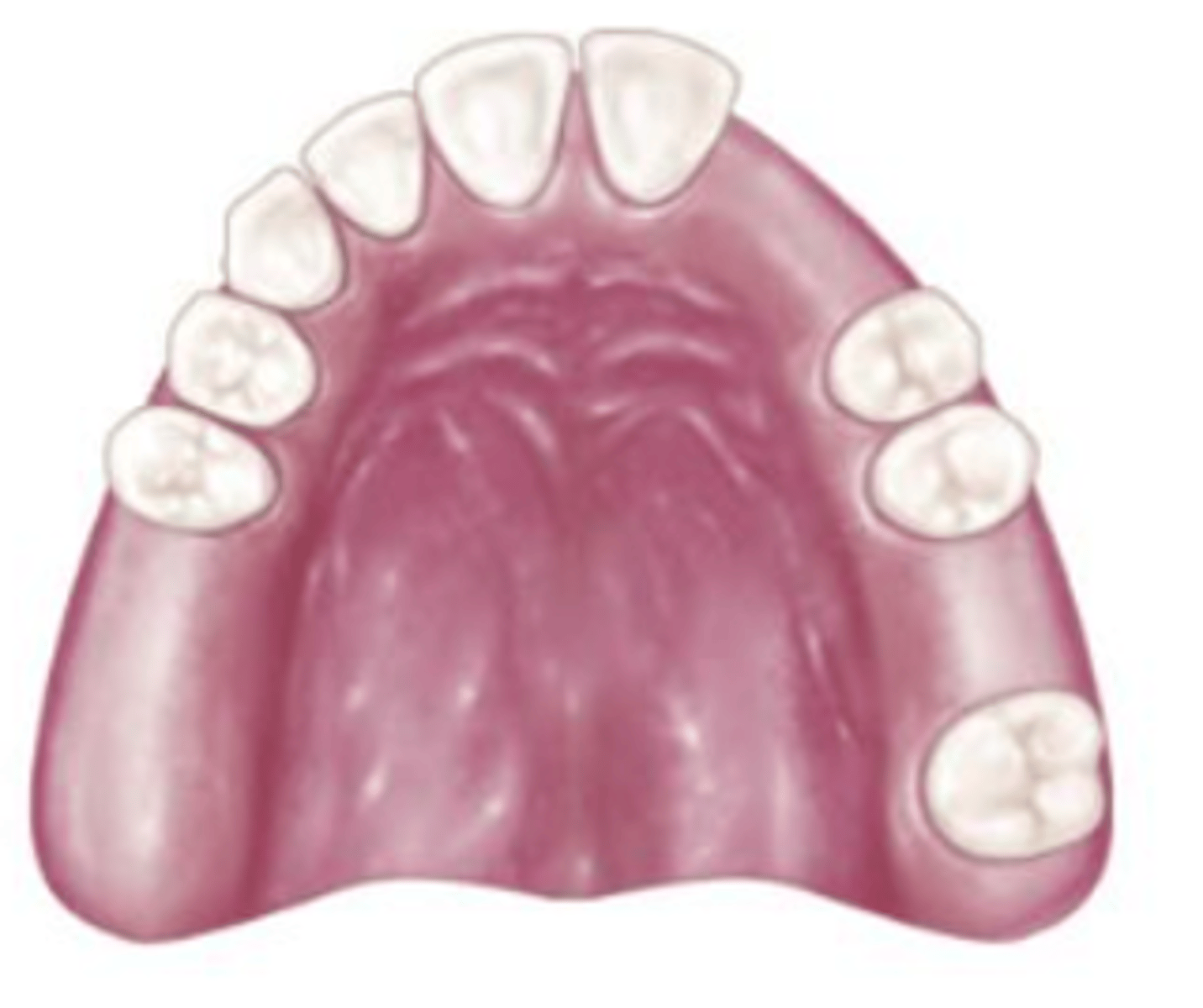
Class I Mod 1
which Kennedy Class?
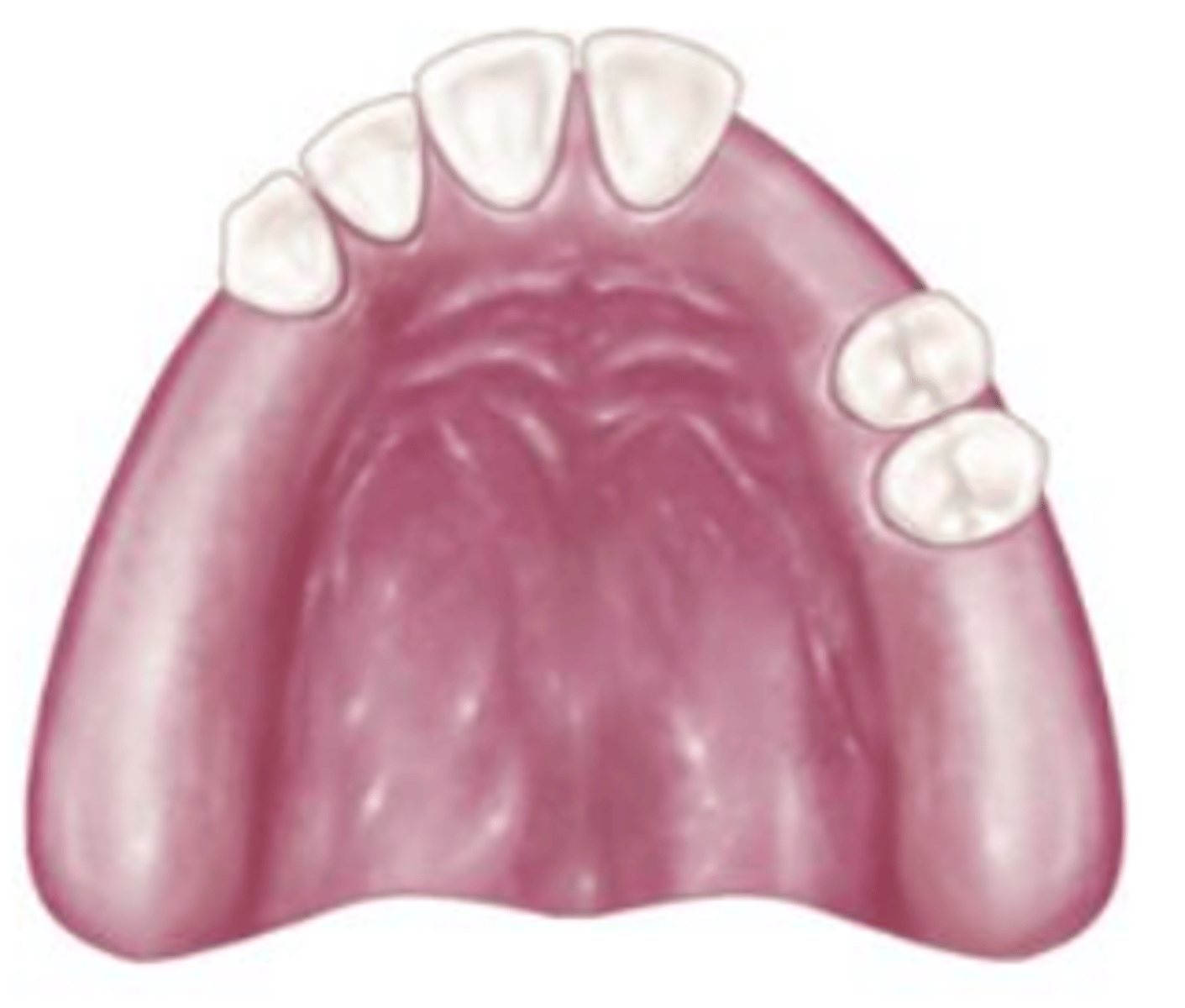
Class III Mod 3
which Kennedy Class?
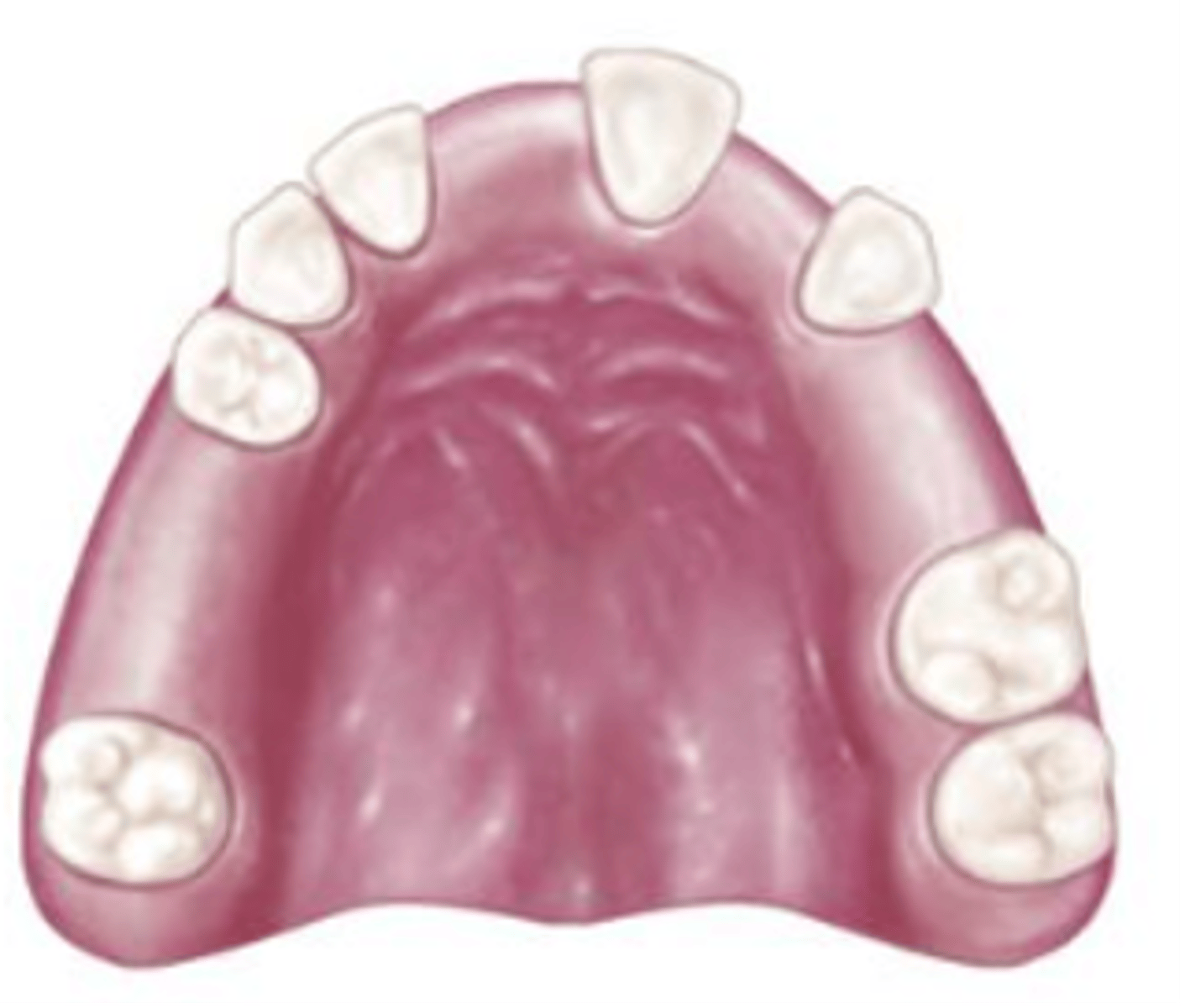
Class III Mod 1 (Class I Mod 2 if replacing 2nd molars)
which Kennedy Class?
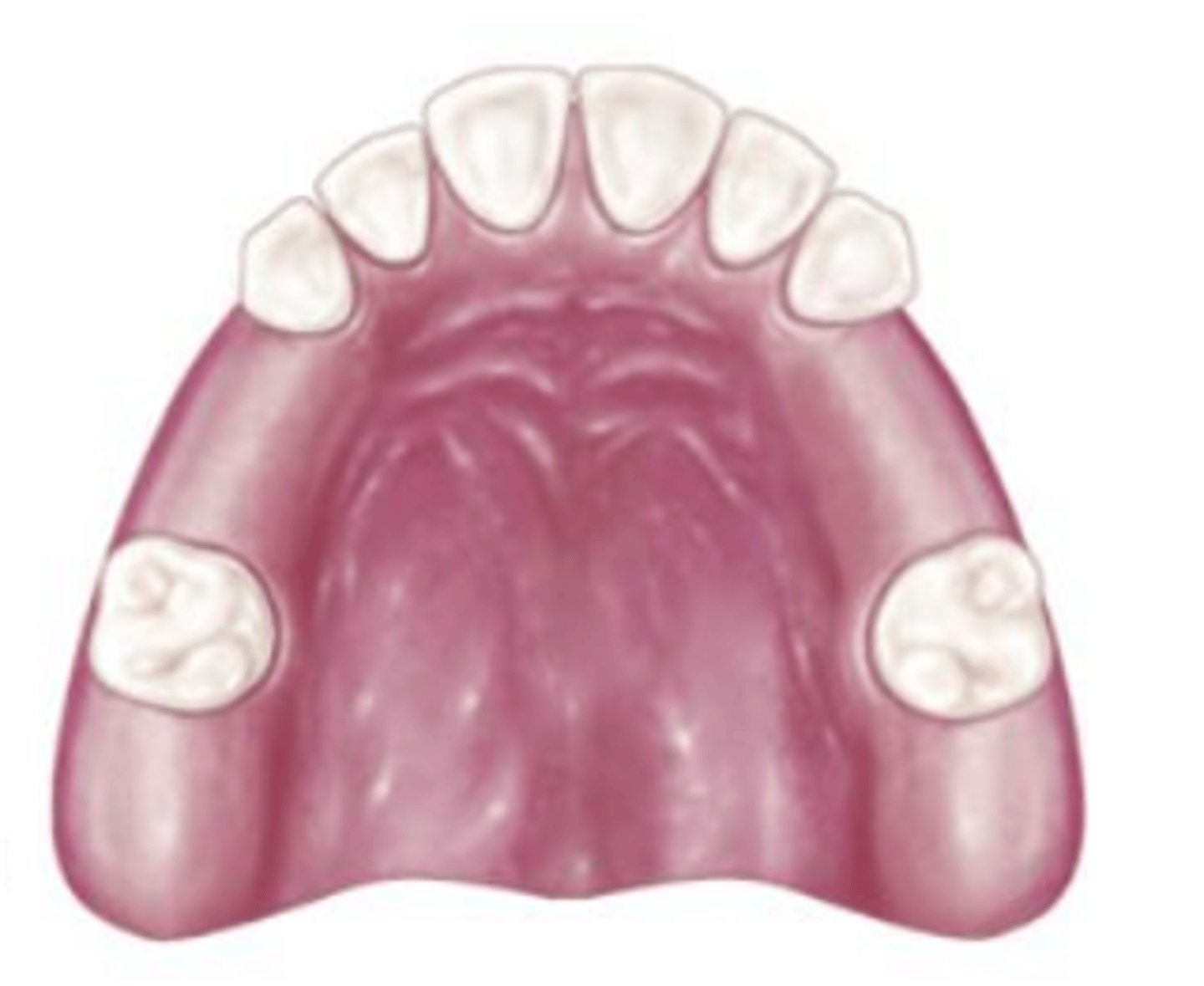
Class III mod 5
which Kennedy Class?
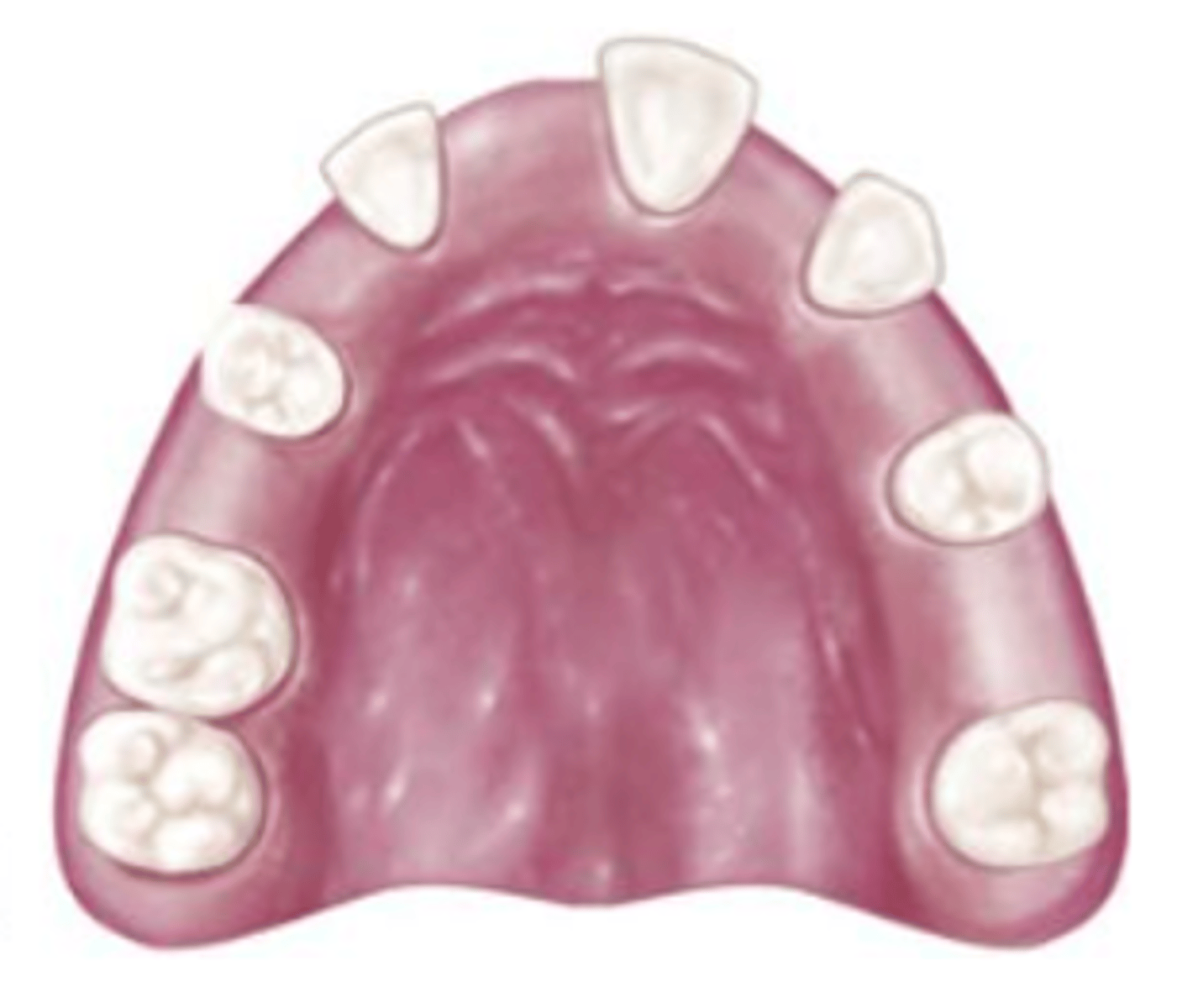
Class III Mod 2
which Kennedy Class?
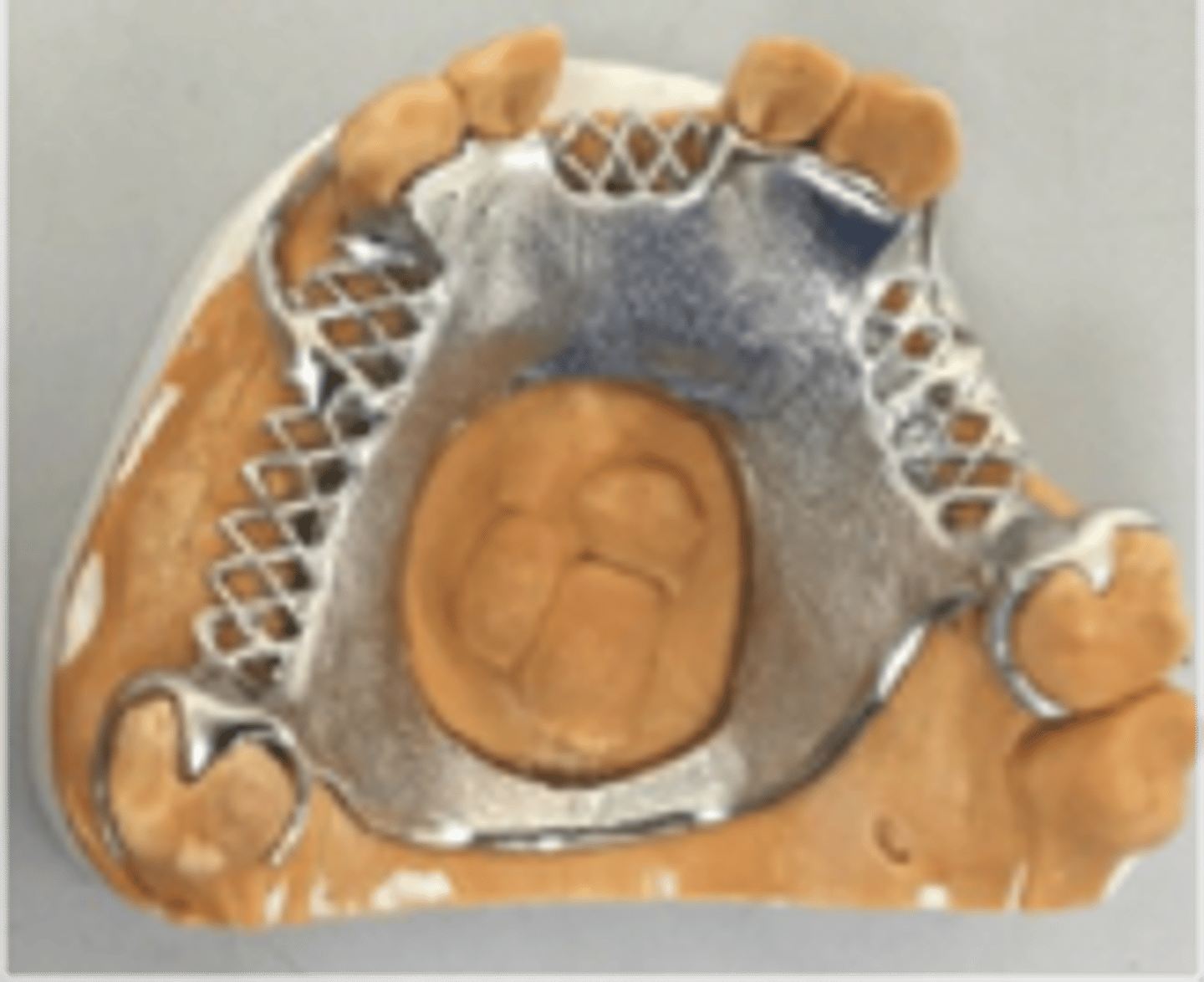
N/A - complete denture
which Kennedy Class?
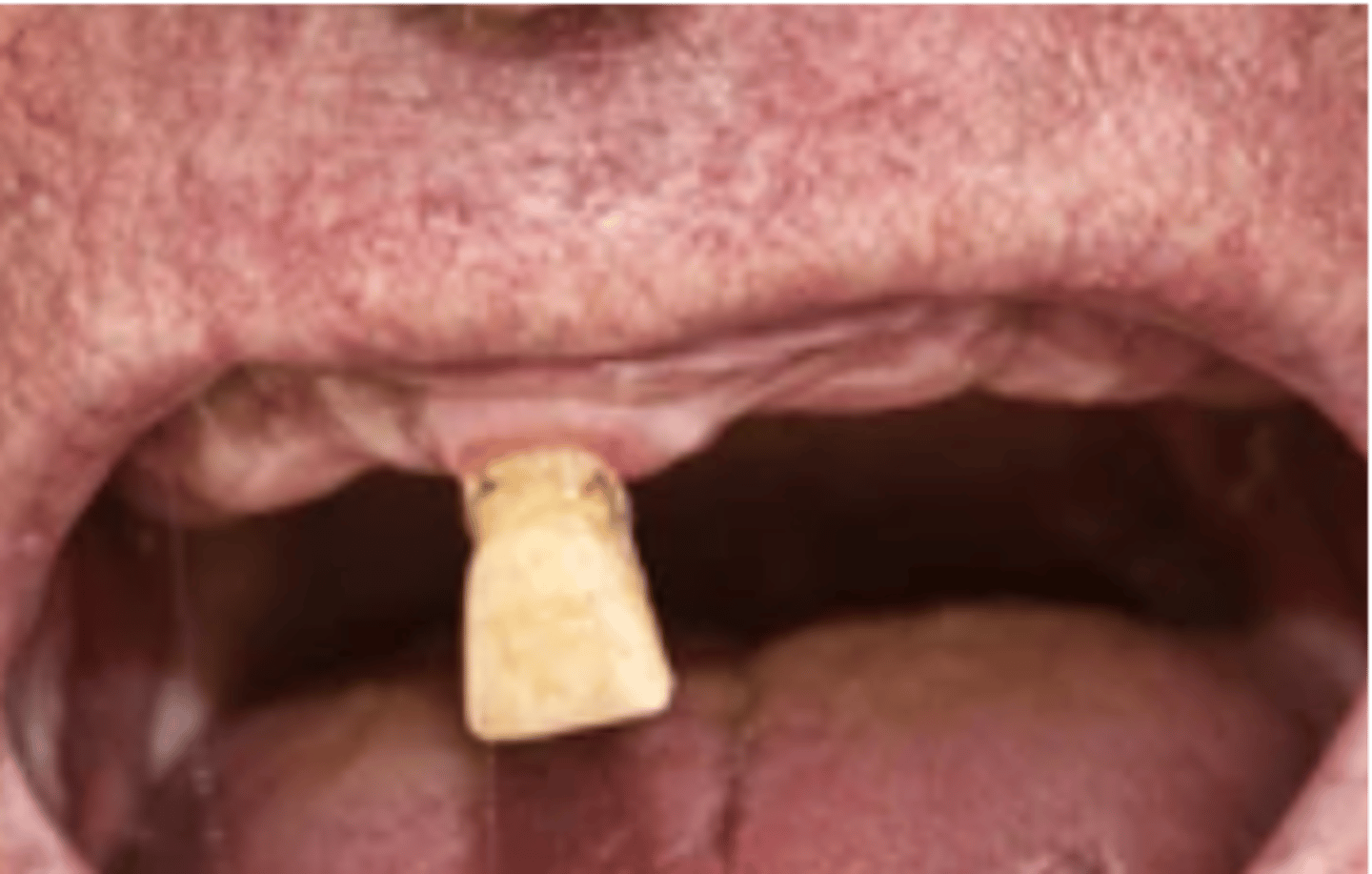
axial loading
In well-aligned, intact dental arches, teeth and periodontium sustain mostly ...
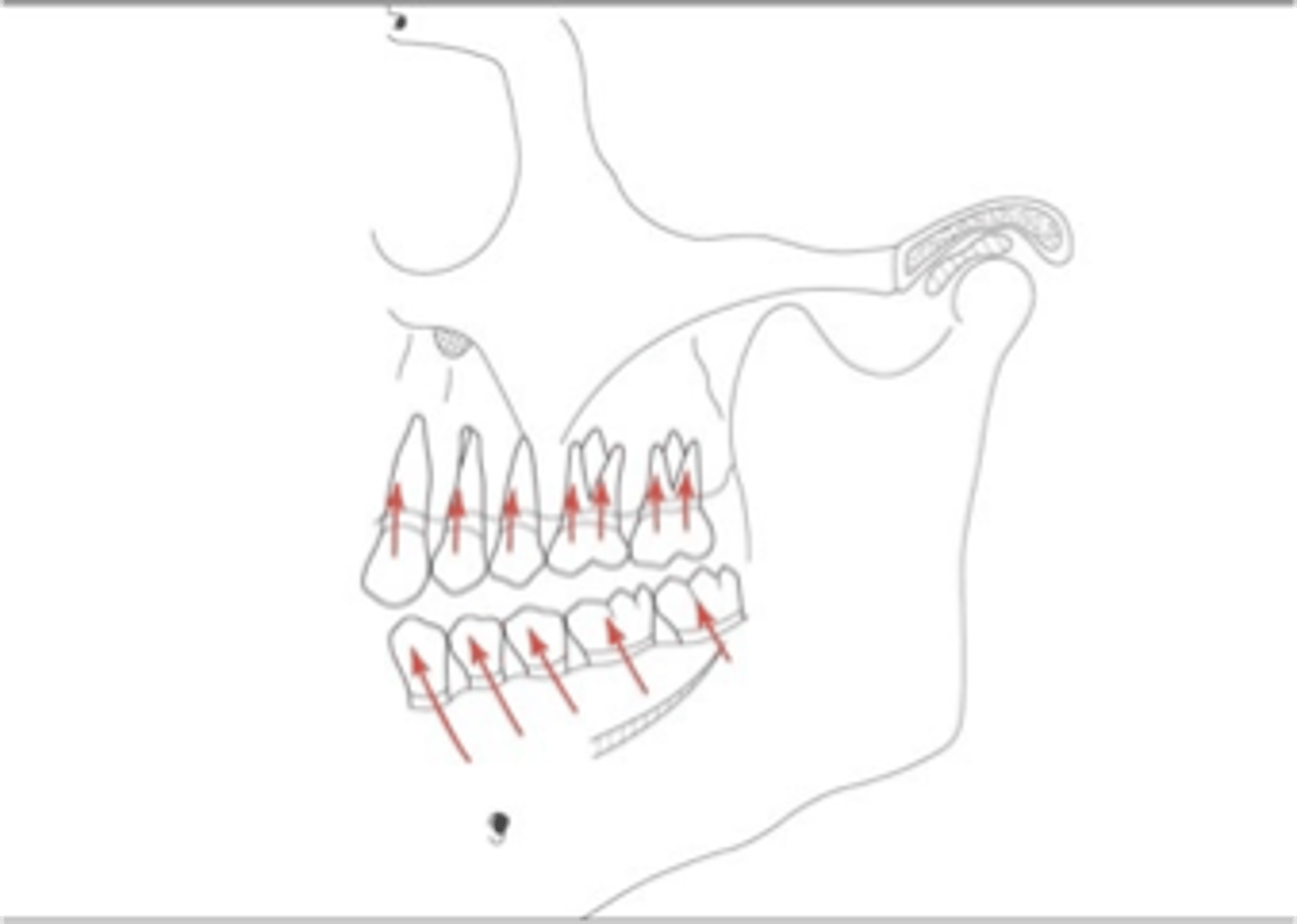
axially directed force
Response of dento-alveolar tissues respond better to which type of directed force
support during function
The goal of any prosthesis is to provide ________to mimic that in natural dentition.