Cellular Metabolism: Anabolism, Catabolism, and DNA
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions in the body
Cellular Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions occurring in a cell; metabolic reactions usually occur in pathways or cycles.
Anabolism
Small molecules are built into larger ones; requires energy
Catabolism
Larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones; releases energy
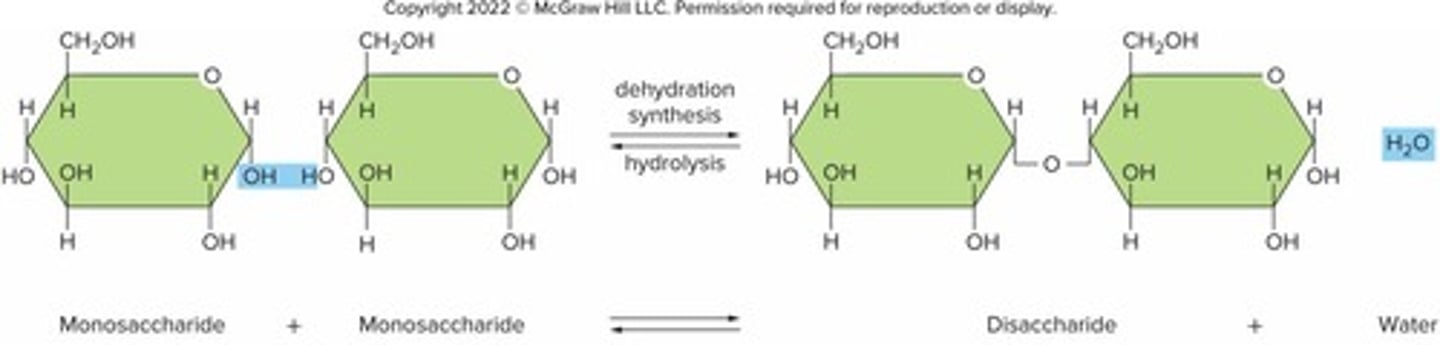
Dehydration synthesis
Smaller molecules are bound together to form larger ones; H2O produced in the process; used to produce polysaccharides, proteins, triglycerides.
Hydrolysis
Used to decompose carbohydrates, proteins, lipids; uses H2O to split the substances; reverse of dehydration synthesis.
Control of Metabolic Reactions
Rates of catabolism and anabolism must be carefully controlled; breakdown/energy-releasing reactions must occur at rates that balance with build-up/energy-utilizing reactions.
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyze specific reactions; increase rates of chemical reactions; lower the activation energy necessary to start reactions.
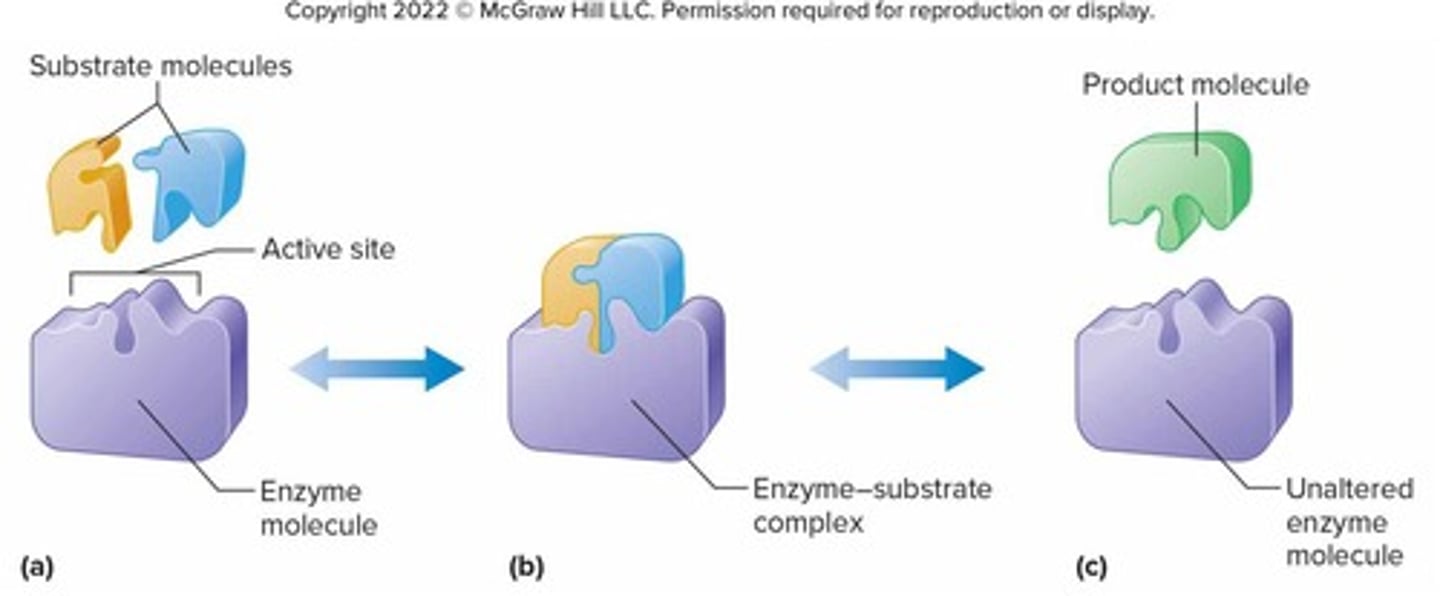
Enzyme Action
Not consumed in the reaction, so are used repeatedly; each enzyme is specific to a particular substrate.
Active site
Shape of active site of enzyme determines the ability to recognize substrate.
Rate-limiting enzyme
A regulatory enzyme that catalyzes one step of pathway typically sets rate for entire reaction sequence; number of molecules of this enzyme is limited.
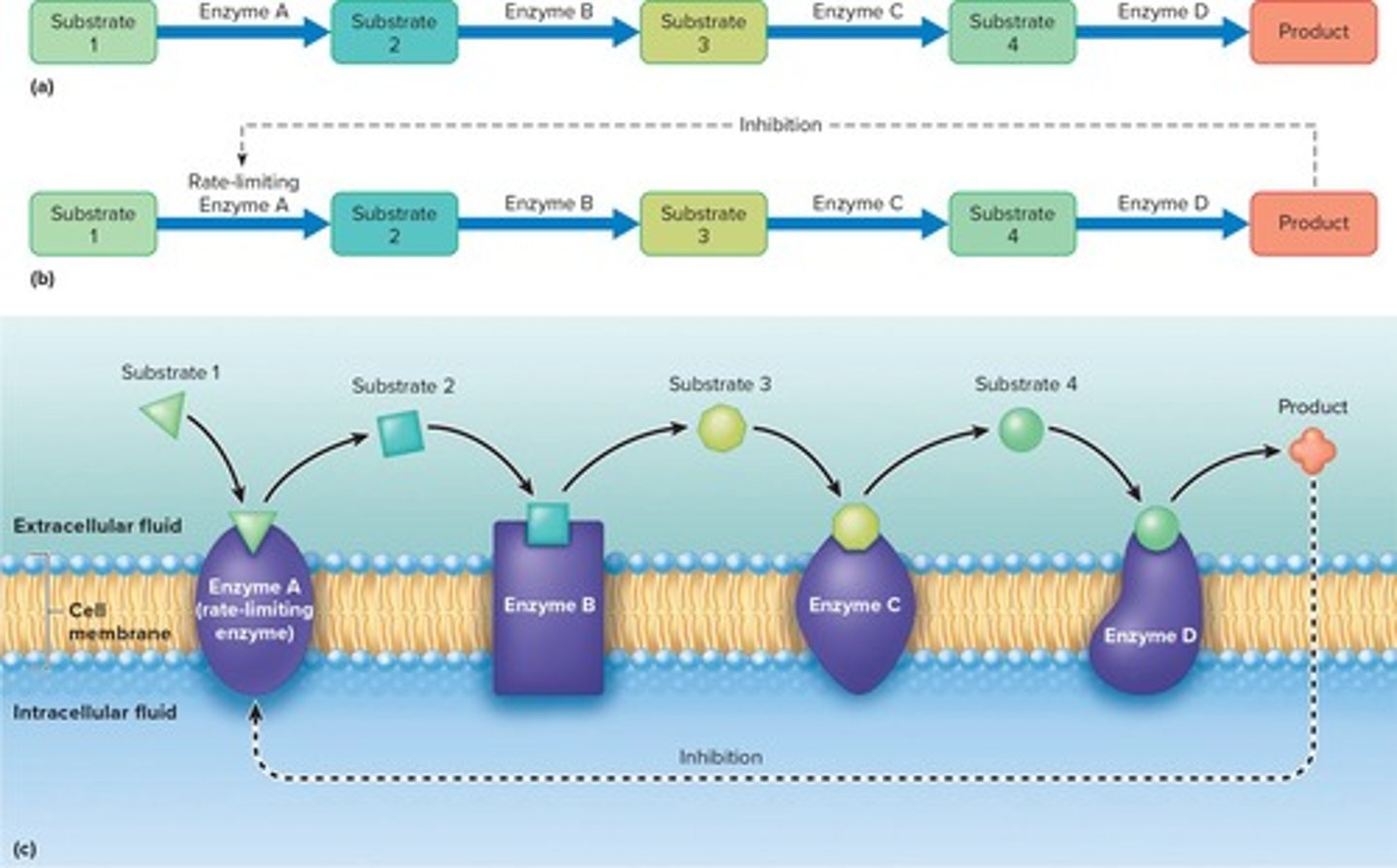
Negative feedback
In some pathways, end product inhibits rate-limiting enzyme.
Metabolic Pathways
Series of enzyme-controlled reactions leading to formation of a product; each new substrate is the product of the previous reaction.
Specificity of Enzymes
Many enzymes are named after substrate, with "-ase" as suffix; example: "lipase" breaks down lipids.
Imbalances in reaction rates
Can damage or kill a cell.
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Each step of a pathway is catalyzed by a different enzyme.
Energy production in Catabolism
A T P is produced.
Energy requirement in Anabolism
Requires A T P made during catabolism.
Cofactor
Non-protein substance that combines with the enzyme to activate it
Coenzyme
Organic molecule that acts as cofactor
Denaturation
Inactivation of an enzyme (or any other protein), due to an irreversible change in its conformation
Energy
Capacity to change something, or the ability to do work
Common forms of energy
Heat, light, sound, electrical energy, mechanical energy, chemical energy
Cellular respiration
Process that transfers energy from molecules, and makes it available for cellular use
Chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds, released when bonds are broken
Oxidation
Releases energy from glucose and other molecules, via loss of hydrogen atoms and their electrons
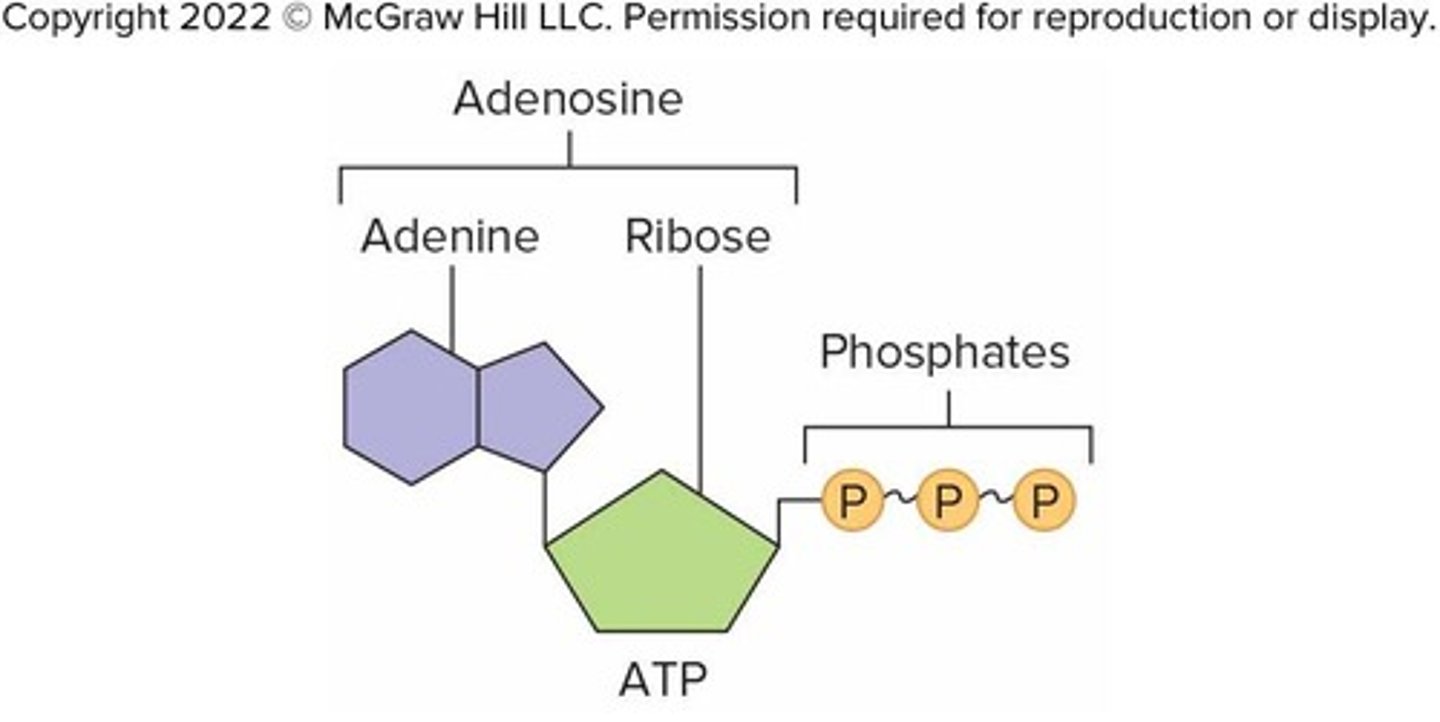
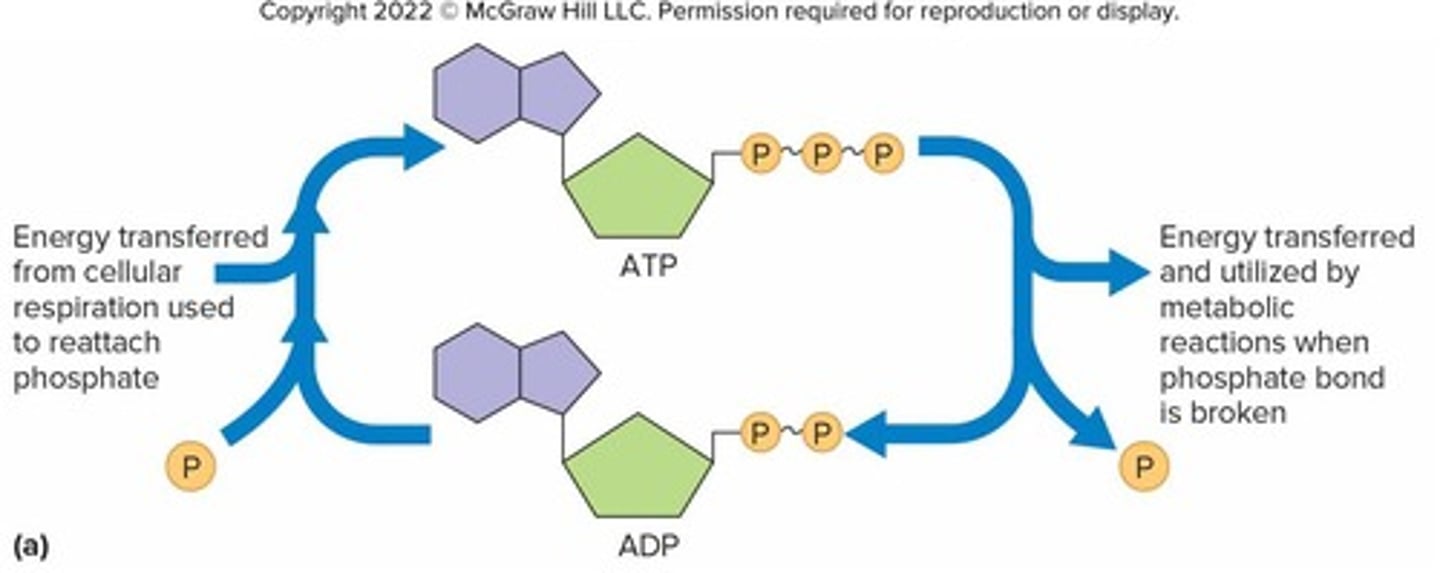
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Molecule that carries energy in a form the cell can use
ATP breakdown
Energy from ATP breakdown is used for cellular work
Glycogen
Excess glucose can be converted into and stored as glycogen; most cells, but liver and muscle cells store the most
Fat
Excess glucose can be converted into and stored as fat for storage in adipose tissue
Energy transfer to ATP
40% is released as chemical energy; 60% is released as heat; maintains body temperature
ATP structure
Consists of 3 portions: Adenine, Ribose (a sugar), 3 phosphates in a chain
High-energy bonds in ATP
Second and third phosphates are attached by high-energy bonds; energy can be quickly transferred to other molecules
Metabolic reactions
Most metabolic reactions use chemical energy
Enzymes in cellular respiration
In cells, enzymes lower activation energy needed for oxidation in reactions of cellular respiration
Catabolic pathways
Carbohydrate molecules from foods can enter catabolic pathways for energy production
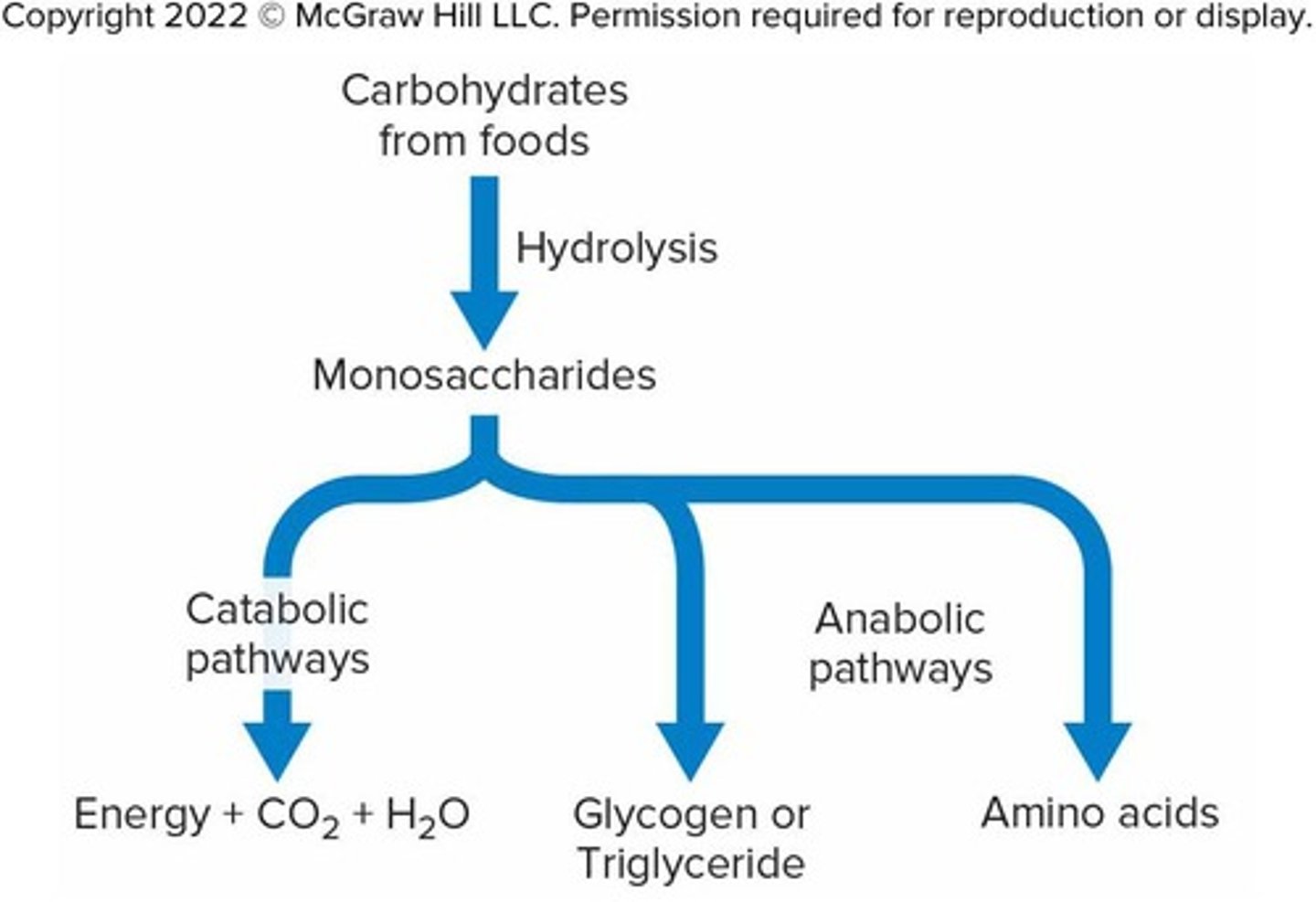
Anabolic pathways
Carbohydrate molecules from foods can enter anabolic pathways for storage
Amino acids formation
Carbohydrate molecules from foods can react to form some amino acids
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
The genetic material that stores information on its sequence of nucleotides, that instructs a cell on how to synthesize certain proteins.
Genetic Information
Instructions to tell cells how to construct proteins; stored in DNA sequence.
Gene
Sequence of DNA that contains information for making 1 protein.
Genome
Complete set of genetic information in a cell.
Exome
Small portion of the genome that codes for proteins.
Gene Expression
Control of which proteins are produced in each cell type, in what amount, and under which circumstances.
Double helix
Double-stranded molecule, consisting of 2 chains of nucleotides that resembles a ladder twisted into a spiral.
Backbone of DNA
Each strand is a sugar-phosphate chain.
Complementary Base Pairing
Bases pair only with specific pairs: A ̶ T and C ̶ G.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA, consisting of a 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine).
Antiparallel
The 2 nucleotide chains of the double helix point in opposite directions.
Purines
A and G are purines.
Pyrimidines
C and T are pyrimidines.
Histone proteins
DNA wraps around histone proteins to give the double helix a compact form in chromatin and chromosomes.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA
Bases from the 2 complementary strands are linked together by hydrogen bonds: C ̶ G, A ̶ T.
Structural proteins
Proteins coded for on DNA that function as structural proteins of muscle and connective tissue.
Antibodies
Proteins coded for on DNA that function as antibodies.
Cell membrane components
Proteins coded for on DNA that function as components of cell membranes.
Protein Synthesis
A sequence of 3 nucleotides provides template for complementary RNA.
Genetic Code
Each unit of 3 RNA nucleotides represents genetic code.
Gene Sequence
Sequence of bases in a gene determines the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide.
Nucleotide Sequence
Each sequence of 3 nucleotides either represents an amino acid or signals to start or stop protein synthesis.
Transcription
Process of copying DNA sequence onto an RNA sequence.
DNA
Stores master copy of genetic code, and remains in the nucleus.
RNA
Copies and transfers information from DNA to the cytoplasm.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
The type of RNA that carries genetic code from DNA to ribosome in cytoplasm.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that catalyzes the formation of mRNA from the proper strand of DNA.
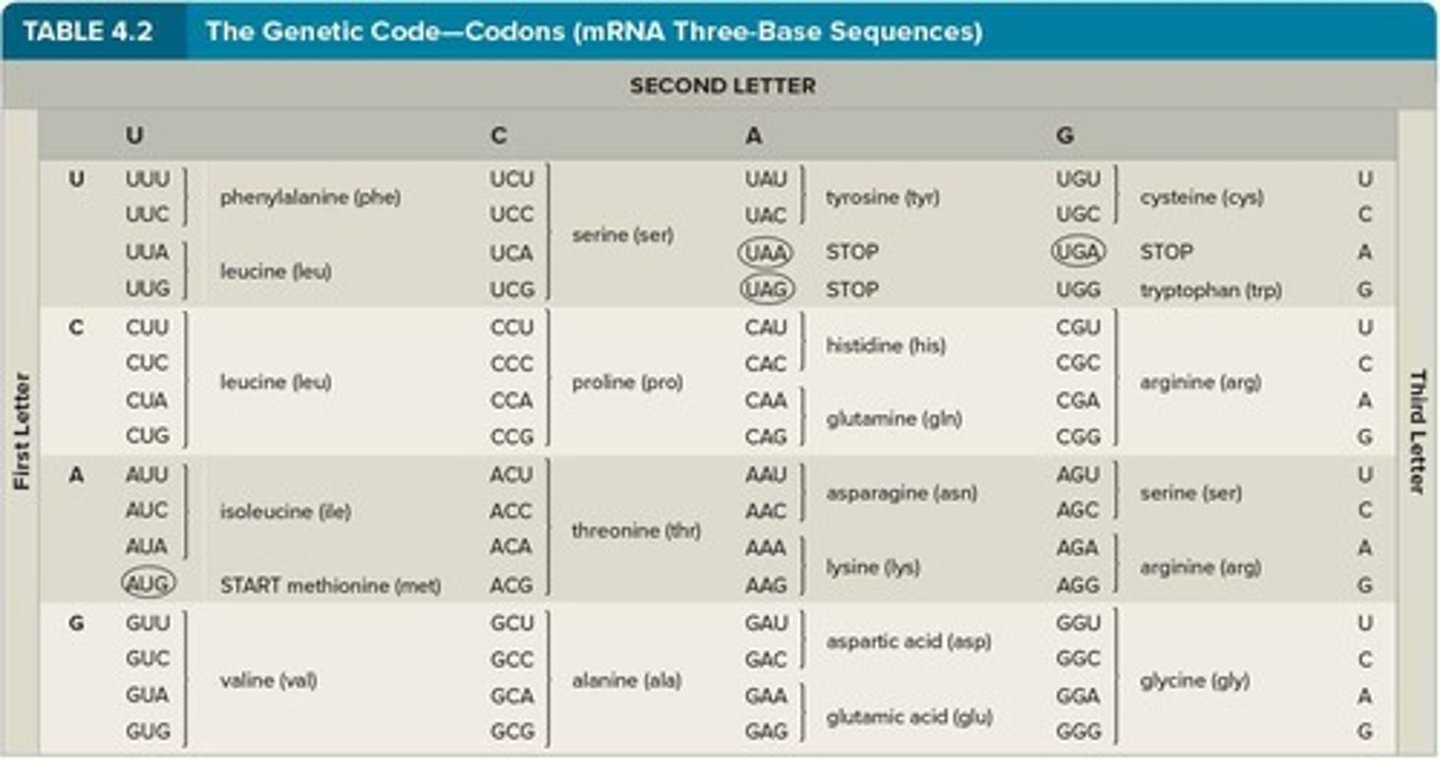
Codons
Each amino acid is specified by a sequence of 3 bases in DNA, called codons.
Ribosome
Organelles composed of Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein molecules.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Aligns amino acids during translation, along the mRNA strand on the ribosome.
Anticodon
Each tRNA contains a sequence of 3 nucleotide bases, the anticodon, which binds to the complementary codon on the mRNA strand.
Amino Acids
There are 20 types of amino acids.
mRNA Codons
There are 64 possible codons (3-base sequences) on mRNA.
Initiation Codon
The Initiation codon, AUG, codes for Methionine and signals the start of a protein.
Stop Codons
3 codons are Stop codons, signaling the end of a protein; these do not have corresponding tRNAs.
Peptide Bonds
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds.
Ribosome Function
Ribosome moves down mRNA molecule, bringing in tRNAs carrying the proper amino acid to add to the growing protein chain.
Reusability of Ribosomes
Ribosomes, mRNA, and rRNA can be used repeatedly.