Topic 9: The Genetic Code and Translation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the genetic code?
Translating nucleotide sequence to amino acids
61 “sense” codons to 20 amino acids
3 STOP (non coding)
What is the start codon?
AUG - methionine
What are the three stop codons?
UAA, UAG, UGA
What does degeneracy mean in terms of the genetic code?
An amino acid can be specified by multiple codons
Ex. Serine has 4 different codons
Is the genetic code the same for all organisms?
Yes - universal for prokaryotes, viruses and eukaryotes
What is the directionality of codons?
Read and written 5’ to 3’, as they appear in mRNA
What are all the reading frame options?
+1 - First ribonucleotide
+2 - Second ribonucleotide
+3 - Third ribonucleotide
dictated by AUG - methionine start
Why is there no +4 reading frame?
It is the same as +1 reading frame
What are tRNAs?
Adaptors between ribonucleotides and amino acids
translates mRNA sequence (codons) to amino acids of polypeptide
Are tRNAs single or double stranded? How do they fold?
Single-stranded RNA
They fold and form a 2-D cloverleaf by self complementary base pairing, as well as other 3-D shapes
What end of the tRNA contains the sequence that an amino acid attaches too?
3’ end contains a 5’-CCA-3’ sequence (amino acid arm)
What is an aminoacyl -tRNA?
A tRNA with a specific amino acid attached to the 3’ terminal adenosine (charged tRNA)
How does the tRNA bind to the mRNA?
Anticodon of tRNA base pairs antiparallel to the codon of the mRNA
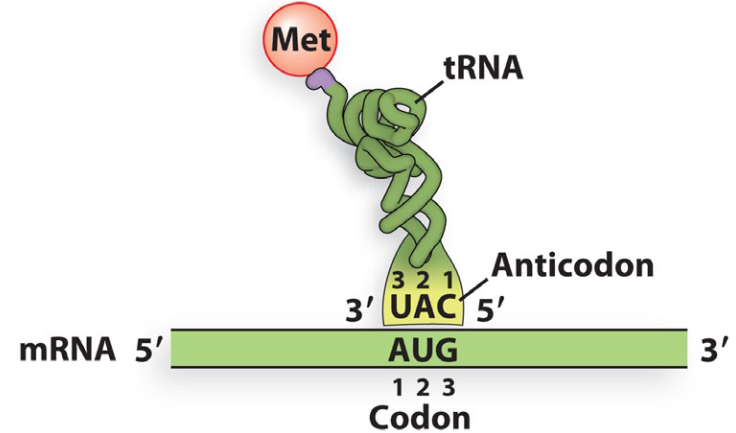
Is amino acid specificity of the tRNAs determined by the anticodon?
No - it is determined by the aminoacyl-tRNA transferases that attach amino acids to tRNAs
specificity of the genetic code lies in the accuracy of protein enzyme-based aminoacylation of tRNA
Are there 61 different tRNAs that bind to the 61 “sense” codons?
No - there is approx. 32 tRNAs because some tRNAs can read more than one codon!
How are tRNAs able to read more than one codon?
‘Wobble’
the base (G or U) at the 5’ end of the anticodon can form weak hydrogen bonds with more than one type of base at the 3’ end of the codon by non-Watson Crick base pairs
Can the 5’ and middle bases in the anticodon wobble?
No, they are precise and undergo Watson Crick base pairing
What forms inosine?
Inosine (hypoxanthine) is formed when adenosine is deaminated by adenosine deaminase
Where is inosine found and what does it base pair with?
Found at the 5’ end of the anticodon of tRNA and can base pair with C, U, or A
What is the large subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes composed of? What does it do?
Large subunit (50S):
5S and 23S rRNA
contains the peptidyl-transferase center for the formation of peptide bonds and the exit tunnel for polypeptide (joins amino acids together)
What is the small subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes composed of? What does it do?
Small subunit (30S)
16S rRNA
decoding center whereby the charged tRNAs read and decode the codons of the mRNA and contains the entry and exit channels of mRNA
What does the unit S measure?
Svedburg unit: measure of sedimentation velocity or mass
Are the two subunits always attached as one unit?
No, they exist as separate subunits in the cytoplasm, but join together on the mRNA
What does the eukaryotic ribosome contain?
Large subunit (60S)
5.8S, 5S, and 28S rRNA
Small subunit (40S)
18S rRNA
Slightly larger than prokaryotic ribosome
What does the P site stand for and do?
Peptidyl site: binds the tRNA attached to the growing peptide chain
What does the A site stand for and do?
Aminoacyl site: binds charged tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added
What does the E site stand for and do?
Exit site: binds the tRNA (uncharged) that carried the previous amino acid
How are the P and A sites positioned?
Optimally positioned close together to allow for peptide bond formation
What catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds within the ribosome? How do we know this?
rRNA catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds
No r-proteins within 18 angstroms of the peptidyl transferase active site in the large subunit
How did they discover rRNA was responsible for peptide bond formation?
Treated isolated 50S subunit with SDS, phenol and proteinase to remove r-proteins, but keeps the rRNA intact
Detect peptide bond formation between N-formylmethionine in P-site and puromycin, an aminoacyl-tRNA analog in the A site
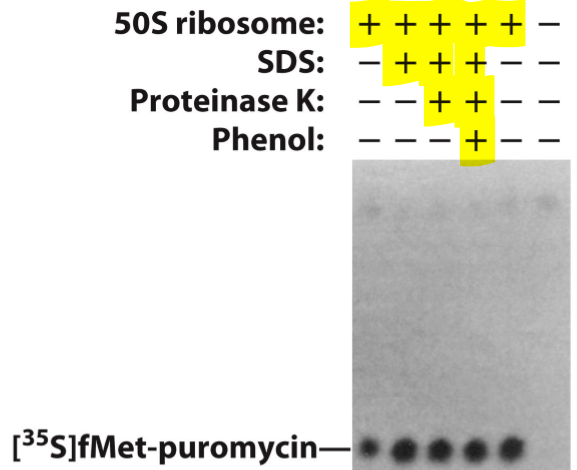
What were most of the contacts between tRNA and ribosome found to be through this experiement?
Via 16S and 23S rRNA - not r-proteins
What do r-proteins do?
Secondary elements in the ribosome that have a stabilizing or regulatory role, rather than an enzymatic role
What do aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases do?
Add amino acid to tRNA (charging)
What is the adenylation step?
Formation of intermediate aminoacyl-AMP whereby a carboxyl group of an amino acid reacts with the alpha phosphate of ATP + pyrophosphate
What is the tRNA charging step?
Aminoacyl group is transferred from enzyme bound aminoacyl-AMP to its specific tRNA either on 2’-OH or 3’-OH of the 3’ terminal adenosine of tRNA
What dictates a class 1 or class 2 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase?
Class 1: adds amino acid to 2’-OH of terminal adenosine of tRNA
Class 2: adds amino acid to 3’-OH
What happens following class 1 amino acyl-tRNA synthetase?
Aminoacyl ester linkage on the 2’-OH spontaneously migrates to the 3’-OH by transesterification
How many aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are there?
20, one for each amino acid
most aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases can add an amino acid to more than one tRNA (32) due to degeneracy of genetic code
What determines the correct binding of tRNA to the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases?
Certain nucleotides on the tRNA, but NOT the anticodon
What is kinetic proofreading?
An incorrect charged tRNA (wrong aa attached) is transferred to a second active site with proofreading activity and hydrolyzed
What determines the fidelity of charged tRNAs?
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and not ribosomes
Ribosomes just take charged tRNAs and form peptide bonds, but does not consider if it is the correct aa
How many types of tRNAs charged with methionine are there with an anticodon that recognizes 5’-AUG-3’
2 types:
Initiator tRNAMet that binds the first AUG codon
tRNAMet for codons in interior of mRNA
What does methionine have attached to it that recognizes a unique feature of the initiator tRNA in prokaryotes?
Methionine has a formyl group added to it by transformylase
it is a bulky group, and therefore stops peptide formation in front of fMet (how most bacterial proteins start)
For eukaryotes, there is a specific sequence in the anticodon arm that is recognized by what?
Initiator protein eIF2
What is the first step in translational initiation in prokaryotes?
Initiation factors IF1 and IF3 bind 30S ribosome (small subunit) and prevents premature binding of 50S and 30S and blocks tRNA premature binding to A-site
What is the second step in translational initiation in prokaryotes?
The mRNA binds to 30S by base pairing to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (ribosomal binding sequence) with 16S rRNA to position AUG start codon to the P-site (est. correct reading frame, because initiator tRNA adds fMet to P-site)
What is the third step in translational initiation in prokaryotes?
GTP-bound IF2 binds to initiator tRNAfMet and brings it to pase pair its anticodon with the AUG start codon of mRNA in the P-site
What is the fourth step in translation initiation in prokaryotes?
Conformation change in 30S subunit releases IF3 enabling association with 50S
What is the last step in translation initiation in prokaryotes?
GTP-bound IRF2 is hydrolyzed to GDP + Pi and all IFs dissociate from the ribosome
this results in a functional 70S ribosome called the initiation complex and is now ready for translational elongation