osmosis, passive, and active transport
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Turgid
plant cells swell in a hypotonic solution
isotonic
when a cell is put into the solution, the water levels inside and outside the cell are the same
Flaccid
a plant cell at homeostasis in a isotonic solution
Fluid Mosaic Model
membrane is held together by weak hydrophobic interactions and can therefore move and shift
Glycoprotein
carbohydrates bonded to proteins
Hypertonic
cells lose water, shrivel
solution has a higher solute concentration
Hypotonic
cells gain water, swell
solution has a higher water concentration
Cholesterol
helps maintain fluidity at high and low temperatures
high- reduces movement
low- reduces tight packing of phospholipids
Lysis
animal cell swelling and exploding after being put in a hypotonic solution
Plasmolysis
plant cells shriveled after being put in a hypertonic solution
Glycolipid
carbohydrates bonded to lipids
osmoregulation
cells must be able to regulate their solute concentrations and maintain water balance
Tonicity
the ability of an extracellular solution to cause a cell to gain or loose water
Water potential
a physical property that predicts the direction water will flow
Mosaic
comprised of many macromolecules
Integral proteins
proteins that are embedded into the lipid layer
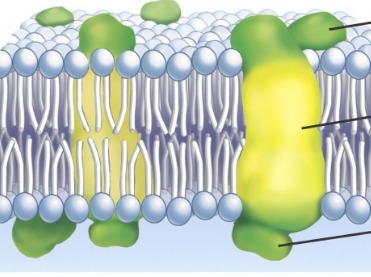
Peripheral proteins
proteins that are not embedded into the lipid bilayer
- loosely bonded to the surface
Membrane carbohydrates
important for cell-to-cell recognition
Pumps
maintain membrane potential
- sodium potassium pump (3Na out, 2K in)
Membrane potential
unequal concentrations of ions across the membrane results in an electrical charge (electrochemical gradient)
Proton pump
integral protein membrane that builds up a proton gradient across the membrane
- pumps H+ put of the cell
Cotransport
the coupling of a favorable movement of one substance with an unfavorable movement of another substance
- uses the energy stored in electrochemical gradients (generated by pumps) to move substances against their concentration gradient
- favorable movement: downhill diffusion
- unfavorable movement: uphill transport
Cotransport is used for
plants use it for sugars and amino acids
- sucrose and H+
- sucrose can travel into a plant cell against its concentration gradient ONLY if it is coupled with H+ that is diffusing down its electrochemical gradient
Exocytosis
the secretion of molecules via vesicles that fuse to the plasma membrane
- vesicles can fuse to the membrane by forming a bilayer
- once fused the contents of the vesicle are released to the extracellular fluid
- ex: nerve cells releasing neurotransmitters
Endocytosis
the uptake of molecules from vesicles fused from the plasma membrane
- phagocytosis
- pinocytosis
- receptor mediated
Phagocytosis
when a cell engulfs particles to be later digested by lysosomes
- cell surrounds particles into a food vacuole
- food vacuole fuses with lysosomes to be digested
Pinocytosis
nonspecific uptake of extracellular fluid containing dissolved molecules
- cell takes in dissolved molecules in a protein coated vesicle
- protein coat helps to mediate the transport of molecules
Receptor mediated endocytosis
specific uptake of molecules via solute binding to receptors on the plasma membrane
- allows cell to take up large quantities of a specific substance
- when solutes bind to receptors they cluster in a coated vesicle to be taken into the cell
Easy passage through membrane
small, nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules
- ex: hydrocarbons, CO2, O2, N2
Difficult passage through membrane
hydrophilic, polar molecules, large molecules, and ions
- ex: sugars, water
Passive transport
transport of a molecule that does not require energy, molecule is moving WITH electrochemical gradient
- ex: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
Diffusion
spontaneous process resulting from the constant motion of molecules
- substances go from high to low concentrations
- move down concentration gradient
- different rates of diffusion for different molecules
Osmosis
the diffusion of water down its concentration gradient across a selectively permeable membrane
- can be thought of as diffusion of water from areas of low solute to areas of high solute
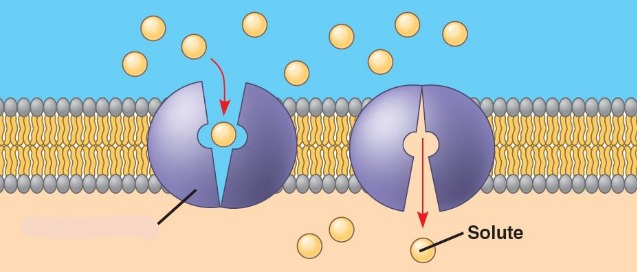
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion of molecules through the membrane via transport proteins
- increases rate of diffusion for small ions, water, and carbs
- can either go through a channel or carrier protein
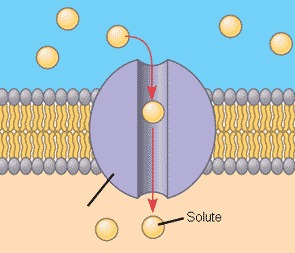
Channel proteins
provides a channel for molecules and ions to pass
- hydrophilic
- many gated channels, only allow passage when there is a stimulus
Aquaporins
specific channel protein for water
Carrier proteins
undergo conformational changes for substances to pass