Topic 4: DNA Mutation & Repair
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Does genome sequence change over time? How and Why?
Yes there are changes due to errors in DNA replication and DNA is susceptible to chemical attack
Low rate of mutations required for evolution where natural selection favors mutations that produce advantageous phenotypes
How many mutations per generation do humans get?
Around 60 mutations per generation out of 3 billion bp (10-8 error rate)
RNA viruses have error rates as high as 10-4 bp/generation, as RNA pol does not have proofreading and mutation rate is beneficial
How are mutations inherited in multiple generations? When are they not mutated?
Germline → inherited
Somatic (like cancer) → not inherited
What are the sizes of mutations? How do they change phenotype? What are the effects of mutations?
Mutations can be:
small (gene level) or large (chromosomal)
Altered gene sequence → possible amino acid change → change in phenotype
The effect on phenotype can be:
harmless/neutral, harmful/deleterious, beneficial/advantageous (most rare)
What are loss-of-function (LOF) genes?
Reduced gene function (partial/complete) relative to WT and are recessive (no mRNA produced)
What are gain-of-function (GOF) genes?
Enhanced gene function relative to WT and are dominant alleles (more mRNA produced)
Where can mutations be located?
Within a gene (open reading frame/promoter) or distant (enhancers)
What is the difference between essential and non-essential genes?
Essential gene mutations: result in death
Non-essential gene mutations: reduced fitness or no effect
What happens when entire genes are duplicated?
Double the mRNA leads initially to GOF, but may lead to new proteins with different functions
What is a transition?
Purine → purine
Pyrimidine → pyrimidine
What is a transversion?
Pyrimidine → purine
Purine → pyrimidine
What is more common, transversion or transition?
Transitions are, even though there is more possibilities for transversions
bases are similar in size so polymerase can more easily exchange the base in its active site
What has less severe effects, transitions or transversions?
Transitions on average due to lower probability of amino acid substitution because of the degeneracy in the genetic code
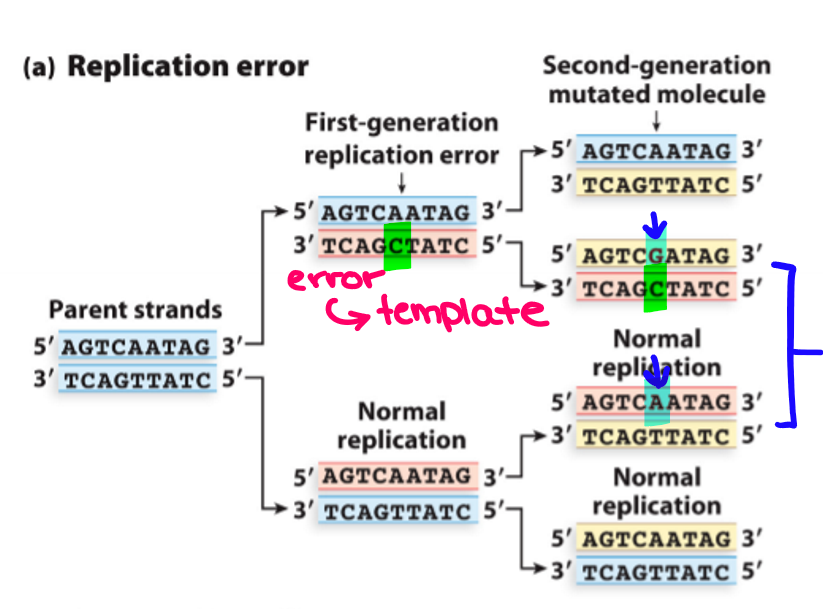
What are the two steps for replication error?
1) An incorrect nucleotide is incorporated into daughter strand by DNA pol during DNA replication
2) Mismatched base is not repaired and after the next round of replication, ¼ daughter cells inherit the mutation
What are the two steps for mutagen-induced damaged base?
1) The damaged base on one of the parental strands by a mutagen causes mispairing after the first round of replication which is not repaired
2) Second round of DNA replication results in propagation of the damaged base and half of daughter cells inheriting the mutation
**pol guesses what base was
What is a missense mutation?
Nonsynonymous: codon change causes change in amino acid
What is a nonsense mutation?
Premature stop: sense codon changes to stop codon (truncated polypeptide)
What is a silent mutation?
Synonymous: codon change does not change amino acid
What is a frameshift mutation?
Caused by indels (insertions and deletion mutations) ranging from 1-1000 bp that usually alter reading frame
What is the size of small and large indels?
Small indels <50 bp
Large indels >50 bp (structural varients)
What is the frequency of stop codons in a random sequence? How does this aid in frameshift mutations making truncated proteins?
1 in 20 codons
transcription keeps occurring until STOP codon, even if in wrong reading frame
When do indels not cause a frameshift mutation?
When they are in multiples of 3
What is sickle cell anemia? What kind of mutation is it?
Missense mutation; RBC: deficiency in oxygen exchange, clog arteries, circulatory problems, higher risk of heart attack and stroke, lower life expectancy
Substitution mutation in beta hemoglobin gene causes 6th amino acid change from glutamic acid to valine
First-approved Crispr-based treatment: edits genome of hemopoietic stem cells to produce functional beta hemoglobin and then infused back into patient (1 gene to edit unlike cancer)
What does template slippage refer to and when does it occur?
In chromosomal regions of short direct repeats (1-4 bps), DNA pol will sometimes pause and temporarily dissociate from the template strand
When DNA pol reassociates with the template strand, it may be one or two repeats ahead or behind its original position, causing spontaneous indel mutations
What if the slippage looping occurs in the daughter strand (upstream)?
Insertion
What if the slippage looping occurs in the template strand (downstream)?
Deletion
How does slippage lead to late-onset neurodegenerative diseases and severity?
Huntington’s and others are associated with amino acid repeat expansion in certain proteins after multiple rounds of DNA replication
Number of repeats = severity
What do glutamine (Q) repeats cause?
Toxic aggregates in the nucleus of neurons
What does aberrant recombination cause?
Regions of intra and extra chromosomal changes
What has more severe effects on phenotype, chromosomal mutations or point mutations/indels?
Chromosomal mutations because expression of more genes are affected
What is deletion, duplication, inversion, insertion and translocation in large-scale chromosomal mutations?
Deletions: loss of genes
Duplications: increasing dosage of genes (2x mRNA)
Inversion: reversing orientation of a segment of the chromosome
Insertion: genes from one chromosome transferred to another
Translocation: interchange of genetic parts from non-homologous chromosomes
What are genes at the junction of intrachromosomal fragments affected by?
Fusion of two different genes creating a hybrid protein with abnormal activity or altered regulation of gene expression by replacement of the native promoter with a promoter from a different gene/chromosome
What are spontaneous mutations?
Naturally occurring mutations caused mainly by replication errors and spontaneous lesions like depurination and deamination by hydrolysis (low frequency)
What are induced mutations?
Natural (environmental) or artificial mutagen that causes mutations at a high rate
How do mutagens induce mutations?
Replace or alter a base so it mispairs with another base or damage a base where it can no longer pair with any base
What are base analogs?
Mimics bases and incorporates into DNA (can cause mispairing during replication)
What do chemicals cause?
Alter base structure to cause mispairing (alkylating - benzopyrene and intercalating agents - doxorubicin)
Describe deamination of bases by spontaneous hydrolysis
Water molecules → reactive OH-
deaminates cytosine, adenine and guanine
Most common: cytosine → uracil (C-G to A-T)
Adenine → hypoxanthine; guanine → xanthine both base pair with cytosine
Methylated cytosine (5-meC; 5% of cytosines) → thymine (5-meC-G to T-G)
5meC is found in eukaryotic promoters and plays a role in repression of gene expression, so deamination could alter gene regulation
Describe depurination of bases by spontaneous hydrolysis
spontaneous hydrolytic reaction cleaves glycosidic bond between nitrogenous base and deoxyribose
creates abasic (AP) site = base is missing along backbone
depurination occurs more than depyrimidination
if not repaired problems arise:
stalling DNA replication as DNA pol does not recognize AP site as dNMP
incorporation of incorrect dNTP during repair by error-prone pols
weakened DNA backbone via spontaneous opening of deoxyribose ring → potential strand breaks
Describe oxidative damage of bases
Cellular respiration and ionizing radiation → reactive oxygen species (ROS)
oxidize and damage all four bases
ROS can oxidize thymine → thymine glycol (distorts the double helix and inhibits DNA replication)
Guanine oxidized to 8-oxoguanine (base pairs with adenine during DNA replication, G-C to T-A transversion mutations - the most common mutation in human cancers)
Describe damage of bases by alkylating chemicals
alkyl groups (methyl, ethyl) are transferred to reactive sites of bases and to the phosphates in the DNA backbone creating adducts (addition of bulky groups)
N3 of adenine and O6 of guanine highly susceptible to alkylation
What does O6-methylguanine mispair with?
Thymine, changing the G-C base pair to A-T base pair after replication
What are examples of alkylating chemicals
Nitrosamines and the mutagens N-methyl-N1-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS) which are used for mutagenesis screens
What does benzopyrene convert to?
an active epoxide form that alkylates purines such as N6 of adenine or N2 of guanine to form bulky guanine adducts that can cause base mispairing
What does nitrogen mustard gas do?
alkylates adjacent guanines to form interbase crosslinks that prevent strand separation which blocks replication and transcription
How was cigarette smoke linked to lung cancer?
p53 encodes a tumor suppression gene and a mutated p53 is found in 50% of all cancers and 70% of lung cancers
mutational hotspot codons (157, 248, 273) in p53 gene are often G to A transversions in lung tumors
codon 157 mutations in p53 gene specific to lung cancer
Benzopyrene is component of cigarette smoke and known carcinogen
Treat Hela cells with benzopyrene → isolate DNA and sequence → guanine adducts at same mutational hotspots in p53 gene
benzopyrene binds p53 at signature hotspot in normal lung cells and causes lung cancer through LOF mutations in p53
How many potential chemical modifications can occur on a single base at the same time?
Multiple can occur simultaneously which are often highly mutagenic
guanine = alkylation, deamination, oxidation
How can UV damage pyrimidine bases?
UV light (260 nm) is strongly absorbed by nucleotide bases
excitation energy from UV causes DNA damage by formation of cyclobutane ring (C5-C6 link) of adjacent pyrimidines (pyrimidine dimers: T-T, T-C, C-T, C-C)
Also induce a 6-4 photoproduct that links C6 and C4 of adjacent pyrimidines
pyrimidine dimers → bend/kink in DNA → prevent base pairing and stops replication because DNA pols cannot read past dimers
What causes fork collapse?
ionizing radiation → ROS and cosmic rays → phosphodiester bond breaks, nicks and DSBs
ROS reaction with deoxyribose
high energy particles of cosmic rays hit DNA
during DNA replication, nicks in DNA will cause fork to collapse leading to disassembly of replisome and a DSB
if unrepaired → truncated chromosomes
What are cancer therapeutics?
DNA damaging agents
break chromosomes and stall replication forks that overwhelm DNA repair machinery so that cancer cells divide with damaged/unreplicated DNA and die
What are the cells that take the least and most damage from cancer treatment
Least: most somatic cells that are non/slow-dividing
Most: actively dividing cells; hair follicle cells, blood cells, intestinal tract cells (hair loss, immunity loss, nausea)
What is Cisplatin?
Alkylating agent that forms crosslinks between N7 of two guanines preventing repair and collapse of replication fork (bone, lung, blood, ovarian cancer)
What is Bleomycin?
Binds iron atoms and activates O2 to form hydroxyl radicals (Hodgkin lymphoma and testicular cancer)
What is Doxorubicin?
Intercalates between bases causing DSBs by preventing topo II from resealing the breaks (leukemias, ovarian and breast cancers)
What are the issues with cancer therapeutics?
Cytotoxity, increased chance of getting cancer again since genomes of normal cells are mutated, treatment may not work
What are next generation cancer therapeutics trying to use?
Cancer genomes to design more effective treatment to precisely target cancer cells (immunotherapy)
Why do cells need to detect and repair all types of lesions(base mispairing, damaged bases, AP sites and DSBs)? How?
To maintain genome integrity by multiple DNA repair pathways with specialized enzymes
What does mismatch repair (MMR) in E. coli repair?
Pol III replication errors not corrected by proofreading or small loops of up to 4 bp of unpaired nt from slippage or recombination
How does MMR differentiate the template and daughter strand, since the mismatch bases are not damaged?
N6 of adenine of 5’ GATC 3’ is methylated by Dam methylase on the template strand
5’GATC3’ sites on newly synthesized daughter strand is not methylated
What first recognizes a mismatch in MMR?
MutS and MutL recognize mismatch and scans bidirectionally to an adjacent hemimethylated 5’GATC3’
What happens when MutS-MutL complex reaches the adjacent 5’GATC3’ site?
Recruits and activates MutH endonuclease that cuts/nicks the unmethylated daughter strand
What occurs after the unmethylated strand is nicked in MMR?
MutS-MutL recruits UvrD helicase which unwinds the daughter strand towards the mismatch site
What happens once UvrD helicase unwinds daughter strand? How does location of cleaved 5’GATC3’ affect it?
If 5’GATC3’ to mismatch is 3’ → 5’ = ExoI/ExoX 3’-5’ exonuclease will degrade displaced daughter strand
If 5’GATC3’ to mismatch is 5’ → 3’ = RecJ/ExoVII 5’-3’ will degrade displaced daughter strand
__stabilizes the single-stranded template strand while __ fills the gap in the daughter strand and is sealed by_
SSB protein, DNA pol III, ligase
How is MMR different in eukaryotes than prokaryotes? What is the equivalent to MutS/MutL?
Similar, but discrimination between template and daughter strand is unknown
repair may involve PCNA
MutS-MutL = Msh2/Msh6
Loss of MMR = susceptibility to hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
What does the direct repair pathway fix? How?
Through photoactivation, DNA photolyase uses energy of visible light to repair pyrimidine dimers in one step
What does photolyase contain (DRP)
Two chromophores
Describe the movement of an electron in DRP
Antenna chromophore in DNA photolyase absorbs light and passes the electron to FADH
FADH then transfers electron to pyrimidine dimer which reverses the cross links
Electron is then transferred back to FADH (regenerating photolyase activity)
Is photolyase found in all cells?
Yes, prokaryotic and almost all eukaryotic cells (except mammalian placenta cells)
How is O6-methylguanine restored?
DRP
O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase removes the methyl group
Methyl group is transferred to a cysteine residue in the enzyme leading to its degradation