Plant Body + Development
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
2 celled stage
establishes polarity of plant (micropylar and chalazal poles)
Chalazal Pole
contains apical cell, develops into embryo
Micropylar Pole
contains basal cell (that produces stalk like suspensor)
3-celled stage
further establish poles
Globular stage
tissue differentiation into protoderm, ground meristem, procambium; suspensor is 2 cells, initiation of protoderm
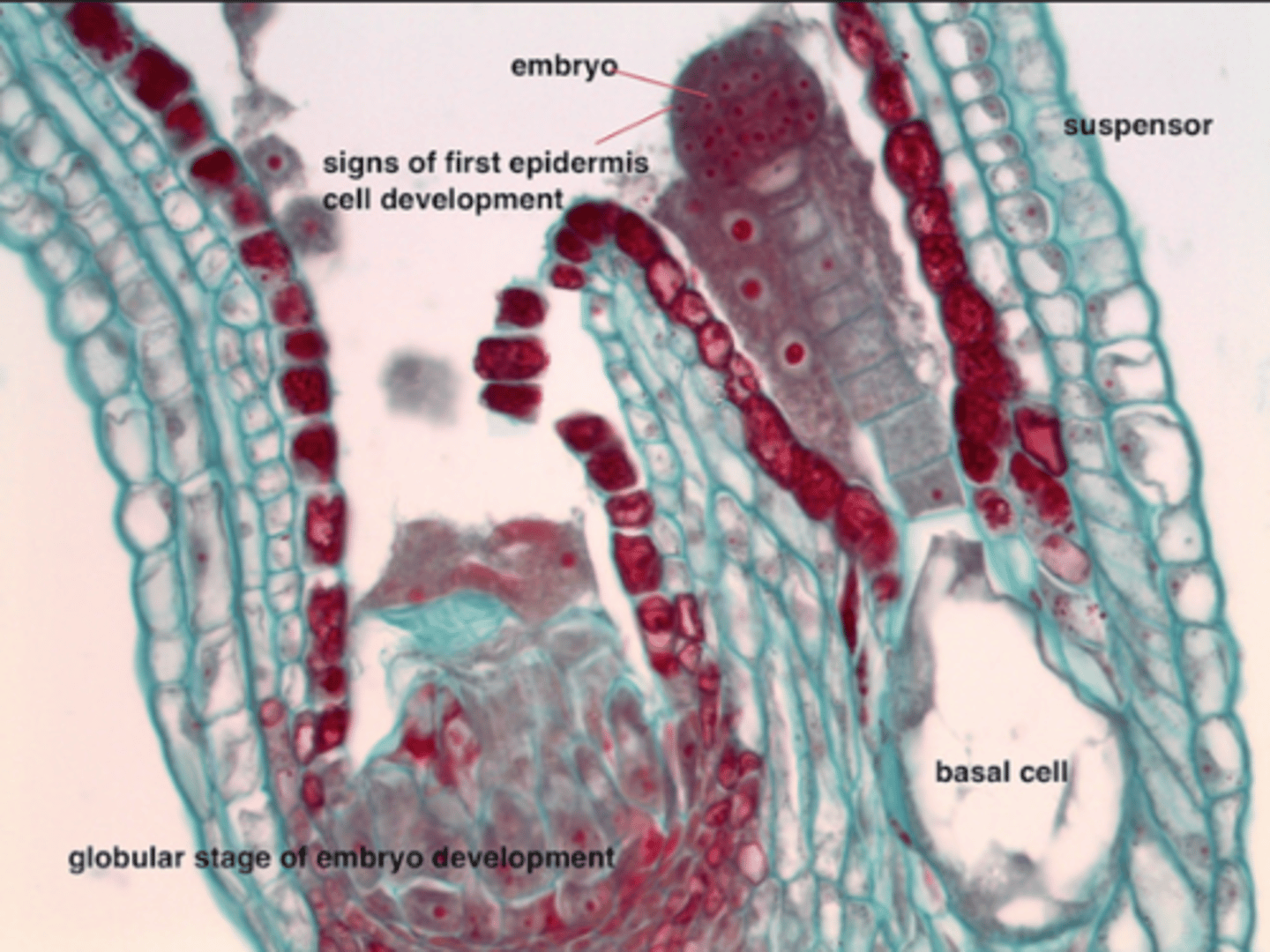
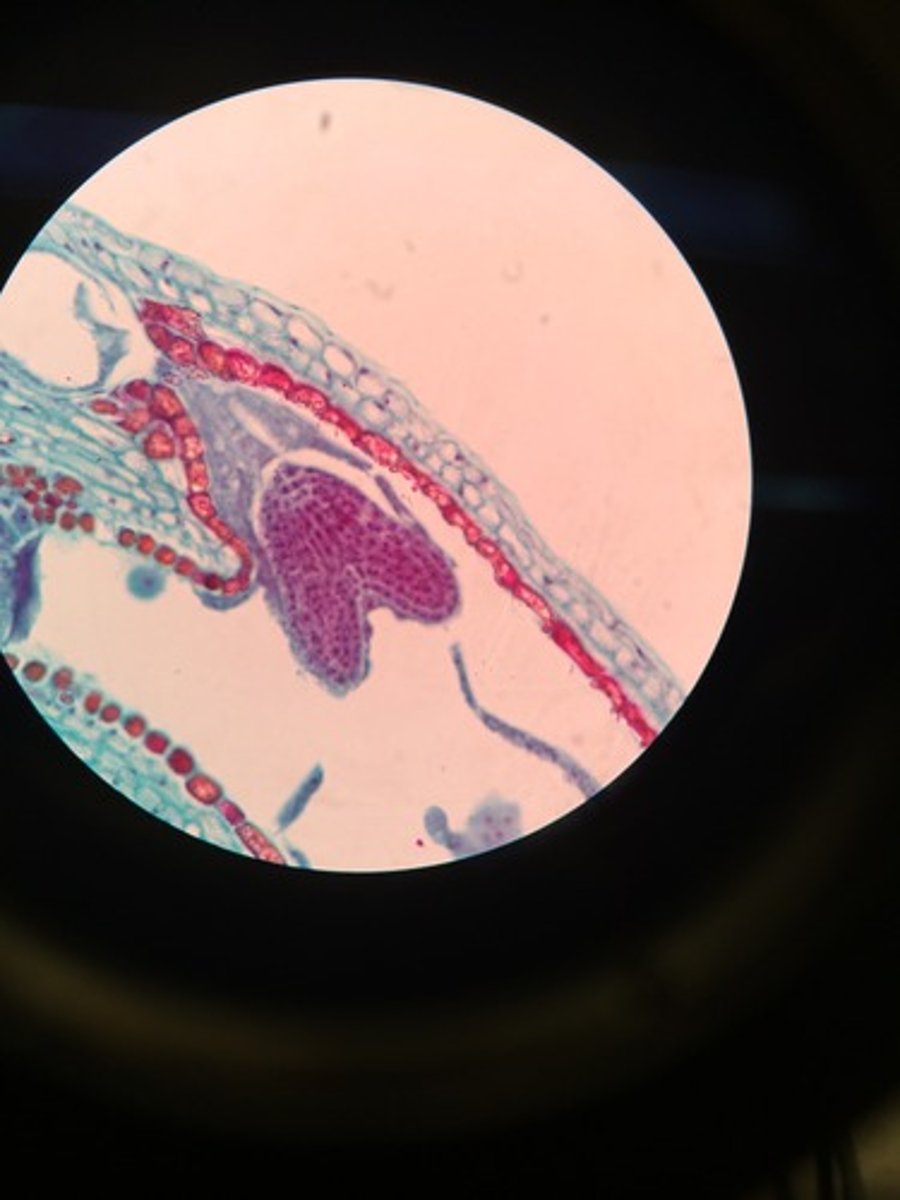
Heart stage
development of cotyledons
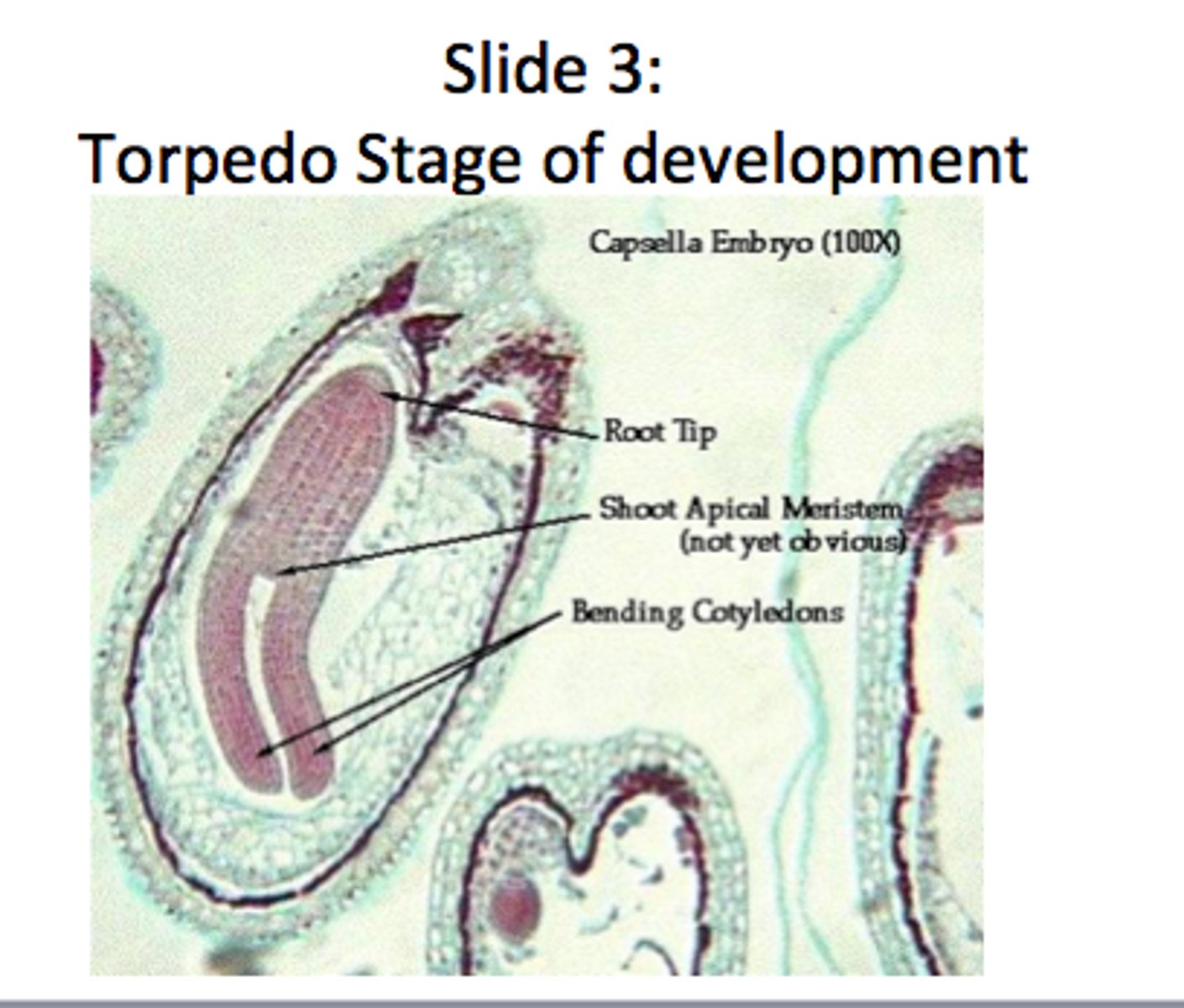
Torpedo stage
development of root/shoot axis; suspensors die
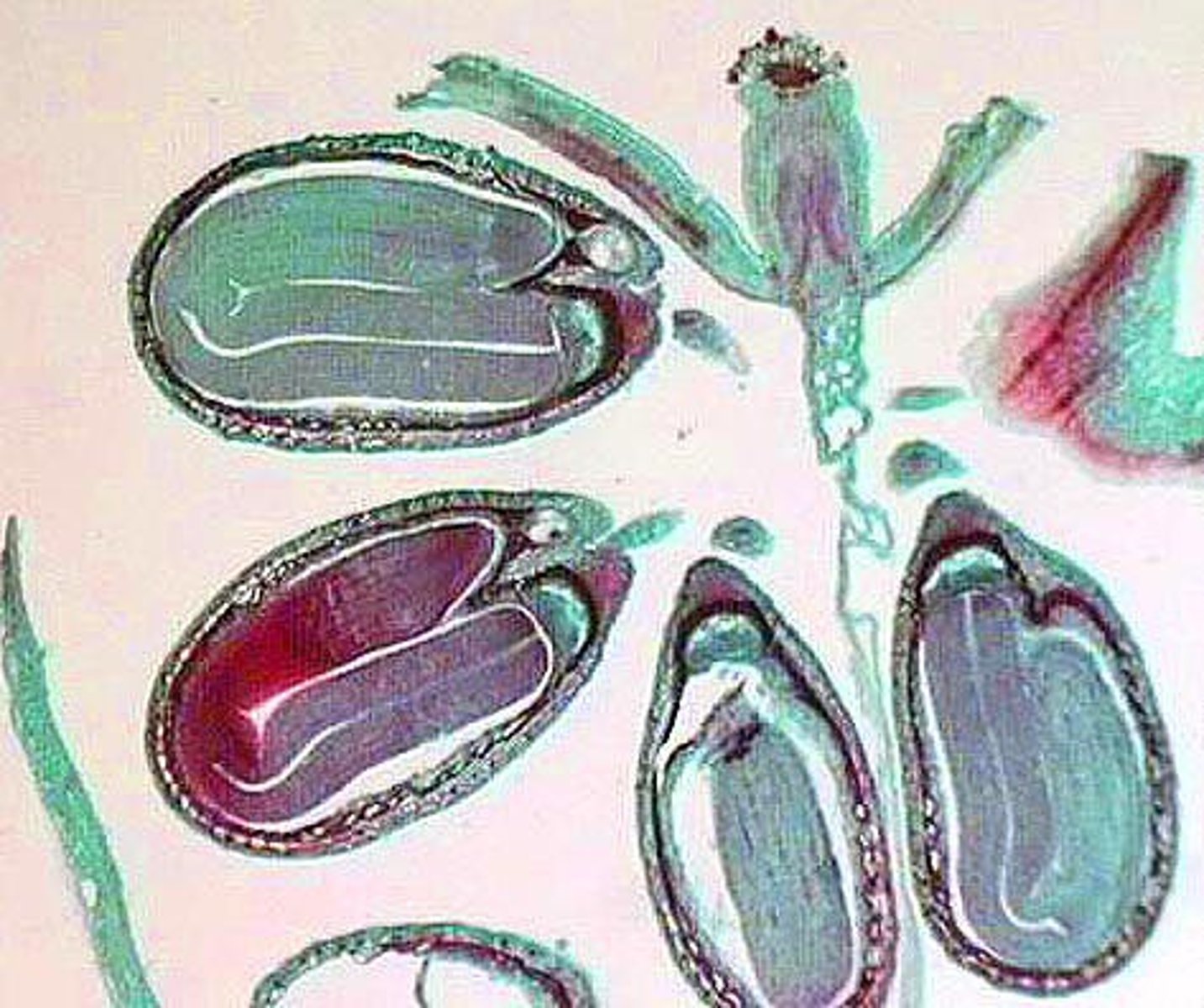
Mature embryo
two cotyledons obvious, developed hypocotyl-root axis
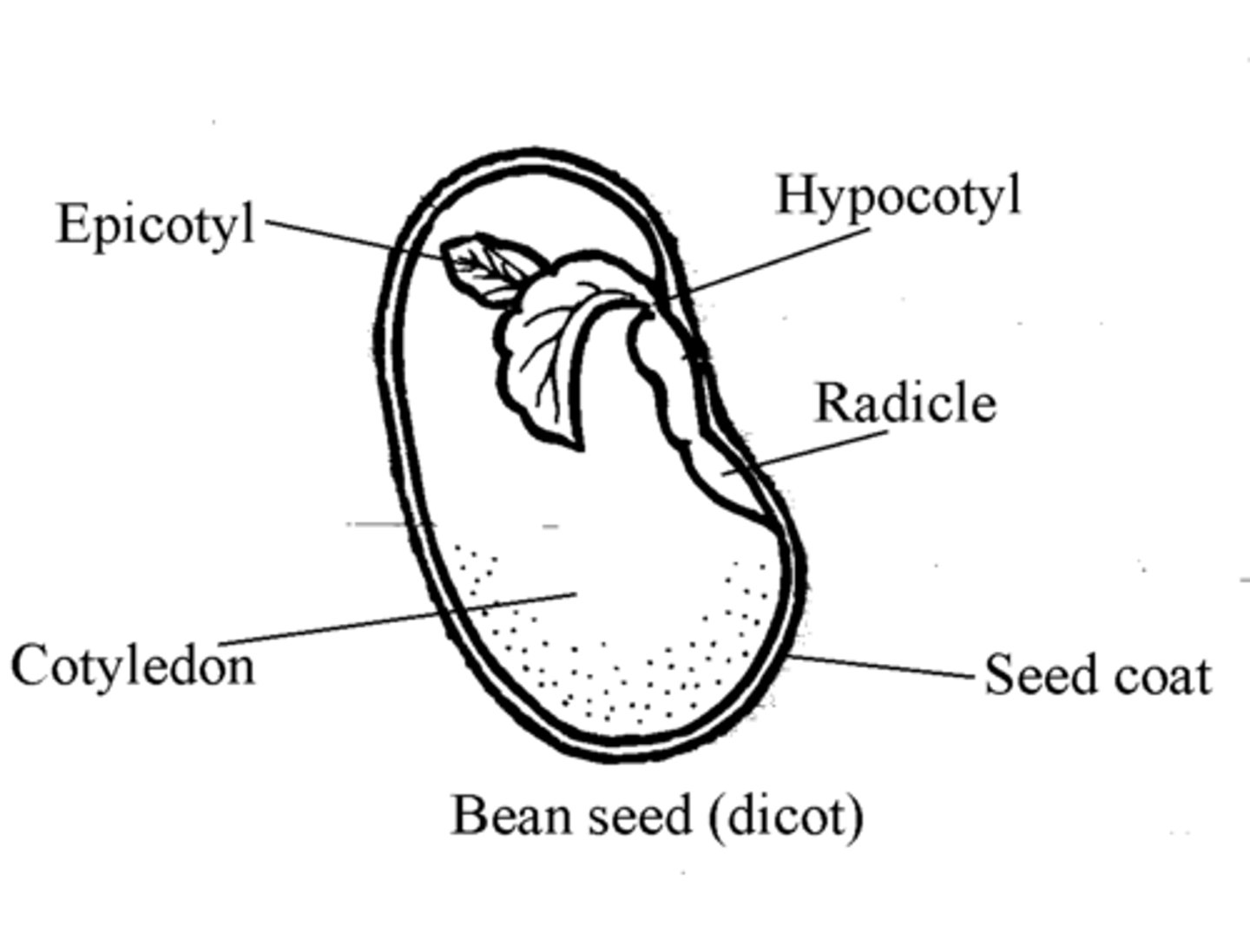
Plumule
embryo shoot; first foliage leaves
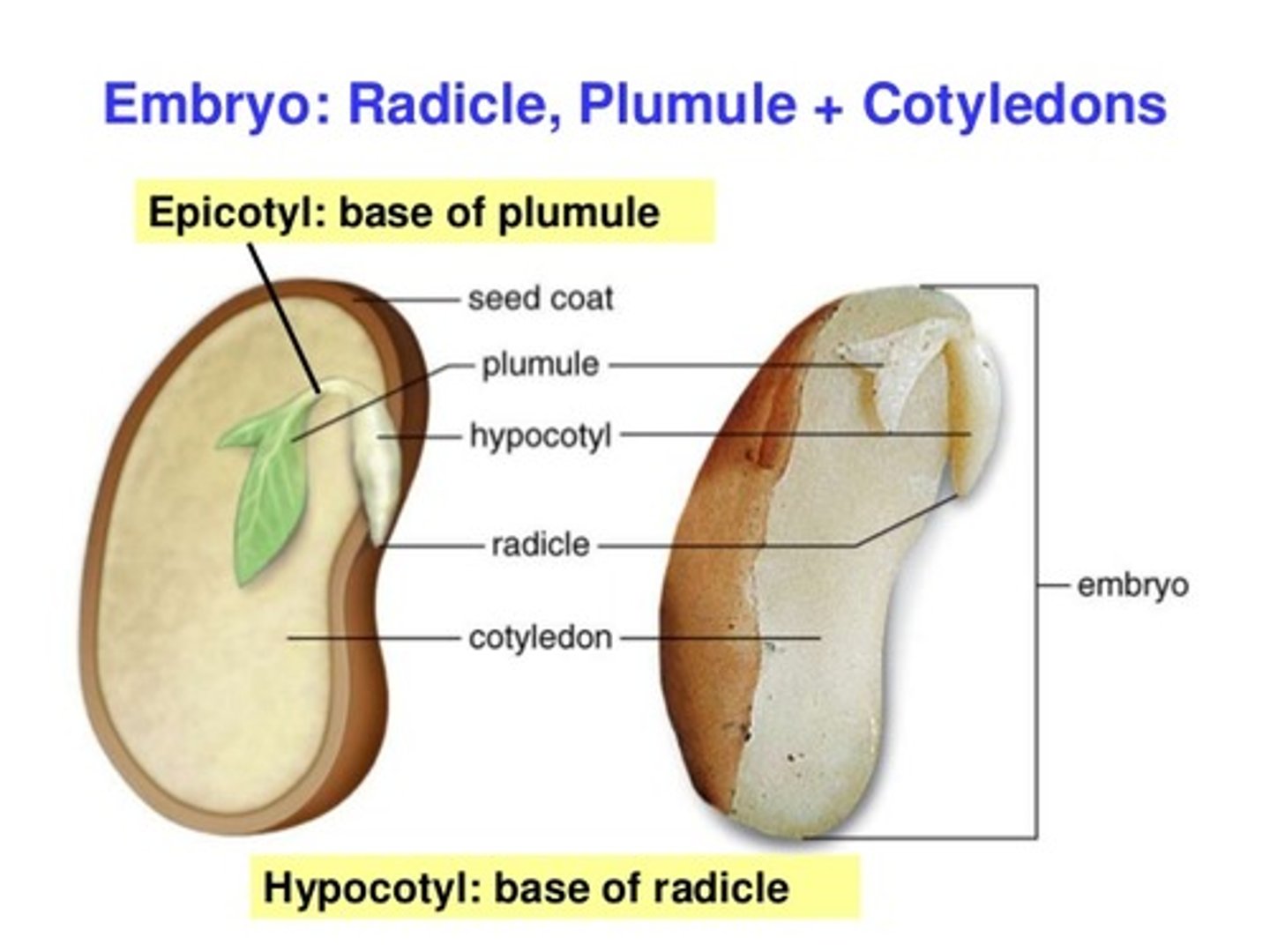
Epicotyl
region of stem above cotyledons and below plumule
Hilum
scar in seed coat where funiculus was attached to seed
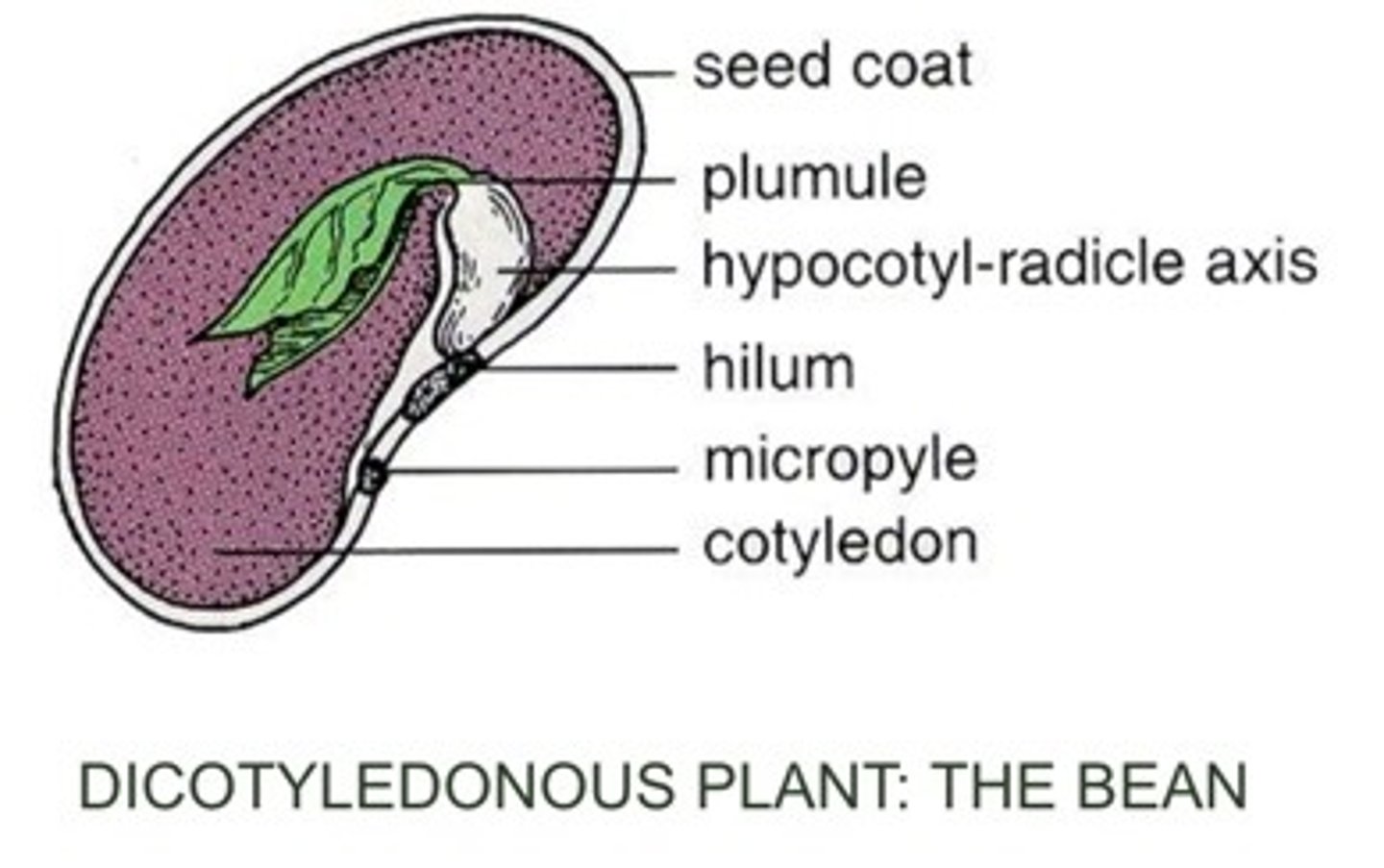
Micropylar scar
small opening in seed coat where micropyle was
Coleoptile
Covers and protects the shoot as it grows upward (monocots)
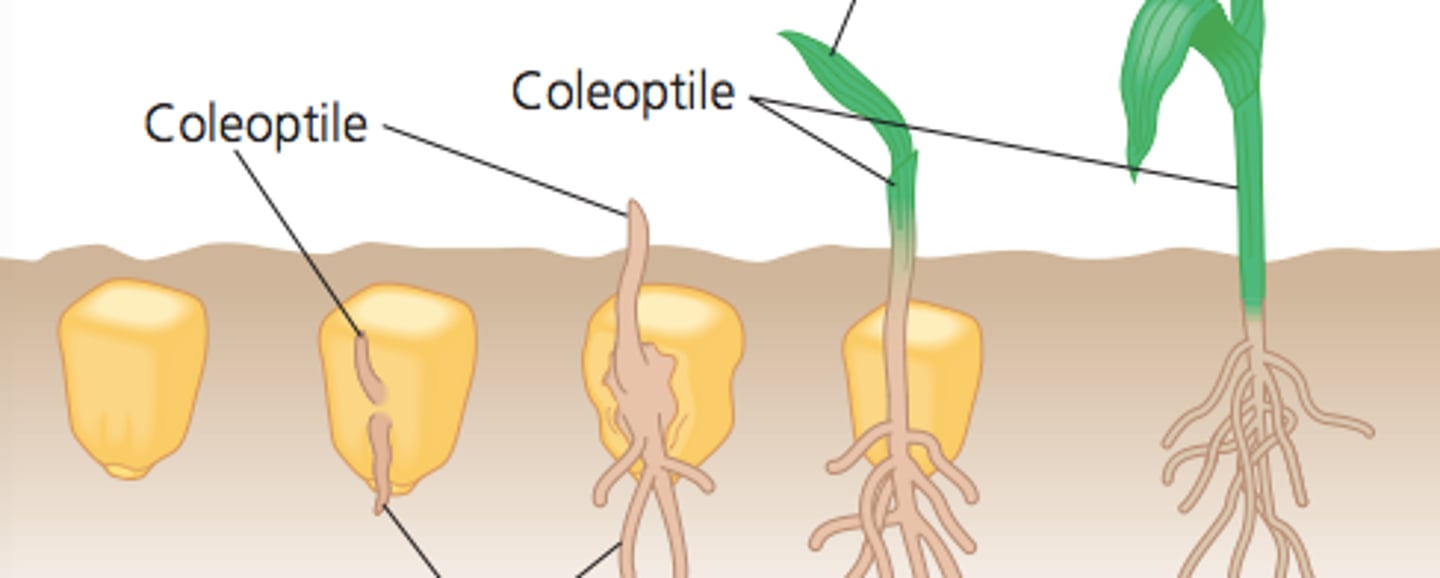
Coleorhiza
protective covering over root (monocots)
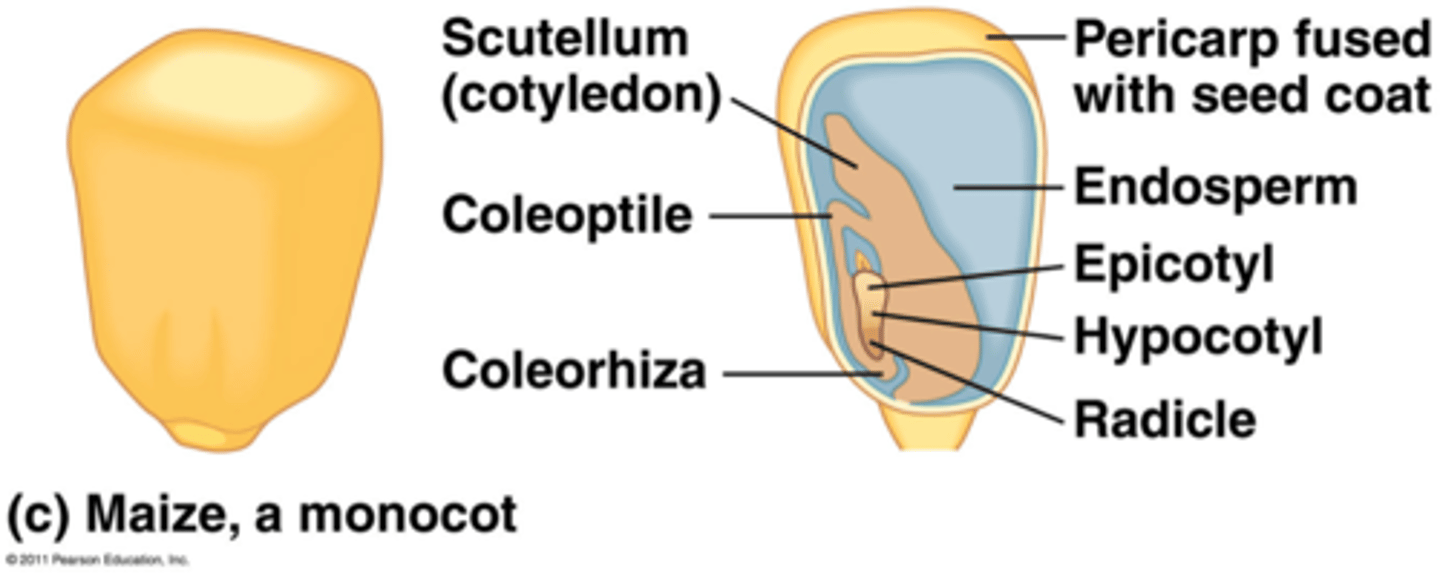
Scutellum
single cotyledon of monocot
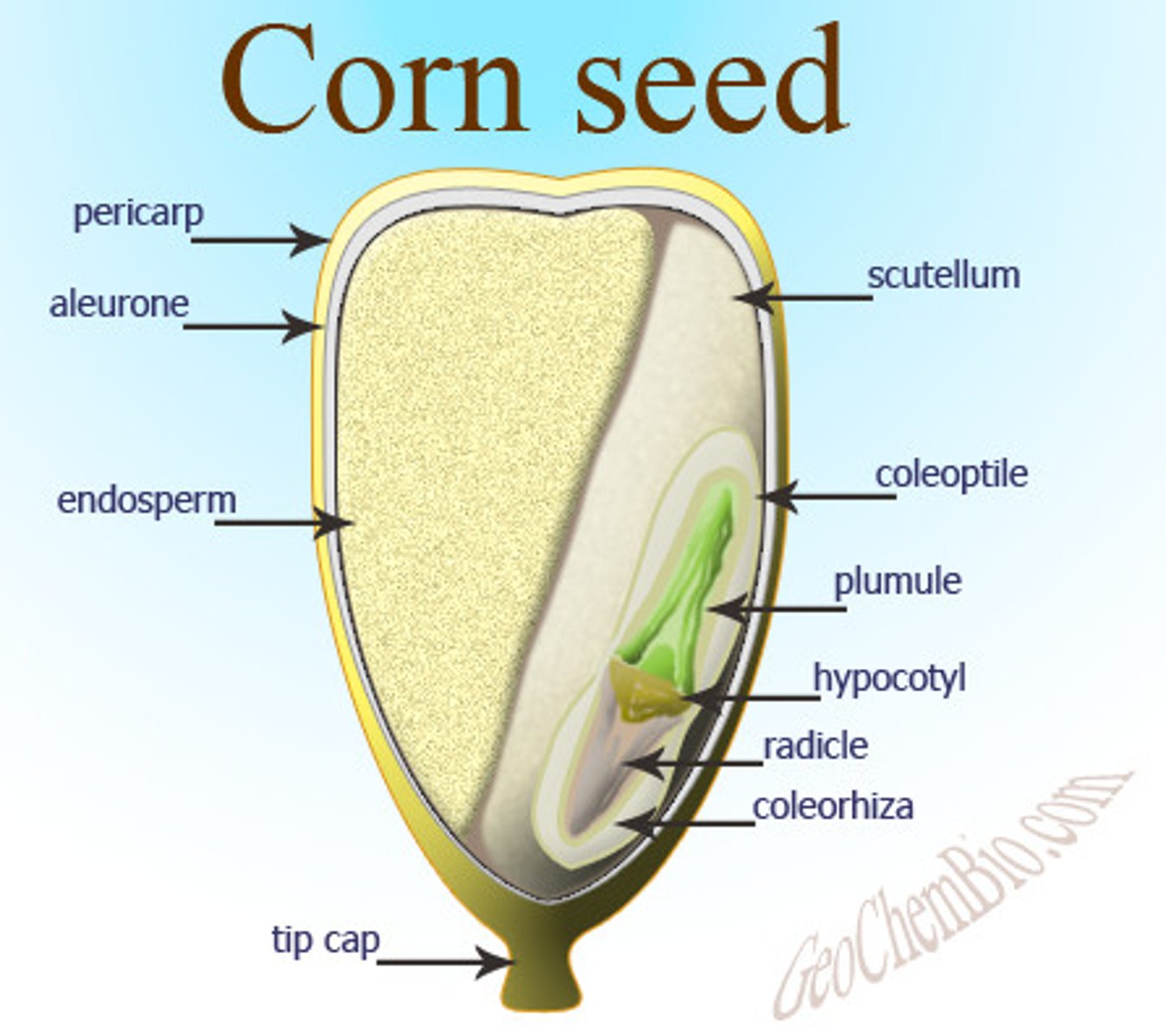
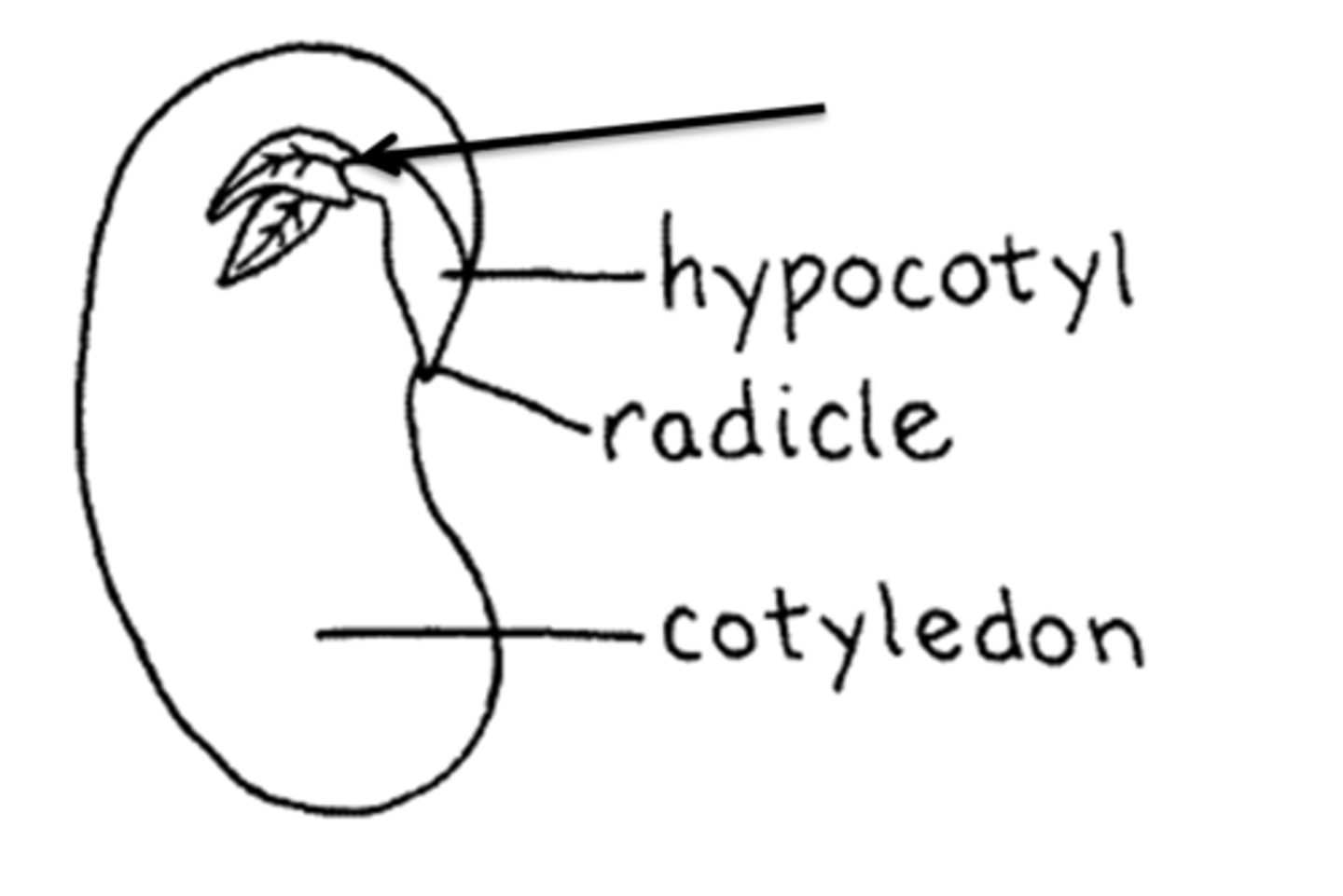
Radicle
embryonic root
Stratification
seed subjected to periods of cold/heat to break dormancy
Scarification
breaking or softening a seed coat to allow absorption of moisture
Imbibition
Absorption of water, activating enzymes