Respiration
4.8(6)
4.8(6)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
What is the musculoskeletal system made up of?
Bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and joints.
2
New cards
How do the bones provide blood production and store minerals?
The bones are hollow with a soft tissue called bone marrow, it is the provider of blood cells and stores minerals such as fats
3
New cards
What is the function for bones of protection?
* Bones such as the ribs that provide protection for the lungs and heart
* The skull provides protection for the brain
* The skull provides protection for the brain
4
New cards
What are skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles are muscles attached to the bones, it contracts to make bones move and joints bend.
5
New cards
What are smooth muscles?
Smooth muscles are made of thin sheets of muscles (e.g. stomach lining)
6
New cards
What are cardiac muscles?
Muscles found in the heart that contracts and relaxes to make blood pump around the body.
7
New cards
What is the role of bone?
They provide structure and support to the body, as well as protection to some organs
8
New cards
What is the role of muscle?
Muscles are used for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is caused by muscle contractions.
9
New cards
What is the role of cartilage?
Cartilage has the ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support on bony areas where there is a need for flexibility.
10
New cards
What is the role of tendons?
Tendons move the bone or structure.
11
New cards
What is the role of ligaments?
Ligaments hold structures together and keep them stable.
12
New cards
What is the cardiovascular system made up of?
Heart and blood vessels
13
New cards
What is the function of arteries?
Arteries bring oxygen rich blood cells from the heart to the rest of the body.
14
New cards
What is the function of veins?
Veins collect oxygen-poor blood from the rest of the body and bring it back to the heart. They also carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
15
New cards
What is the function of capillaries?
They transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen to cells in your organs and body systems.
16
New cards
Arteries structure
Have high pressure, small lumen, muscular/elastic wall
17
New cards
Veins structure
Big lumen, thin muscle wall
18
New cards
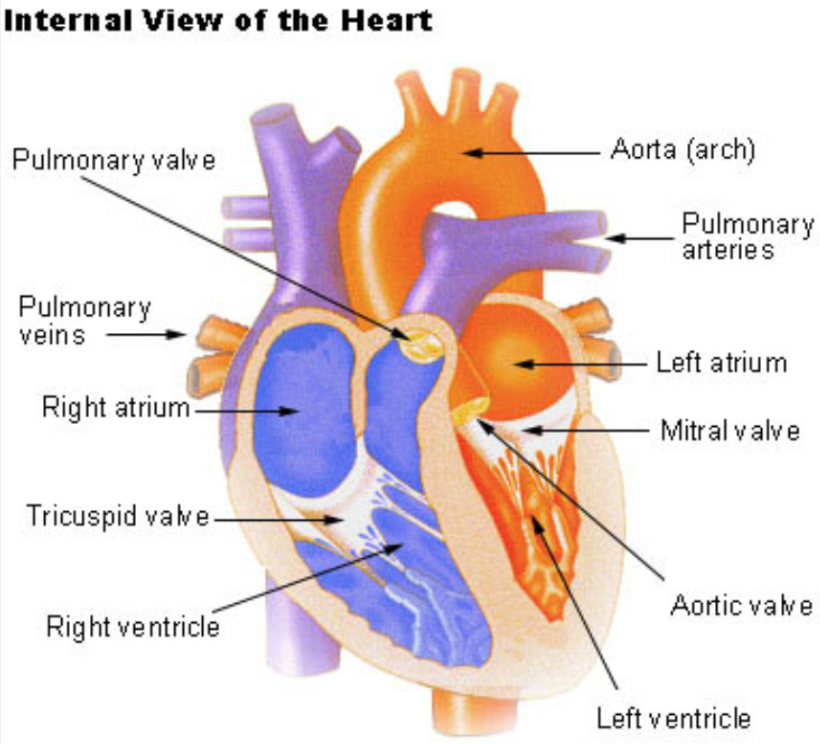
What does the structure of the heart look like?
You have two chambers on the top(atria) and two on the bottom (ventricles), one on each side of the heart. Right atrium: Two large veins deliver oxygen-poor blood to your right atrium. The superior vena cava carries blood from your upper body.
19
New cards
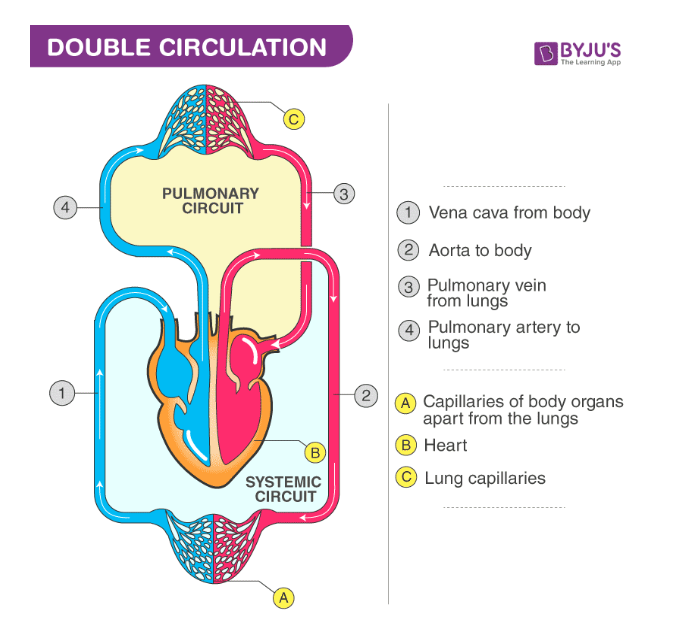
What is the double circulation system?
A mechanism in which blood circulates twice through the heart in one complete cycle is known as double circulation. Double circulation supports a strict separation of both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
The arteries (red) carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body's tissues. The veins (blue) take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
The arteries (red) carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body's tissues. The veins (blue) take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
20
New cards
What is the movement of blood through the heart?
Blood comes into right atrium from body, moves into right ventricle, pushed into pulmonary arteries in the lungs.
After picking up oxygen, blood travels back to the heart through pulmonary veins --> into left atrium, to left ventricle, and out to body's tissues through aorta.
After picking up oxygen, blood travels back to the heart through pulmonary veins --> into left atrium, to left ventricle, and out to body's tissues through aorta.
21
New cards
What is the shape and function of red blood cells?
Red blood cells are microscopic and have the shape of a flat disk or doughnut. Red blood cells don't have a nucleus like white blood cells, allowing them to change shape and move throughout your body easier. They carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our bodies.
22
New cards
What are the lungs made out of?
Trachea, ribcage, intercostal muscles, diaphragm, diaphragm muscles
23
New cards
Structure of lungs
Bronchi → bronchioles (smaller branches) → alveoli (little air sacs), shares a membrane with capillaries to deliver oxygen
24
New cards
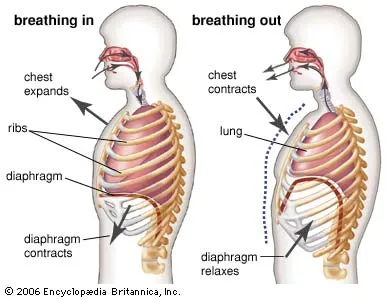
How does inhalation and exhalation work?
* Inhalation works by expanding the chest (ribcage) and the diaphragm contracts
* Exhalation works by contracting the chest and relaxing the diaphragm
* Exhalation works by contracting the chest and relaxing the diaphragm
25
New cards
How do the alveoli work\`?
The alveoli have a large surface area with good blood supply. Moist thin walls to allow diffusion, with millions capillaries sharing the wall.
26
New cards
What is diffusion?
The overall movement of particles of gas or liquid from an area of higher to lower concentration.
27
New cards
How does chemical respiration work?
Requires oxygen and glucose and releases energy as ATP, and that carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product.
28
New cards
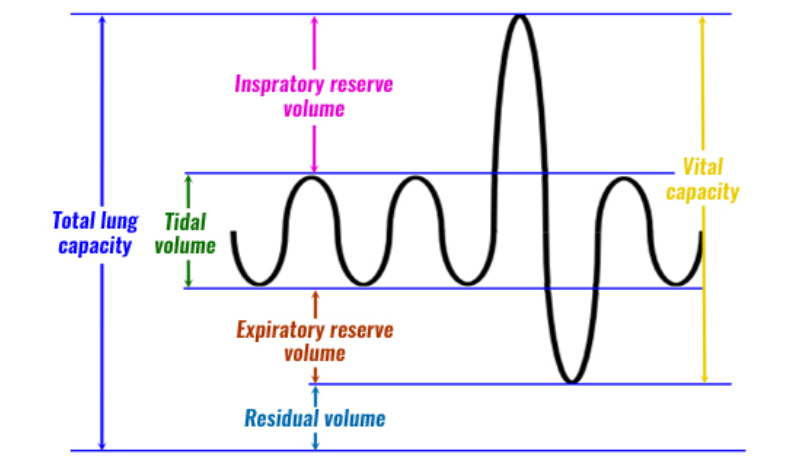
What is the tidal volume and vital capacity on a graph?
Green and yellow
29
New cards
What does the tidal volume mean?
Tidal volume is the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle
30
New cards
What does the vital capacity mean?
Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation.