Cognitive Development
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MBB2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is Cognitive Development?
How children/people think, learn, explore, remember, and solve problems
perception, attention, language, problem solving, reasoning, memory, conceptual understanding, and intelligence
Developmental themes:
Continuity & discontinuity
Nature & nurture
The active child
Universality & context specificity
Mechanisms of change
Theories of Cognitive Development
Theories of cognitive development
psychological frameworks that explain how our cognitive skills develop
Examples:
Piaget’s cognitive-developmental theory
Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory
Information processing theories
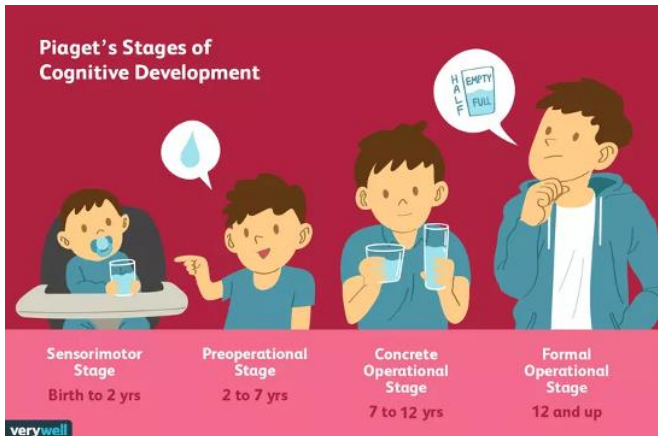
Piaget’s Theory
Four stages of cognitive development:
sensorimotor stage
preoperational stage
concrete operational stage
formal operational stage
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory
Individuals’ cognitive development is largely shaped by the social and cultural context.
1. Infants have basic cognitive skills (attention, sensation, perception, memory)
2. As infants interact with others, these skills become more sophisticated.
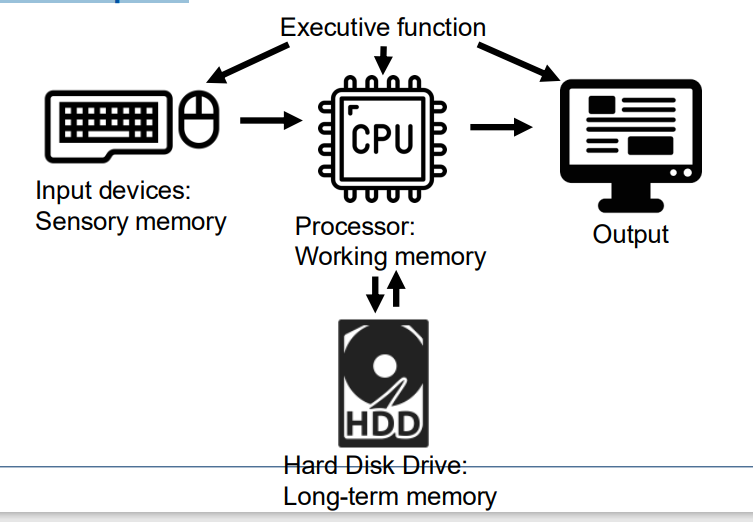
Information Processing Theories
Human mind is a complicated information-processing system like a computer
What is Intelligence?
The capacity to learn from experience and adapt to one’s environment.
It is a developmental concept
Intelligence means different things at different ages
The definition could vary in different contexts.
General Intelligence
A person possesses a certain amount of general intelligence (g), that influences their ability on all intellectual tasks
Multiple Theories of Intelligence
Intelligence can be measured as:
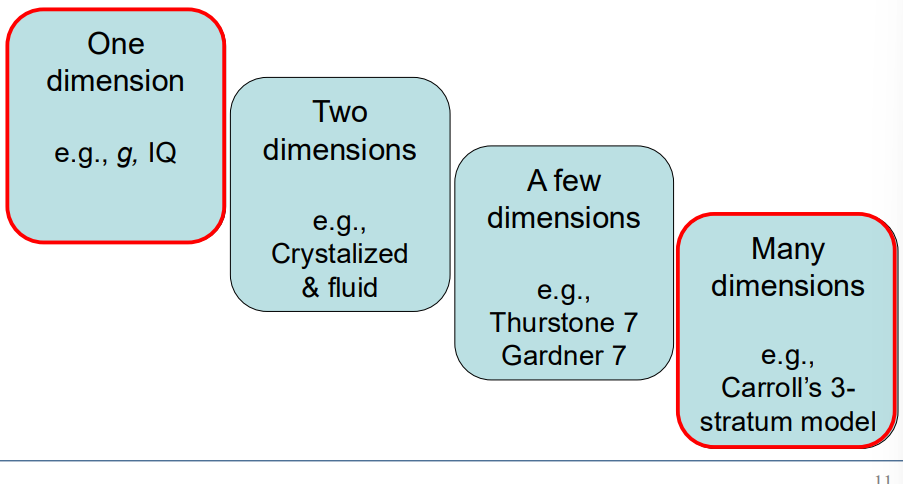
Intelligence as One Dimension: Mental Age/IQ
Mental Age (MA)
The average age at which children achieve a given score on Binet and Simon’s test
Intelligence Quotient (IQ):
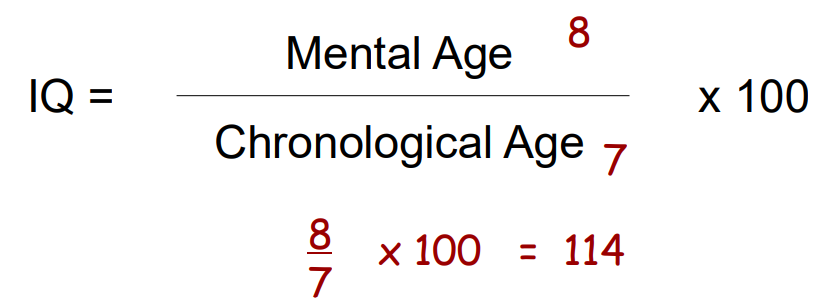
Intelligence as One Dimension: IQ
-
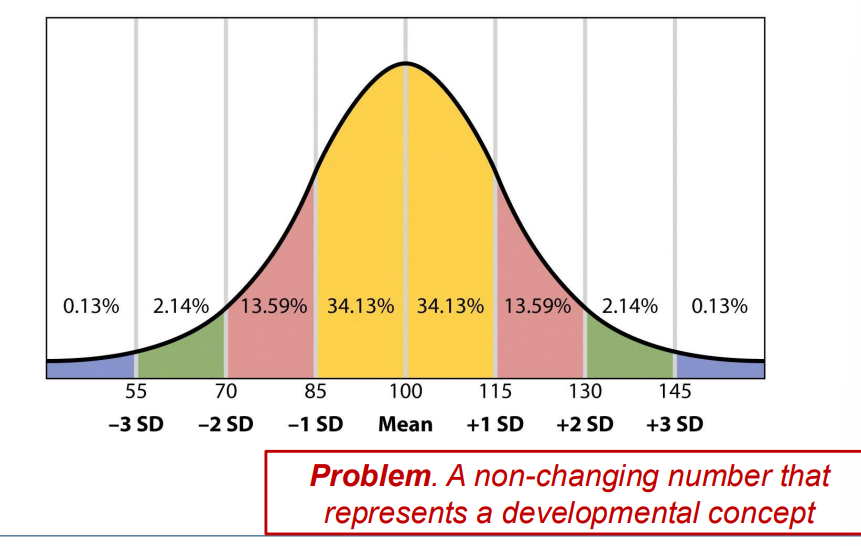
Intelligence as Many Processes
John Carroll proposed a: Three-stratum theory of intelligence
A hierarchical integration of:
g
eight generalized abilities
many specific processes
Intelligence as Many Processes
-
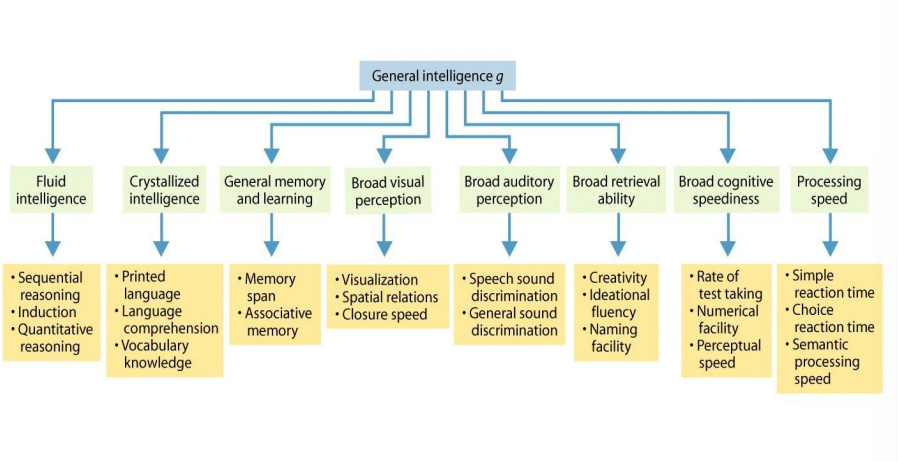
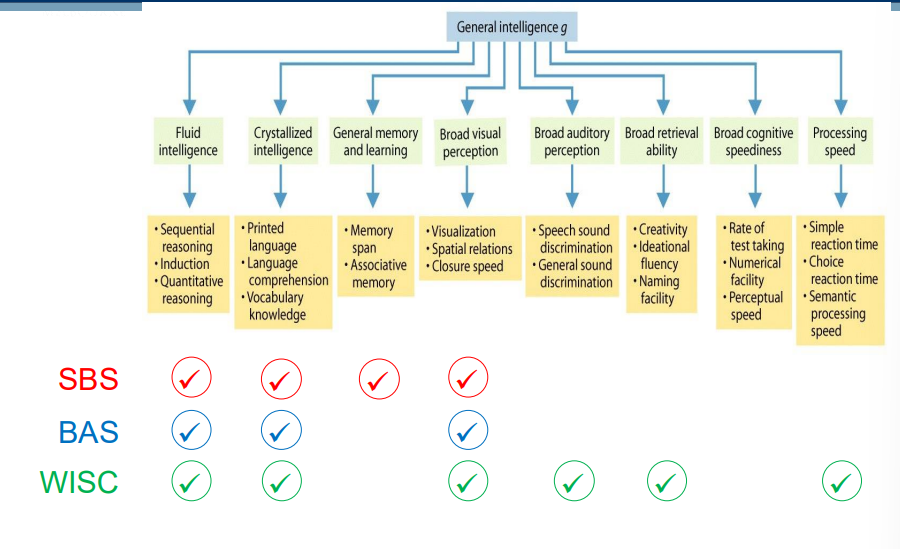
Stanford-Binet Scales
Five cognitive abilities:
Fluid reasoning
Knowledge
Quantitative reasoning
Visual-spatial processing
Working memory
Popular in U.S For ages 2 to 23 Uses MA to calculate IQ
British Ability Scale
Three domains:
Verbal ability
Non-verbal reasoning
Spatial ability
Popular in U.K For ages 3 to 17 Uses g
The WISC-R Intelligence Test
Wechsler Intelligence Test for Children (WISC)
The most widely used instrument for children 6+ years Two main sections:
Verbal: general knowledge, language skills
Performance: spatial & perceptual abilities
Uses MA to calculate IQ
The WISC-R Intelligence Test - Verbal Section:
Information: “What is the capital of France?”
Vocabulary: “What is a helicopter?”
Similarities: “How are a hammer and a chisel alike?”
Arithmetic: “If 4 friends divided 20 lollies equally, how many would each person get?”
Comprehension: “Why do we have prisons?”
Digit Span: “Repeat the following numbers in order when I have finished: 5, 3, 7, 4, 9.
The WISC-R Intelligence Test - Performance Section:
Block design: Arrange 9 blocks to match a picture.
Coding: Identifying patterns from series of simple shapes or numbers, each paired with a simple symbol.
Mazes: A set of increasingly difficult mazes printed in a response booklet. No pencil lifting or entering blind alleys.
Object assembly: Assemble puzzle parts to form a meaningful whole.
Picture completion: ‘What part of this picture is missing?”
Picture arrangement: Arrange cartoon frames to tell a coherent story
Issues of Measurement?
WISC scores differ among ethnic groups:
Average IQ of Euro-American children is higher than that of African-American children.
Does this indicate a cultural difference in intelligence?
NO
Examples of culturally insensitive questions:
“Who discovered America?”
“What should you do if you find someone’s wallet?”
The Koori IQ test demonstrates:
how value of knowledge is culturally constructed
what it is like to be assessed and graded on the basis of unfamiliar criteria
sensorimotor stage
the period (birth to 2 years) within Piaget's theory in which intelligence is expressed through sensory and motor abilities
preoperational stage
the period (2 to 7 years) within Piaget's theory in which children become able to represent their experiences in language, mental imagery, and symbolic thought
concrete operational stage
the period (7 to 12 years) within Piaget's theory in which children become able to reason logically about concrete objects and events
formal operational stage
the period (12 years and beyond) within Piaget's theory in which people become able to think about abstractions and hypothetical situations