A1.2 Nucleic Acids
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
A1.2.1. universal genetic material
dna; genes instruct the body of performing actions (construct proteins) and pass information between generations. DNA; DioxyRibonucleicAcid. All living organisms use DNA, some viruses use RNA but non-living as not all functions of life.
A1.2.2. Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA/RNA are nucleic acids; Phospahte group (PO4)-Pentose Sugar ((de-)oxyribose) - Nitrogenous base
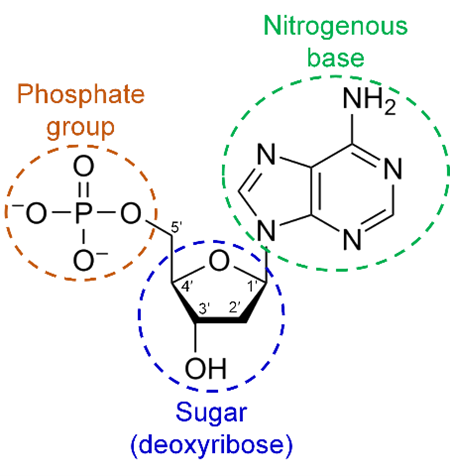
A1.2.3. Sugar backbone
Sugar–phosphate bonding makes a continuous chain of covalently bonded atoms in each strand of DNA or RNA nucleotides, which forms a strong “backbone” in the molecule. Occurs between C3 and C5 (phosphate), builds onto 3’ end. Condensation reactions polymerize
A1.2.4. Nitrogenous bases
5 different bases. 3 common for RNA and DNA, 2 different. Sequence of these basis of genetic code to store info.
A1.2.4. The nitrogenous bases
Uracil, Cytosine, Thymine (Pyrimidine-1ring)
Adenine, Guanine (Purine-2ring)
DNA: AT-CG, RNA: AU-CG
A1.2.5. Forming of RNA
RNA: ribose, single stand of covalently bonded sugar-phosphate bonds; GUAC, grows on 3’ end (3rd carbon), condensation (produce H2O) - polymerization of monomers
A1.2.6. DNA
DNA: double strand; linked by hydrogen bonds, A-T (2H) and C-G (3H), complementary base pairs. Antiparalel strands. Wound together into double helix. Both have sugar backbone w bases in centre. Always build 5’ to 3’
A1.2.7. RNA vs. DNA - differences
Ribose vs Deoxyribose (C2 OH vs H bottom)
Uracil vs Thymine (bonds with Adenine)
Single vs Double stranded
Used in protein synthesis vs used for conserving hereditary information
Both are nucleic acids formed by nucleotides, used in cells.
A1.2.8. Complementary base pairs roles
Weak hydrogen bonds holding together strands.
Roles:
DNA replication: accurate copies using template
Transcription: mRNA also matches to carry code
Translation: use sequence on tRNA and mRNA to place the right a.a. codon
A1.2.9. DNA sequences
4n options of sequences, and n is the nr of nucleotides in the nucleid acid, so very many….even 10 bases has 1.048.576 options. DNA can store infinite amount of information in its code
A1.2.10. Conservation of genetic code
Because all cells use the same genetic code, we know all life evolved from the same original ancestor. Genetic code is how that the 43=64 different codons (3 bases) code for 20 different amino acids
A1.2.11. 3’ and 5’ ends
3’: the 3rd carbon, where theres a spot for the phosphate to bind - the OH here + the H on the phosphate bind into H2O during condensation
5’: the phosphate group attached to the 5th carbon, where the 3’ end attaches to.
New nucleotides add onto the 3’ end, of the growing strand with their 5’end; 5’→3’ growth. Because in DNA the strands run antiparallel; 5’ and 3’ end
A1.2.12. Purine bond with pyrimidines
Purine: 2, Pyrimidine: 1 ring. Each purine (AG) bonds with a pyrimidine (CTU) - equal distance bonds for complementary; keep DNA stable and allow any sequence of bases.
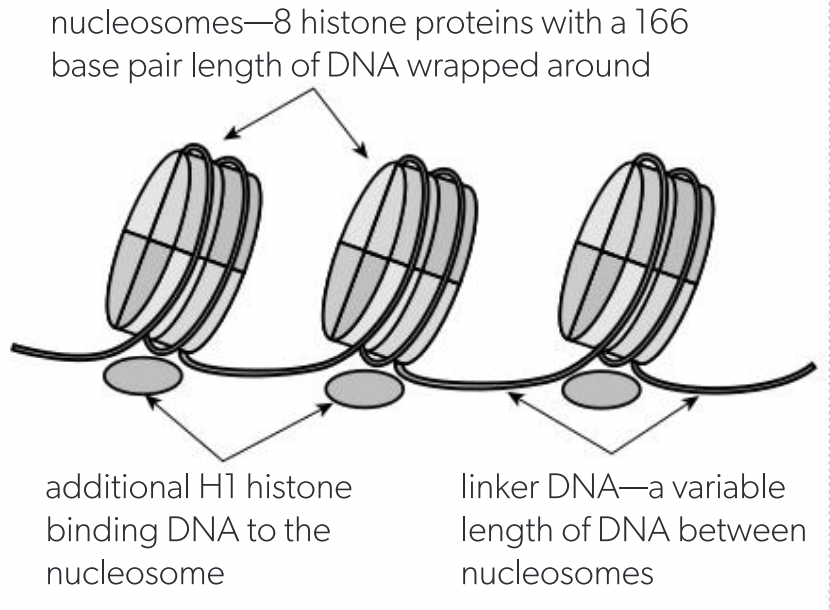
A1.2.13. Nucleosomes
disc like; package DNA into condensed chromosomes. Has 8 histones (2×H2a, 2×H2b, 2×H3, 2×H4) in a square with DNA rapped around it (double loop), H1 histones help secure structure. Linker DNA is between adjacent nucleosomes to form chromatin: chain of nucleosomes.
A1.2.14. Hershey-Chase
E-coli viruses labelled with radioactive S protein coat and P DNA, let the virus infect bacteria, then centrifuged, and end up with Sulfur outside of the cell, and Phosphorus still inside the cell; proof for DNA as genetic material
A1.2.15. Chargaff’s data
Evidence for complementary base pairs:
Purine always bonds to pyrimidine; AT, CG
Chargaff showed no matter what the percentages of nucleotides were, but A=T and C=G, A+G=T+C=50%