W7 - Hemolytic Anemia, Maternal Allo, G Antigen, Serological
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
What is polyagglutination?
A group of cells that agglutinate regardless of blood group
Cryptic antigen on rbc membrane is exposed and polyagglutinin are naturally occurring
detected when preforming crossmatch if donner cells are polyagglunatble
What are the categories of polyagglutination?
1) Acquired —> due to bacterial enzyme on rbc membrane
2) Inherited —> due to somatic mutation of hemopoitic tissues
What is the dolichos biflorus used for?
To differentiate between A1 and A2 cells
Which plant lectin is used to differentiate between A1 and A2 cells?
Dolichos Biflorus
Which plant lectin is used to screen for anti-H ?
Ulex europaeus
What is Ulex europaeus used for?
To screen for bombay pt aka pt for anti-H
What is HTLA?
High Titer; Low avidity
aka the description of the antibodies, NOT an antibody itself
What are the criteria for HTLA?
High titer: >64 and low avidity: weak to 1+
What does the serology screen look for HTLA?
Screen & panel cells reacting w+ to 1+
Autocontrol: Nonreactive
1:10 dilution: w+ to 1+
Double titration: Tubes 1 to 7: 1+
What are some examples of aquired polyagglutination?
T, Tk, Acquired-B
What are some example of inherited polyagglutination?
Tn
Which antibodies exhibits HTLA characteristics?
Anti-Chido
ANti-Rodgers
Anti-York
ANti-CsA
Anti-Knops
Which antigen has two name depending on where it’s loctated? What are the name?
Bg
RBC —> Bg antigen
Platelets —> HLA class I
What is the notation for Bennet-Goodspeed antigen?
Bg
What is the signficance of Bg antigen?
Can cause immediate and delayed hemolytic transfusion rxn
What would you use to remove Bg antigen?
Chloroquine diphosphate and EGA
Which HLA antibodies are found on RBC?
Bg antigens
What are some characteristics of Anti-CD38?
monoclonal antibody used to treat multiple myeloma
normal rbc contains weak CD 38
anti-CD38 interferes w/ antibody screen, ABID and cross match
What should you use to remove CD38 from RBC?
DTT
Why is it important to treat Anti-CD38?
Pt w/ multiple myeloma has a bunch of CD38 and so they need to be washed with DTT or else they cannot tell which antigen is on the cell : (
What is some characteristics of Anti-CD47?
CD47 present on RBC and platelets
Might cause ABO discrepancy
Not denatured by DTT
correlates to hematologic and solid malignancies
What type of antibody is Anti-CD47? Why might it cause a problem?
anti-CD47 is IgG4 —> not detected by Gamma-clone anti-IgG
How to resolve anti-CD47?
Allogeneic adsorption
What is IVIg used to treat?
WAIHA, humoral immunodeficiencies, chronic immune thrombocytopenia purapura
So when youre doing panel cells and you see weak reactions; what should you think of?
Bg antibodies,Anti-CD 38, Anti-CD47 or IVIg
What is the definition of hemolytic anemia?
Shortened RBC survival mediated through the immune response specifically by humoral antibody
What are some classification of Immune HA?
1) AIHA
2) Alloimmune HA
3) Drug induced HA
What are some categories of AIHA?
Warm AIHA
CAS
Mixed type
PCH
What are some categories of Alloimmune HA?
Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
HDFN
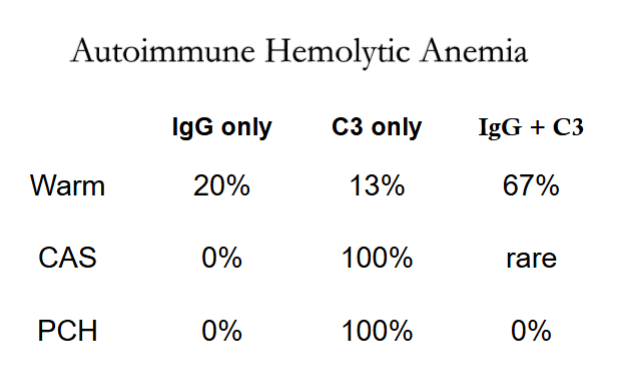
What is the % of C3 only in the warm?
13%
What is Cold agglutinin syndrom?
When IgM autoagglutinin binds to RBC in peripheral circulation and then binds/activates complement
IgM dissociates when RBC returns to warmer parts of circulation but RBC remains coated w/ complements
What are the types of Drug-Induced Hemolytic anemia?
1) Drug-adsorption
2) Autoantibody
3) Drug-dependent
What are the 2 forms of HTR?
1) Alloantibody —> Patient makes antibody against donor’s antigen
2) Passive: Donor’s antibody against recipient’s antigens
What is the binding site of antigens to RBC?
Fab
What is the binding site of antigen to complement?
Fc
What is the main antibody in Warm IgM AIHA?
IgM agglutinins reactive @ 37C
What would you expect from DAT and IAT in Warm IgM AIHA?
DAT Control +; IAT: w= @37C and v weak @AHG
What is the eluate of Warm IgM AIHA?
Hemolysis at 37C
What is the antibody in WAIHA?
Usually IgG
What is the IAT / DAT of WAIHA?
IAT: Panagglutination
DAT: IgG only
What should you see in the Eluate and Adsorption in WAIHA?
Pannagglutination; Adsorbed plasma non-reacive if no alloantibody is present
What is the specificity of WAIHA?
Usually anti-e
Why is Warm IgM AIHA more fatal?
Because it involves IgM which can bind complement thus resulting in intravascular hemolysis and severe hemolysis
What is antibody responsible in Mixed Type? What temps is it usually reactive at?
IgM and IgG; cold reactive @ 4C and >30C
What is the expected DAT of mixed type?
IgG and C3 or C3 only
Which temperature do we do adsorption for mixed type? Why?
37C first and then 4C ; Because we have both IgG and IgM :^]
How can you get a negative DAT AIHA?
When there is not enough IgG /IgM or IgA that is undetectable
What happens when you have a DAT negative AIHA?
Send to LARC fo super Coombs :^]]]]]]
What are the criteria to do phenotyping?
Pt has no transfusion in the last 8 weeks
Clean the cells with EGA or Chloroquine diphosphate
What are some treatment of WAIHA?
Corticosteroid
IVIg
Splenectomy
Immunosuppressive drug
What are some characteristics of Cold Reactive Antibodies?
Reactive @ IS
Enhanced reactivity @RT, 18C, 0-4C
ABO discrepancy in reverse typing
Positive antibody screen
What are the usually suspect for cold reactive antibodies?
anti-IH, anti-I, anti-i
What is the DAT for Cold Reactive Antibodies?
DAT positive for complement only
What is the difference in elution and adsorption?
Elution is testing the pt RBC and getting the antibody that was covering their cells
Adsorption is testing the pt plasma and checking which cells adsorbs it
What are the 4 mechanisms that leads to drug-related antibodies?
1) Immune complex/ innocent bystander
2) Drug adsorption
3) Membrane modification
4) Methyldopa induced
What is immune complex?
When the drug binds with the antigen to form a neo antigen on the RBC which complement will bind to the cell and cause acute intravascular hemolysis
What are the drugs involved with immune complex?
Quinidine
Phenacetin
What is drug adsorption?
When you take the drug and then your body makes an antibody to the drug
What are the drugs involved in drug adsorption?
Penicillin
streptomycin
cephalosporin
What is membrane modificaiton?
When the drug changes the RBC membrane that causes protein to attach to the membrane
What are the drugs involved in membrane modification?
Cephalosporins
What is Methyldopa induced drug-related antibodies?
When the drug forms antibodies that mimic autoantibodies found in WAIHA
Which drug is involved in Methyldopa induced?
Methyldopa
What are the 2 disease associated with Maternal alloimmunization?
1) Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN)
2) Fetal/Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (FNAIT)
What is Fetal Maternal hemorhage?
When there is an injury to the mother —> resulting in maternal IgG crossing the placenta and causing UgG RBC to be removed from circulation —> resulting fetal anemia —> immature RBCs are released in response —> enlarged spleen and liver —> liver dmg due to plasma protein —> cardiac failure will cause edma —> hydrops fetalis —> fetal demise
What is the bio-marker that we check for to see if there is extra vascular hemolysis?
Increase bilirubin
What are the 2 different ways to monitor the progression of anemia?
1) Amniocentesis
2) Doppler
What is HDN?
Hemolytic Disease of the New Born
What is the path of HDN?
Hemolysis —> Increase unconjugated bilirirubin —> Kernicterus —> permanent brain dmg
What is Kernicterus?
High level of bilirubin —> causing dmg in the brain
What is some treatment of HDN?
Neonatal exchange transfusion
Phototherapy
What are some antibodies that cause HDFN?
Anti-A,B
Rh antibodies (D>E>C>c)
Anti-K, -Kpa, -Jsa, -Jsb
Anti-Jka, -Jkb, Jk3
Anti-Fya, -Fyb
Anti-S
What can increase the titer of ABO antibodies?
Yeast-Based food (yogurt), tetanus injection
What is the pathogenesis of Fetomaternal hemorrhage?
Baby Rh+ antigen yeets into the mother —> the mom body is like oh hell naw and make anti-Rh antibodies —> shoves the anti-Rh back into the baby (or the next one) and murders the RBC
What is para?
number of birth
What is gravita?
Number of pregnancy
What is included in Prenatal Testing?
Antibody screen to evaluate the risk of HDFN and to see if mom would be a good candid for Rogam (or Rh-immune globulin prophylaxis (RhIG)
What is the significant titer for anti-D?
32
What is the significant titer for other anti-bodies?
16
What are the procedures during labor and delivery?
Collect cord blood in EDTA tube (both the mom + baby) —> ABO/Rh and DAT are performed on the cord blood —> collect mom postpartum specimen an hour after delivery
Why do you need to test Rh on the new born after it’s been popped out?
Because we need to know if its Rh pos or neg so that if it is a weak D then mom needs to recieve rogam to prevent making anti-D
What happens when the mom and baby is Rh Neg but DAT is positive?
Cancel Rosette and order Kleihauer-Betke test —> Baby’s Rh is invalid due to positive DAT —> Calculate how many vials of RhIg needed
What happens when the mom is Rh neg and the baby is Rh neg and the DAT is also neg?
Perform Weak D testing on cord blood —> RhIg is given within 72 hours after delivery
What is the protocol when Mom is Rh Neg and baby is Rh Pos w/ DAT neg
1) Perform Rosette testing on the mom
Neg Rosette —> Give 1 vial of RhIg
Pos. Rosette —> Send to hematology for Kleihauer-Betke test
2) Calculate how much RhIg is needed based on KB results
What is the Rosette test?
D positive fetal RBC that is coated with Anti-D and clings to a D positive indicator cells
What is methodology of Kleihauer-Betke Stain?
Hgb F is resistant to acid elution —> fetal cell will appear pink and adult cells will be ghost
How much blood can 1 vial of RhIg neutralize?
30 ml of whole blood or 15ml of packed cells
How much is in 1 vial of RhiG?
300 ug
What is the formula to calculate how much RhiG to give a pt?
# of RhiG = (% of feta; cells x maternal blood volume) / 30
What is the example of RhIG calculation?
Fetal Cells: 6
Total cells counted: 2000
6/2000 = .003 × 5000 = 15/30 =.5 —> give 2 vials
What are some situations we should give RhiG?
Fetal death
Abortion
Amniocentesis
Antepartium hemorrhage
Ectopic pregnancy
Is RhoGam given intramuscularly or intravenously?
Intramuscularly
Is WinRho given intramuscularly or intravenously?
Intravenously
Where is the G antigen found?
Mostly D+ or C+ cells
Which haplotypes would you find G antigen?
R1: DCe
R2: DcE
R0: Dce
Rz: DCE
r’: dCe
ry: dCe
Which haplotypes do NOT have the G antigen?
r’’: dcE
r:dce
What are the exception phenotype for G antigen?
rGr (G+D-C-)
DCe (G-D+C+)
What are the characteristics of Anti-G?
Appears as anti-D plus anti-C
Made by:
D- person transfused w/ D-C+ cells
D-C- person transfused w/ rGr cells
Pregnant women who delivered a D-C+ child
How can you tell the difference between anti-D, anti-C, anti-G?
Distinguished by adsorption and elution studies