3 Macromolecules - Protein, Carbohydrates
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Hydrolsis Reaction
when a water molecule is inserted across a covalent bond and breaks it resulting in a split H2O. One polymer gains a H atom and the other a OH- molecule.
What is the purpose for a hydrolysis reaction?
to break down complex molecules into simpler components so enzymes have an easier time breaking them down for digestion. (breakdown of polymers)
Condensation or Dehydration reactions
release of a molecule of water and the formation of a covalent bond on 2 monomers
What is the purpose of a dehydration/condensation reaction?
joins two molecules to form a compound, H2O. helps with polymer synthesis and forming a macromolecule.
Polymer
a chain of monomers linked together by covalent bonds
Monomer
small units chemically bonded to make polymers
What type of chemical reaction adds monomers to lengthen polymers?
dehydration/condensation reaction
What type of reaction removes monomers to shorten polymers?
hydrolysis reaction
Carbohydrates
represented by the formular (CH2O)n
n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule
3 types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
What are the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates called?
monomer: monosaccharides
polymer: disaccharides & polysaccharides
Monosaccharide
may exist as a linear chain or ring-shaped in aqueous solutions
polar because of OH-
Ex. glucose, fructose
Glucose
glucose monomers in long branches
important source of energy in living species (ATP)
an aldehyde - carbonyl is at the end of the carbon skeleton
stored in liver and muscle
C6H12O6
Disaccharide
formed when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction
covalent bond = glycosidic bond
Ex. maltose, sucrose (table sugar)
Maltose
glucose + glucose
Sucrose
glucose + fructose
Polysaccharide
Polymers of sugar
can be branched or unbranched
Storage and structural roles
Ex. cellulose, glycogen, starch (glucose monomers in long chains)
Amylose
linear polysaccharide
Amylopectin
branched polysaccharide
Starch
storage polysaccharide
glucose monomers in long chains
amylopectin
synthesized by plants → stores excess glucose in roots and seeds
easily digestible
Glycogen
storage polysaccharide
glucose monomers in long branches
used by animals → store excess glucose
stored in liver and muscle cells
easily digestible
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide
every other glucose monomer is flipped over and packed tightly as extended long chains
rigid and has high tensile strength important for plant cells
cell walls of plants are mostly made of cellulose
cellulase can break down cellulose into glucose which is used as an energy source by the animal
Sugar Isomers
same molecular formula, but different structure
Ex. glucose and fructose are structural isomers
Starch breakdown
Starch is broken down to maltose by enzymes called amylases found in your saliva and your small intestine. maltase breaks down maltose into glucose. Glucose is absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine.
Protein
most abundant organic molecules in living species
What are the monomers, polymers, and covalent bonds of protein?
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: Polypeptide
Covalent bond: Peptide bond
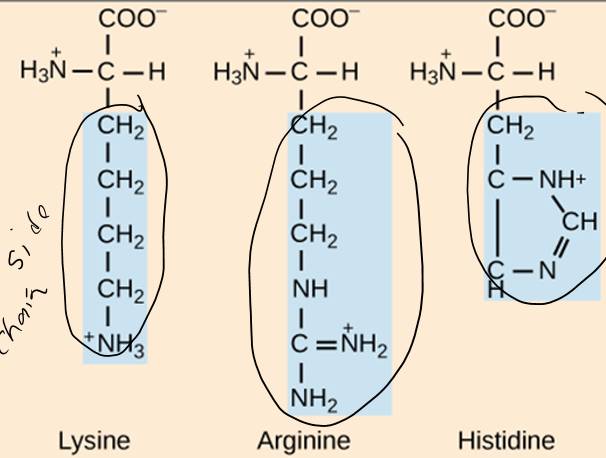
What are the three groups that can be found attached to the central carbon of an amino acid?
Carboxyl group, animo group, hydrogen atom
How do amino acids differ from each other?
The side chain is different in each aa. Based on this, the aa could be hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acidic (-), or basic (+)
How many standard aa are there?
20
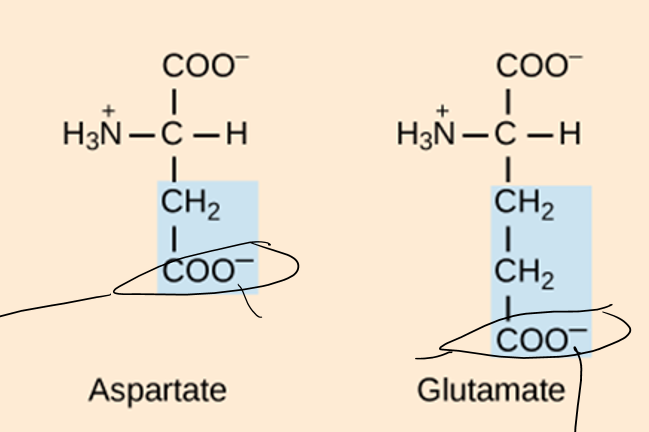
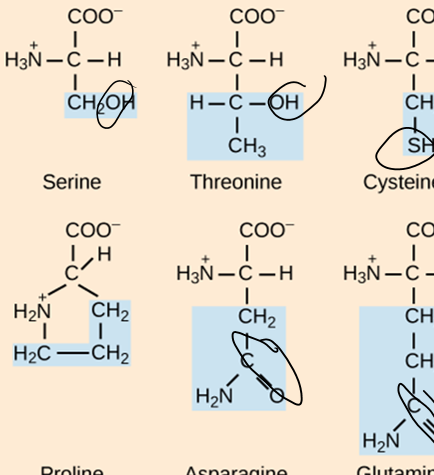
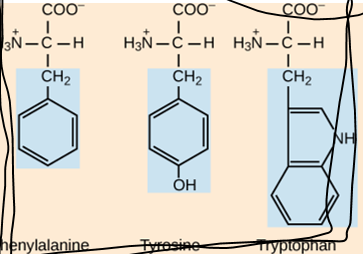
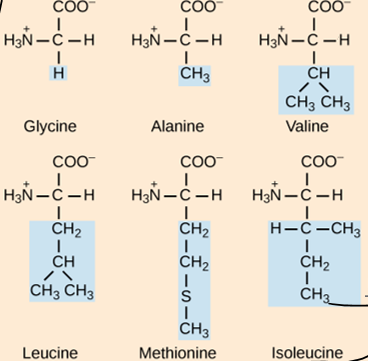
How are protein structure and function related?
The sequence of amino acids determines the shape of the protein and its function. If even one aa is changes in the structure, the function of the protein can change.
Primary Protein Structure
dehydration/condensation that formed peptide bonds
amino acid sequence
n-terminal (NH2) and c-terminal (COOH)
Secondary Structure
a helix and B-pleated sheets
amino acid subunits
hydrogen bonds between parts of peptide backbone causes the aa to fold into a repeating pattern.
Tertiary Structure
due to side chains interactions
a helix and B-pleated sheets folded together
Hydrophobic Interactions: amino acids “push” into middle
Weak bonds: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds
Disulfide bridges: covalent bonds between -SH groups or separate cysteine amino acids
Quaternary Structure
2+ polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
can be the same or different
composed of multiple tertiary structures that interact and form
Ex. fibrous (3 subunits), globular (a chains and b chains)
Protein Denaturation
occurs when protein is subject to changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals. The structure may change and lose its shape. It can be reversible because the primary structure is often preserved, allowing it to continue its function
Ex. egg (heat causes vibration causing it to lose its shape)