Praxis 5002
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Phonology
Producing & understanding speech sounds
Morphology
The study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language.
Syntax
The rules, principles and processes that govern the ways words are arranged in sentences
Semantics (Meaning)
Does it make sense? Making sense of text and relaying meaningful connections
Prosody
Intonation & rhythm of speech: pitch, stress
Pragmatics
All factors besides the words themselves that effect how someone interprets your meaning. (verbal tone, body language, etc.) Vary greatly between cultures
Syntactic (Structure)
Does it sound right? Making sense of the actual words in the sentence. Knowledge of how structure of language works
Graphophonic (Visual)
Does it look right? Ability to sound out words or recognize them holistically (visually)
Forms of emergent writing
Drawing, scribbling, letter-like, prephonemic spelling (real letters but random), Copying, Invented spelling (alphabetic principle, represents sound), Conventional spelling
Stages of Reading Development
Emergent, Early, Transitional and Fluent
Emergent Reader
Recognizing letters, words and some language patterns. Beginning to focus attention on letter-sound relationships
Early Reader
Use several strategies to predict a word. Uses Pictures to confirm predictions. Pays close attn. to visual cues & language patterns
Transitional Reader
Likes to read series books as a comprehension strategy. Reads at a good pace. Strategies to figure out most words.
Fluent Reader
Understand & confident about text and how it works. Maintains meaning through longer & more complex stretches of language.
Compound Sentence
Two independent clauses joined by: a conjunction with a comma, a semicolon, a colon, a dash or a conjunction with a semicolon
Complex Sentence
Has an independent clause AND at least one dependent clause
Simple Sentence
One independent clause
Compound-Complex Sentence
At least two independent clauses AND at least one dependent clause
Qualitative Factors
Are subjective. Factors that only a person can see
Quantitative Factors
Are objective. Sentence length, # of difficult words in a sentence. doesn't take outside factors into account
Ways of segmenting words
Morphemes, syllables, onsets & rimes, phonemes
Affixes
Morphemes that can't stand alone
Types of Affixes
Prefixes and suffixes
Prefix
Placed BEFORE a root word to form a new word w/different meaning
Suffix
Placed AFTER a root word to form a new word w/different meaning or grammatical function
Two types of suffixes
Inflectional and Derivational
Inflectional Suffix
Make word plural or indicate tense (-s, -es, -ed, -ing, -er, etc)
Derivational Suffix
Alter a words meaning & its grammatical function (-ic, -ly, -ish, -ance, -al, -ive, -ness, etc.)
Superlative
Of the highest degree
Noun
Person, place or thing
Pronoun
Takes place of a noun (he, she, it, they, etc)
Verb
Identifies action or state of being (sing, dance, believe)
Adjective
Modifies a noun (hot, lazy, funny, healthy)
Adverb
Modifies a verb, adjective or other adverb. Answers When, where, how, in what manner and to what extent
Preposition
Shows a relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence. (up, over, against, into, close to, etc.)
Conjunction
Joins words, phrases & clauses (and, but, or, yet, etc.)
Interjection
Expresses emotion & can usually stand alone (ah, whoops, ouch, etc.)
Etymology
The study of the origin of words and the way in which their meanings have changed throughout history; How a word comes to mean what it means
Connotative
Refers to an implied meaning apart from the thing that is explicitly described. (wall street is an actual street in Manhattan, Its connotatively means wealth and power)
Colloquial
Informal words, phrases or slang in a piece of writing
Rhetorical
Intended to produce an effect or to make a statement rather than to elicit information.
Which two insights about language do children need to acquire to become successful readers?
Alphabetic Principle and Phonemic Awareness
Alphabetic Principle
Insight that spoken sounds can be represented by written letters
Phonemic Awareness
Insight that spoken words are made up of a sequence of somewhat separable sounds, called phonemes
Head Word
The word that determines the syntactic type of the phrase
Omniscient
Knows everything
Telegraphic Speech
Simplified manner of speech where only most important words are used to express ideas (approx. 2 years old)
Slant Rhyme (half rhyme)
Either vowels or the consonants of stressed syllables are identical (ex. eyes, light; years, yours)
Stanza
An arrangement of a certain # of lines, usually four or more, sometimes w/fixed length, meter or rhyme scheme, forming a division of a poem
Amphiboly
Ambiguity which results from ambiguous grammar, as opposed to one that results from the ambiguity of words or phrases
Imperative Sentence
Gives a direct command
Literal Comprehension
Identifying facts directly stated in the passage
Critical Comprehension
Recognizing the strengths & weaknesses of arguments
Dyadic Communication
Refers to dialogic relations or face-to-face verbal communication between two people involving their mutual ideas, thought, behaviour, ideals, liking, disliking, and the queries and answers concerning life and living in nature
Anticipation Guides
Builds interest and activates prior knowledge
Strategy Guides
Help students comprehend & organize
WIRC Thinksheets
(Writing Intensive Reading Comprehension) Guide students through brief segments of text w/specific questions. To be used "during" reading to effectively help students bridge reading and writing and to improve comprehension, vocabulary, and writing skills in all subject areas.
Dialogue Journal
Alternative to conferences. Student responds freely to a piece of writing or to a prompt about the writing
Informal Reading Inventory Levels
Independent, Instructional, Frustration and Listening Capacity
Independent Reading Level
Free reading level. Student can read without teacher assistance
Instructional Reading Level
Students need assistance. Too many unknown words and concepts or background of experience is insufficient
Frustration Reading Level
So difficult student can't read, even with teacher assistance
Listening Capacity Reading Level
Highest level that student can understand what has been read to them. (Informal measure of ability to comprehend spoken language)
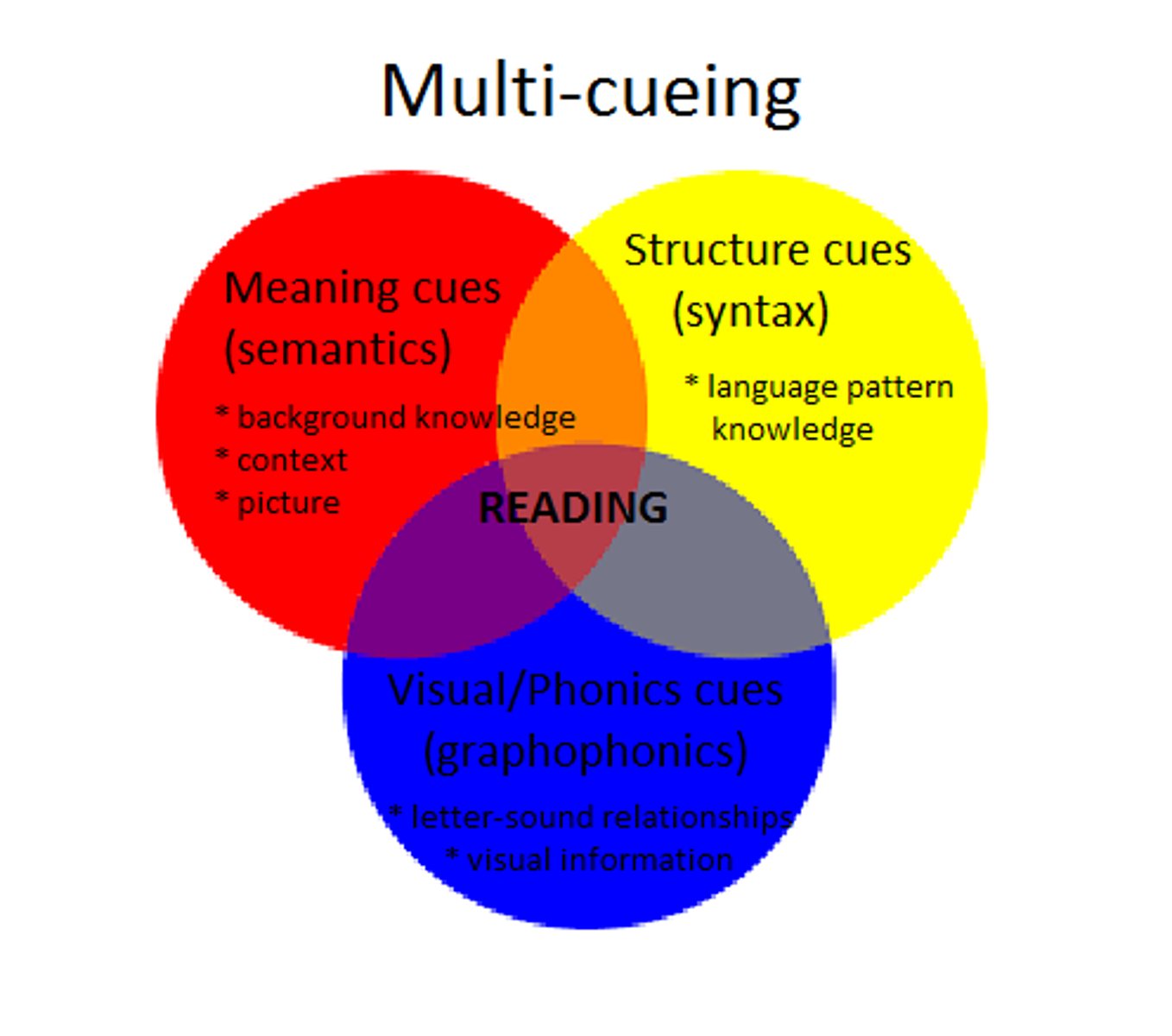
Goodman's Model of 3 cueing systems
Syntactic, Semantic and graphophonic
Maze Passages
Timed measures that measure reading comprehension. Students read Maze passages silently during assessment, so Maze can be administered to a whole class at one time. (above grade 3)
Co-shaping
Teachers provide prompts that help students shape responses that make use of scientific language
Wiki
Used to create a database of information about topic
Six Traits Plus (writing)
Ideas, organization, voice, word choice, sentence fluency and conventions & presentation
Conventions
Grammar, mechanics, spelling, usage, paragraphing, use of capitals & punctuation
Purpose of conventions
Enhances readability and makes it enticing and accessible to read
Traits of writing
Prewriting, drafting, revising, editing and publishing/presentation
Phonics
Study of speech sounds related to reading
Partial Alphabetic Stage
Use letter-sound relationships to read words, may use only two letters and context, may represent word w/first letter and known sound (KR for car)
Full Alphabetic Stage
Process all letter in words, focus on learning how to decode, applying letter-sound relationships, reading is slow & full of effort
Consolidated Alphabetic Stage
Consolidate & process longer & more sophisticated units,
In spelling they use final "e" & double vowels, printed representation bonded w/spoken equivalent, needs lots of opportunities to see words in print to create the needed bond
Integrated Approach - Four processors for decoding
Orthographic, phonological, meaning, and context
Onsets
The consonant or consonant cluster preceding the rime (ex: c at, sh eep)
Rime
Is a vowel or vowels and any consonants that follow the onset (the part of the word that rhymes)
Two approaches to teaching phonics
Analytic and Synthetic
Analytic approach
Consonants aren't isolated, taught within context of whole word
Synthetic approach
Words are decoded by sound, both consonant & vowel sounds are pronounced in isolation
Scope of Reading - Preschool
Exploration of consonants
Scope of Reading - Kindergarten
Beginning and ending consonants, short-vowel patterns
Scope of Reading - First Grade
All major single-syllable vowel patterns, consonant clusters, digraphs, syllabic analysis
Digraphs
Sounds spelled with two letters but have one sound (e.g., sh, ph, ch, th, ey)
Scope of Reading - Second Grade
Major patterns & clusters reviewed, Some advanced patterns & syllabic analysis presented, long vowels
Scope of Reading - Third Grade
Emphasis on syllabic analysis
Closed Syllable Rule
Vowel is short when followed by a consonant
Open Syllable Rule
Vowel is usually long when found at end of word or syllable
Final "e" Rule
Vowel is usually long when followed by a consonant and a final "e"
Choral Reading
Involves two or more people reading in unison
Refrain Reading
Leader reads most, group reads refrain
Antiphoral Reading
Two or more groups alternate
Syllabication
Division of words into syllables
Five approaches to teaching reading
Basal/Anthology, Literature-based, Individualized, Language-experience, Integrated
Five stages of second language acquisition
Pre-Production, early production, speech emergence, Intermediate and advanced
Three areas of knowledge in speaking
Mechanics, Functions and social & cultural rules and norms
Pre-production Stage (2nd language acquisition)
Very little vocabulary, understands 500 words
Early production Stage (2nd language acquisition)
Understand and use common words, listens and speaks 1000 words
Speech Emergence Stage (2nd language acquisition)
Everyday expressions, participates in class, 3000 words