Anatomy & Physiology : The Intergumentary System
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
function of the dermis
basis of epidermis and makes up most of skin , flexibility
functions of the hypodermis
- loosely anchors skin to underying structures, mostly muscles
- shock absorption and insulation
the epidermis consists mostly of _____ _____ _____ _____
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
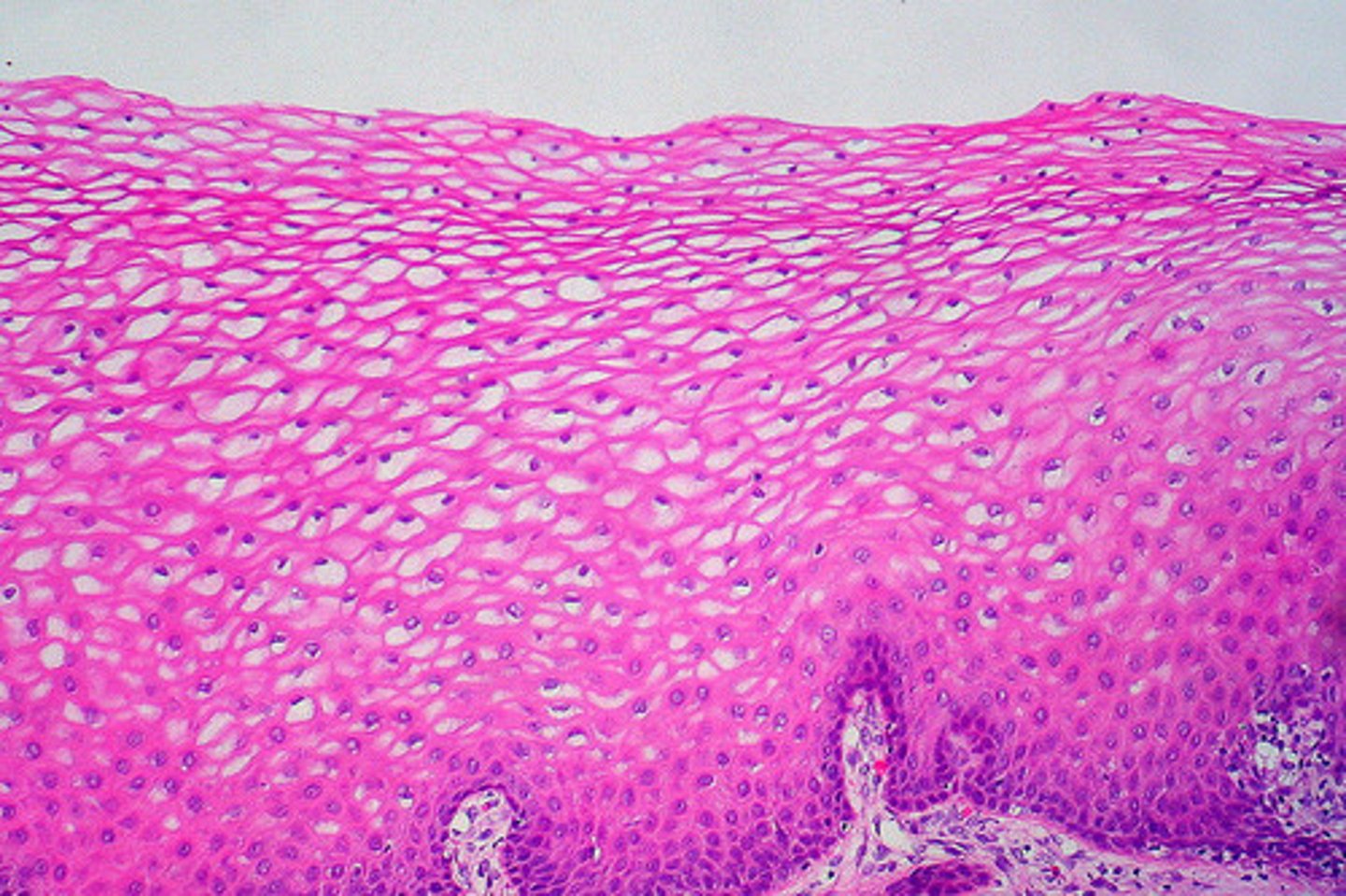
the four ( 4 ) cell types of the epidermis :
- keratinocytes
- melanocytes
- dendritic cells
- tactile epithelial cells
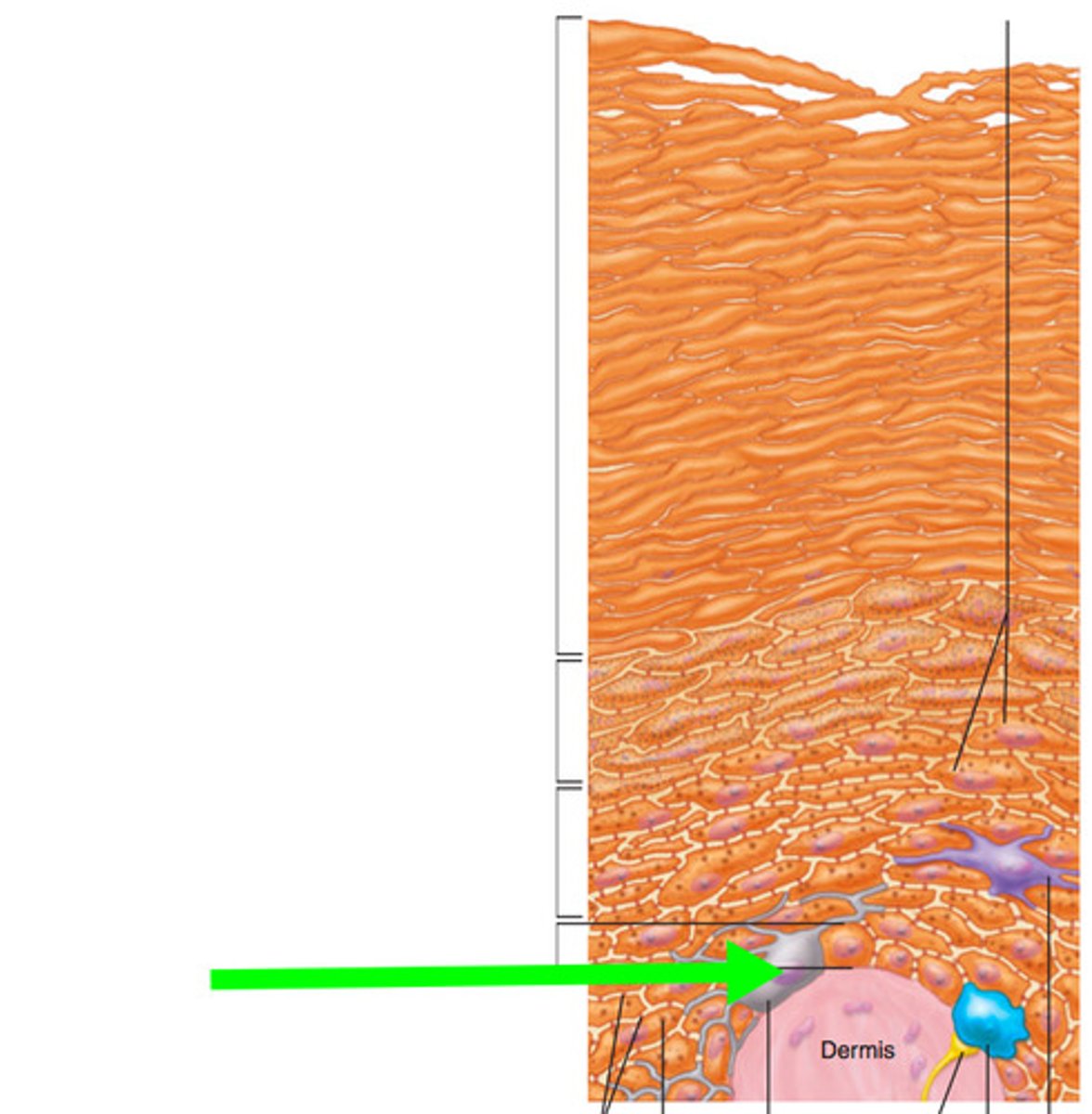
four or five distinct layers of the epidermis :
deep to surface order :
- stratum basale
- stratum spinosum
|----------------------|
- stratum granulosum
- ( stratum lucidum )
- stratum corneum
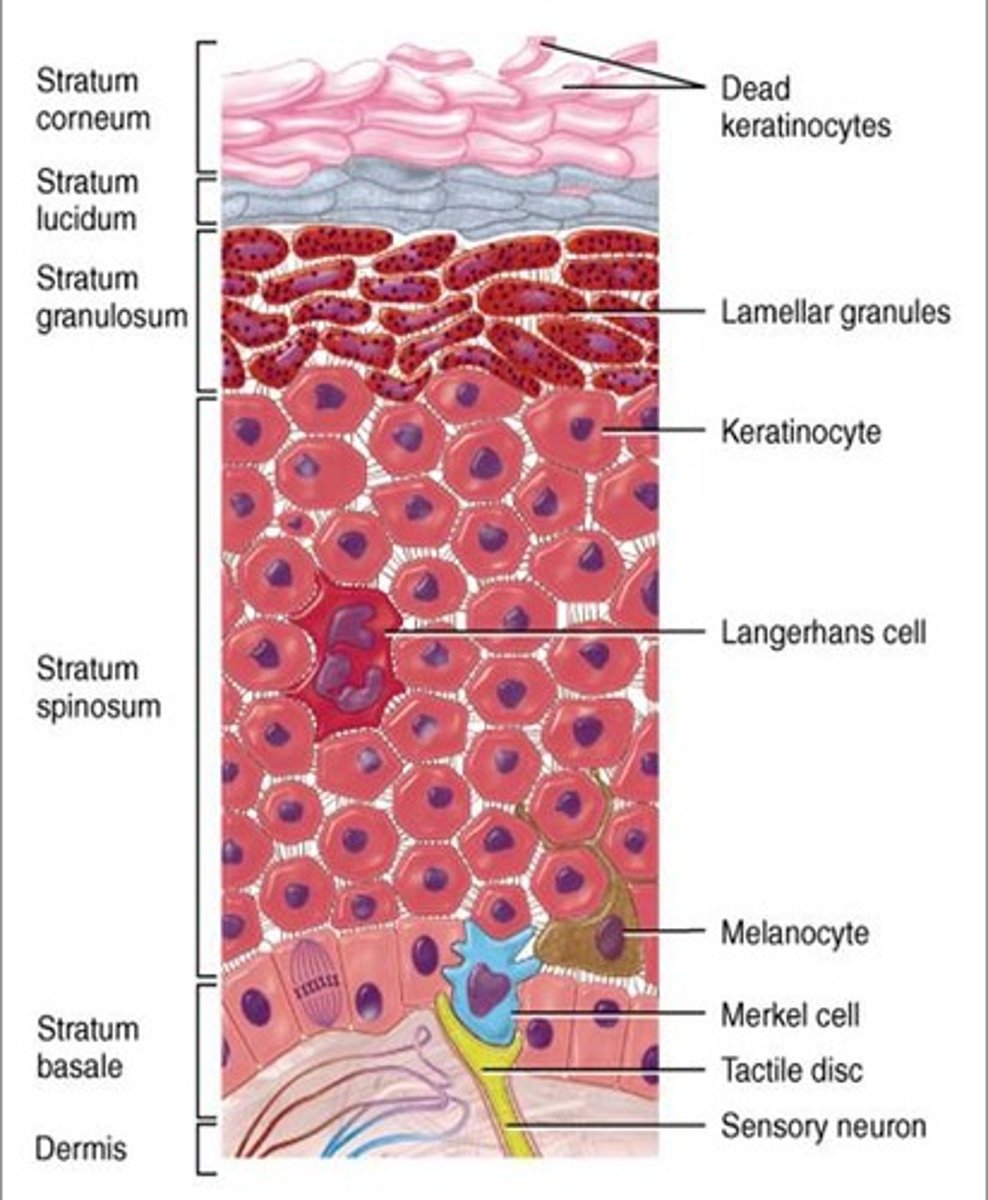
thick skin is located where?
the palms, fingertips and soles (foot)
the thickest skin on the body is?
upper back skin
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis where new skin cells are produced
- active mitosis , attached to the dermis
stratum spinosum
prickly layer where cells start to produce keratin
- mutiple layers , attached to desmosomes
- resists tension and pulling
- keratinocytes in the layer appear spikey, so they're called prickle cells
stratum granulosum
a layer where cells further develop keratin and flatten.
- 4 to 6 cells thick but still thin layer
- where keratinization begins , helps form keratin fibers in upper layers
- cells above this layer die , cant survive
stratum lucidum ( only in thick skin )
a thin and clear layer present only in thick skin like the palms and feet
- 2 to 3 rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes
- superficial to the stratum granulosum
stratum corneum ( horny layer )
the outermost layer composed of dead, keratinized cells that are constantly shedding
- 20 to 30 rows of flat dead cells
- three-quarters of epidermal thickness
dead cells still function by
- protecting deeper cells from the environment
- prevent water loss
- protecting from abrasion and penetration
- acting as a barrier against biological, chemical and physical assaults
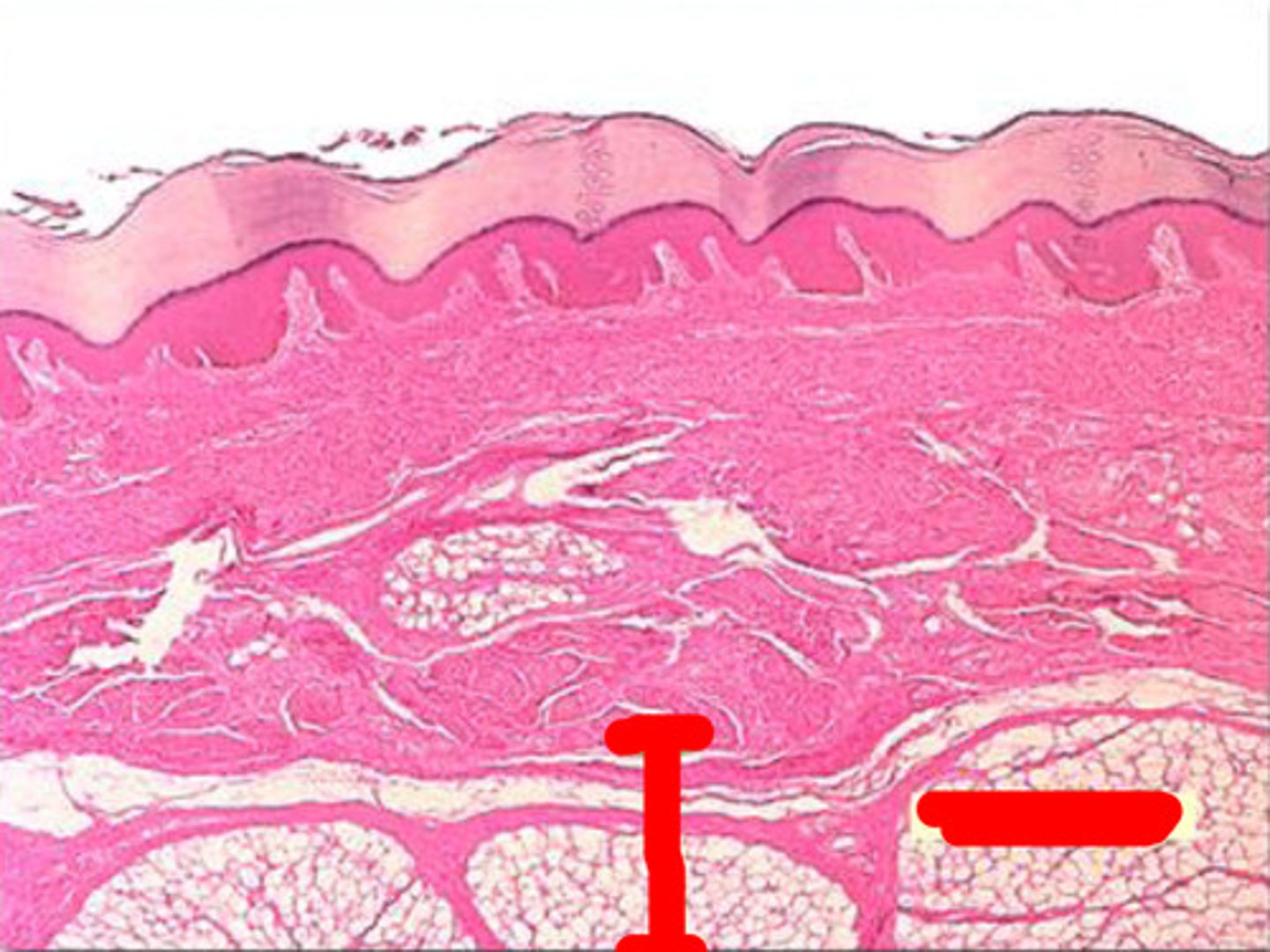
dermis
strong, flexible connective tissue
- fibroblasts, macrophages and occasionally mast cells and WBCs
- contains nerves, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, epidermal hair follicles, oil glands and sweat glands
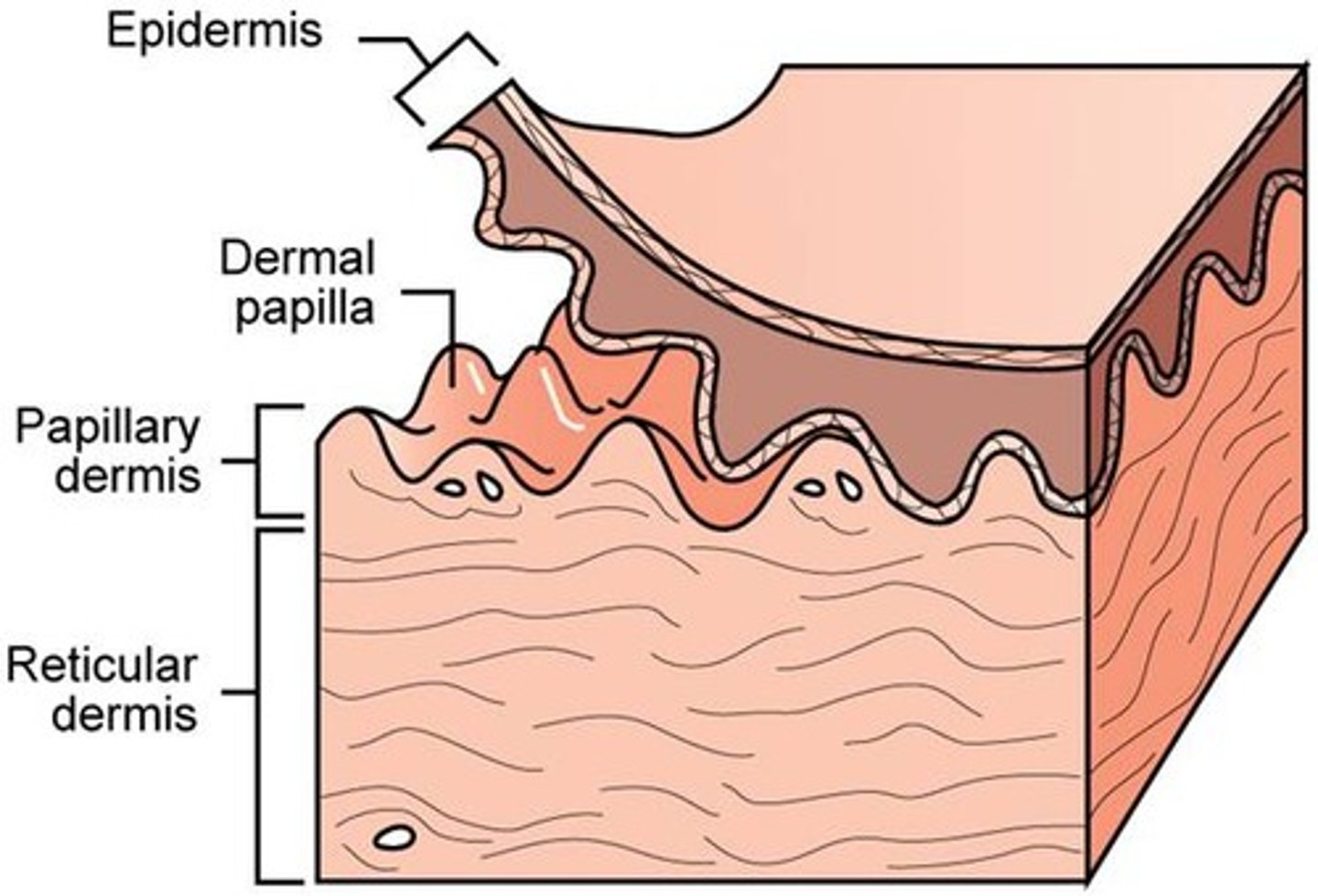
the two layers of the dermis
papillary dermis and reticular dermis
papillary dermis
the thin, superficial layer of areolar connective tissue ,
- contains loose, interlacing collagen and elastic fibers and blood vessels
- loose fibers allow phagocytes to patrol for microogranisms
The Integumentary system consists of :
- skin
- sweat glands
- oil glands
- hair
- nails
- subcataneous tissue
the skin consists of 2 layers ..
epidermis and dermis
epidermis
outermost protective shield of body
- epithelial tissue and avascular
dermis
underlies epidermis and makes up bulk of skin
- dense connective tissue and vascular
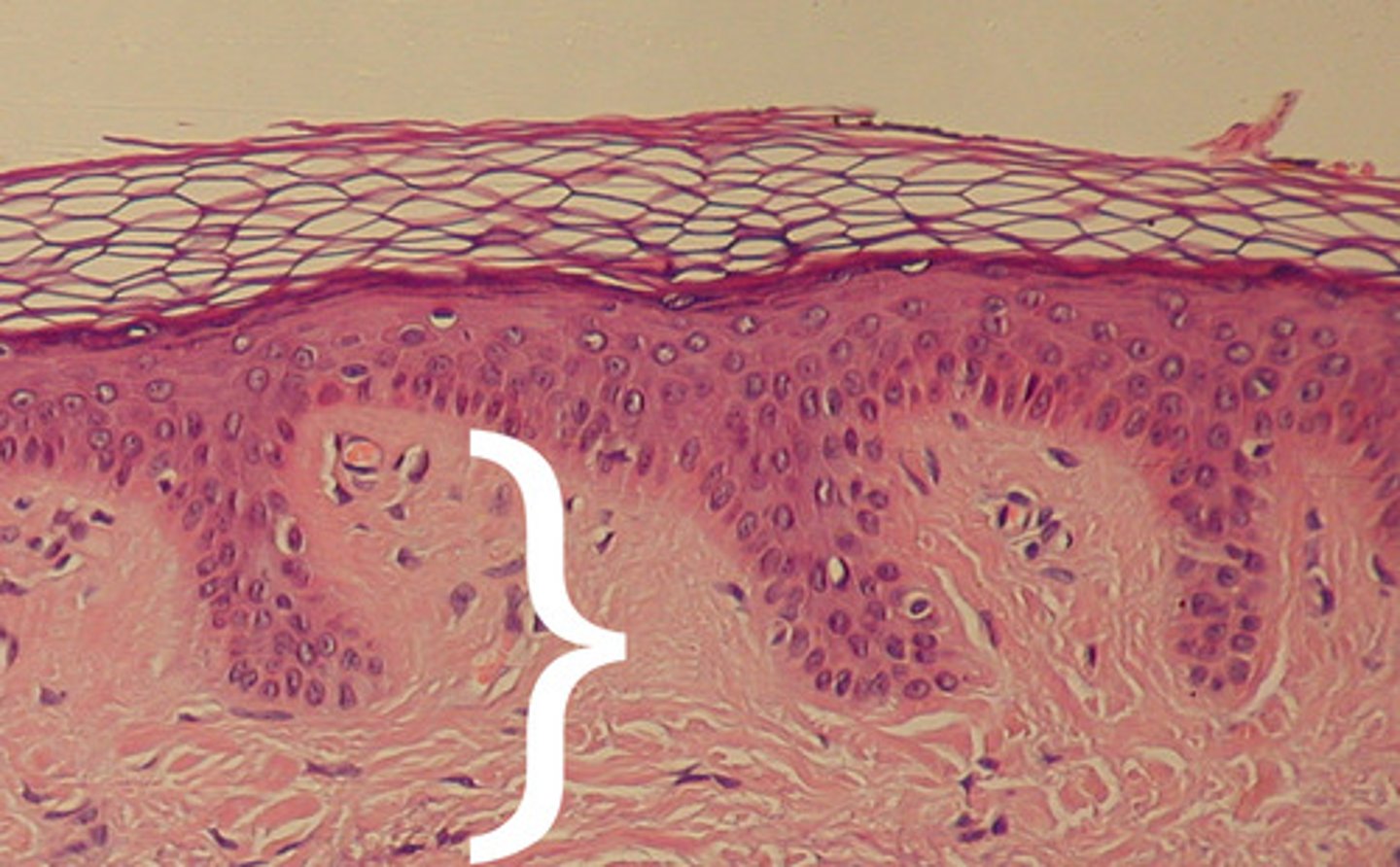
avascular
having a few or none blood cells
vascular
consisting of blood cells or blood vessels
hypodermis (subcataneous tissue )
not apart of the skin but shares some functions
- adipose tissue with some areolar connective tissue
function of the epidermis
protection
keratinocytes
produces fibrous keratin ( protective properties )
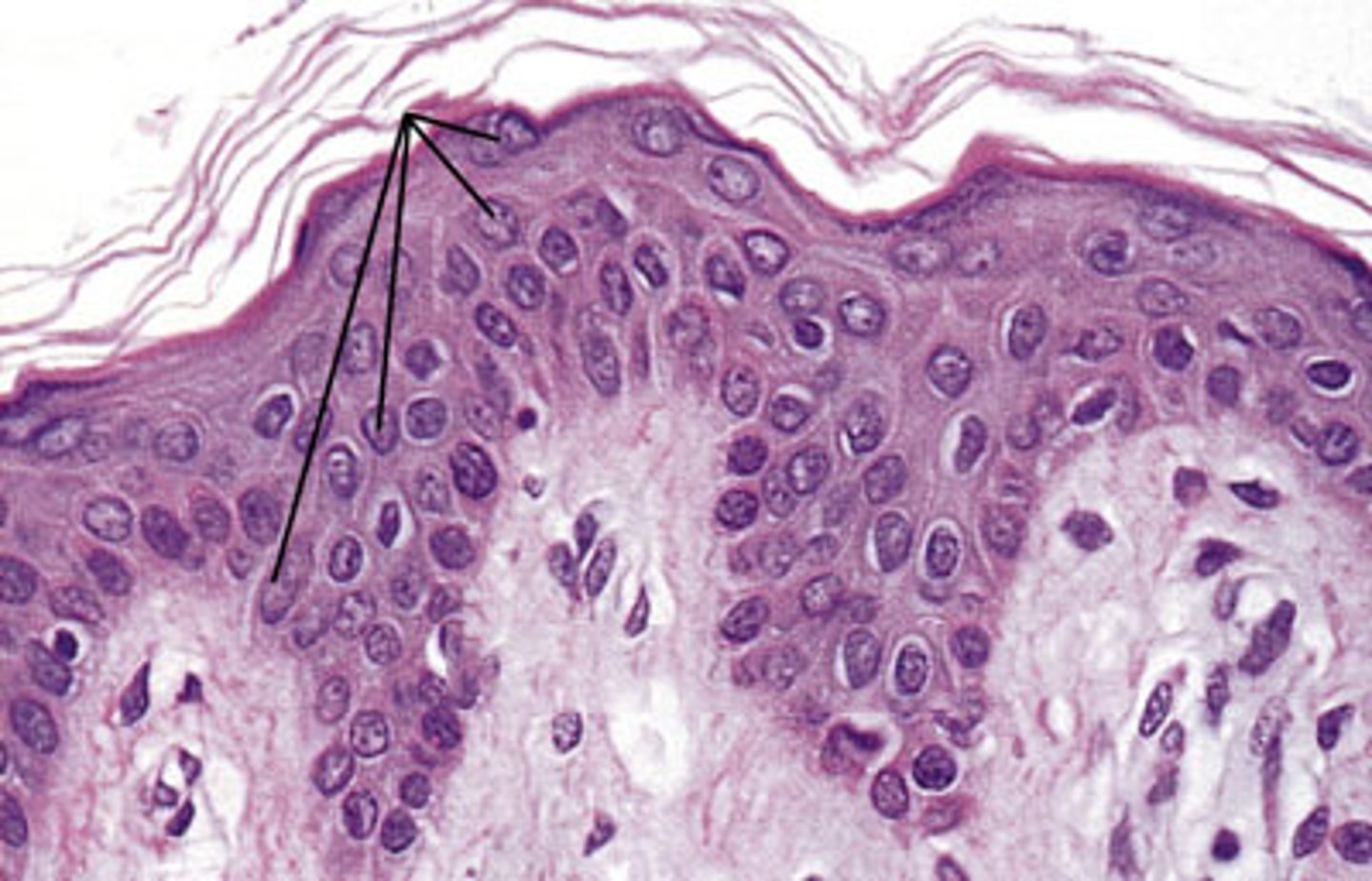
melanocytes
- spider-shaped cells in the deepest epidermis
- produces pigment melanin, which is then packaged into melanosomes
melanin protects keratinocyte nucleus from __ ______
UV damage
dendritic cells
- star-shaped macrophages ( WBCs ) that patrol the deep epidermis
- immune system
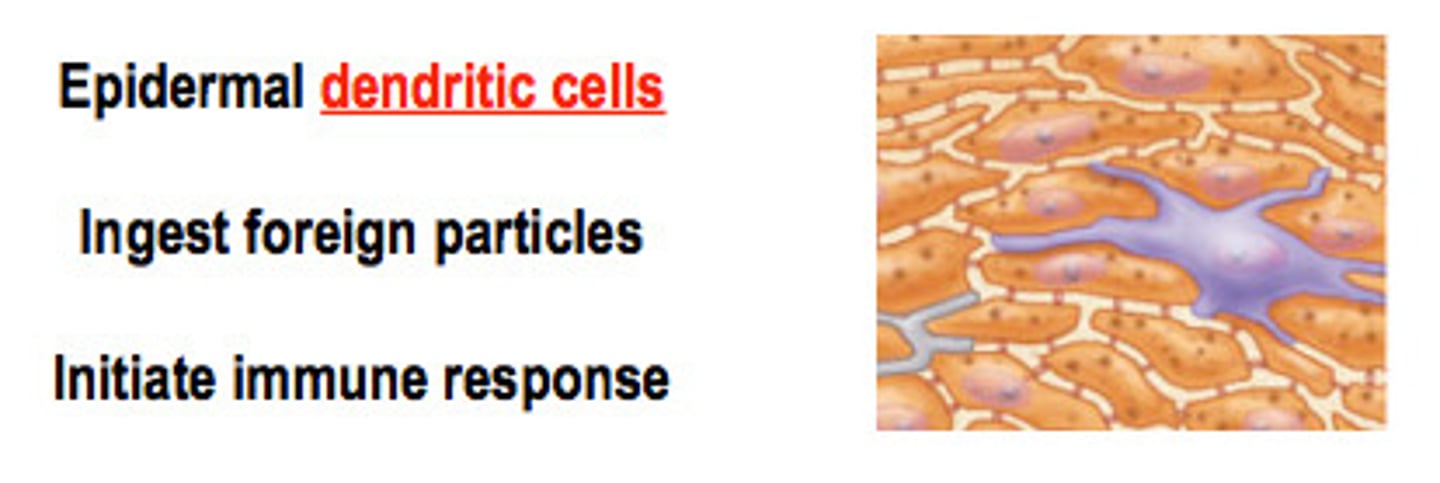
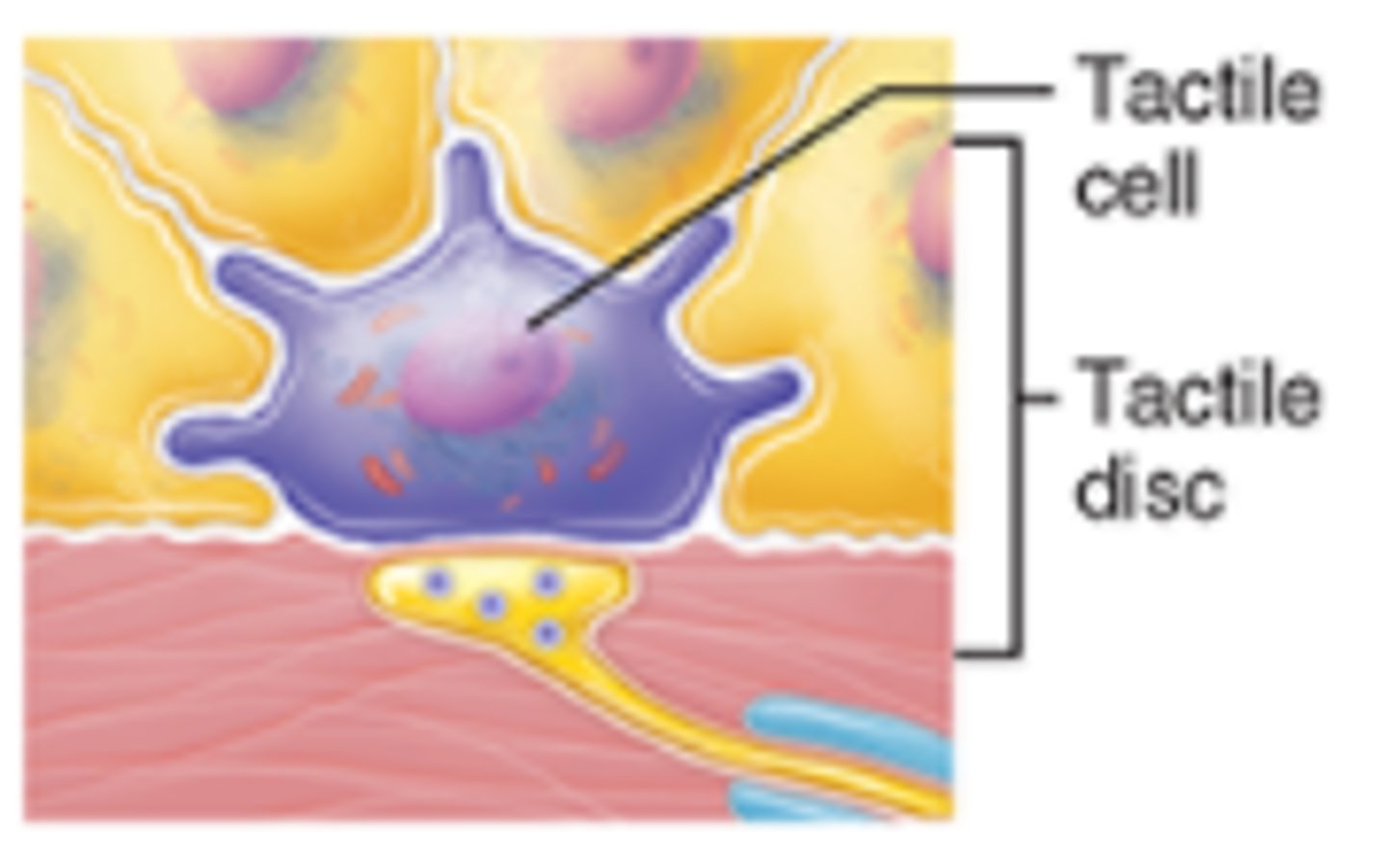
tactile epithelial cells
function in the sensation of touch at the epidermal-dermal junction
thick skin contains _ layers
5
thin skin contains _ layers
4
dermal papillae
superficial region of dermis that sends fingerlike projections up into epidermis
- contains capillary loops, free nerve endings
( pain and touch , tactile corpuscles )
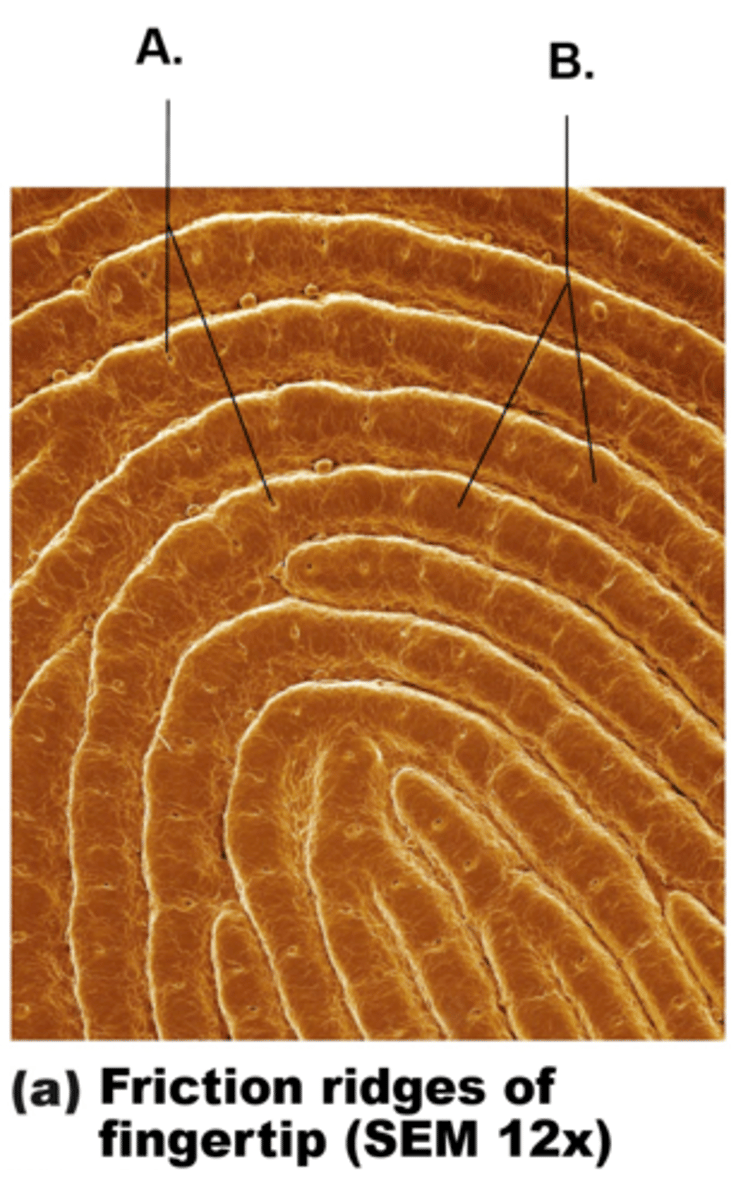
friction ridges
the markings on the fingertips that leave oily fingerprints on surfaces we touch
dermal ridges
surface ridges of the epidermis of the palms and feet, where the sweat pores open
epidermal ridges
downward waves of epidermis
the functions of friction ridges
- enhances gripping ability
- contribute to sense of touch by enhancing vibrations detecting by receptors ( lamellar corpuscles )
friction ridges determined by :
genetics and womb environment
reticular dermis
80 - 85% of dermal thickness
- made up of coarse, dense irregular connective tissue
- tons of elastic fibers & collagen fibers help with stretching
- keeps skin hydrated by binding with water
dermal vascular plexus
network of blood vessels between reticular layer and hypodermis
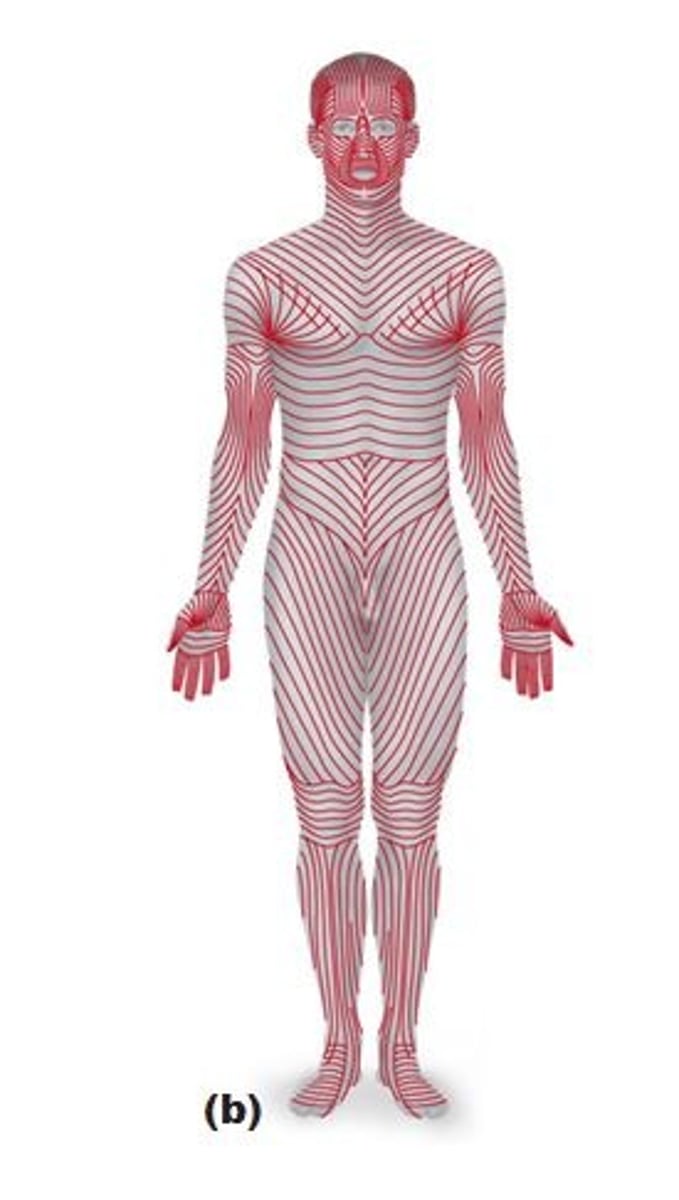
what are cleavage ( tension ) lines ?
in reticular layer are caused by many collagen fibers running parallel to skin surface
- externally invisible
- important to surgeons because incisions parallel to cleavage - lines heal more readily

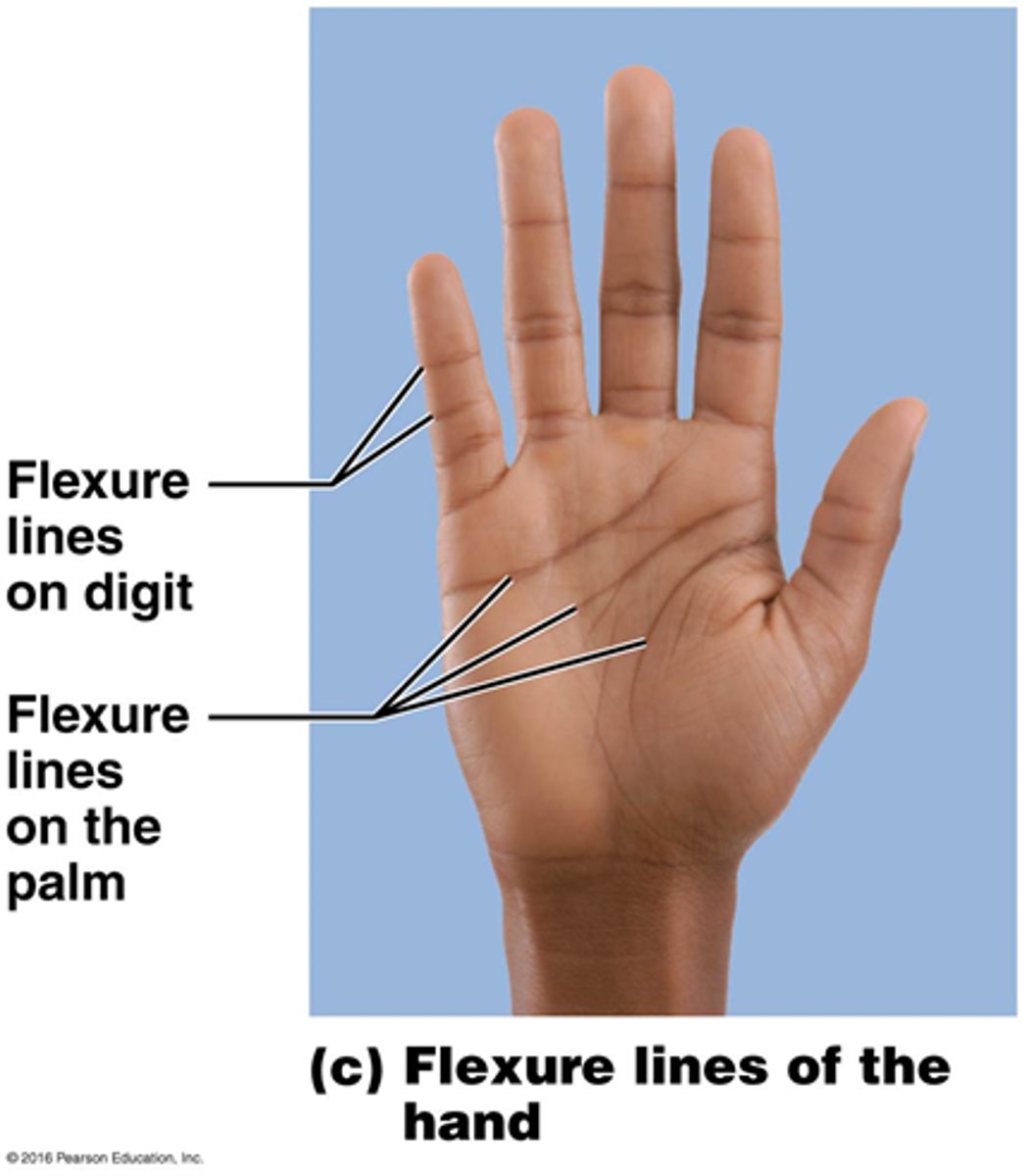
flexure lines
dermal folds at or near joints
flexure lines are visible on :
hands, wrists, fingers, soles ( feet ) and toes
striae
stretch marks
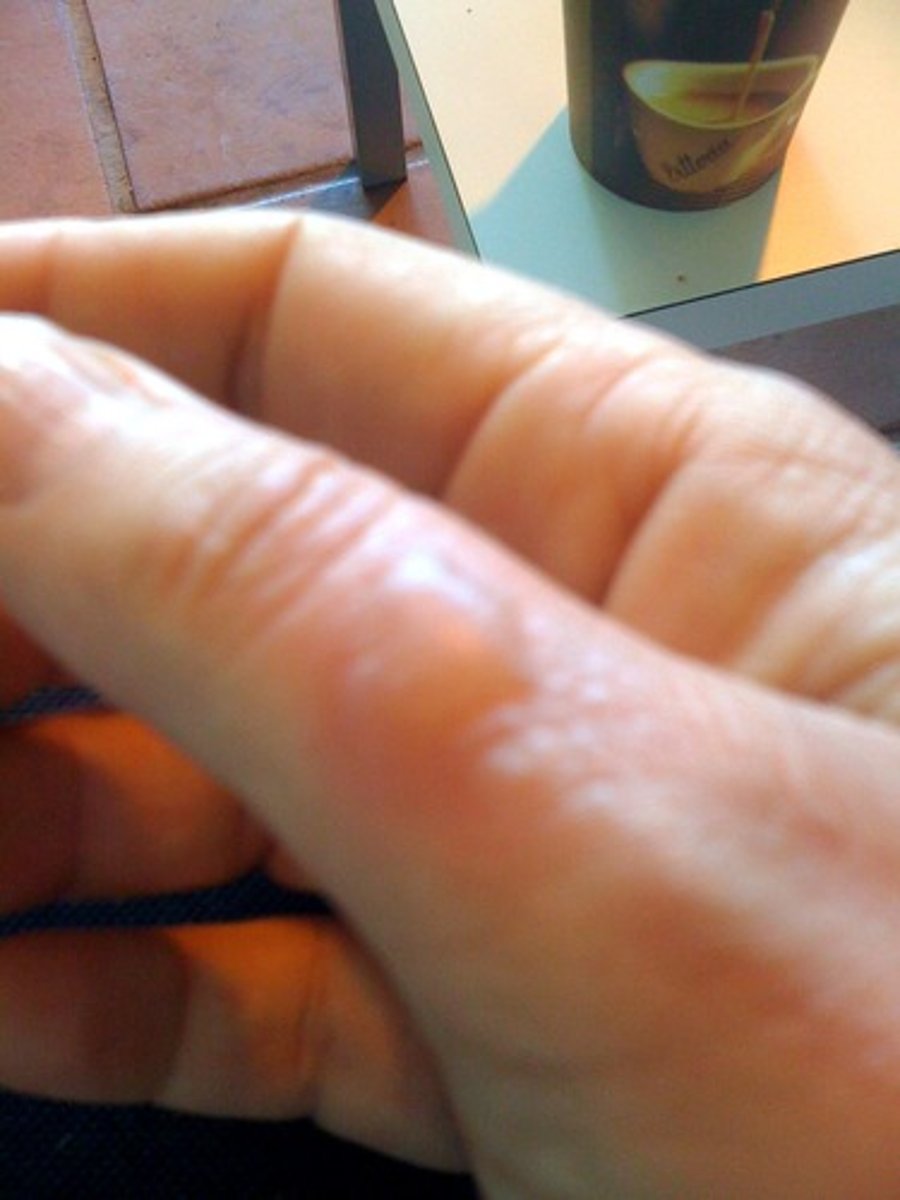
acute short-term traumas to the skin causes
blisters

three pigments contribute to skin color
melanin, carotene ( carrots ), hemoglobin
freckles and pigmented moles are local accumlations of what ?
melanin
excessive sun exposure damages skin and
causes alterations in DNA that may lead to skin cancer
UV light destroys
folic acid
blueness or cyanosis
low oxygen and hemoglobin , respiratory or cardiovascular issues
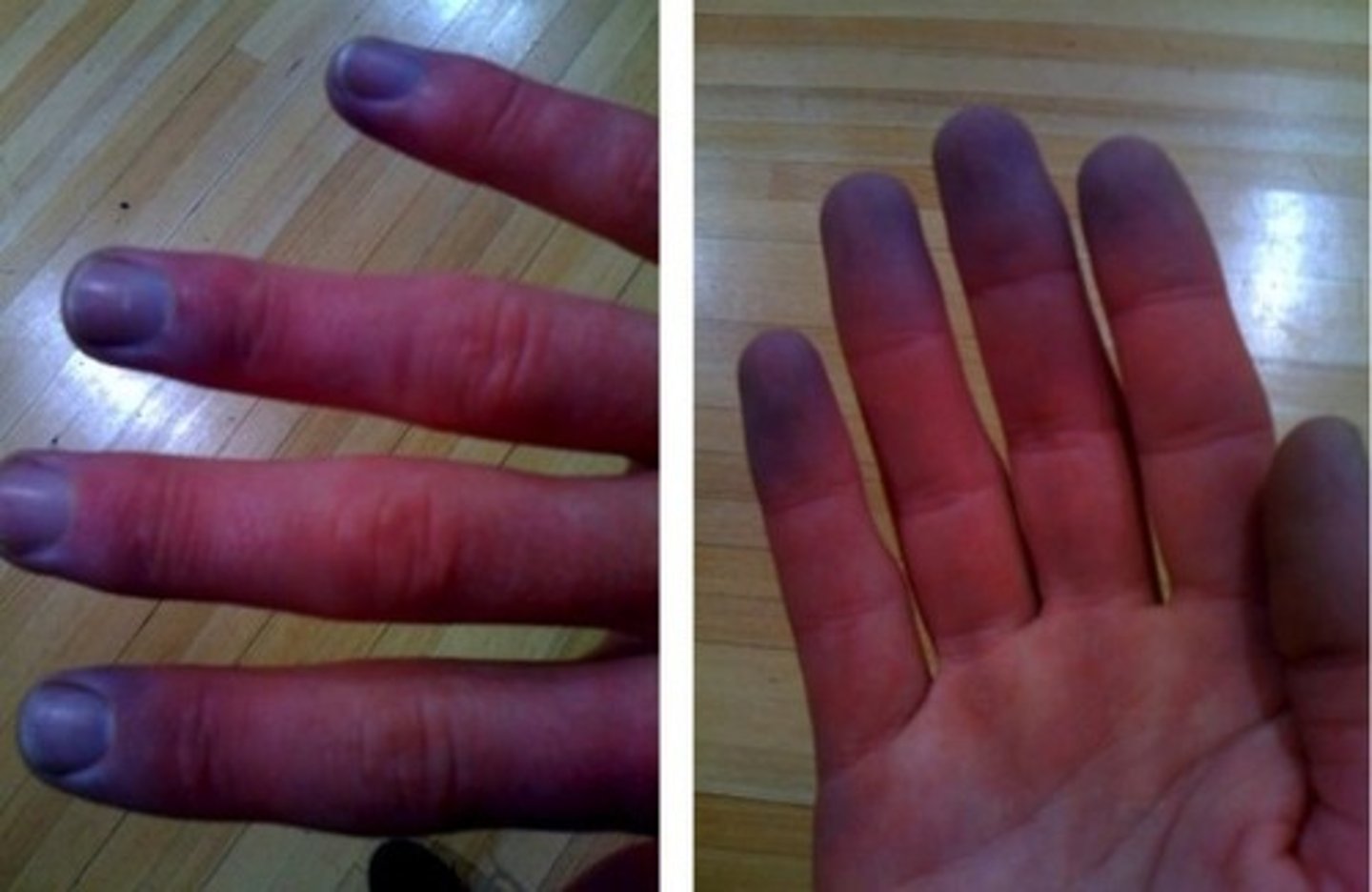

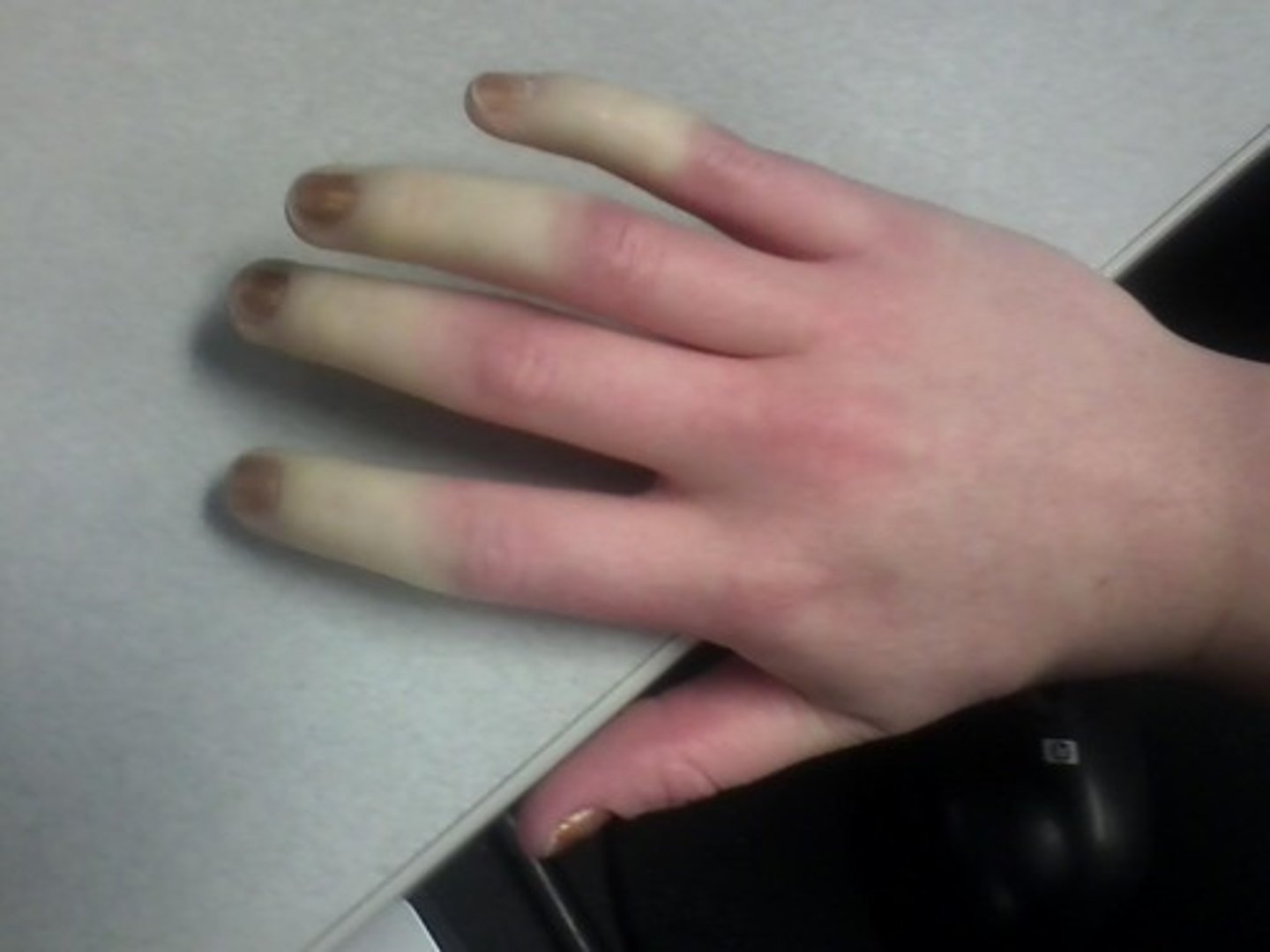
pallor or blanching
emotional stress, low blood pressure, anemia
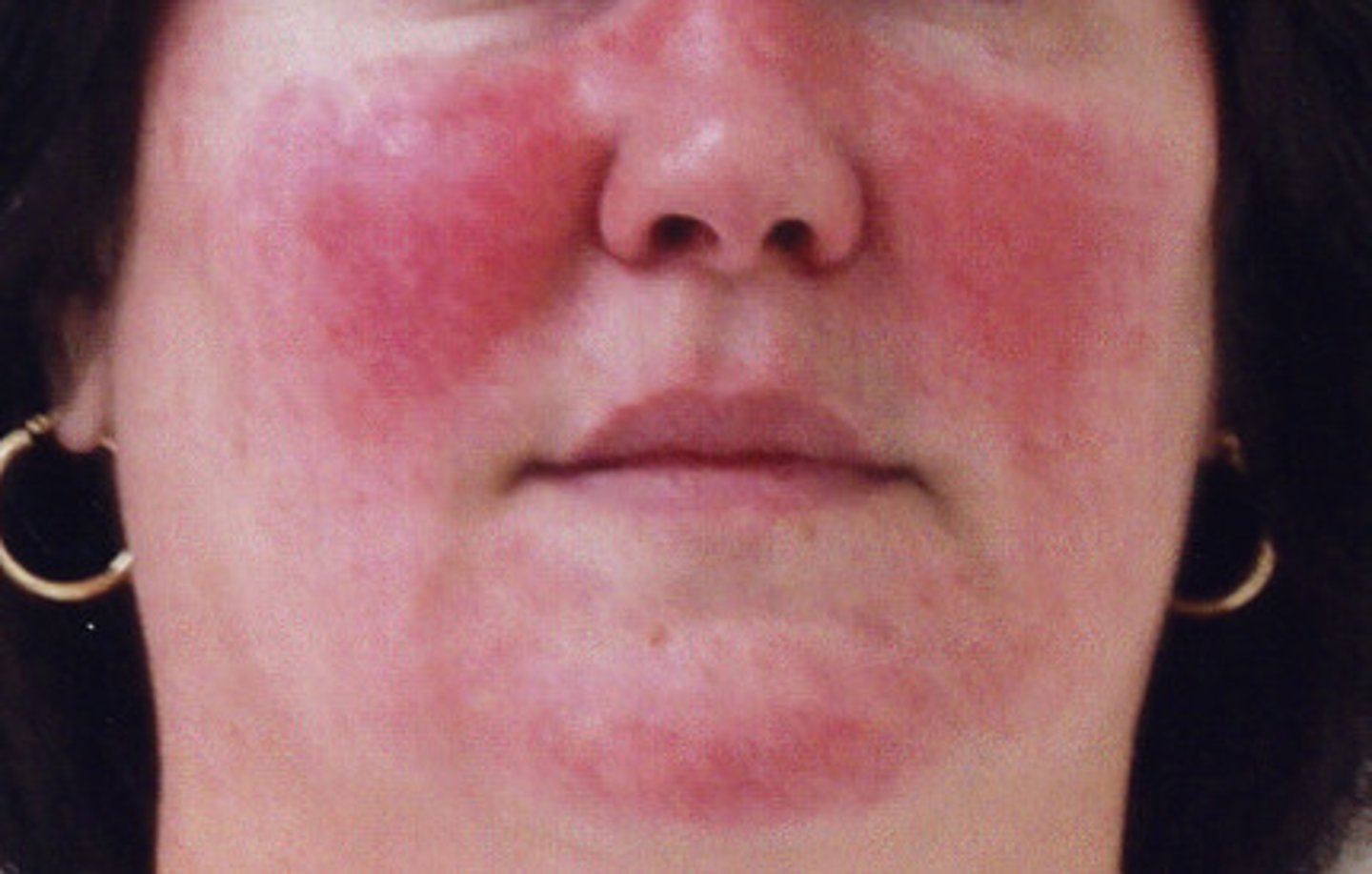
redness or erythema
embarrassment, fever, inflammation or allergy
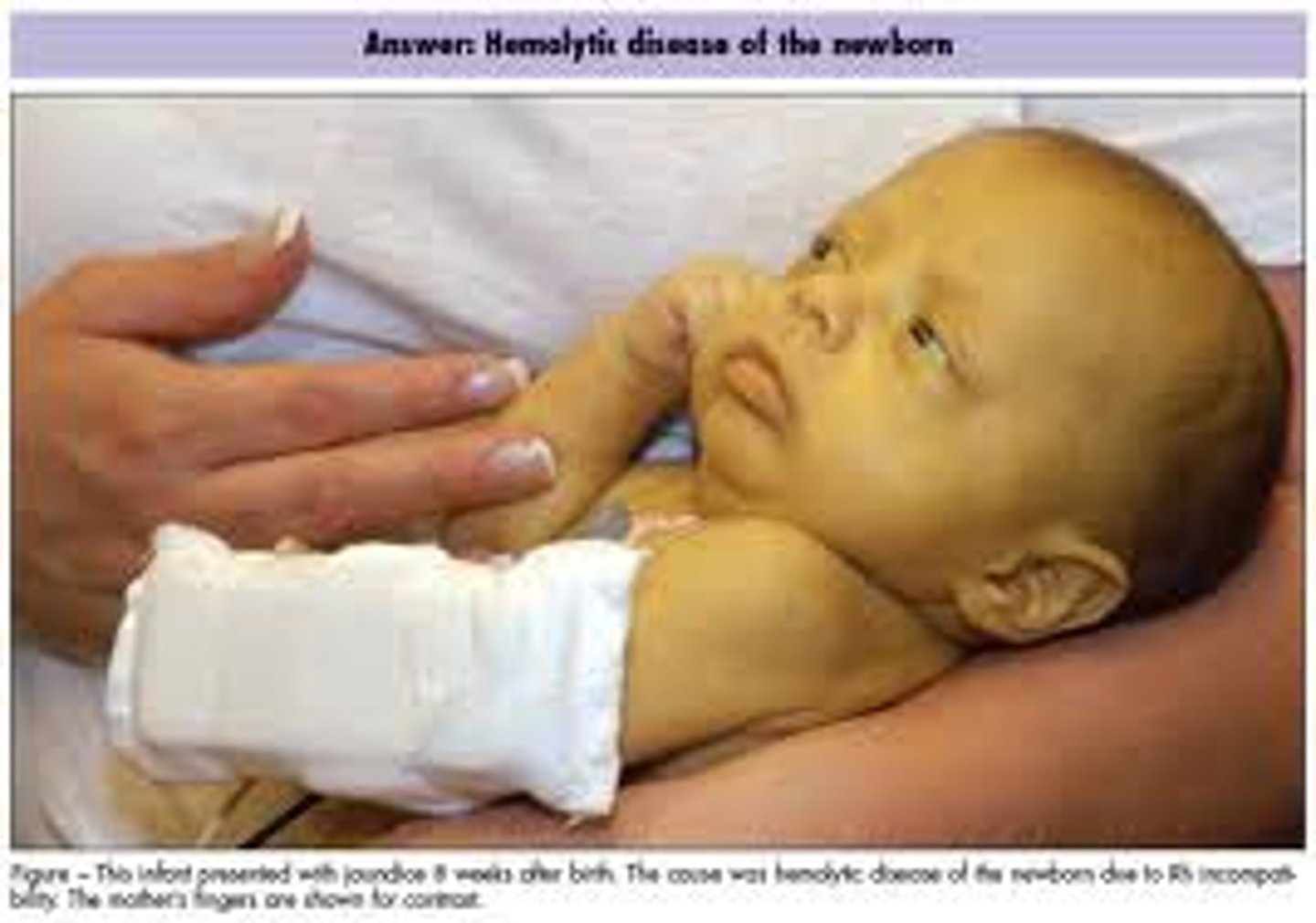
yellowness or jaundice
liver disorders
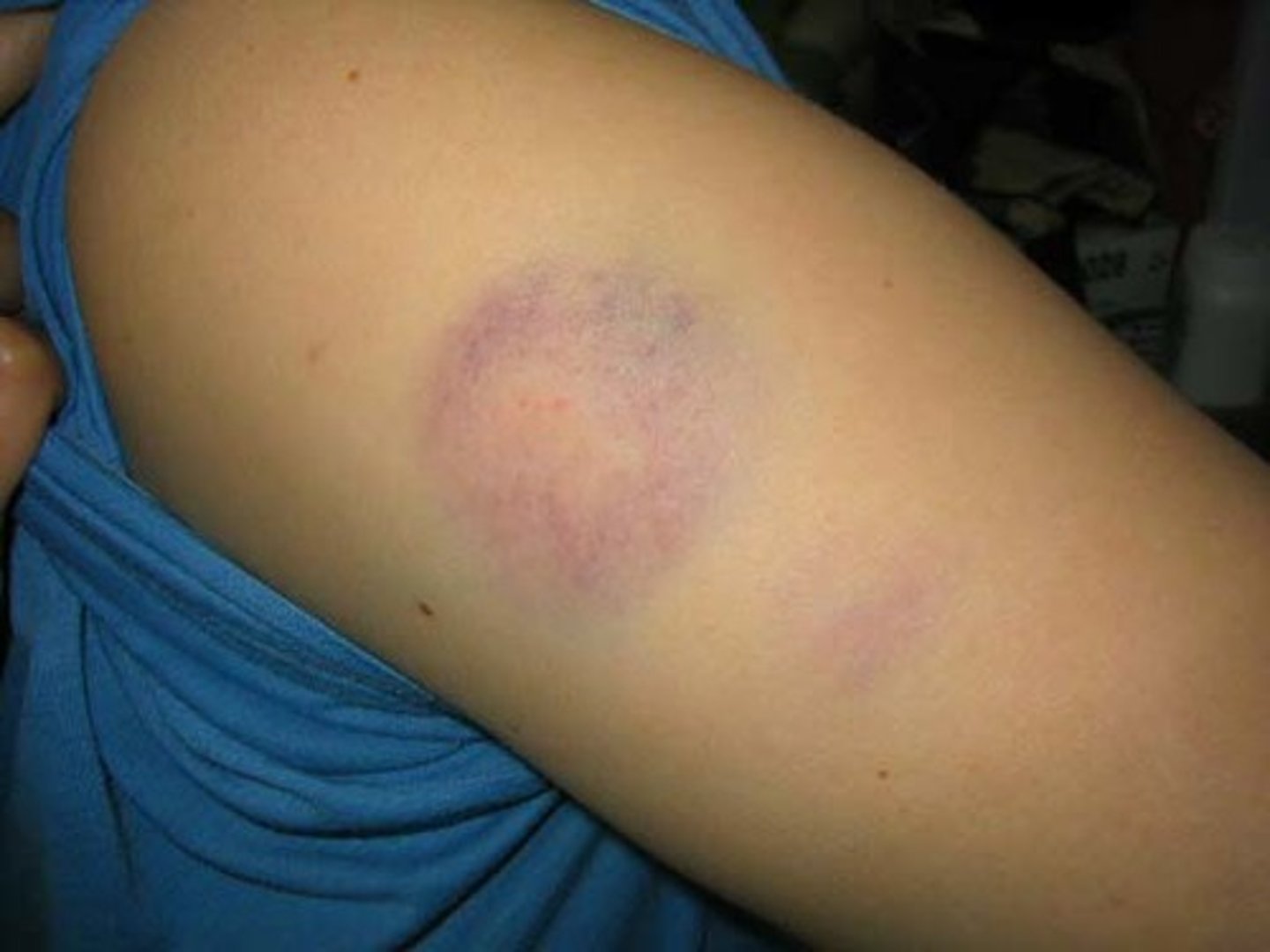
red/purple/green/yellow marks
blood leakage from damaged blood vessels under skin
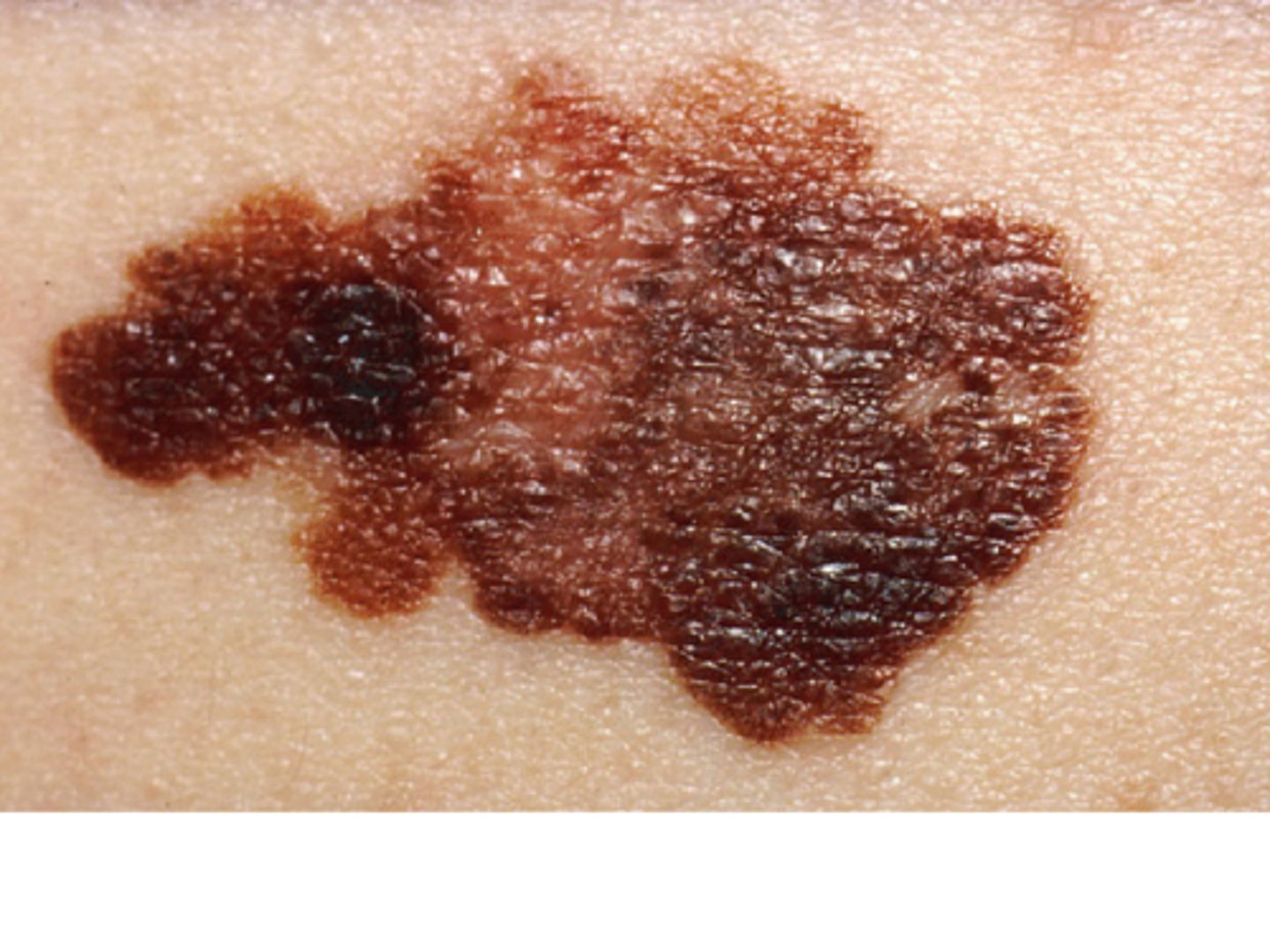
brown or black patches
hyperpigmented, thickened skin in folds may be a sign of endocrine disorder
the more further away from the equator you are, the worse of a vitamin _ deficiency you'd get
D
repair can occur in two major ways:
regeneration: same kind of tissue replaces destroyed tissue, so original function is restored
fibrosis: connective tissue replaces destroyed tissue, and original function lost
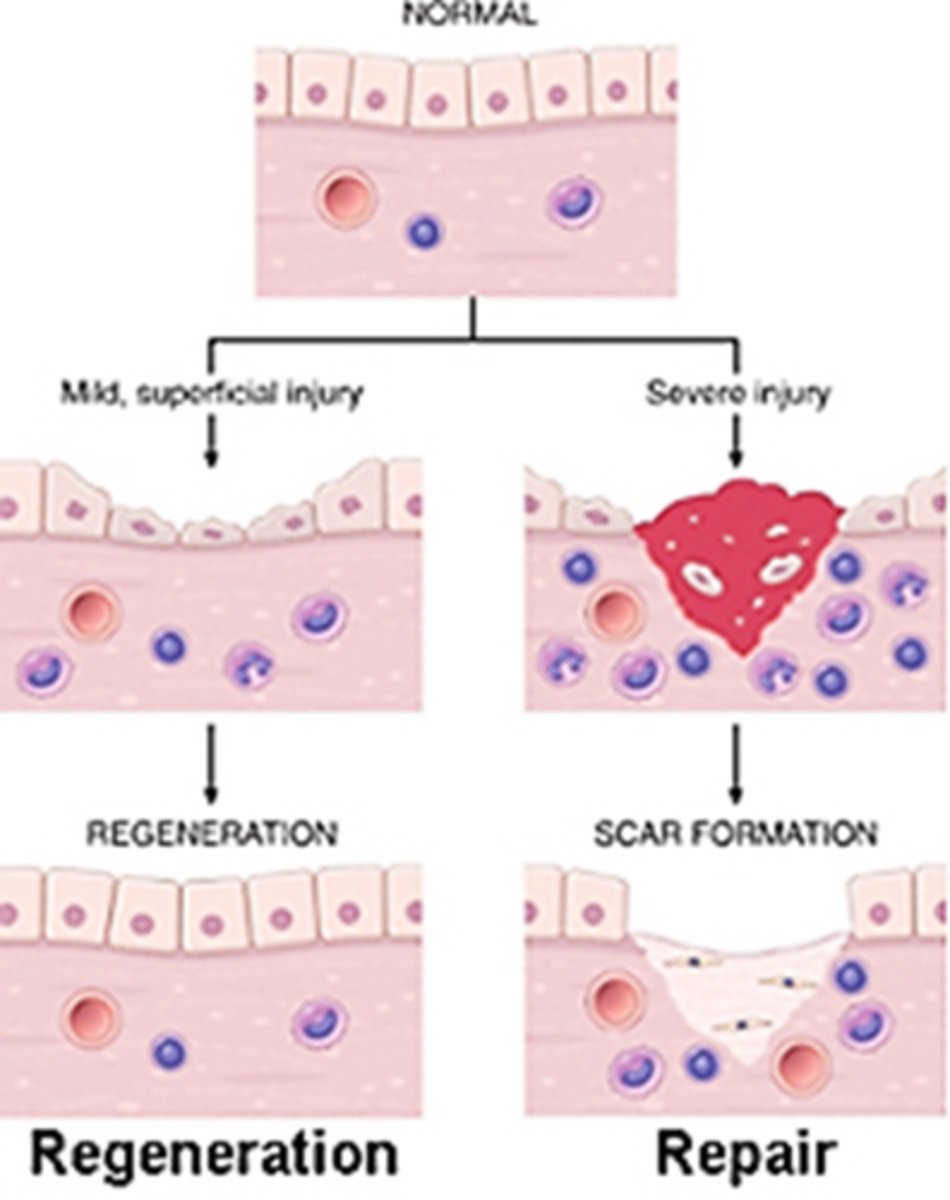
tissue repair
repair starts very quickly, and inflammation is the function of repair
developmental aspects of tissues
- as the body ages, epithelia thin, so they are more easily breached
- tissue repair is less efficient
- bone, muscle tissues, and nervous tissues begin to atrophy
DNA mutations increase cancer risk
what does hair consist of?
dead keratinized cells
the functions of hair
- senses insects on skin before bite or stings
- hair on head guards against physical trauma
- protect from heat loss
- shield skin from sunlight
- eyelash shield eyes
- nose hairs filter particles from inhaled air
pili
hair
hair is produced by what
hair follicles
hair contains
hard keratin
root of the hair
the portion within the scalp, where keratinization is still going on
shaft
the portion that extends above scalp, where keratinization is complete
the three parts of the hair shaft include
- medulla : central core
- cortex : flattened cellls around the medulla
- cuticle : outer layer of single cells
red hair has an additional
pheomelanin pigment

how do gray hairs come about?
it happens when melanin production decreases and air bubbles replace melanin in the shaft
hair follicle
extends from epidermal surface to dermis
hair bulb
expanded area at deep end of follicle
hair is a sensory _____ receptor
touch
capillaries
smallest blood vessels that supply nutrients to growing hair
arrector pili
responsible for "goose bumps"
hair matrix
actively dividing area of the hair bulb that produces hair cells
vellus hair
pale, fine body hair of children and adult females

terminal hair
coarse, long hair
nutrition and hormones affect
hair growth
average _mm growth per week
2
terminal hair is replaced by vellus hair causing what?
wispy hair
testosterone
male sex hormone , helps body builders grow muscle and leads to hair loss
causes of thinning and texture change in hair :
- low thyroid hormone levels
- drugs
- severe dietary deficiencies of proteins or minerals
nails are
scale-like modifications of the epidermis with hard keratin
nails consist of
- root embedded in the skin
- nail plate or body visible attached portion
- free edge
nail bed
the epidermis underneath keratinized nail plate
nail matrix
thickened portion of bed responsible for nail growth
nail folds
skin folds that overlap border of nail
cuticle
nail fold that projects onto surface of the nail body
hyponychium
edge of nail that accumulates dirt
lunule
thickened nail matrix, appears white
sweat glands help control
body temperature
eccrine sweat glands
respond primarily to elevated body temperature
apocrine sweat glands
produce true sweat plus fatty substances and proteins; found in the axillary (armpit) and anogenital areas of the body
apocrine sweat glands begin to functioning at puberty ...
may act as a sexual gland
mammary glands
secrete milk
ceruminous glands
ear wax
oil glands secrete
sebum
acne
inflammation of the sebaceous glands, pimples, pustules, or cysts
the functions of skin
- protection
- body temp regulation
- cutaneous sensations
- metabolic functions
- blood
- excretion
skin has three barriers
- chemical
- physical
- biological
500 ml/day of unnoticeable sweat
insensible perspiration