Lab 6 & 7: Appendicular Skeleton
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
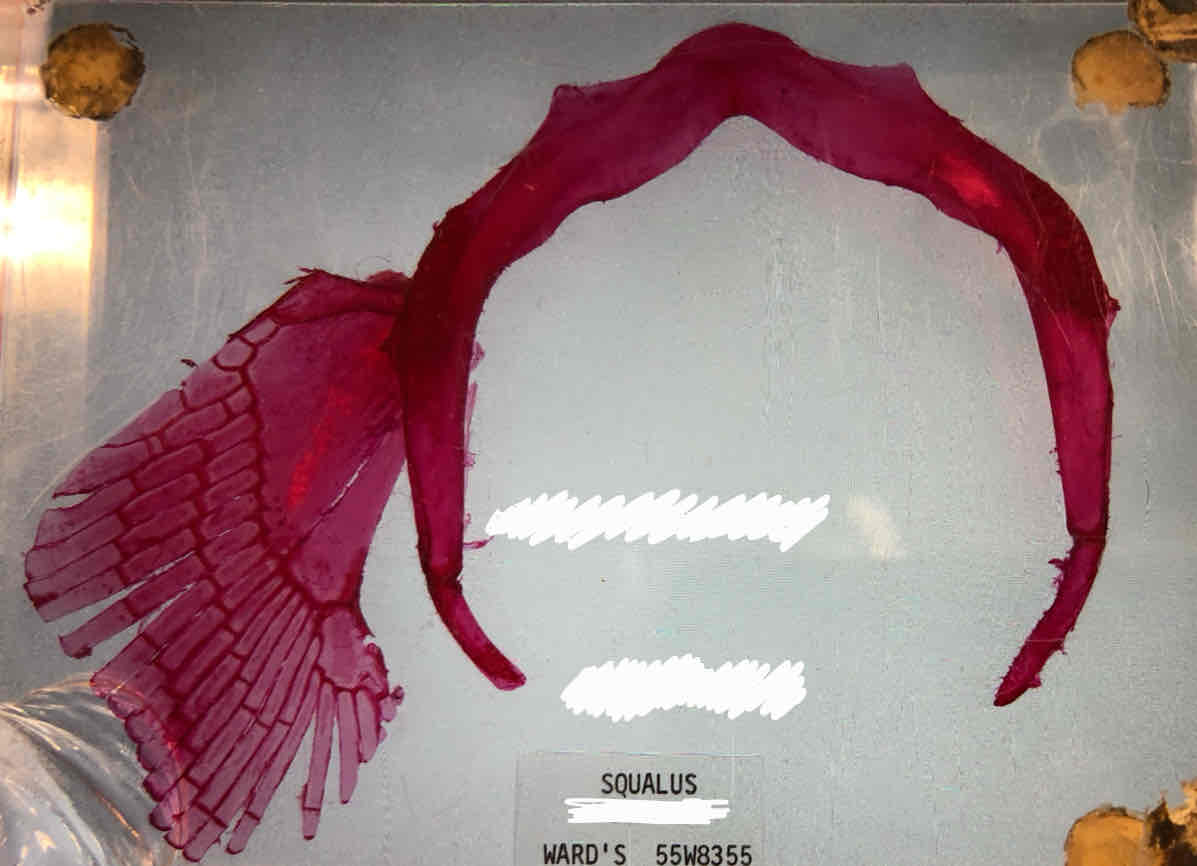

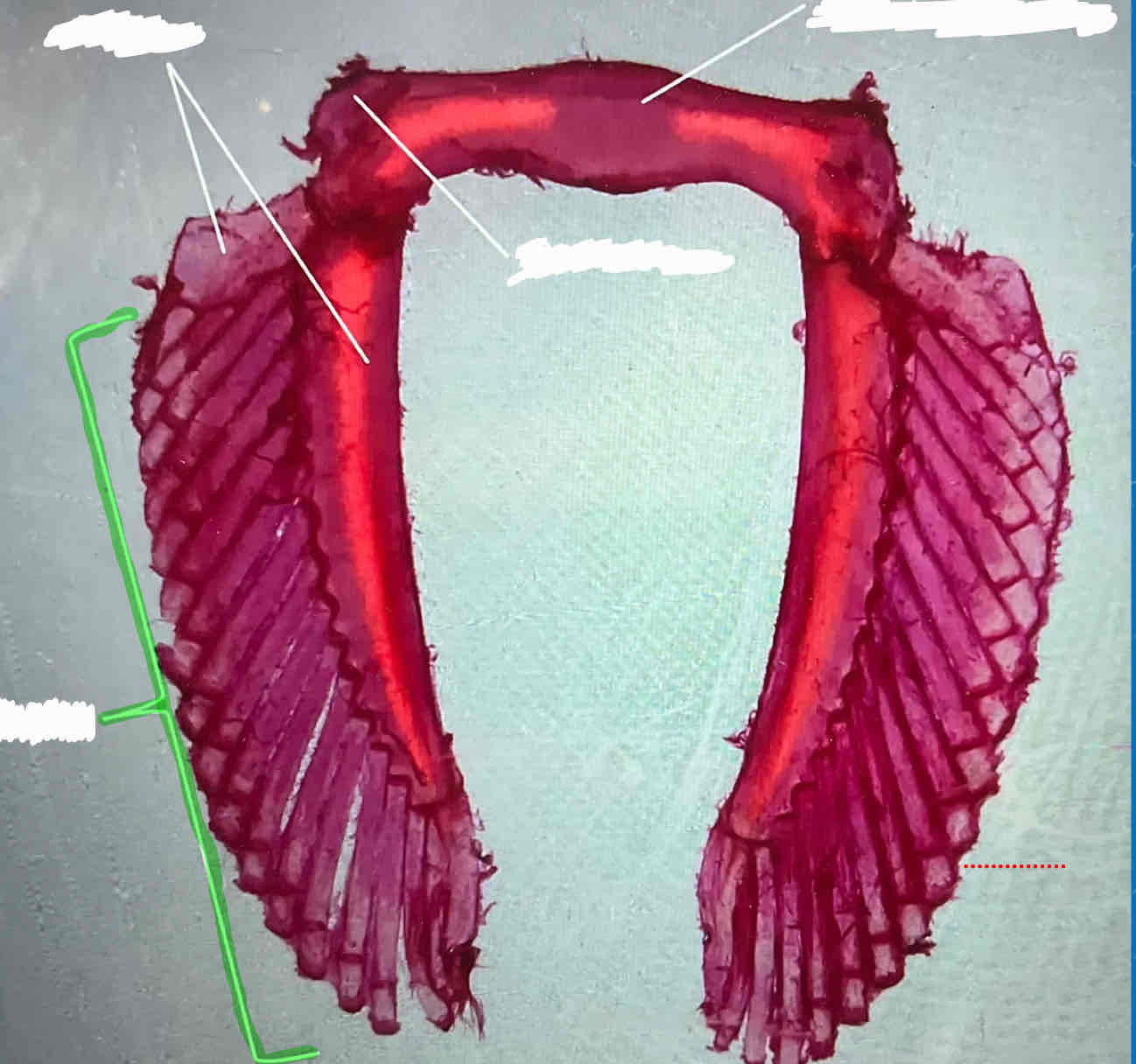
What type of girdle is this?
Shark pectoral girdle; you can tell because there are three basals
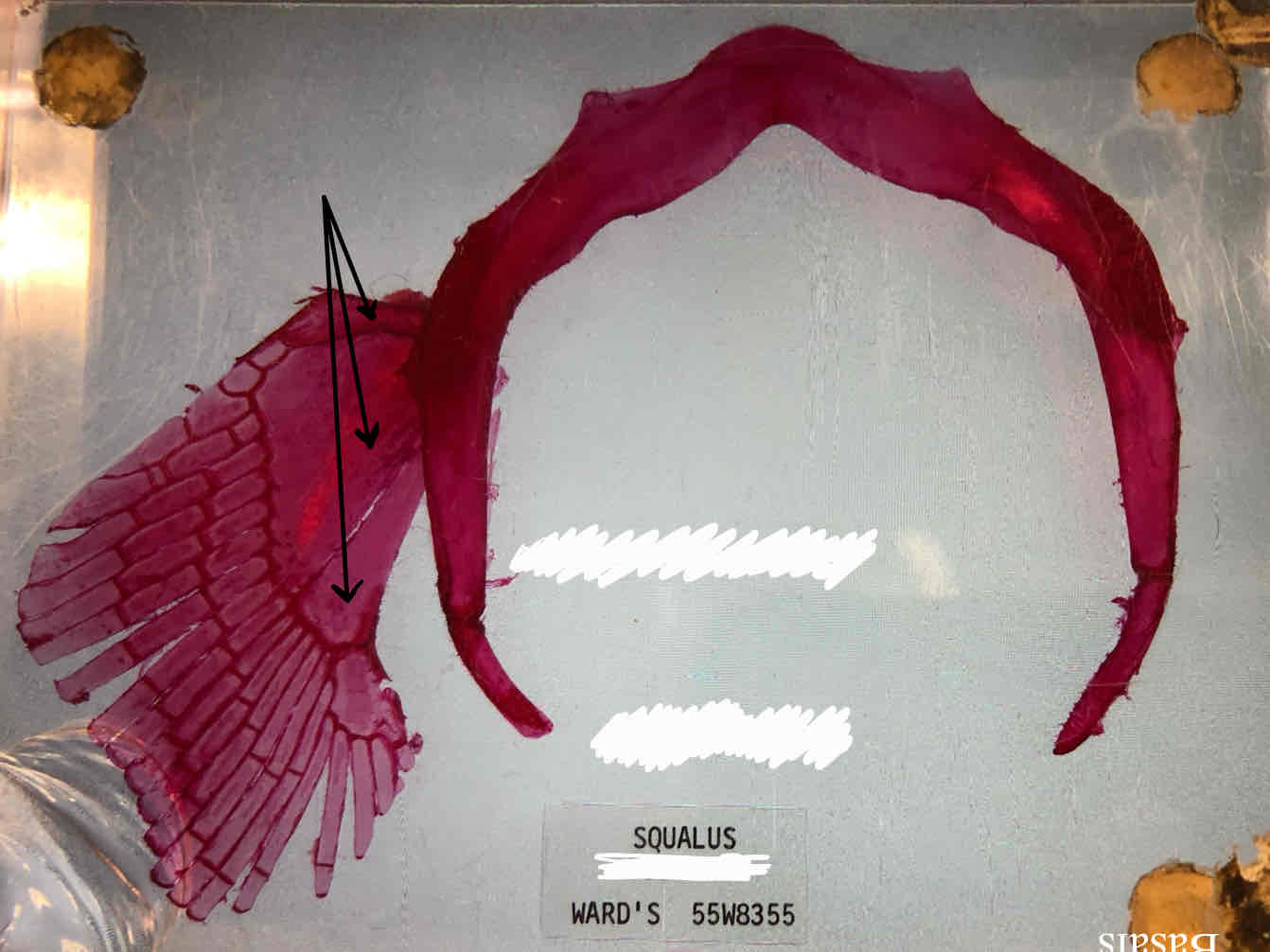

basal pterygiophores

radial pterygiophores
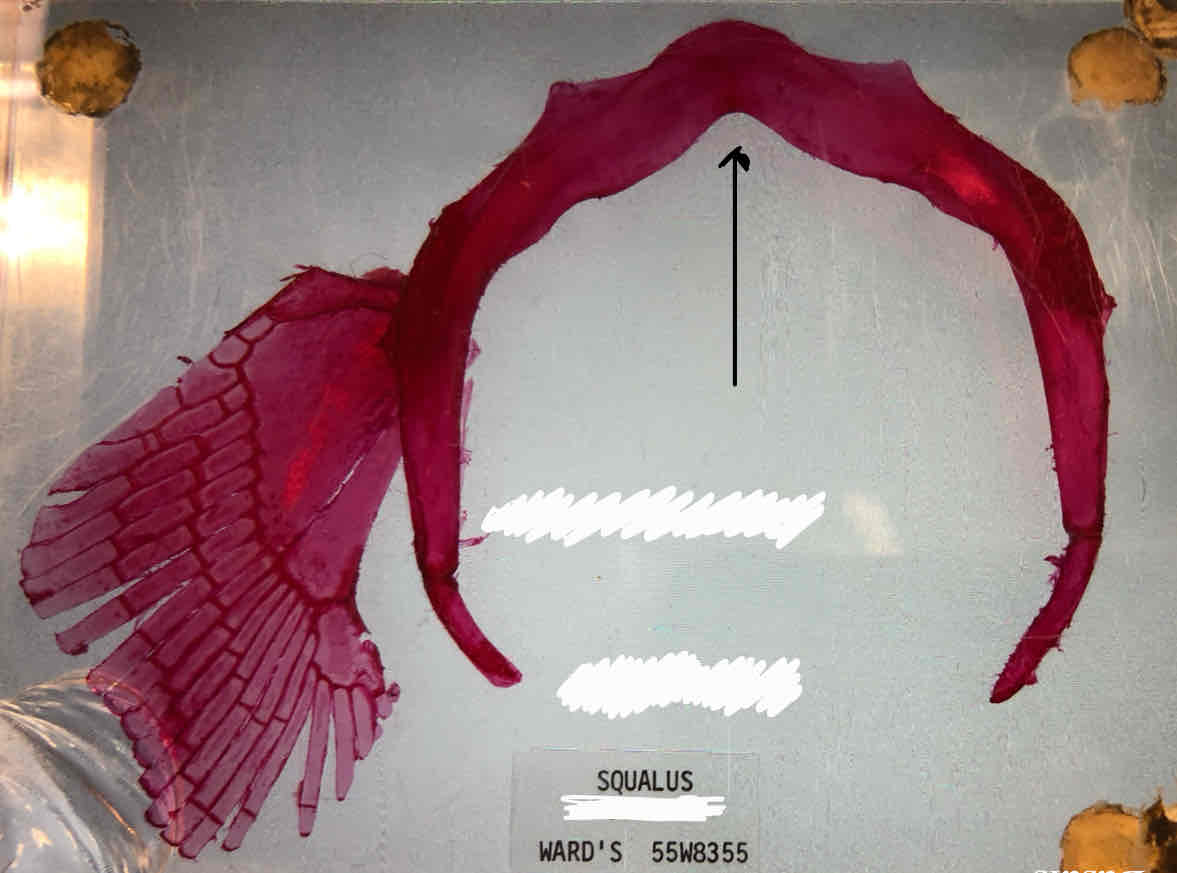

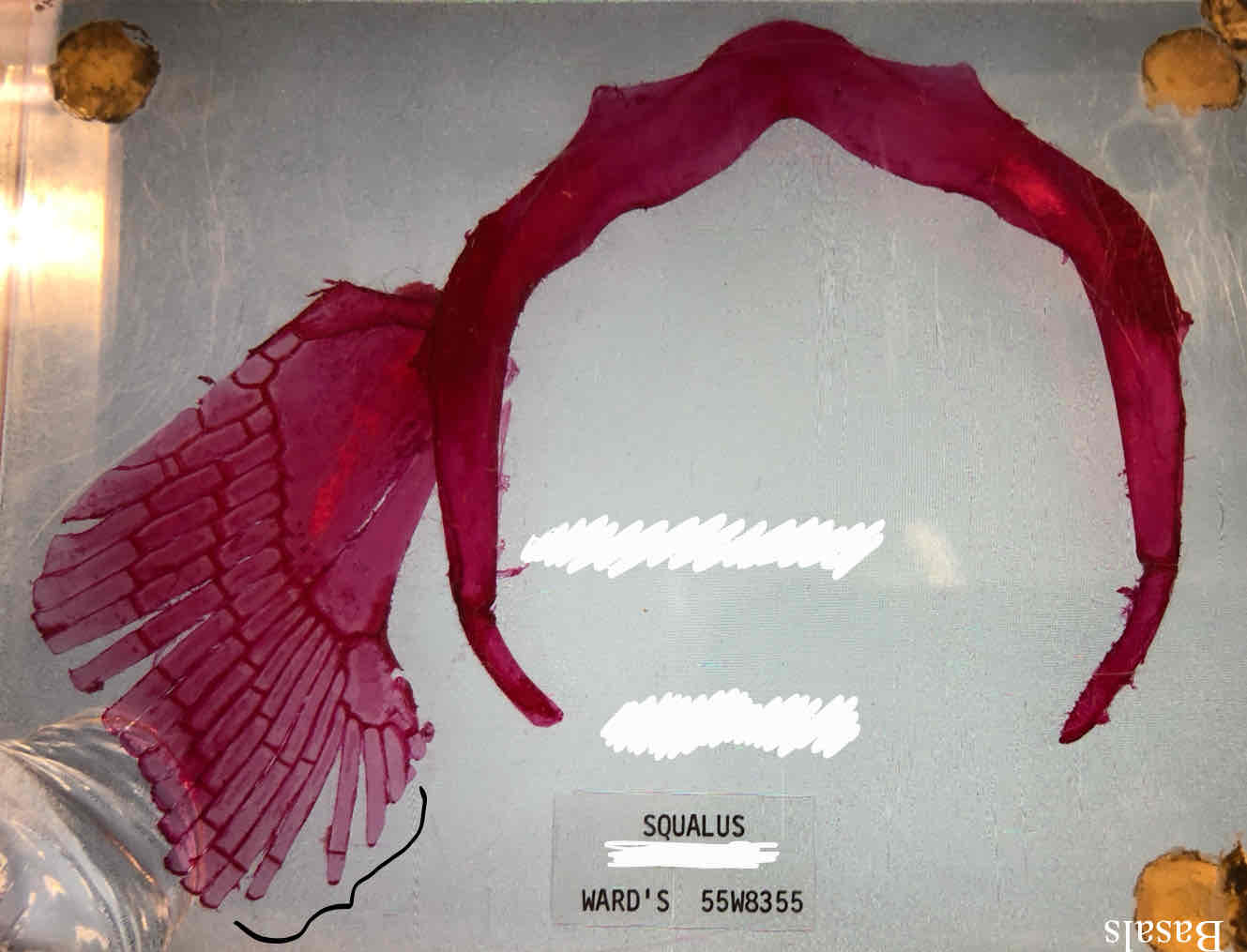
coracoid bar
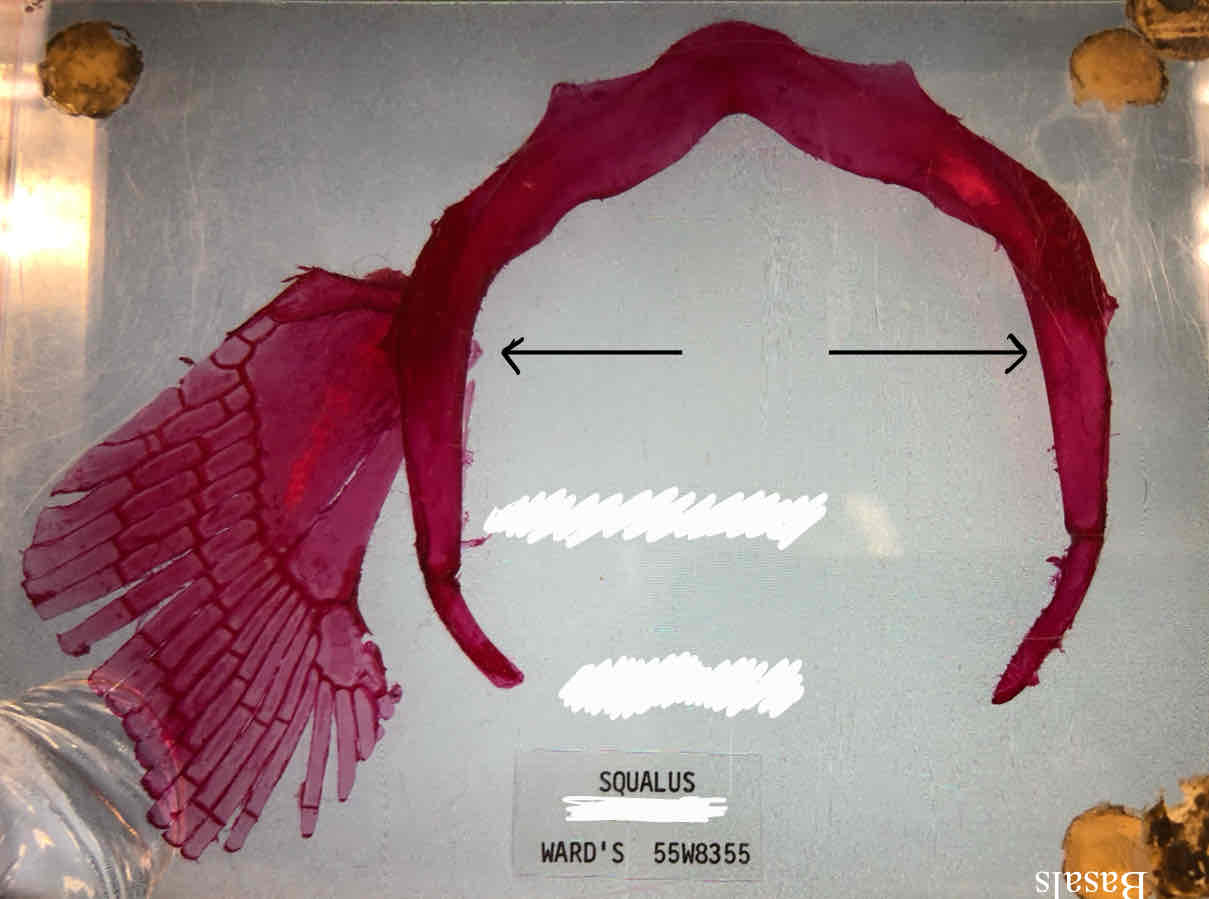

scapular cartilage
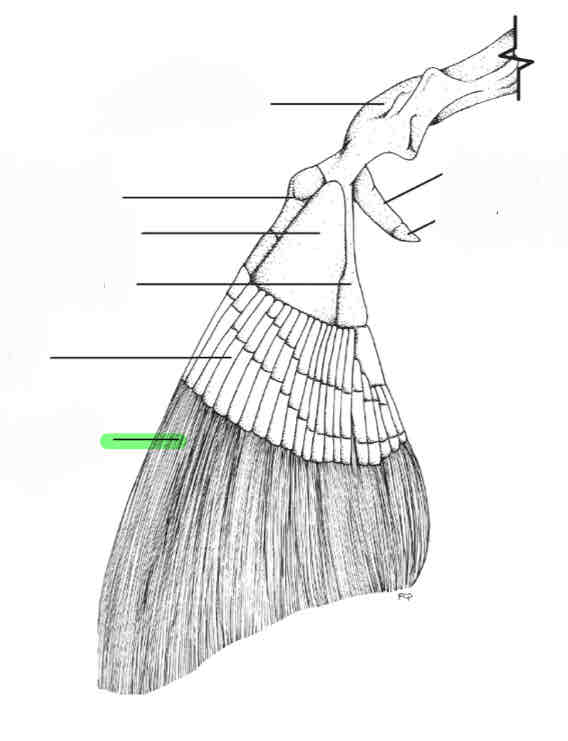
ceratotrichia (fin rays)
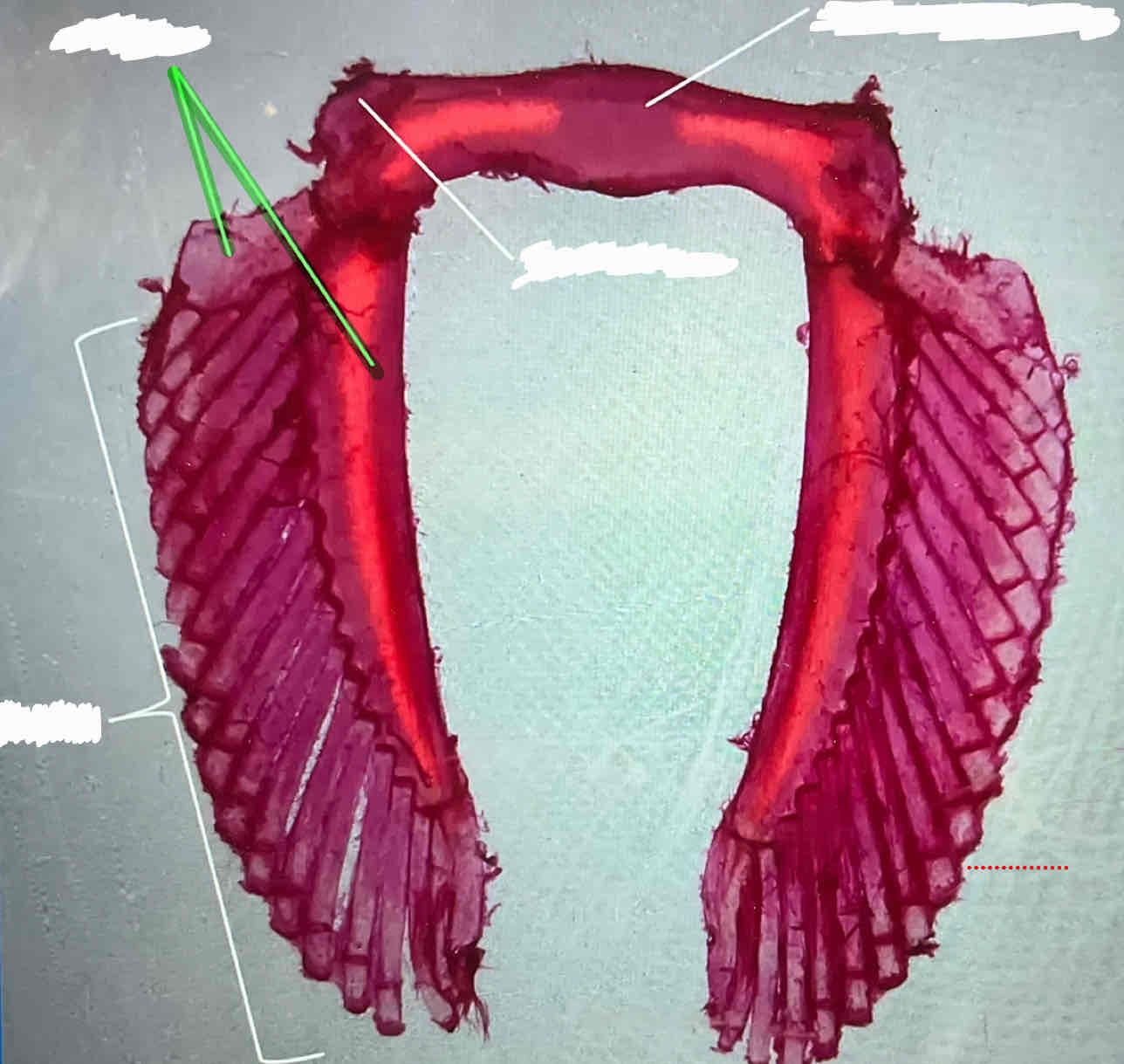
basals (female shark)
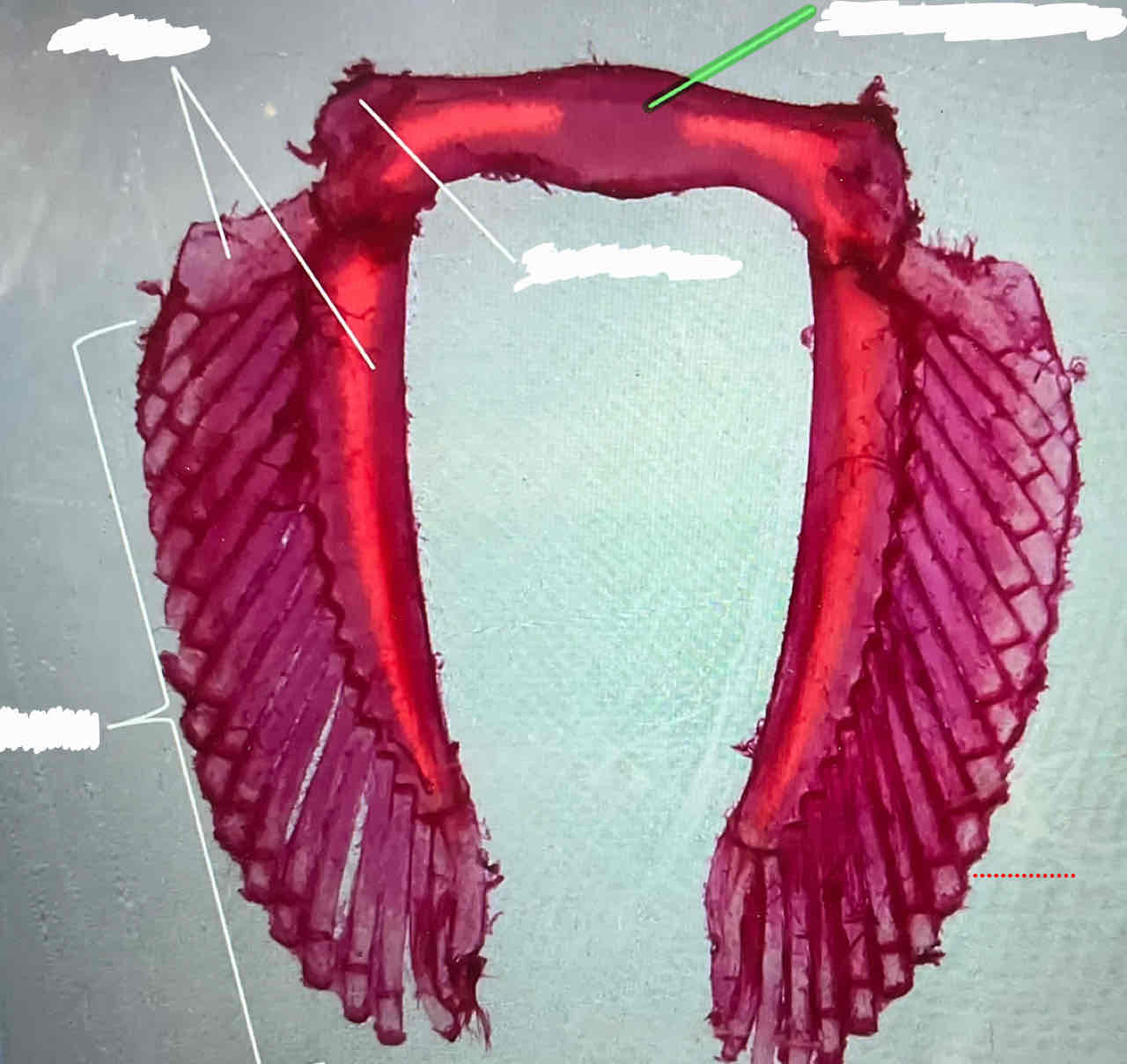
puboischiatic bar (female shark)
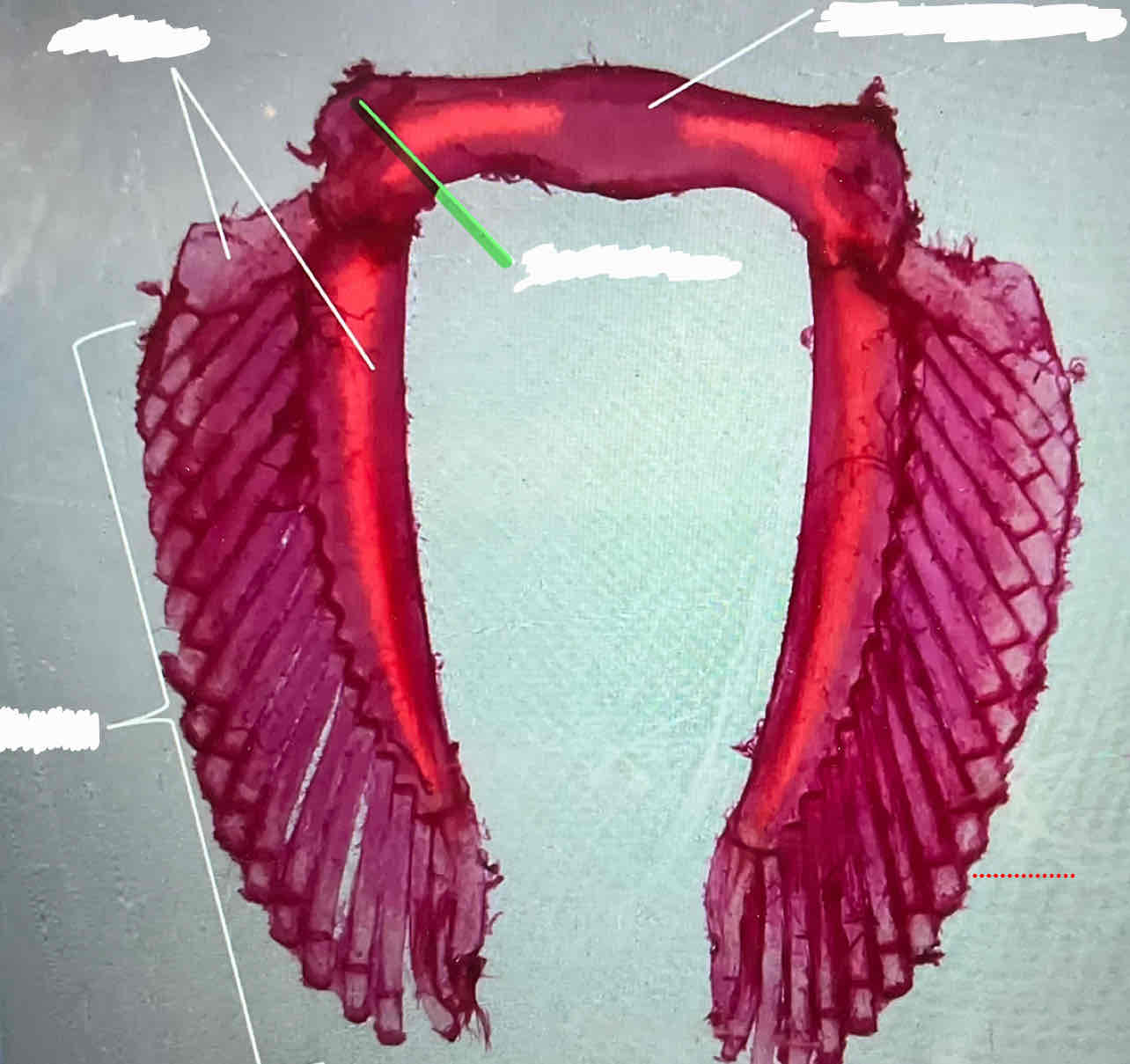
iliac process (female shark)
radials (female shark)
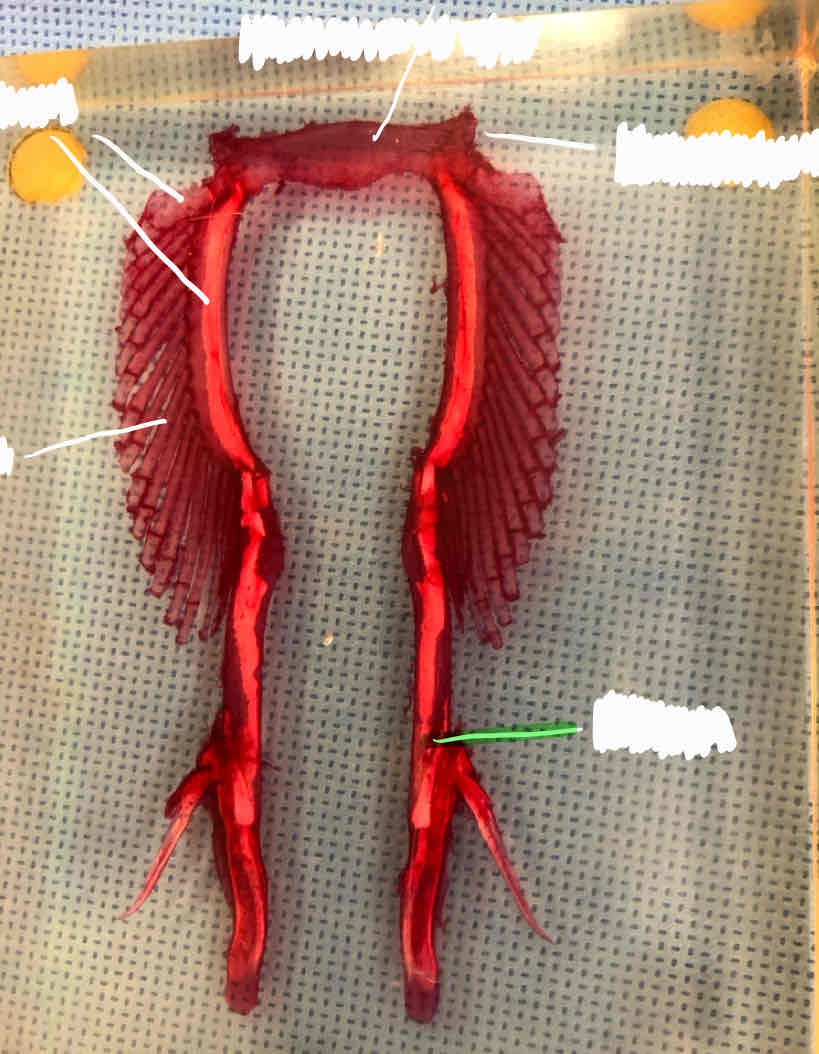
clasper (male shark)
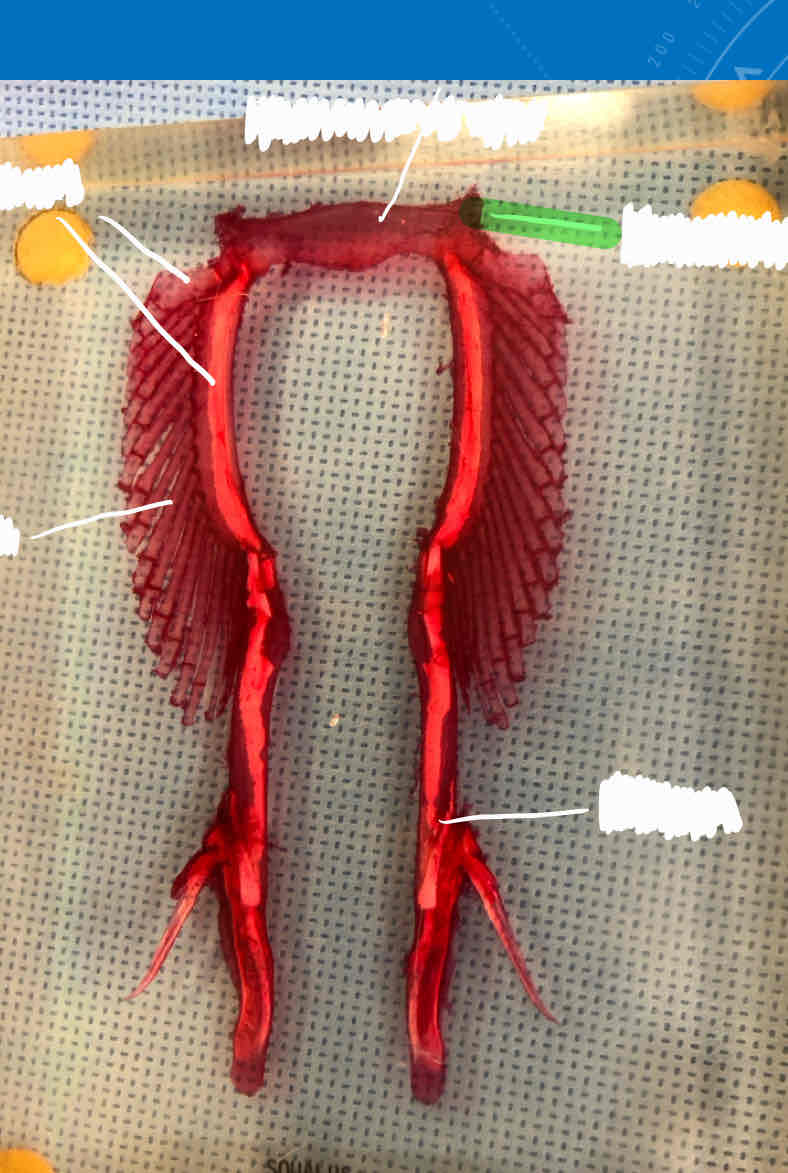
iliac process (male shark)
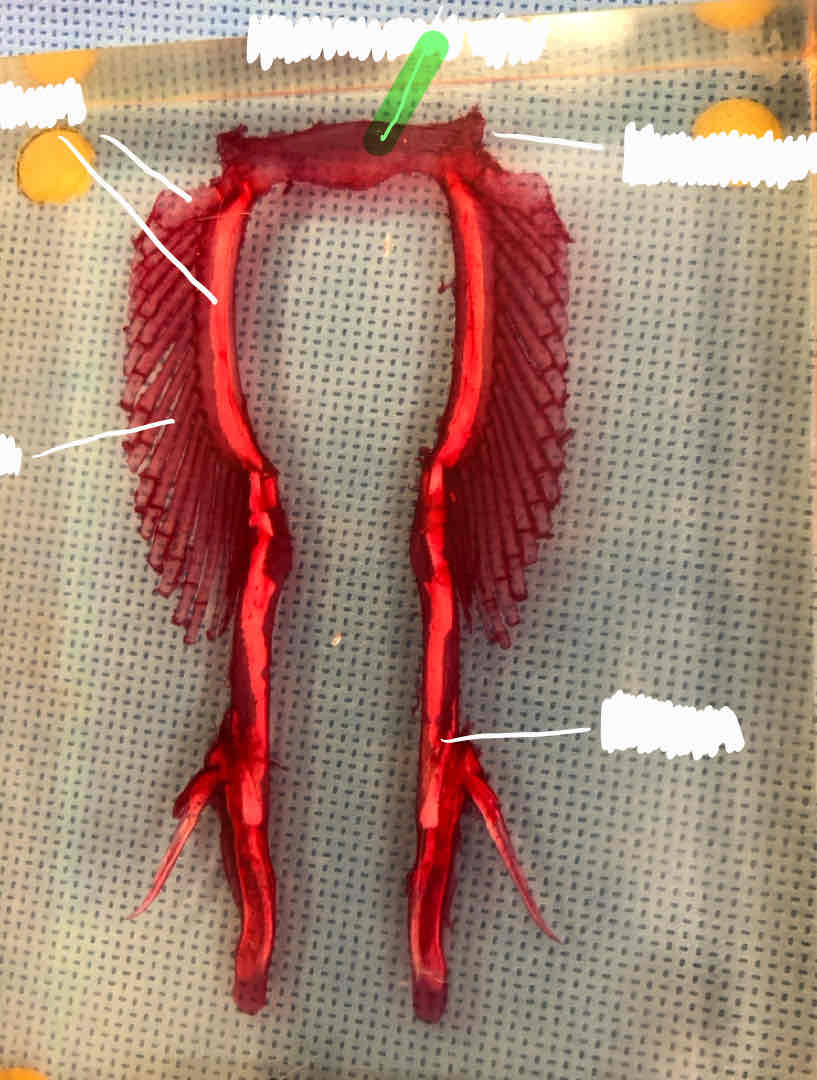
puboischiatic bar (male shark)
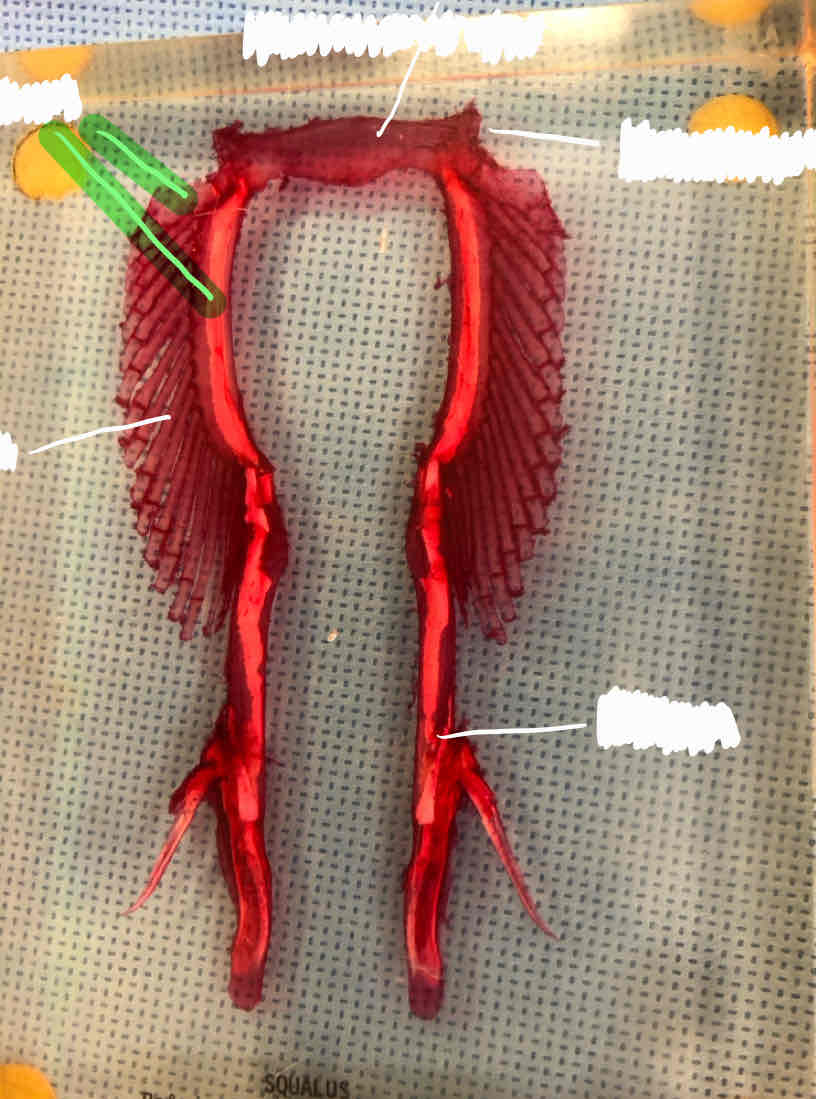
basals (male shark)
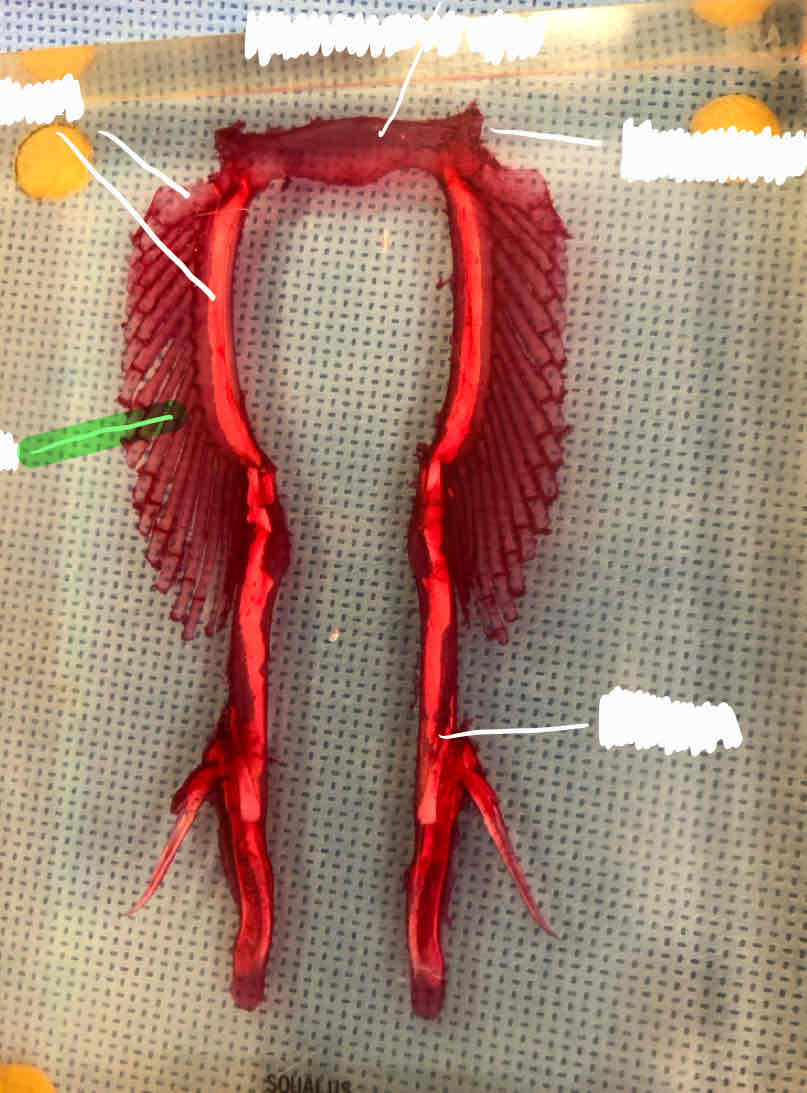
radials (male shark)
How can you tell a pectoral girdle apart from a pelvic girdle in sharks?
Pectoral girdles have three basals while pelvic girdles have two basals.
What is the alternate name for fin rays?
ceratotrichia
What are ceratotrichia made of?
keratin
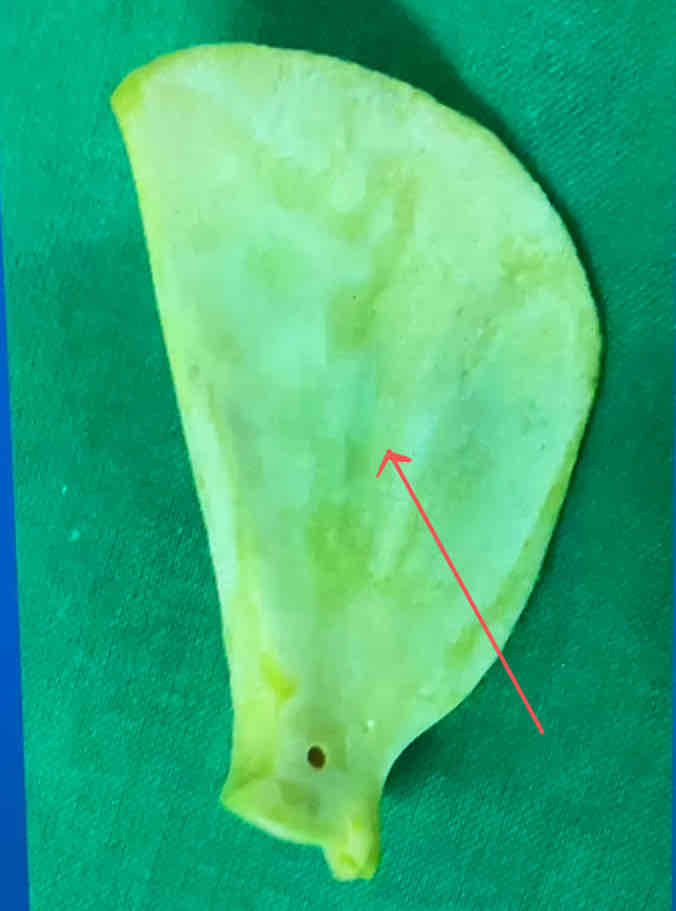
subscapular fossa (medial landmark)
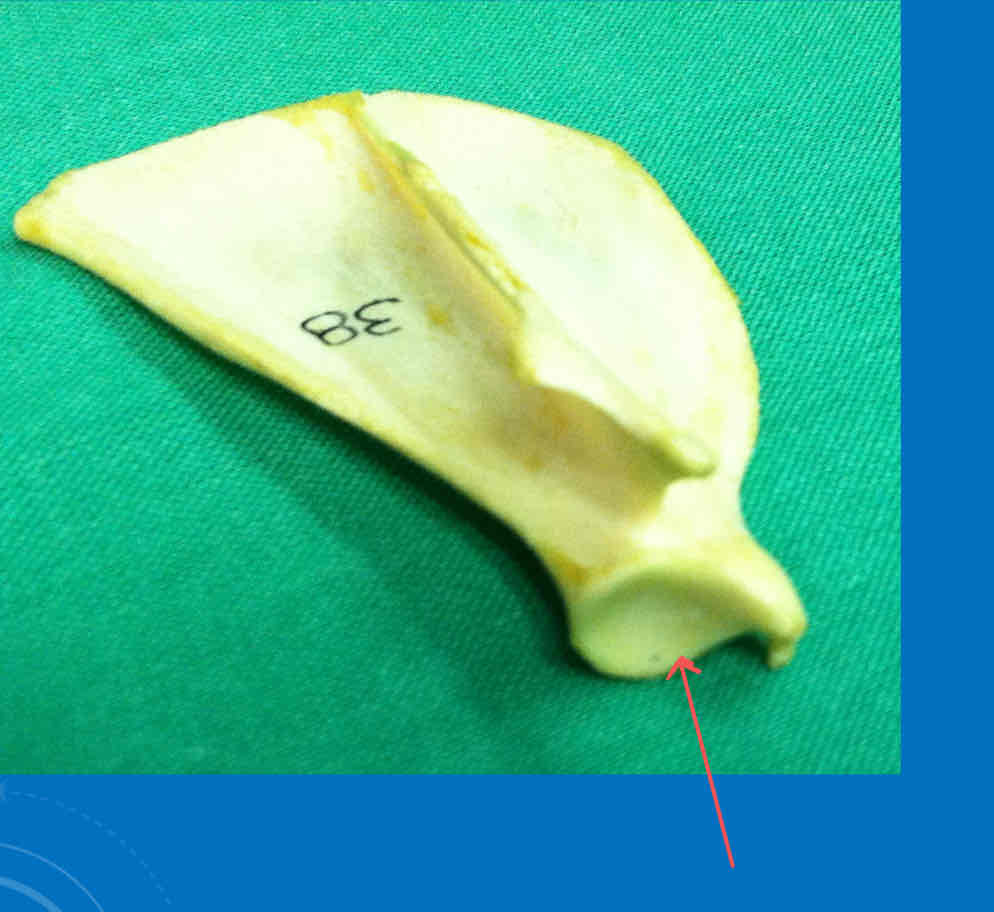
Glenoid fossa - articulates with the head of the humerus
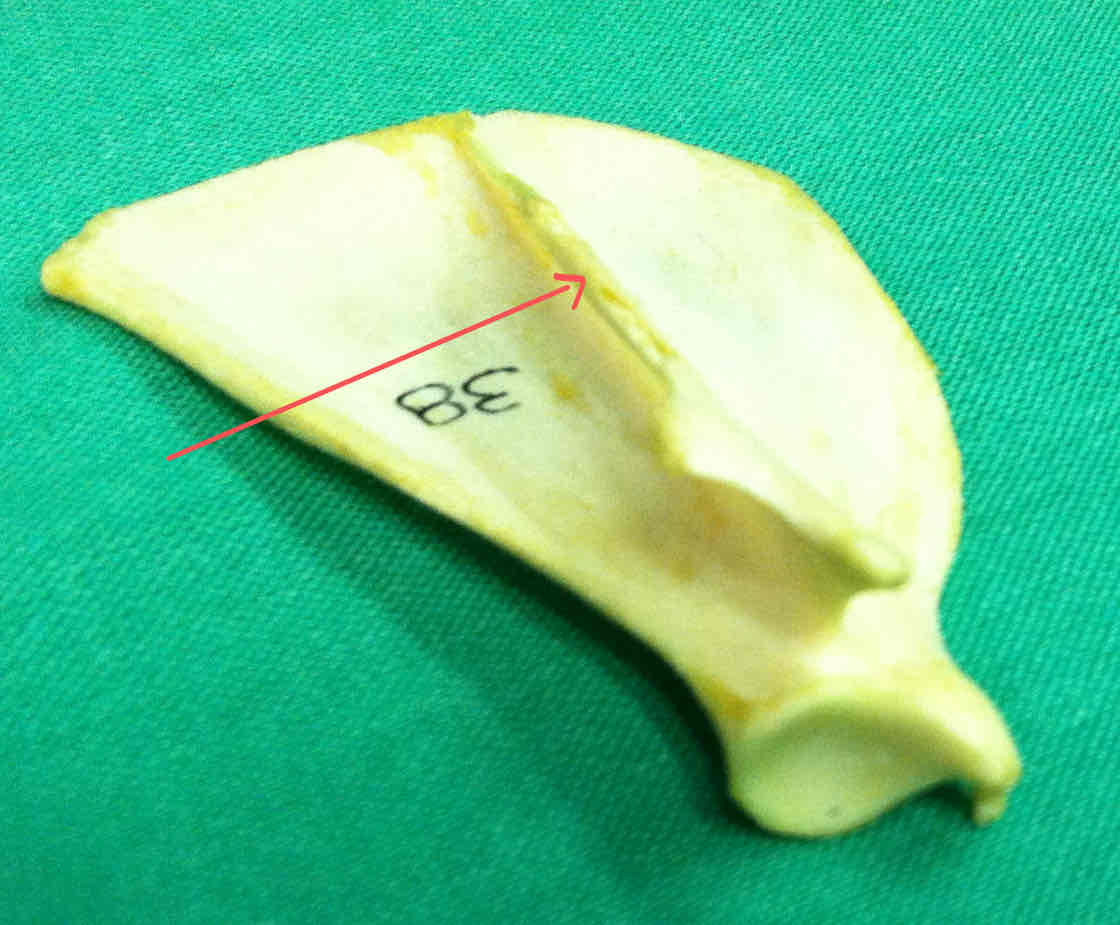
scapular spine (lateral landmark)
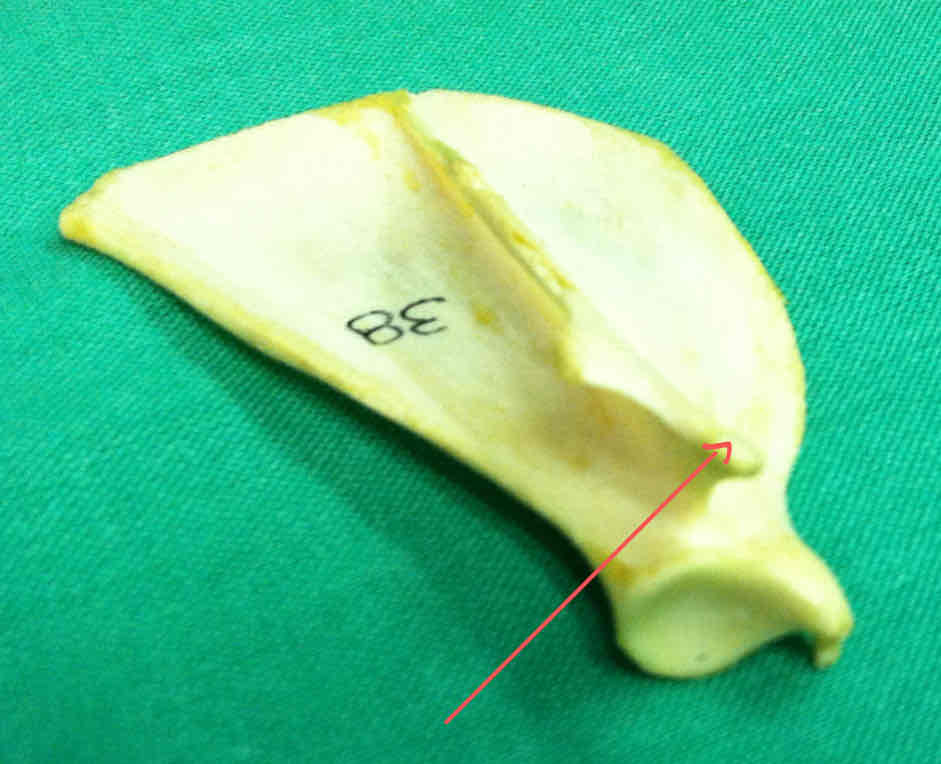
acromion process
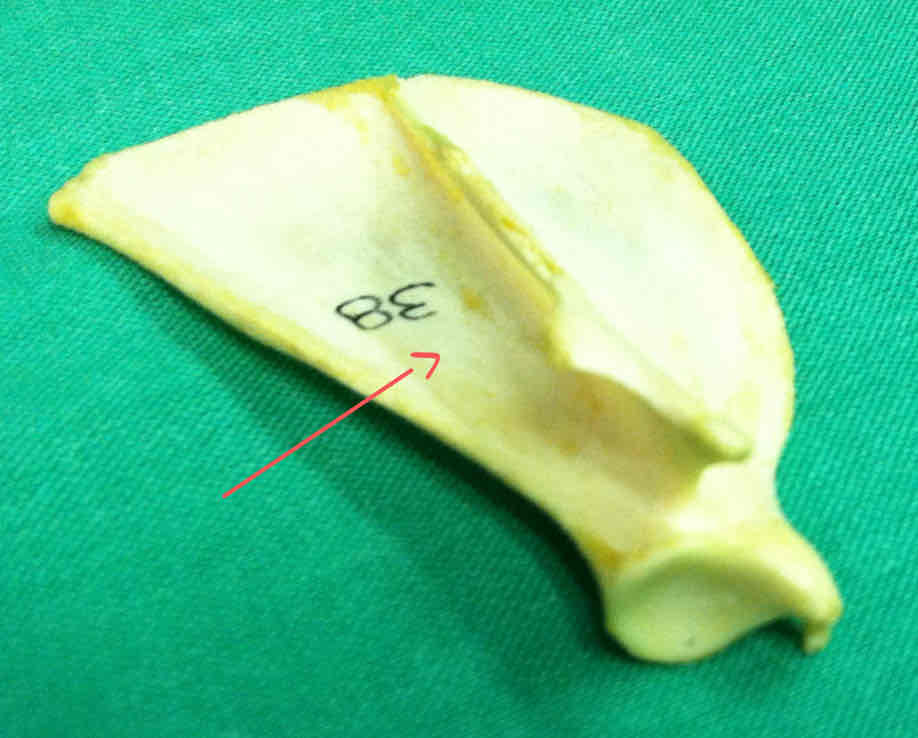
infraspinous fossa
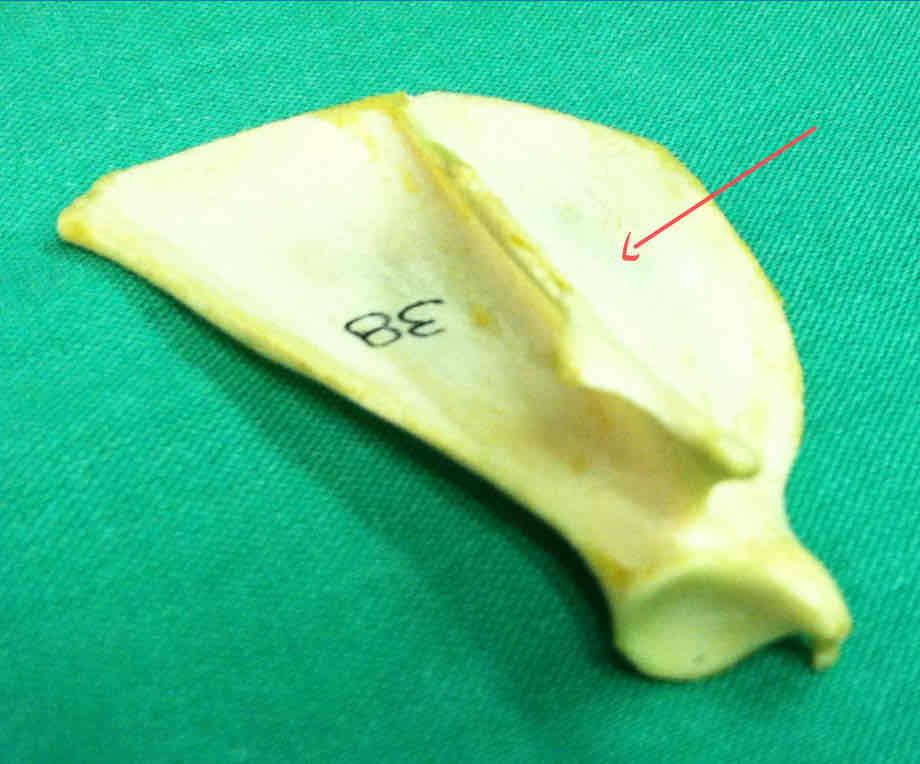
supraspinous fossa
What is the medial landmark of the scapula?
the subscapular fossa
What is the lateral landmark of the scapula?
the scapular spine
How do you determine if a scapula is right or left?
Look for the Glenoid fossa, which helps you determine the cranial portion of the scapula. Then, look for the rounded edge of the flat portion of the scapula to help you determine which part is the part pointing down.
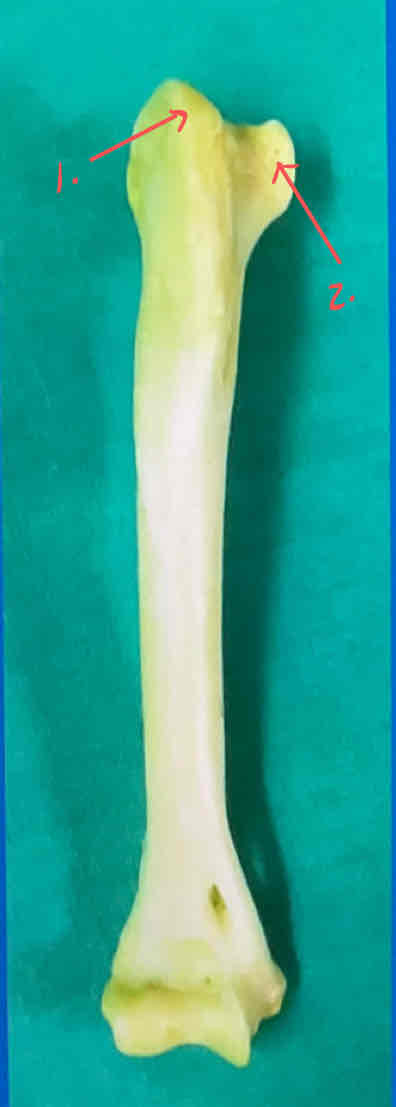
greater tuberosity
lesser tuberosity

bicipital groove - where the bicep tendon passes
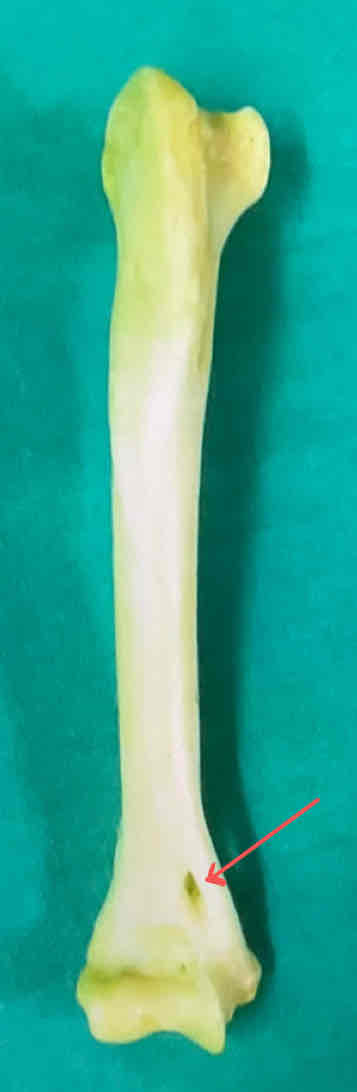
supracondyloid foramen (medial landmark)

epicondyles
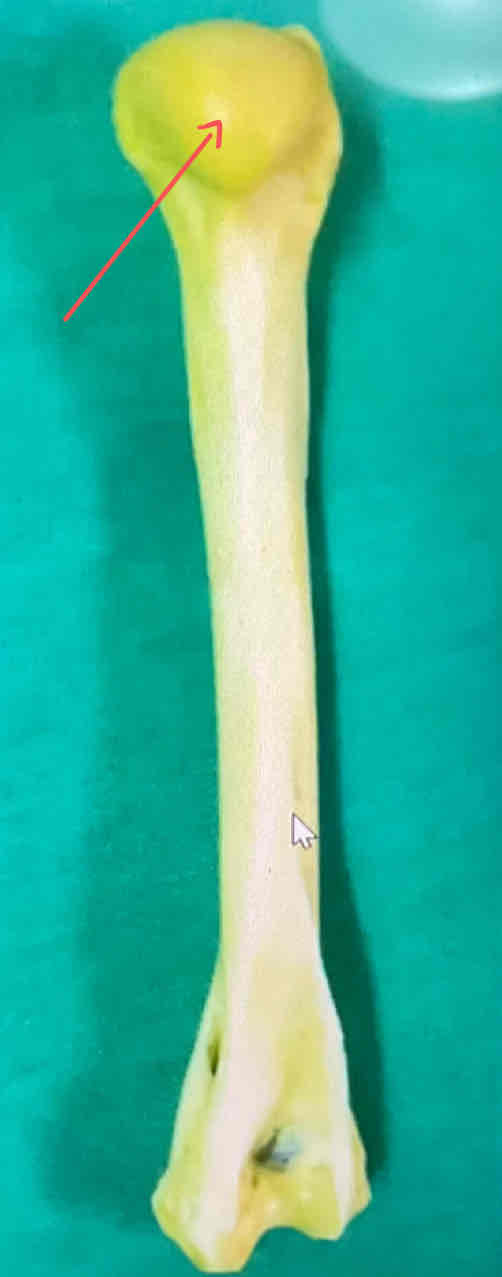
head of the humerus (caudal landmark)
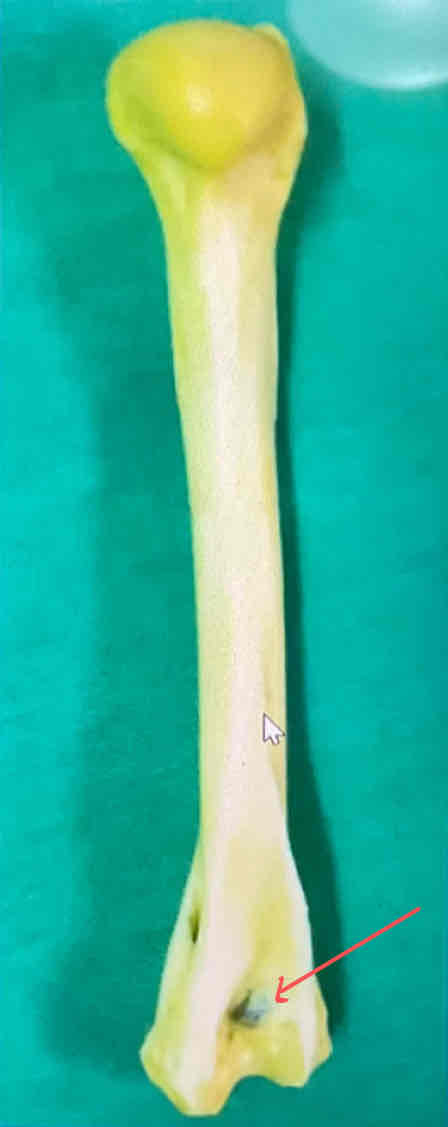
olecranon fossa (caudal landmark) - articulates with the olecranon of the ulna
What is the medial landmark of the humerus?
supracondyloid foramen
What are some caudal landmarks of the humerus?
the head of the humerus and the olecranon fossa
How do you determine if a humerus is right or left?
Look for the supracondyloid fossa, the medial landmark, to determine right or left.
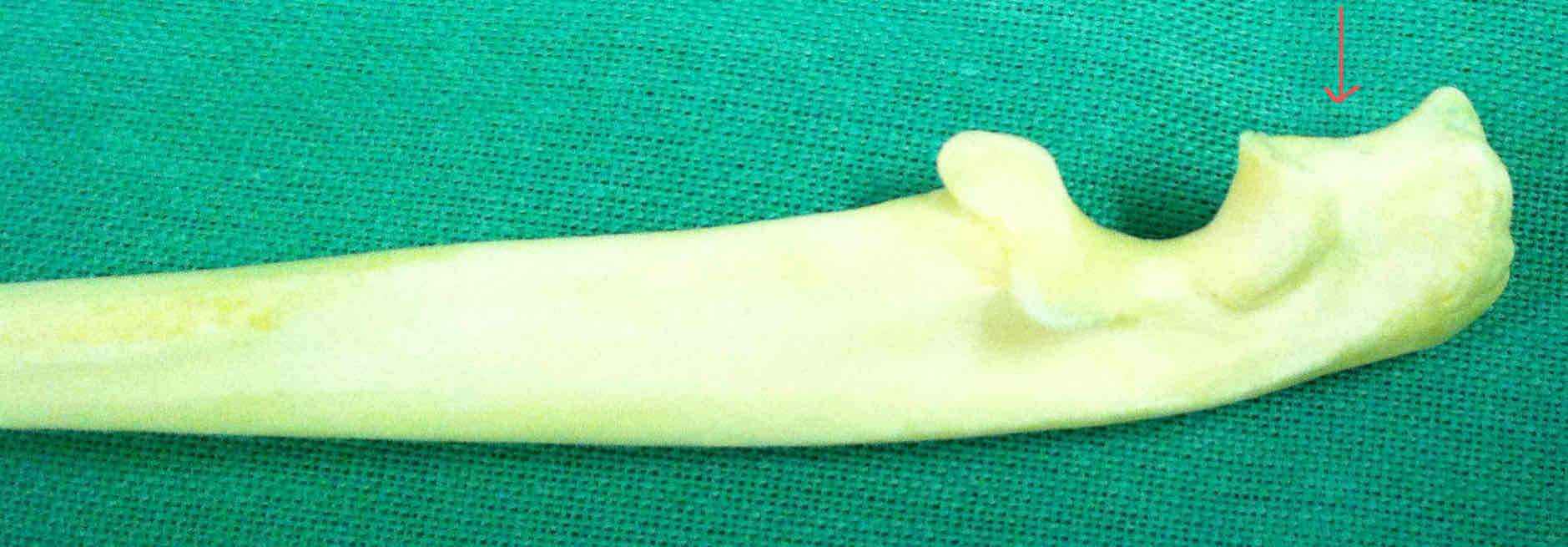
olecranon - articulates with the olecranon fossa of the humerus
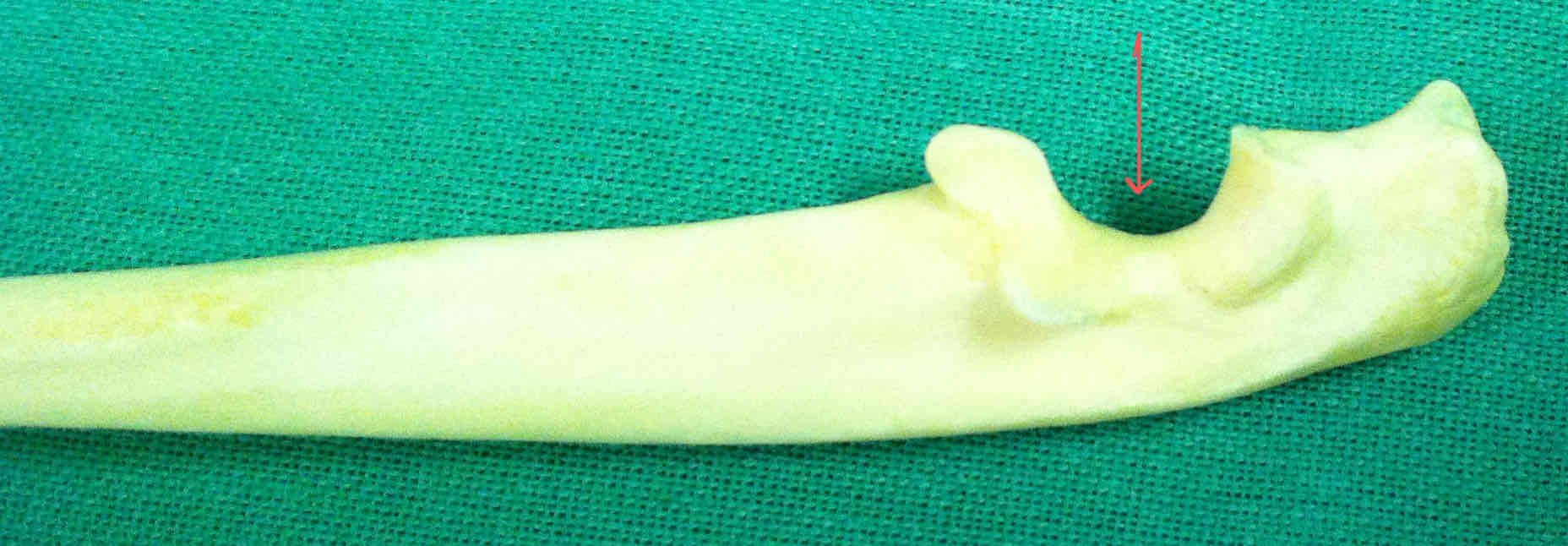
semilunar notch (cranial landmark of the ulna)
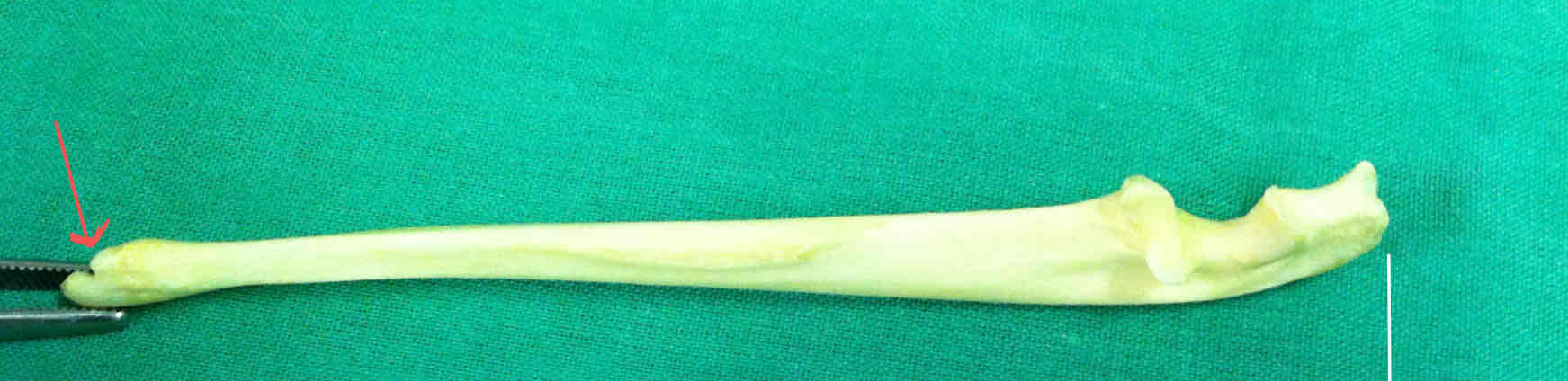
styloid process of the ulna (lateral landmark)
How can you determine if the ulna is right or left?
Look for the semilunar notch to find the cranial side, then use the styloid process (lateral landmark) to decide.
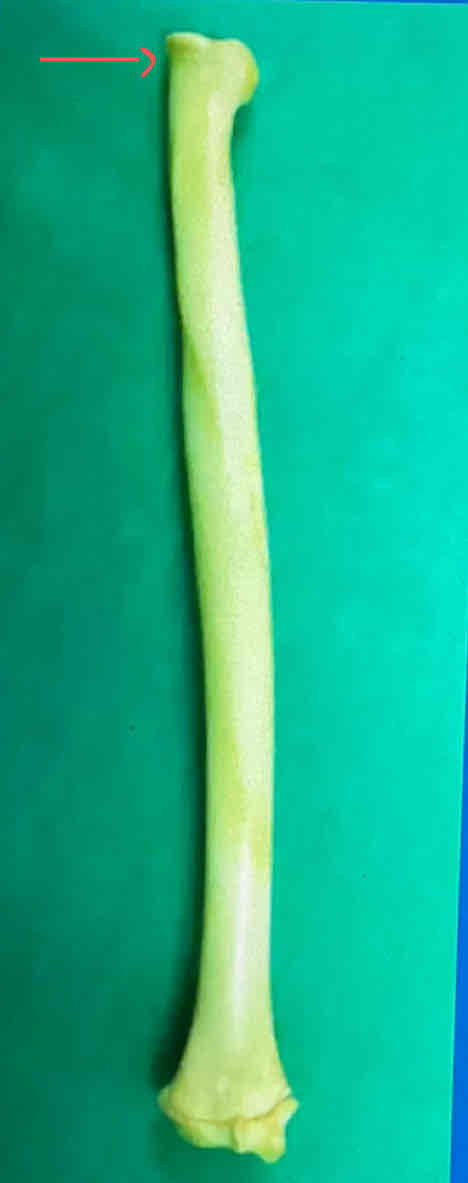

head of the radius
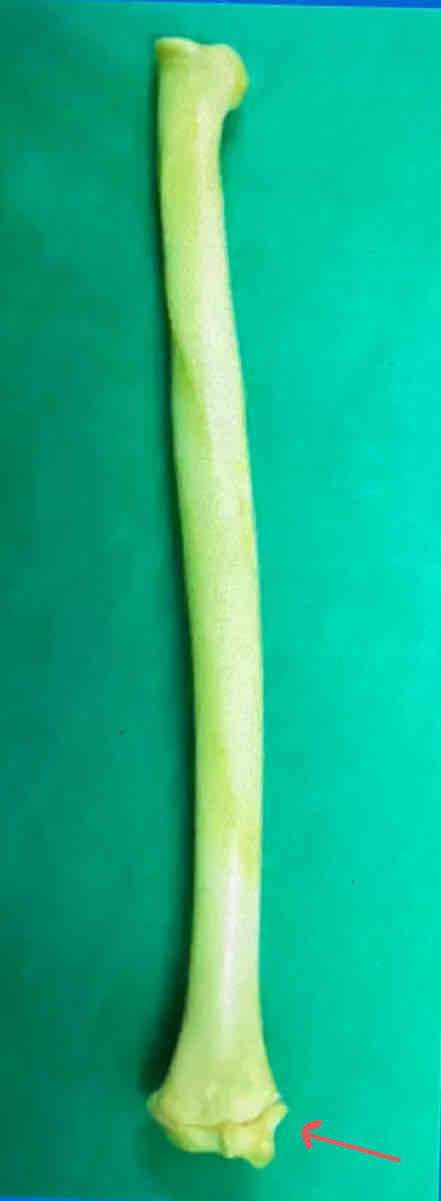

styloid process of the radius (medial landmark)
What is the difference between the styloid processes of the radius and ulna?
The styloid process projects medially in the radius and laterally in the ulna.
Describe the orientation of the radius and ulna in the cat arm.
The radius starts off laterally at the proximal end, but it crosses over the ulna and becomes more medial as you move distally.
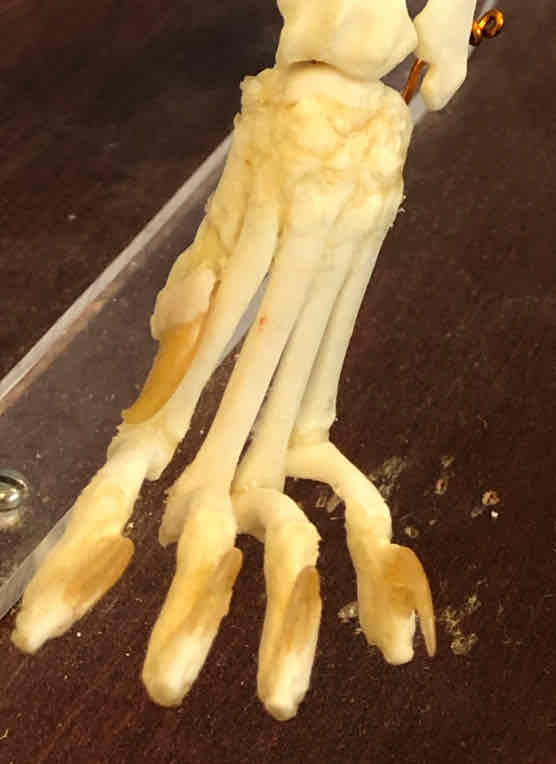
What is this whole structure called?
the manus
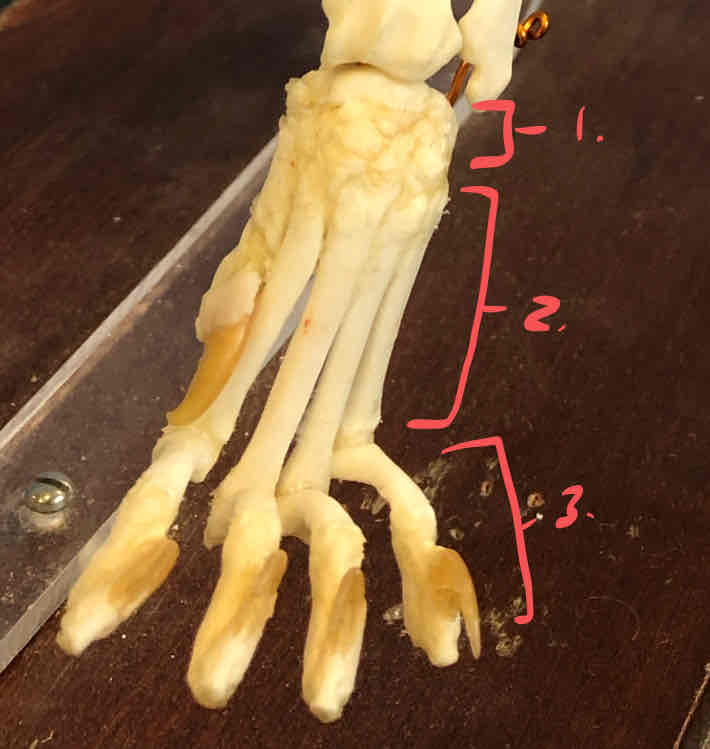
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
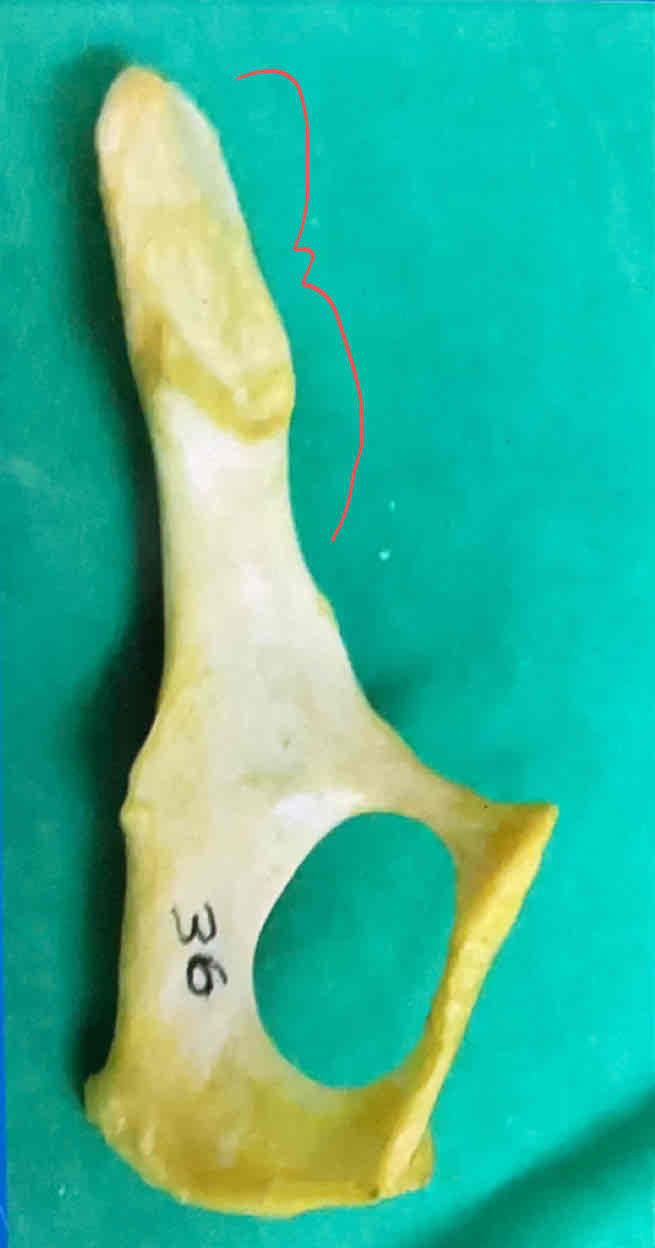
ilium (projects cranially)
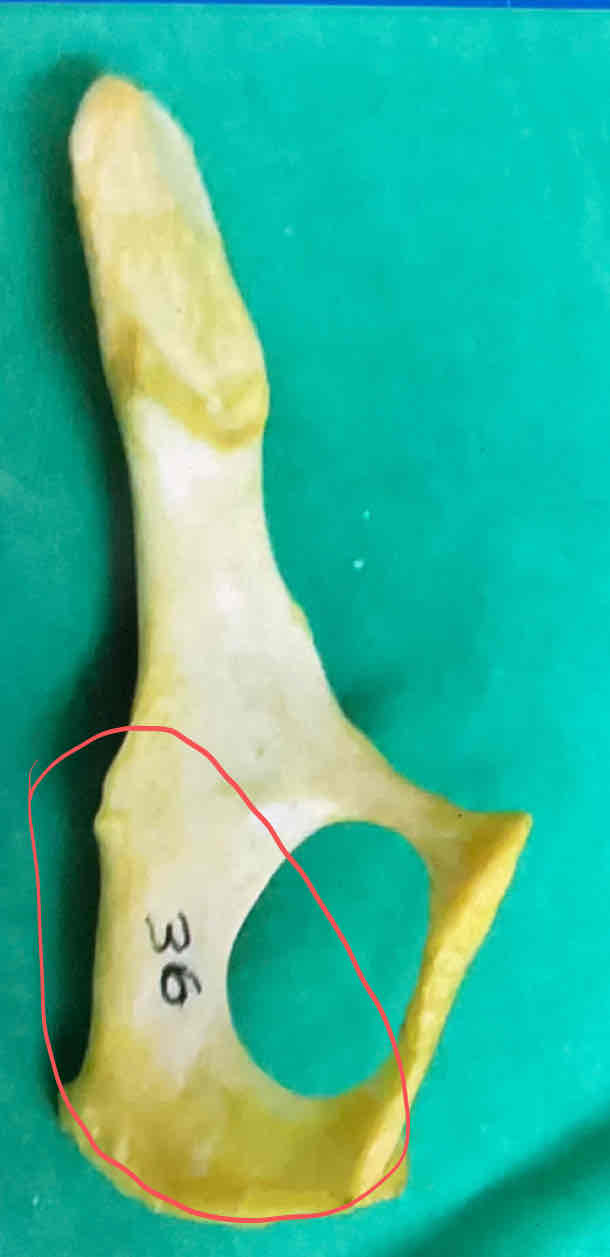
pubis (ventral)
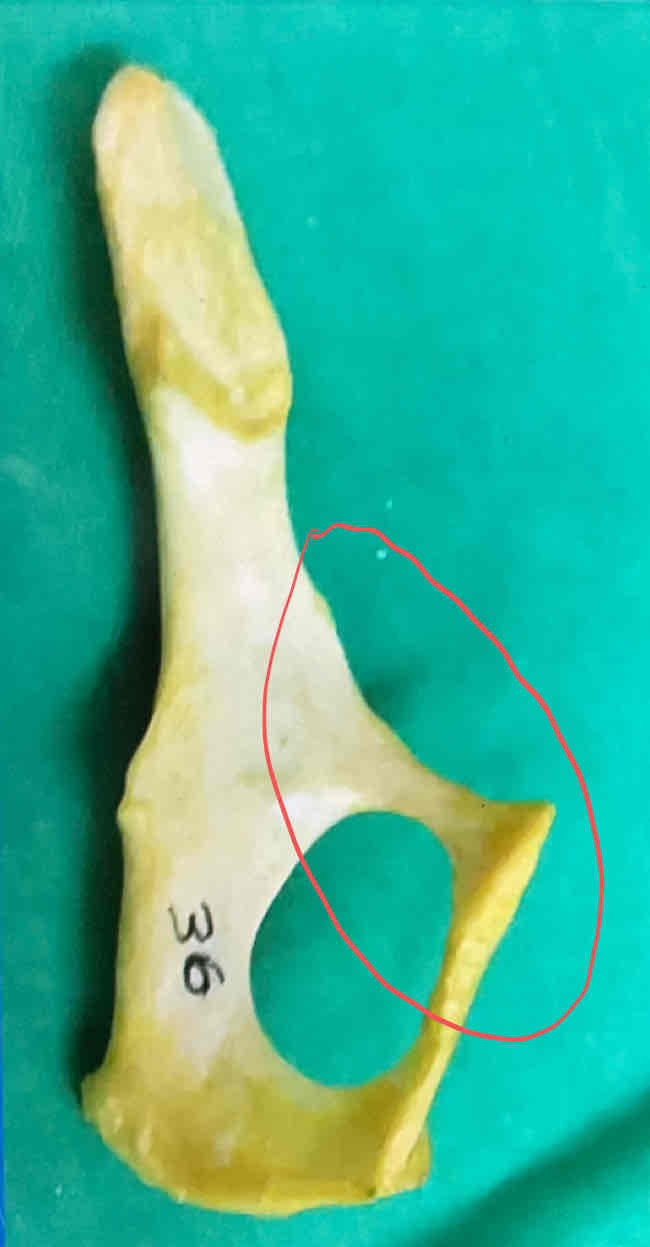
ischium
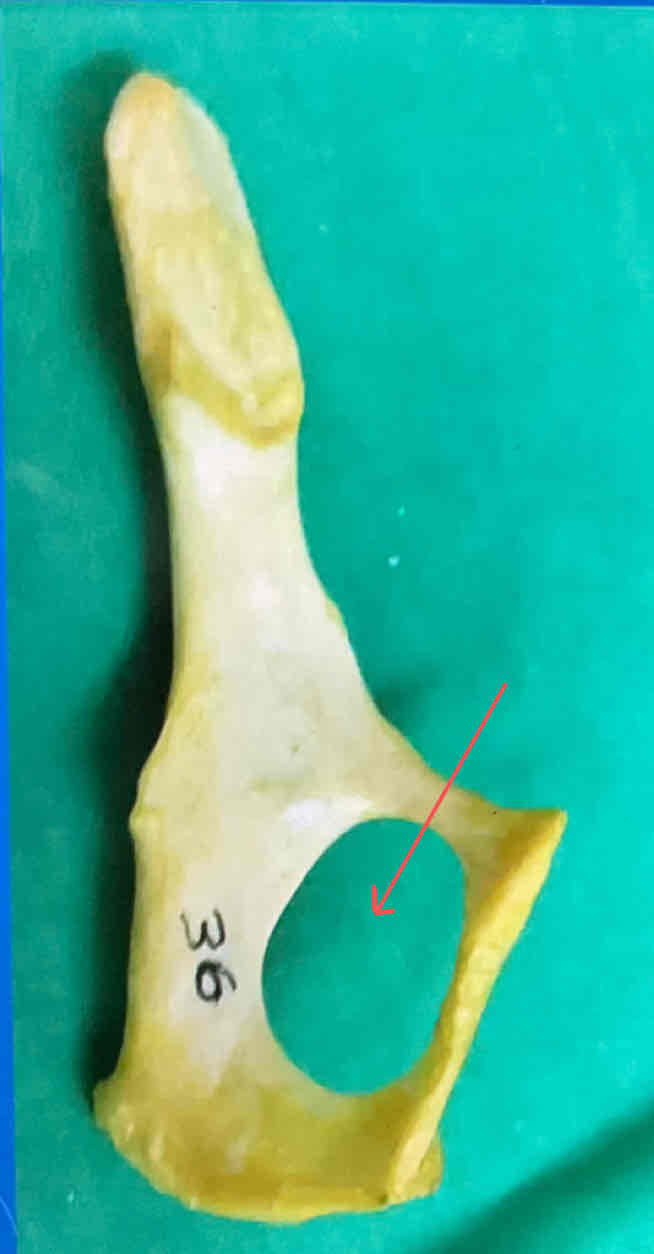
obturator foramen
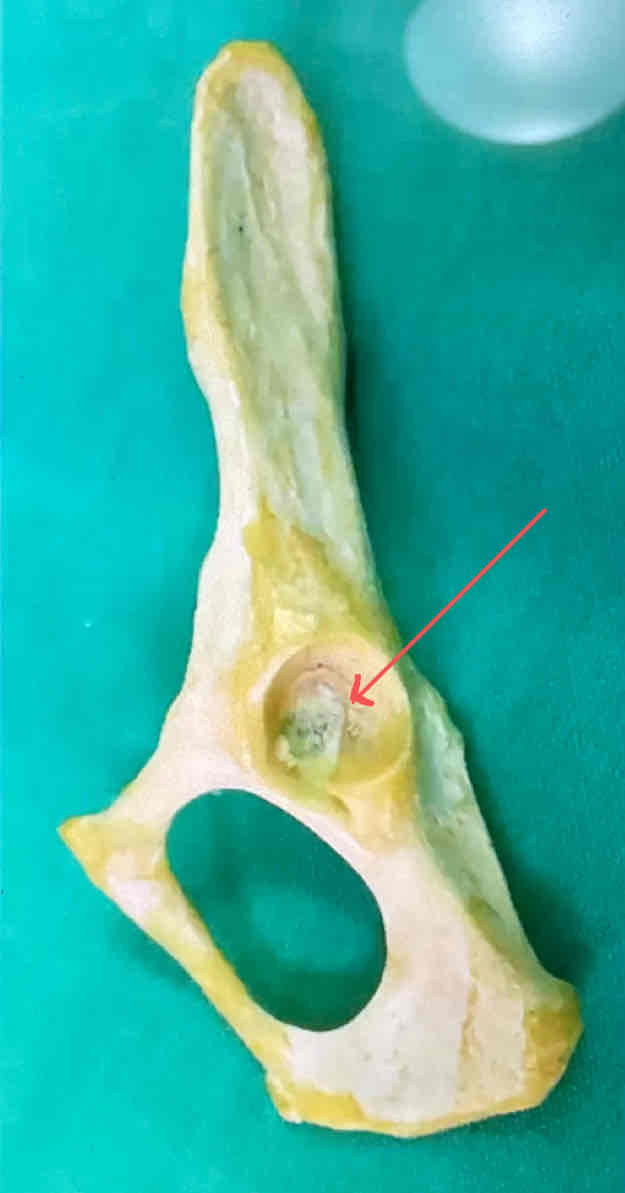
acetebulum (lateral landmark) - articulates with the head of the femur
How do you determine if an os coxa is left or right?
Look for the acetabulum, the lateral landmark. Then, the ilium should project cranially and the pubic should be toward the floor.
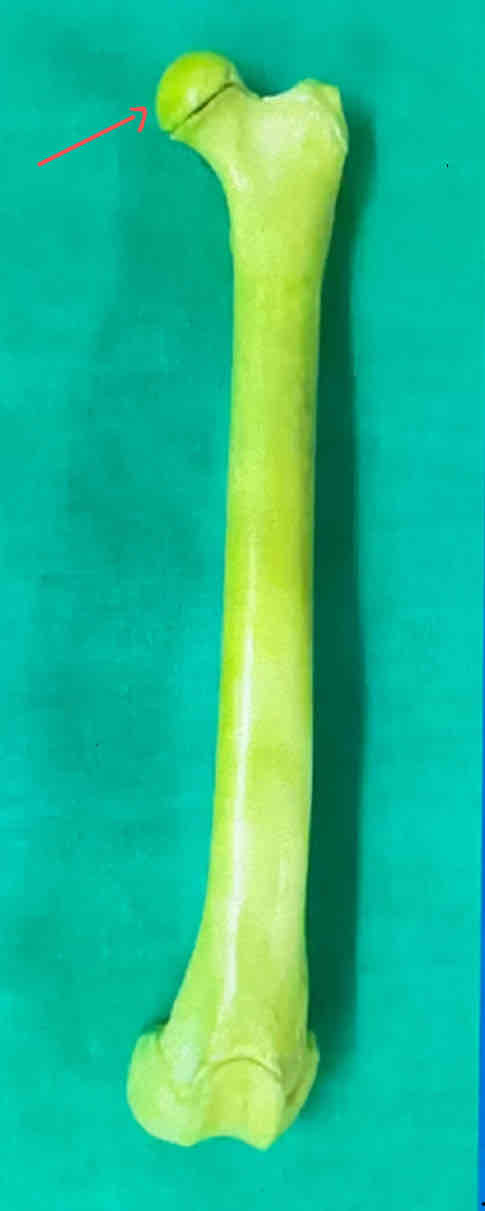

head of the femur (medial landmark)
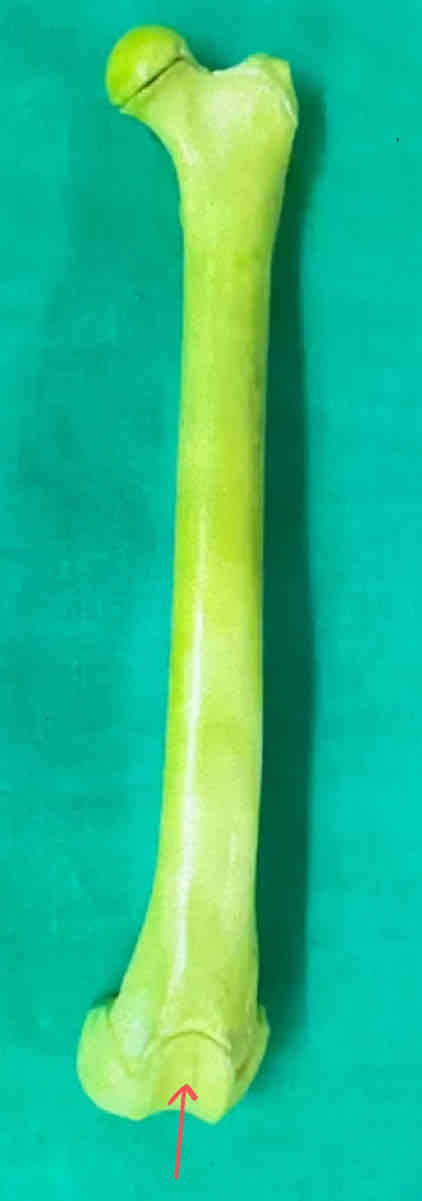

patellar groove
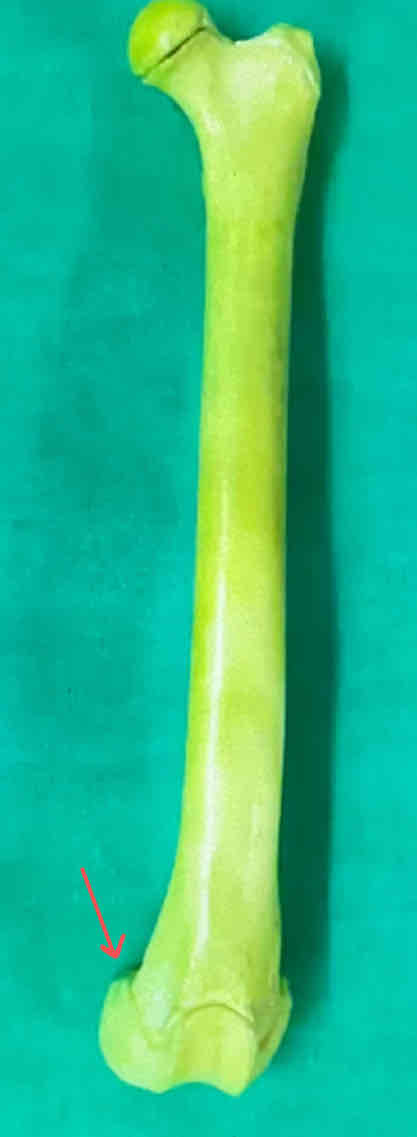

epicondyle

condyles (caudal landmark)
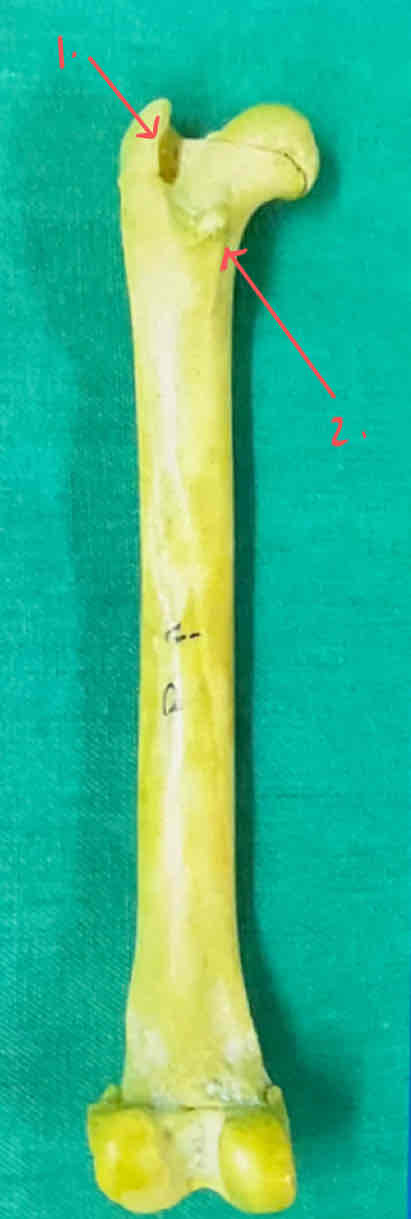
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter (caudal landmark)
neck of the femur
What is the medial landmark of the femur?
Head of the femur
What are some caudal landmarks of the femur?
the lesser trochanter and the condyles

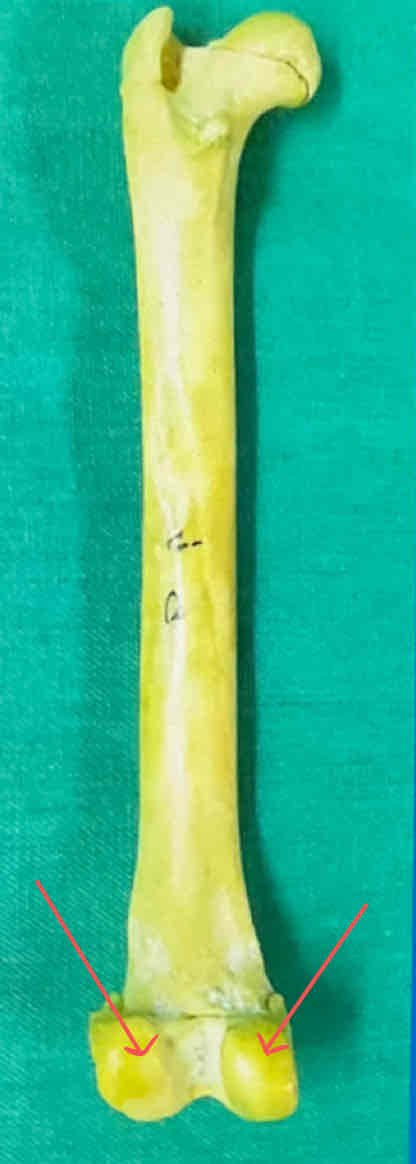
patella

Tibial tuberosity (cranial) - patellar tendon attaches here

tibial crest

medial malleolus (medial landmark - the longer part of the “cup” is on the medial side)

fibula - lateral to the tibia
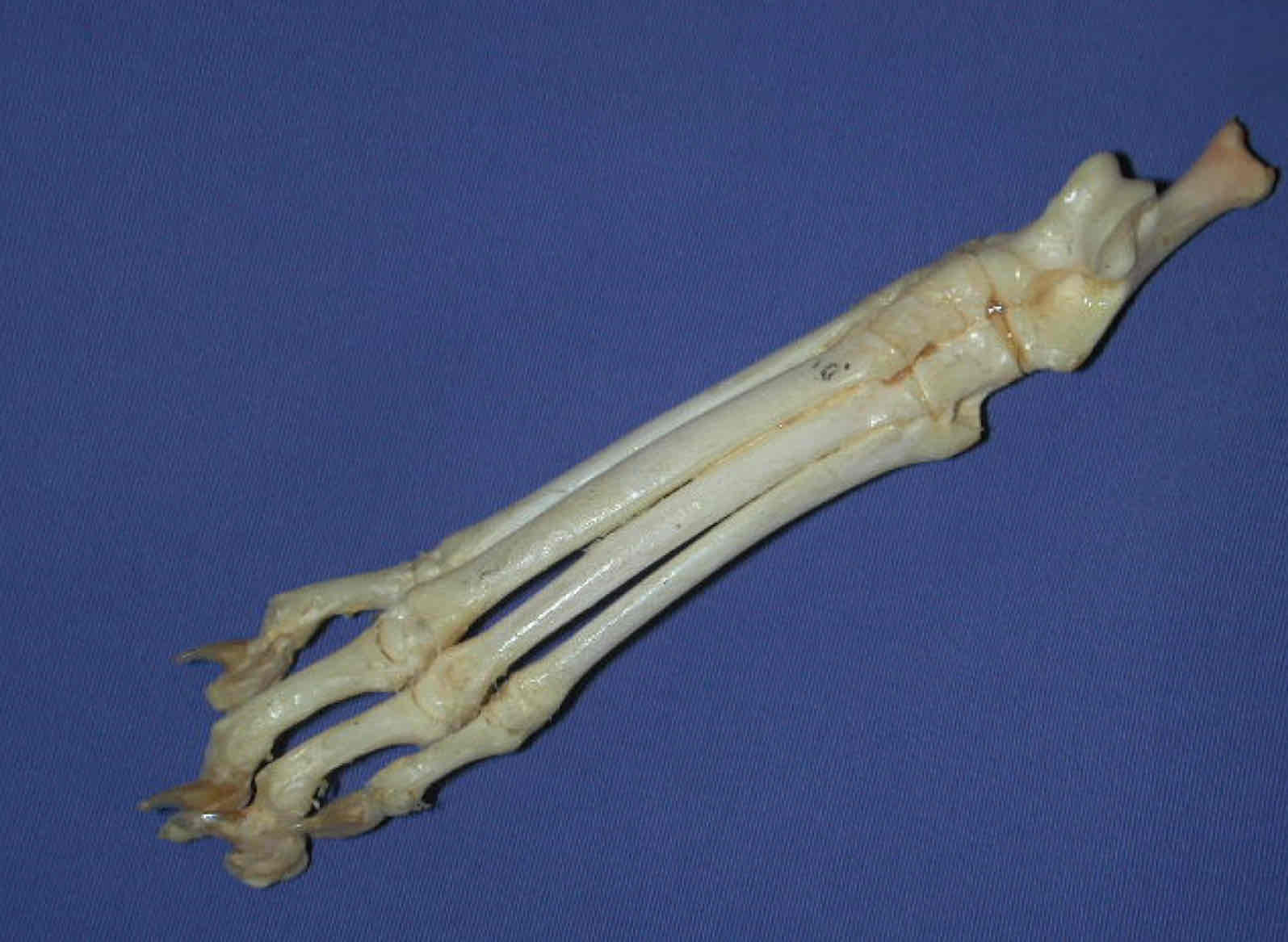
What is this whole structure called?
the pes
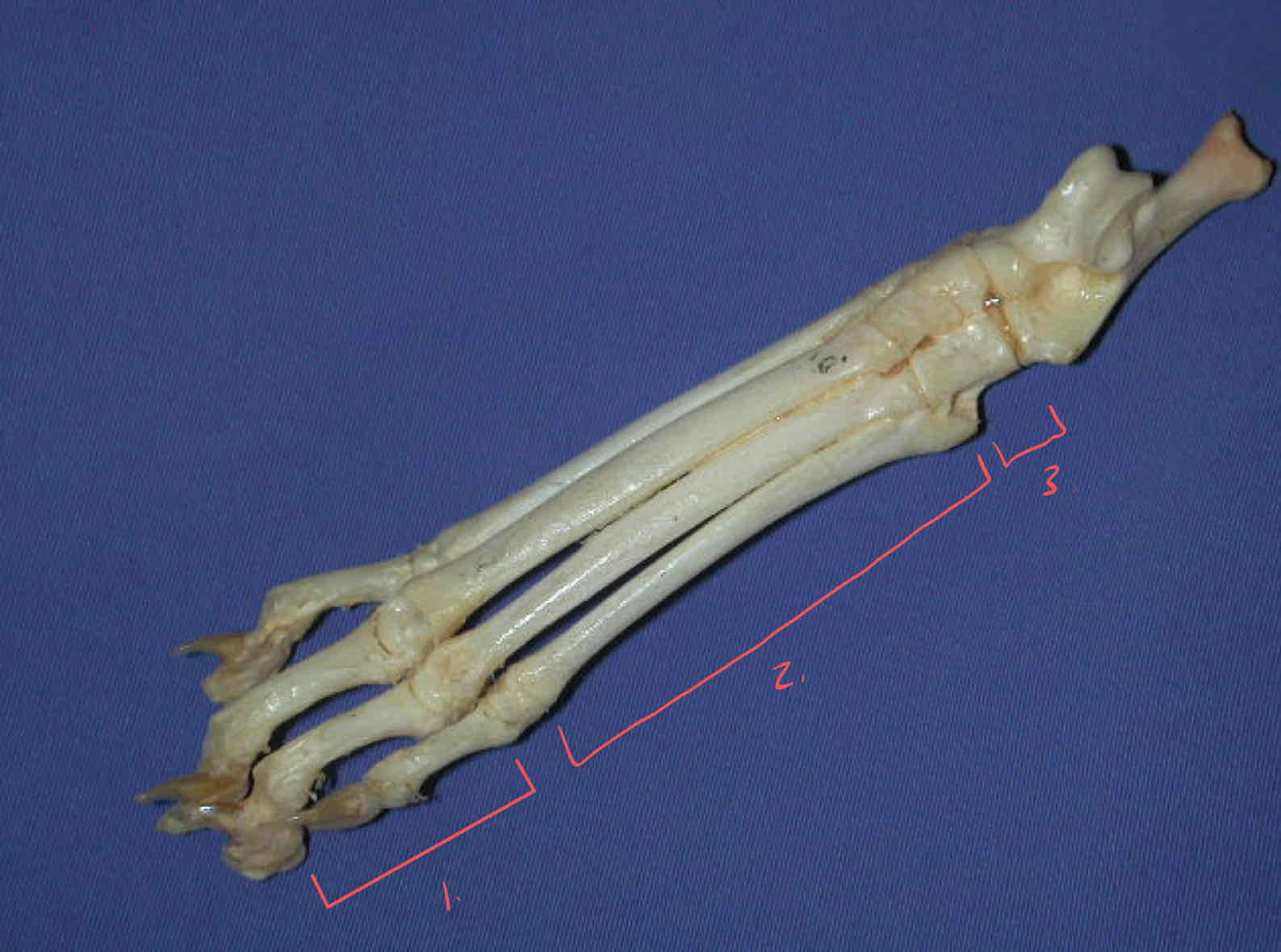
phalanges
metatarsals
tarsals
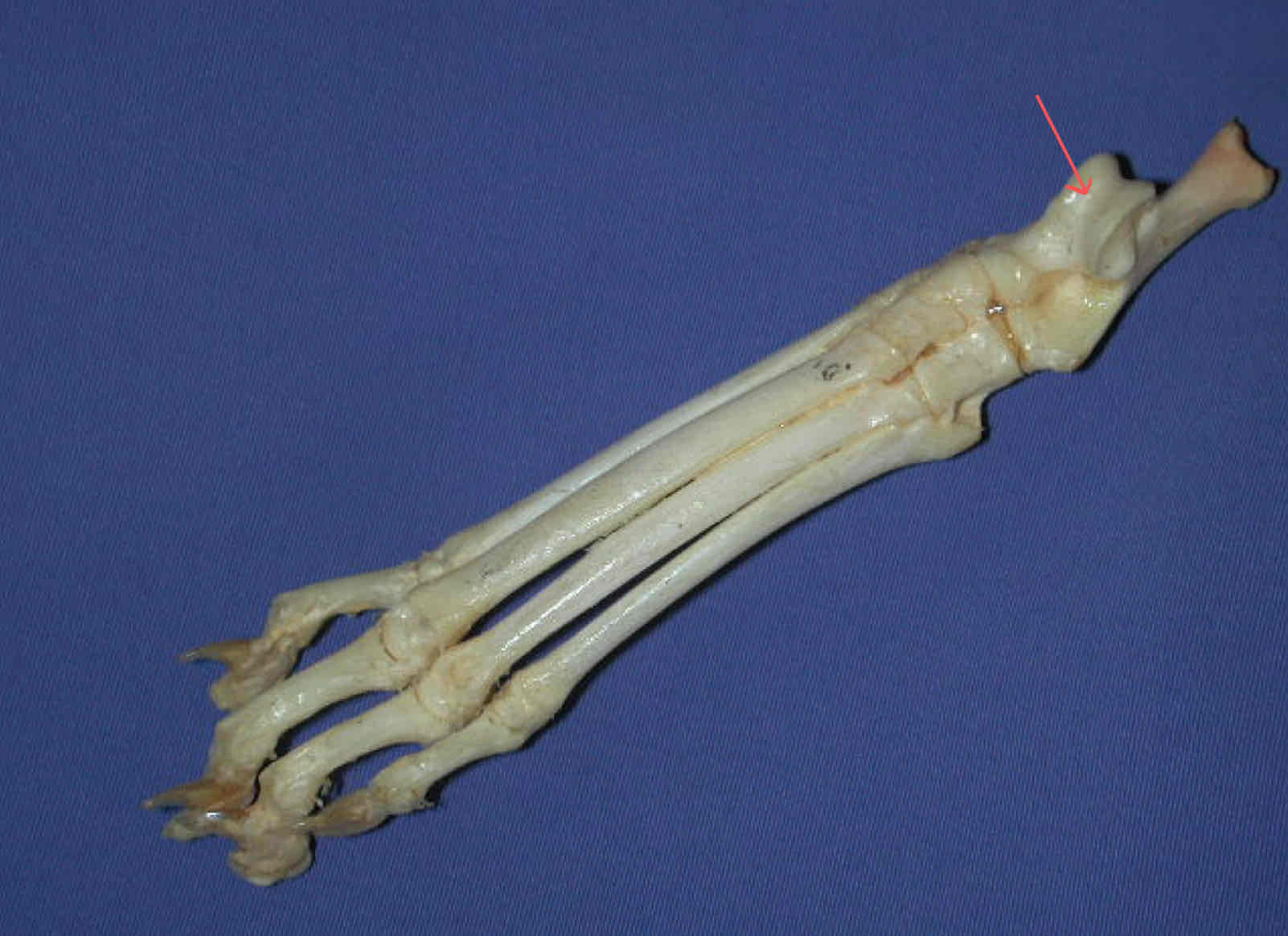
talus
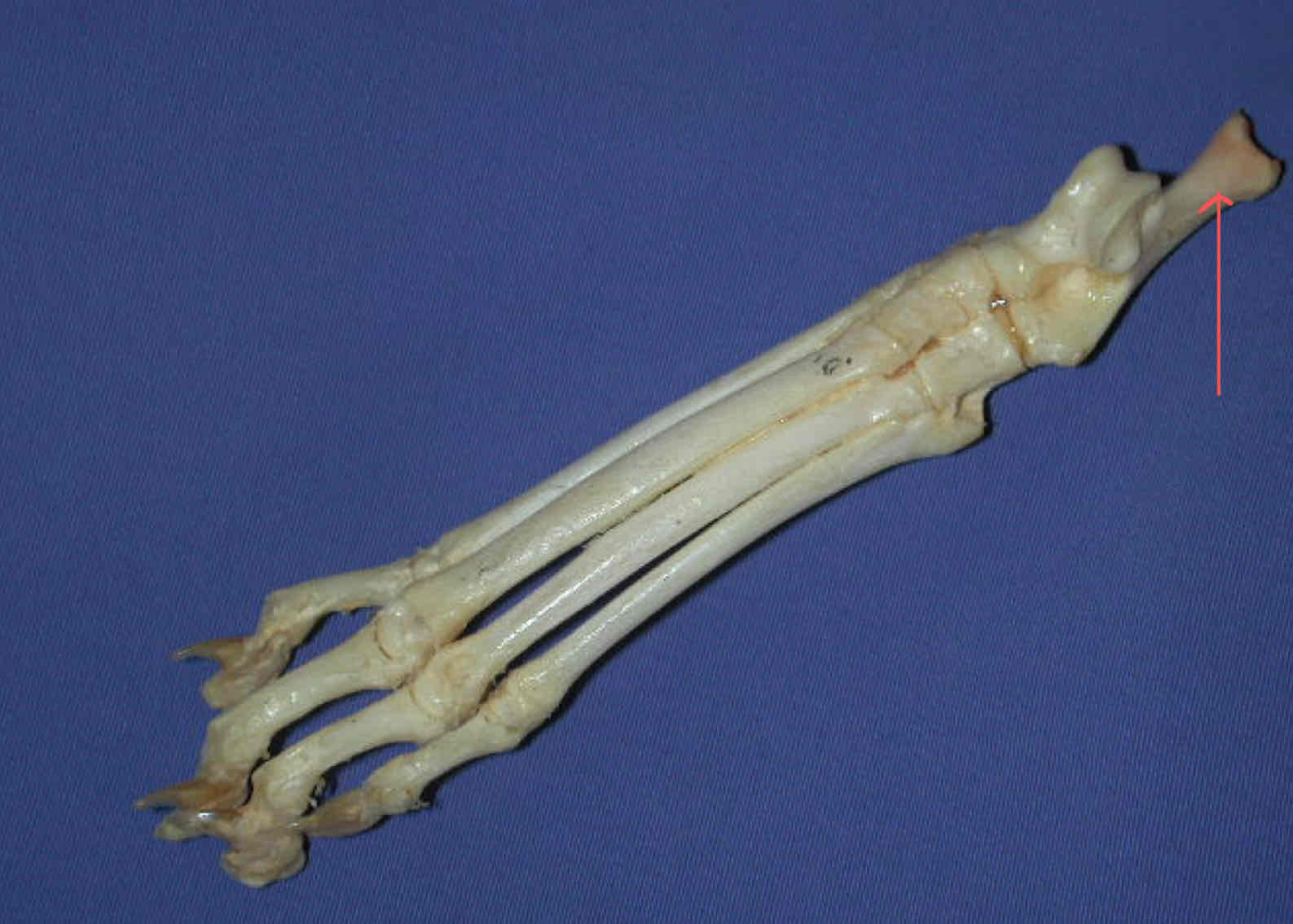
calcaneus - lateral to the talus and the lateral landmark
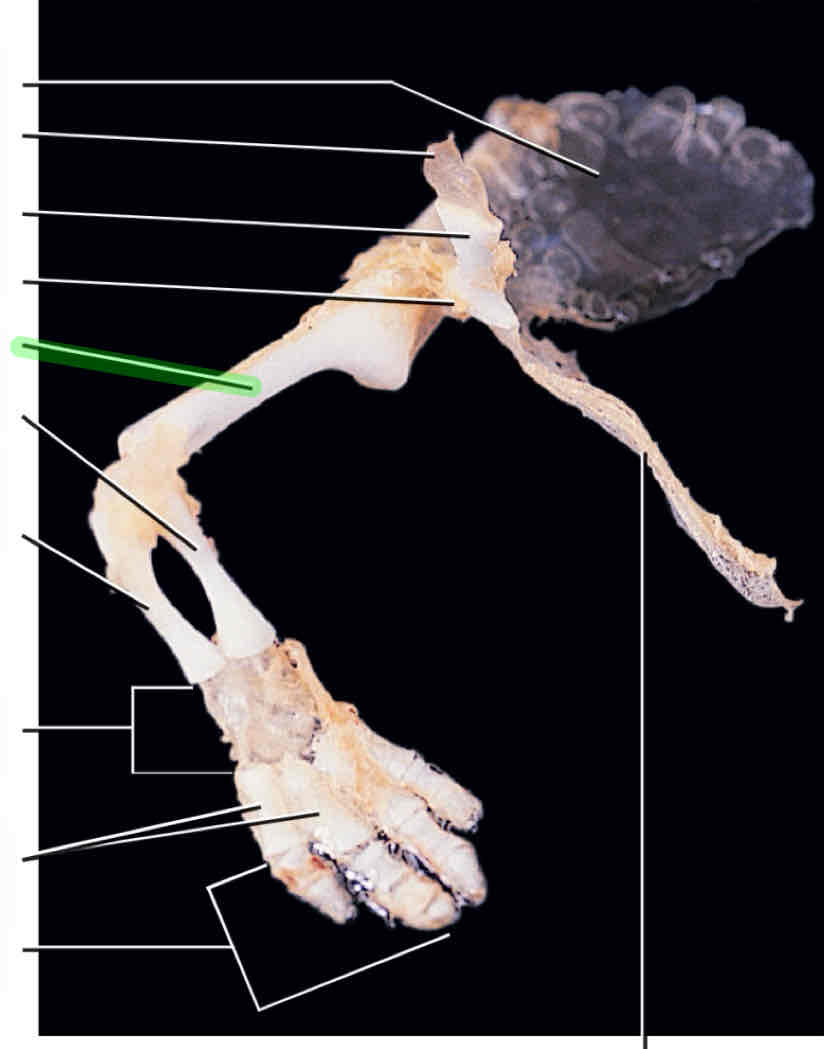
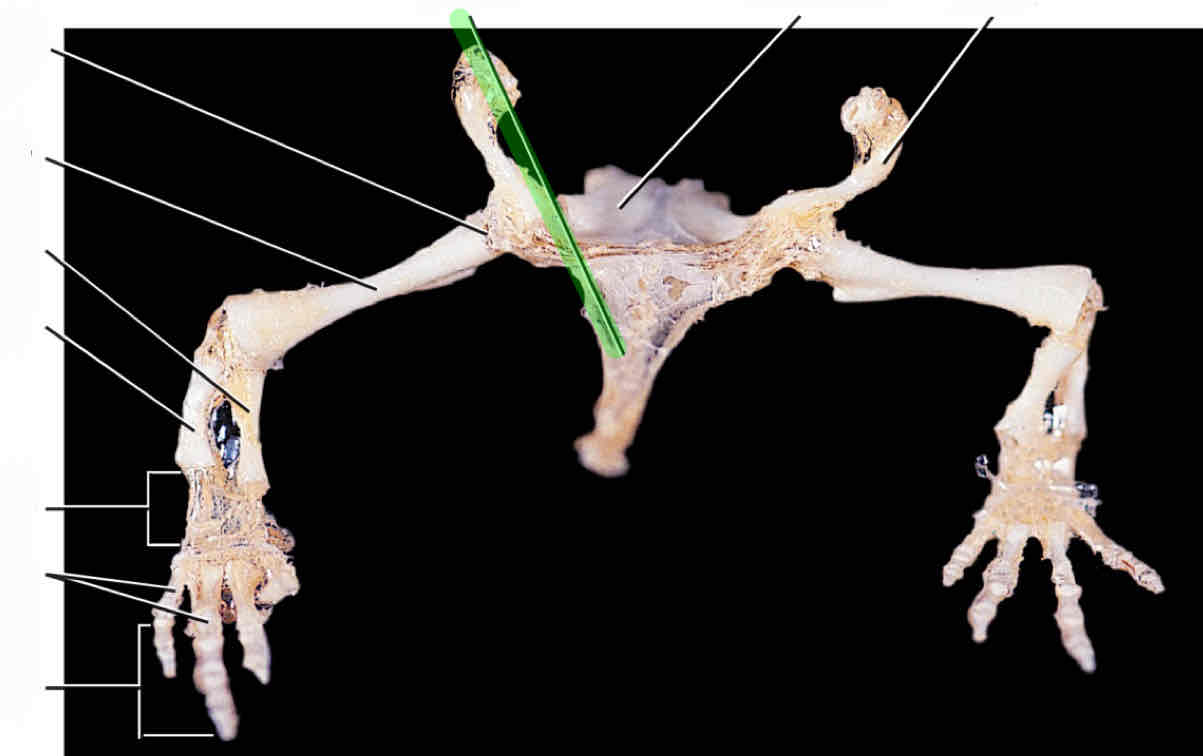
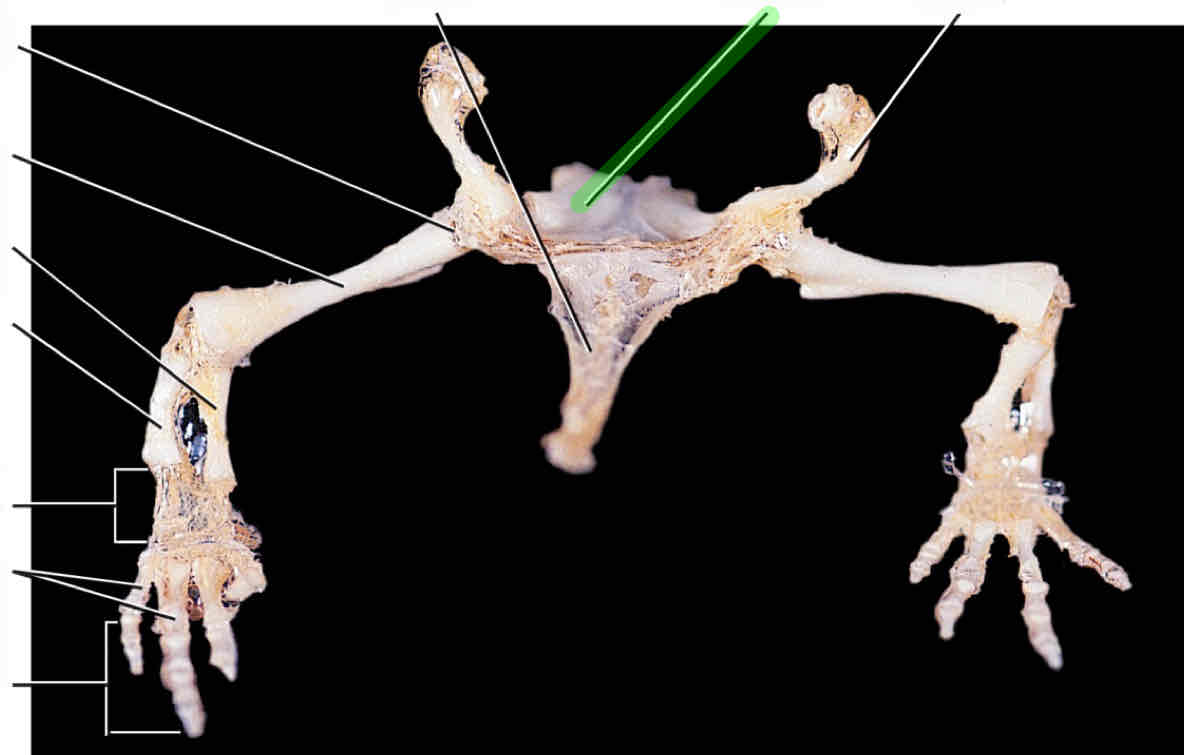
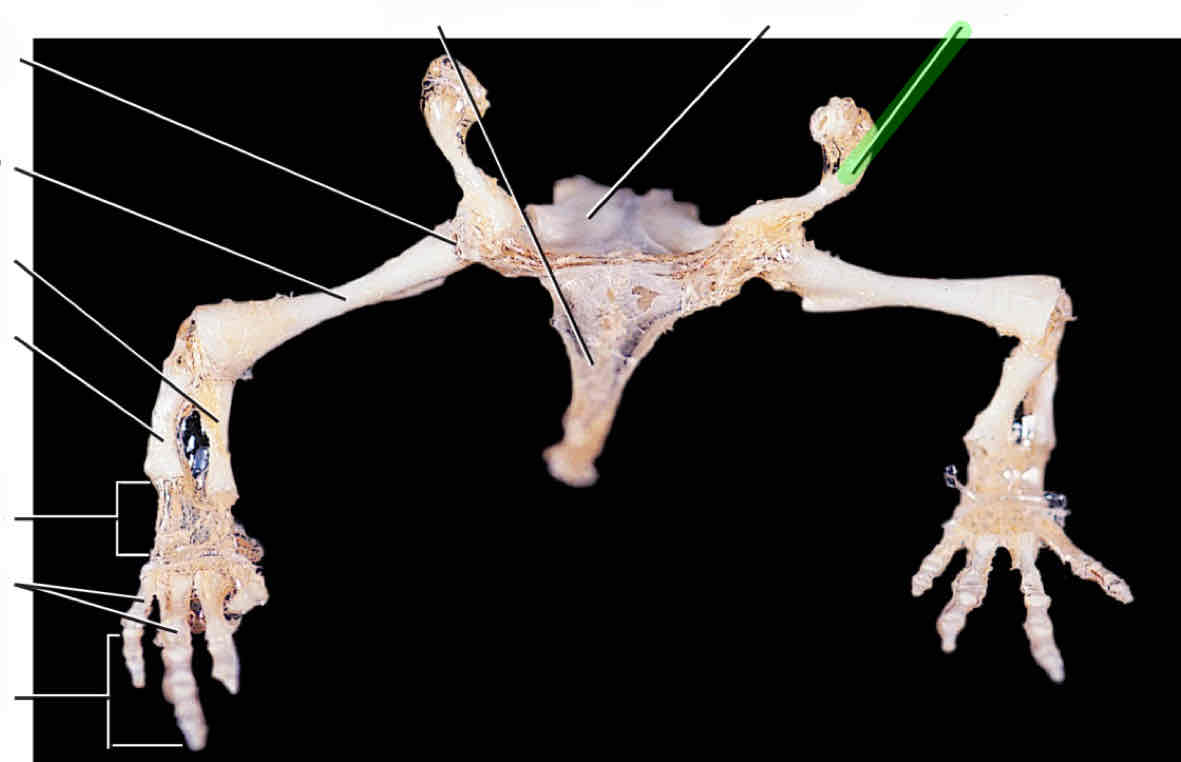
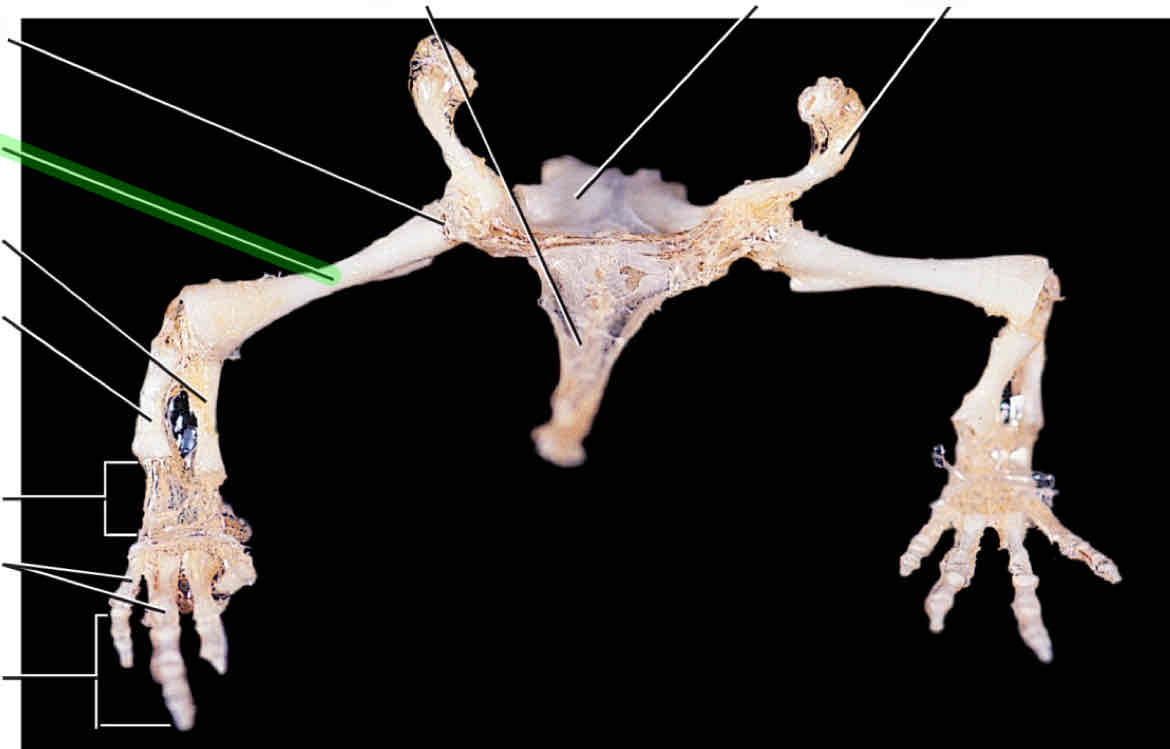
humerus
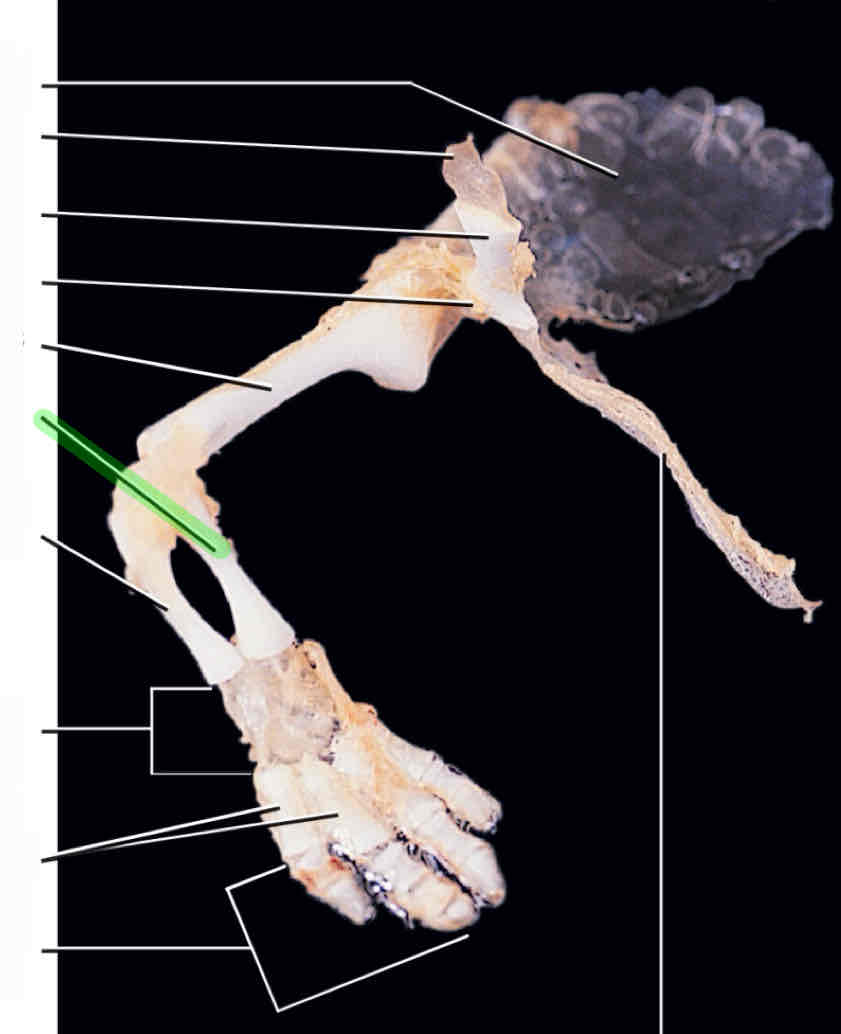
radius
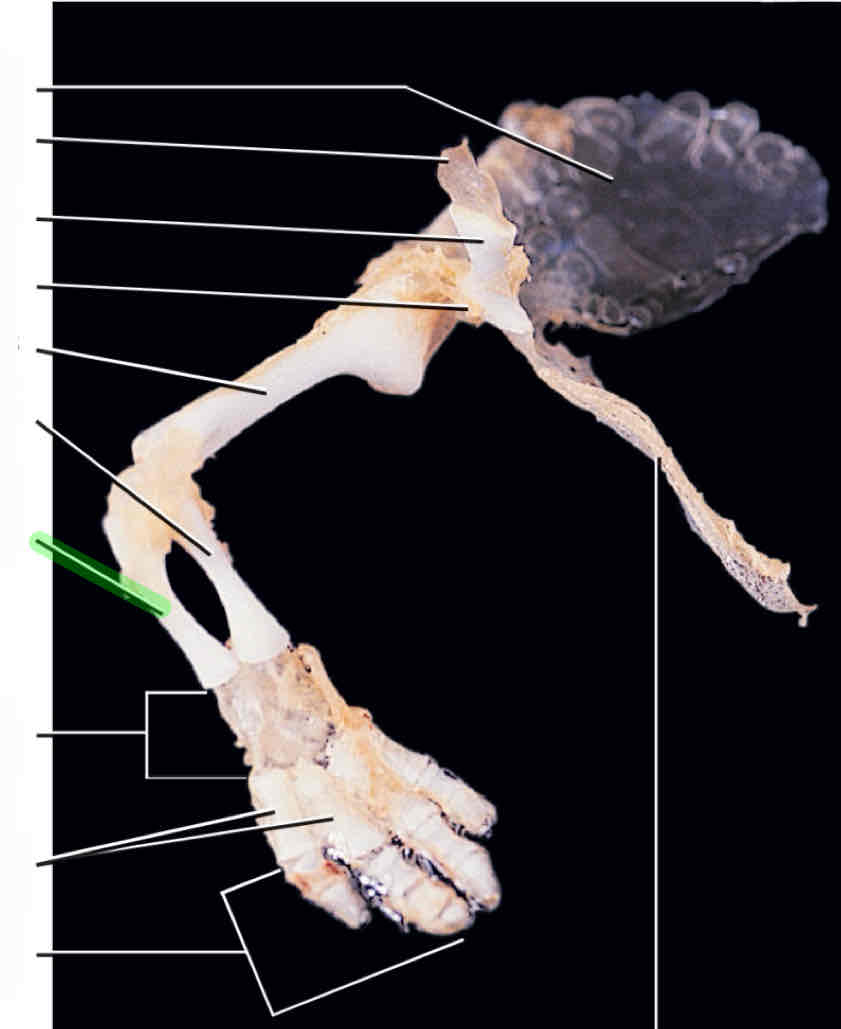
ulna
In Necturus, the radius is ________ to the ulna.
medial
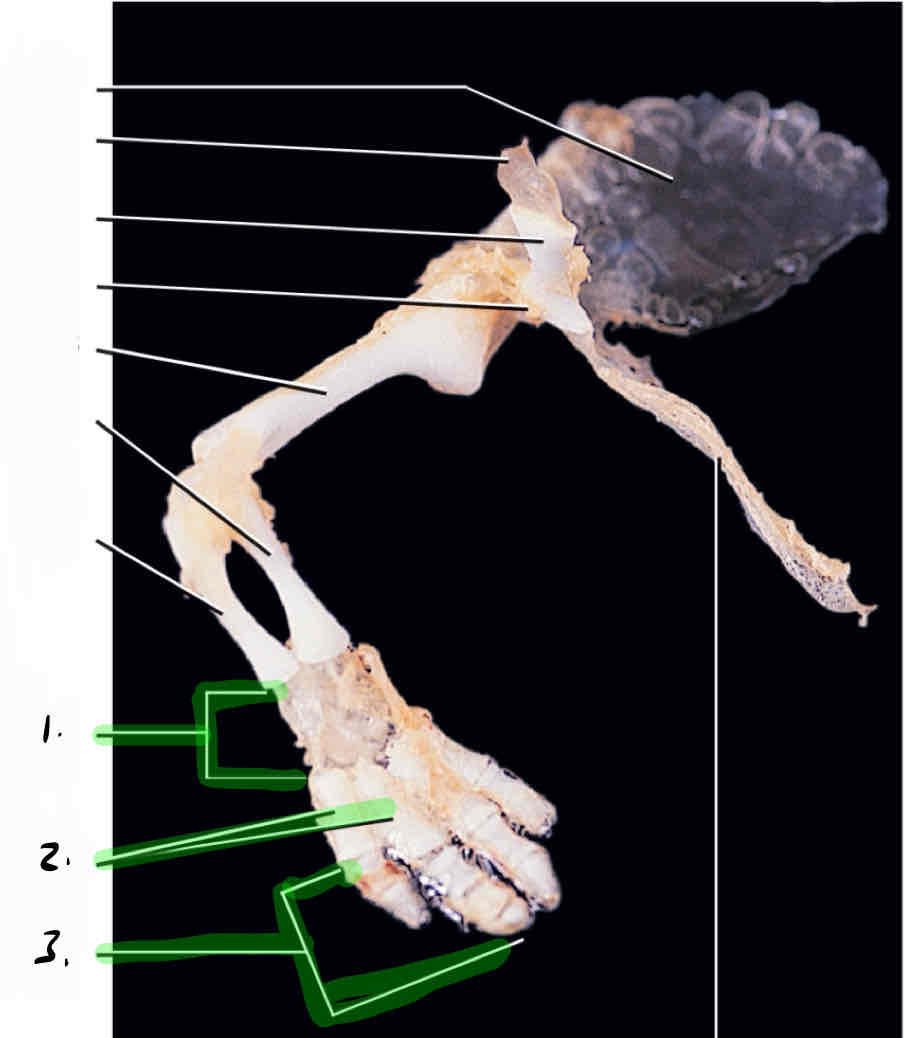
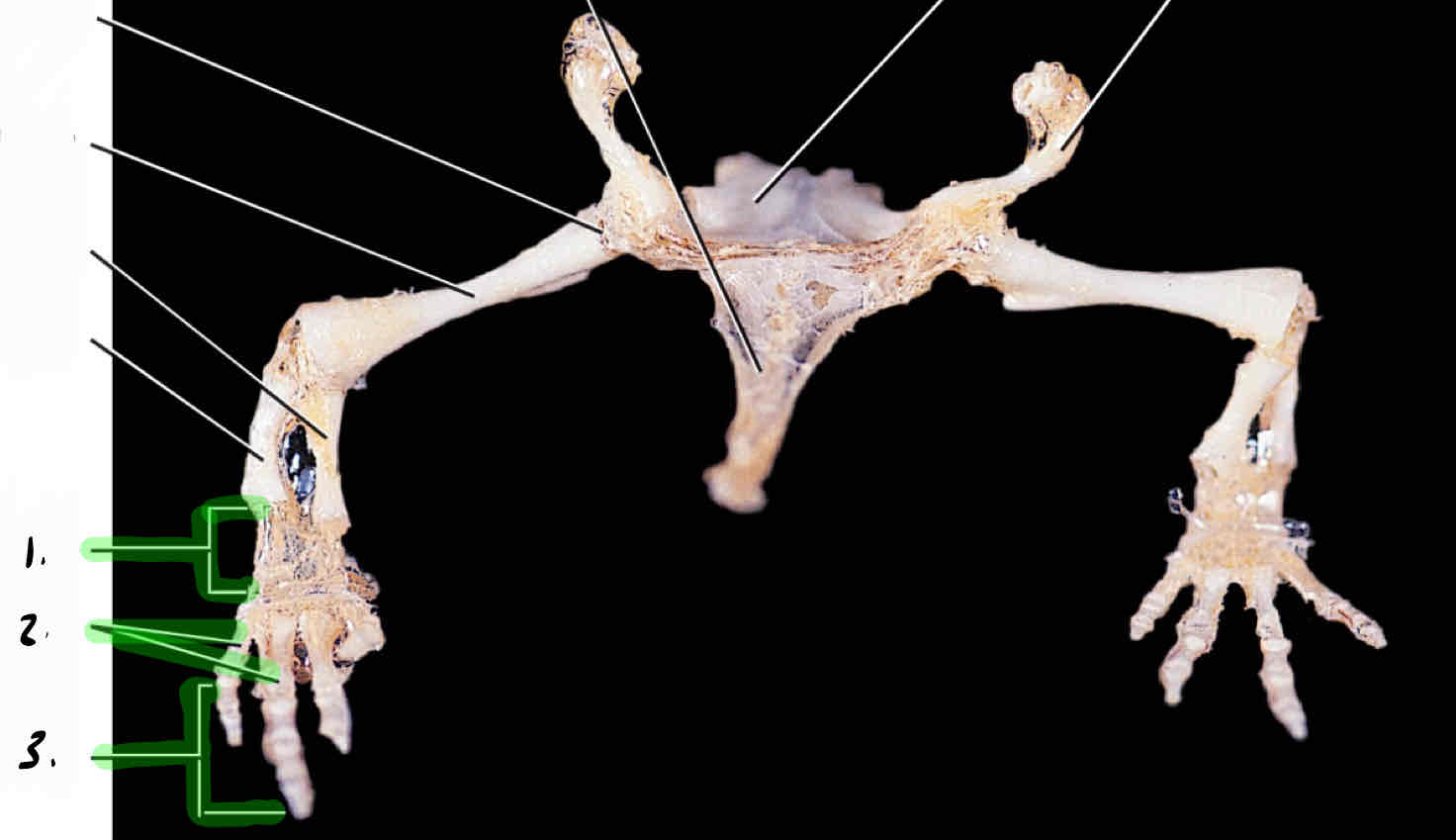
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
pubis
ischium
ilium
femur
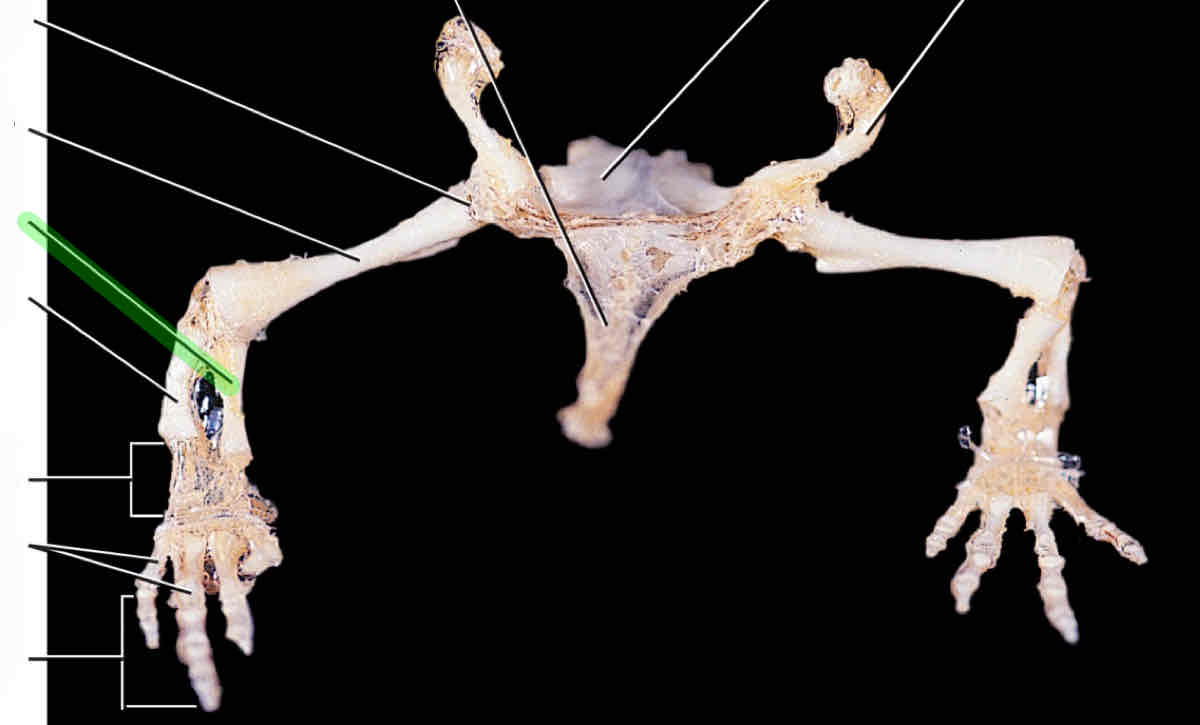
tibia
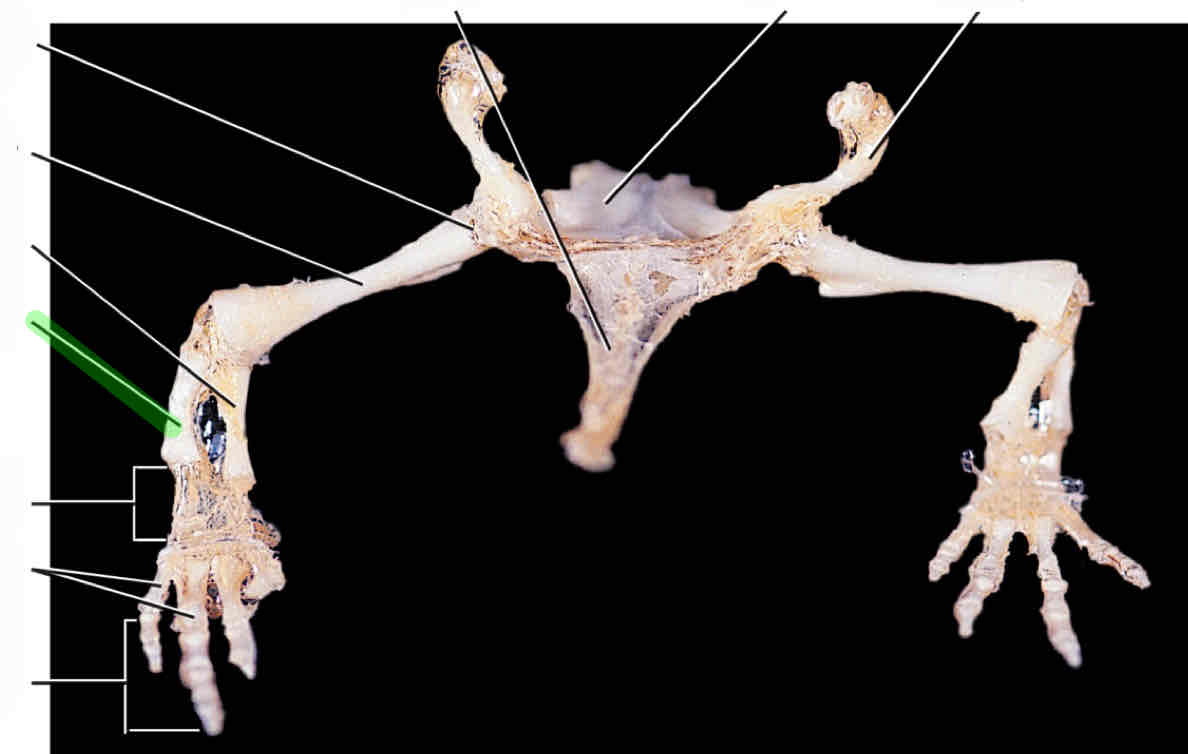
fibula
tarsals
metatarsals
phalanges
What does stylopodium refer to?
the upper arm of the forelimb and the thigh of the hindlimb
What does the zeugopodium refer to?
the forearm of the forelimb and the shank of the hindlimb
What does autopodium refer to?
the manus of the forelimb and the pes of the hindlimb
List some bones that fall under stylopodium
the humerus and femur
List some bones that fall under zeugopodium
radius & ulna; tibia & fibula
List some bones that fall under autopodium
carpals, metacarpals, phalanges; tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges