Chapter 23, Lesson 4: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 23, Lesson 4 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Reabsorbs about 65% of glomerular filtrate, removes substances from blood and secretes them into tubular fluid
Mostly for absorption with long length, microvilli, and mitochondria (6% of resting ATP)
Tubular reabsorption
The process of reclaiming water and solutes from tubular fluid and returning them to blood; has a transcellular and paracellular route
Transcellular route
Passing substances through the cytoplasm of PCT epithelial cells and out their base
Paracellular route
Passing substances between PCT cells
Solvent drag
The carrying of a variety of dissolved substances as water passes through the paracellular route
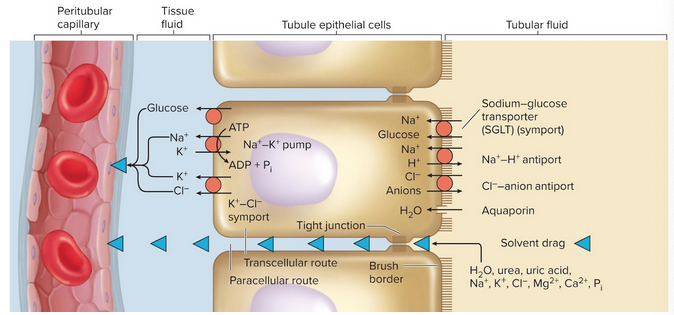
Sodium-glucose transporters (SGLTs)
Transporters of glucose using facilitated diffusion; normally all glucose is absorbed with none in the urine
Nitrogenous waste absorption
Urea passes through with water; about half is reabsorbed to safe levels
PCT reabsorbs nearly all uric acid, later portions secrete it
Creatinine is passed in urine
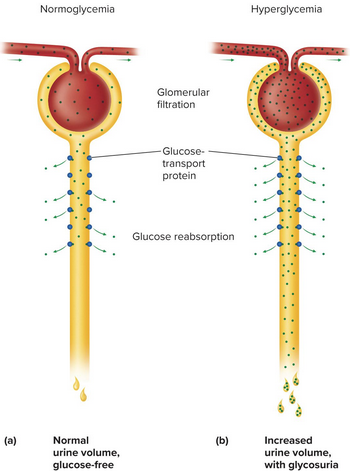
Transport maximum
The maximum rate of reabsorption for a solute, which is reached when all transport proteins are saturated—any excess appears in urine
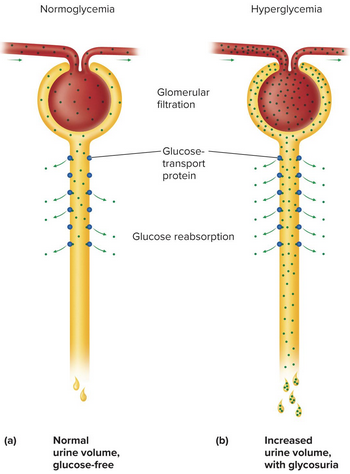
Glycosuria
Glucose in urine as a result of blood glucose over 220 mg/dL, a sign of untreated diabetes mellitus
Tubular secretion
Process where the renal tubule extracts chemicals from capillary blood and secretes them into tubular fluid; aiding acid-base balance, waste removal, and drug clearance
Nephron loop
Urinary organ that functions to generate osmotic gradients to enable urine concentration, water conservation by collecting duct
Principal cells
The most abundant cell in the DCT, sensing aldosterone, natriuretic peptides, antidiuretic hormone, parathyroid hormone for salt and water balance
Aldosterone
Steroid hormone that simulates sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion; secreted by the adrenal cortex for use in ascending nephron loop, DCT, cortical portion of collecting duct to maintain blood volume and pressure
aldos = salt retaining
Natriuretic peptides
Peptides secreted by the heart in response to hypertension, resulting in more salt and water excretion to reduce blood volume and pressure
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Stimulates water retention by the kidney, caused by dehydration, loss of blood volume, rising blood osmolarity for a more water permeable collecting duct
Aquaporins
Water channels for transcellular absorption through osmosis
Obligatory water reabsorption
Reabsorbing water independent of hormones in the PCT at a constant rate
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Secreted from parathyroid glands in response to hypocalcemia to increase calcium reabsorption