structures and properties of materials finals
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is specific strength?
Strength divided by density (strength-to-weight efficiency)
What is specific stiffness?
Elastic modulus divided by density (stiffness-to-weight efficiency)
Compare carbon fiber composites vs metals in specific properties
Carbon fiber = much higher specific strength and stiffness than steel or aluminum
Role of the matrix in fiber composites?
Holds fibers, transfers load, protects fibers, provides shape, adds toughness
Common matrix materials
Epoxy, polyester, vinyl ester, thermoplastics (PP, PEEK), metals and ceramics
Role of fibers in composites?
Carry load, provide strength and stiffness, control directional properties
Common composite fivers?
Carbon fiber, glass fiber, Kevlar, natural fibers
Example of particulate composite in automotive use
Brake Pads, tires (carbon black), SiC-reinforced engine parts
Advantages of particulate composites over carbon fiber
Cheaper, easier to manufacture, good wear resistance, isotropic, durable
Composite desnity formula
ρc = Vfρf + Vmρm
Maximum stiffness condition?
Iso-Strain (parallel loading):
Emax = VfEf + VmEm
Minimum stiffness condition?
Iso-stress (series) loading): 1/Em in = Vf/Ef + Vm/Em
What is a hybrid composite?
Composite containing 2+ fiber types (e.g., carbon + Kevlar).
What is a laminar composite?
Composite made of stacked bonded layers (plywood, laminated CFRP)
Thermoset structure
Highly cross-linked 3D network. Strong permanent covalent bonds between polymer chains. (Epoxy resin)
Thermoset recyclability?
No—cannot be remelted
Thermoplastic structure?
Linear or branched chains, lightly engtangled. Weak IMF between polymer chains. No cross-links between chains. Softens when heated.
Thermoplastic recyclability?
Yes—can be reheated and reshaped
What is an elastomer?
Lightly cross-linkled polymer with large elastic deformation
How are elastomers strengthened?
Vulcanzation + fillers (carbon black, silica)
What is Tg (glass transition temperature?
Temperature where polymer changes from brittle to rubbery
Why is Tg important
Determines safe operating temperature of polymers
Repeat unit of polyethylene (PE)
–(CH₂–CH₂)–
Repeat unit of PVC
–(CH₂–CHCl)–
Repeat unit of polypropylene PP
–(CH₂–CH(CH₃))–
Repeat unit of polystyrene PS
–(CH₂–CH(Ph))–
Repeat unit of PTFE (teflon)
–(CF₂–CF₂)–
Why plastics replace metals in cars
Lighter, corrosion-resistant, cheaper, impact damping, easier to mold, fuel efficient
What is the purpose of heat treatment?
To change microstructure —alter strength, hardness, ductility and toughness
What microstructure forms when steel is slow cooled?
pearlite (coarse or fine depending on cooling rate
What microstructure forms when steel is rapidly cooled?
Martensite: very hard, very brittle
What does tempering do?
Converts martensite to tempered martensite: decreases hardness, increases toughness
Why do fine grains increase strength?
grain boundaries block dislocation motion
Where do cracks and corrosion often initiate?
At grain boundaries
What is a composite?
A material made from 2+ phases that reamin distinct, working together for improved properties
What is the role of the matrix?
Holds fibers, transfers load, protects reinforcement, adds toughness
What is the role of the reinforcement?
Provides strength and stiffness
Main composite types?
Fibrous, particulate, laminar, hybrid.
Why use composites in vehicles?
High strength-to-weight, hgih stiffness-to-weight, corrosion resistance, fuel efficiency
Stiffness and lower bounds formulas
Parallel loading: E=VfEf+VmEmE = V_fE_f + V_mE_mE=VfEf+VmEm
Series loading: 1/E=Vf/Ef+Vm/Em1/E = V_f/E_f + V_m/E_m1/E=Vf/Ef+Vm/Em
What are thermoplastics?
Linear/branched chains, no permanent crosslinks, recyclable, soften when heated
What are thermosets?
Cross-linked polymers with large elastic deformation
What strengthens elastomers?
Vulcanization and fillers (carbon black, silica)
Below Tg
Too brittle
Above Tg
Rubbery/ductile
Why use Mohr’s Circle?
To find principal stresses and maximum shear stress when under plane stress
Center of Mohr’s Circle?
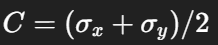
Radius of Mohr’s Circle
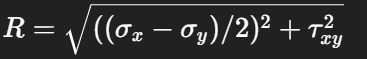
Principal stresses
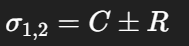
Maximum shear stress?
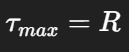
Steps to solve deflection by integration

How do material classes compare in stiffness?
Ceramics > Metals > Composites (varies) > Polymers