Pre-DP Ps3 terminology
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finnish pre-dp ps3 terminology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Localization
A theory that associates some areas of the brain with some activity
some areas can be divided further with further specific function regions
evaluation:
can predict behavior - damage
may be oversimplifying
memory sexuality disgust have bio and sociocultucognitivital factors
modernly it is said that vast majority of behaviors delocalized and done by many parts
fMRI (used to study localization) requires subject to stay still, limiting ecological validity and opportunities, not always applicable outside lab
Schemas
mental representations that organize and guide behavior
neurons (that gray matter controls)
sensory (detect stimuli), motor (ctrl muscles, glands), relay/inter (transfer information between the aforementioned two, majority of all neurons are these)
neurons use electrical impulses to transmit info, communicate with synapses chemically
limbic system
amygdala - emotions
hippocampus - encoding
pre-frontal cortex - decisions and problem solving
thalamus - sensory signal relay to cortex (except smell)
hypothalamus - primarily controls many autonomic functions (metabolism, body temp), motivated;) behaviors
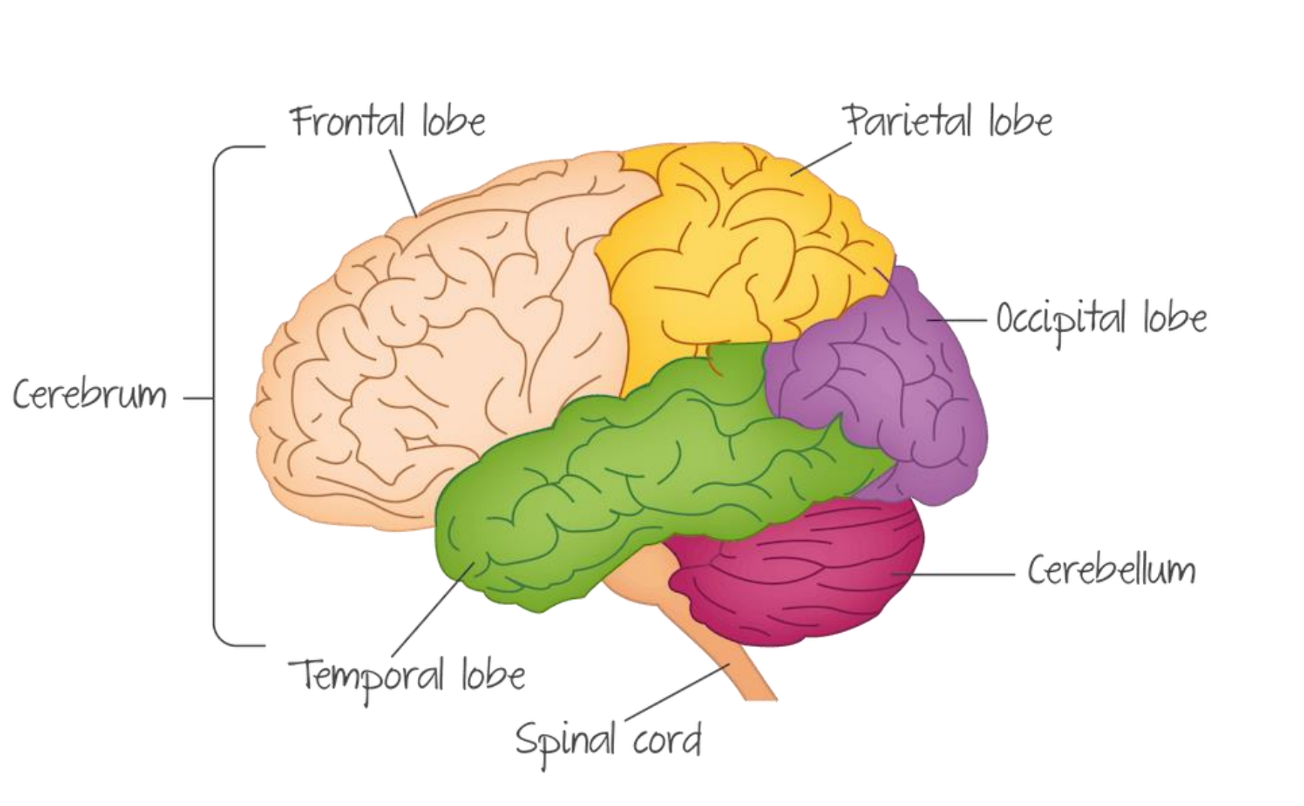
lobes of the cerebral cortex
frontal - has PFC and motor cortex, used for decisions (memory, prob-solve)
parietal - perception, sensory processing (touch temp etc) and speech
occipital - vision
temporal - audio info, memory processing, making meaning from speech and language
Cerebral cortex cerebellum
pikkuaivot, motor control
Cerebral cortex brainstem
Medulla - BP
Pons - many neurons regulates sleep
Reticular formation - information relay, alertness, focus, awareness when awake
MRI
uses mag field and RWaves to map activity of hydrogen molecules
radio waves switch on/off align molecules
MRI captures alignment → image
can find tumors bleeding injuries blood vessel diseases, infections
used in sports
high degree of detail
STATIC - no real time data
may overemphasize a large area
does NOT explain behavior
fMRI
measures blood flow changes (hemoglobin), can measure brain activity
highlights active parts during behavior
shows correlation btwn behavior and activity in area
can examine effects of degenerative diseases, str
oke trauma etc
fMRI requires subject to stay still, limiting ecological validity and opportunities, not always applicable outside lab
a highlighted area may not be as important as shown
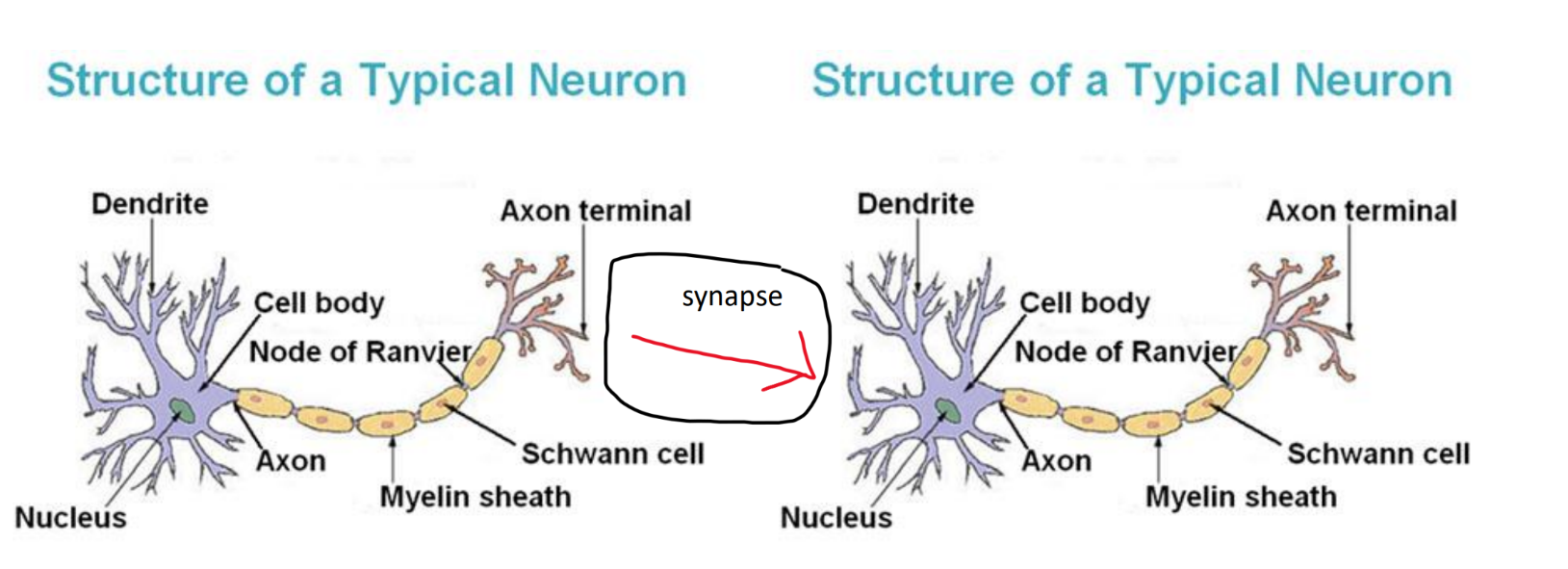
a dendrite
treeish extension of neuron, more = more potential neuron connections
neural network
a group (a network) of neurons that are interlinked and connected which combine to produce a specific neurological function or process e.g. learning a new language; spatial navigation
long-term potentiation
long-term signal transmission improvement btwn certain neurons
D|A/B HAPPENS
cause: repetition
dendritic arborization/branching
neurons grow more dendrites, more complex actions possible due to more synapses
synaptic pruning
less practice/repetition → we get worse (long-term depression)
neural connections are pruned if not used regularly to improve function of more frequent networks
benefit: damaged connections (by toxins etc) are removed and stop harming us, can also help us unlearn bad habits and bad/outdated behavior
neuroplasticity
brain can change its structure following bodily changes or lifestyle/behavior changes, uses dendritic branching and pruning
can be studied to examine how environment affects us biologically
like poverty etc
explains how humans get more smart from kid→adult
also explains changes in adult brains when learning new things
remember maguire taxi study (2000)
research very correlational
used for identifying & treating diseases etc
response to env, all studies affected by the participants’ lives too

neurotransmitters
chemical messengers made by neurons
associated with some behaviors
e.g. dopamine - pleasure
neurotransmission
neurotransmitters are sent from neuron to other neuron
released from axon terminal buttons of the sending(presynaptic) → synapse (gap btwn neurons)
post-synaptic neuron has dendrites that receive NTs by binding them
each receptor is for one transmitter only
lock and key
some stuff can mimic key
excess neurotransmitters are either enzymed to oblivion or absorbed by terminal buttons = reuptake
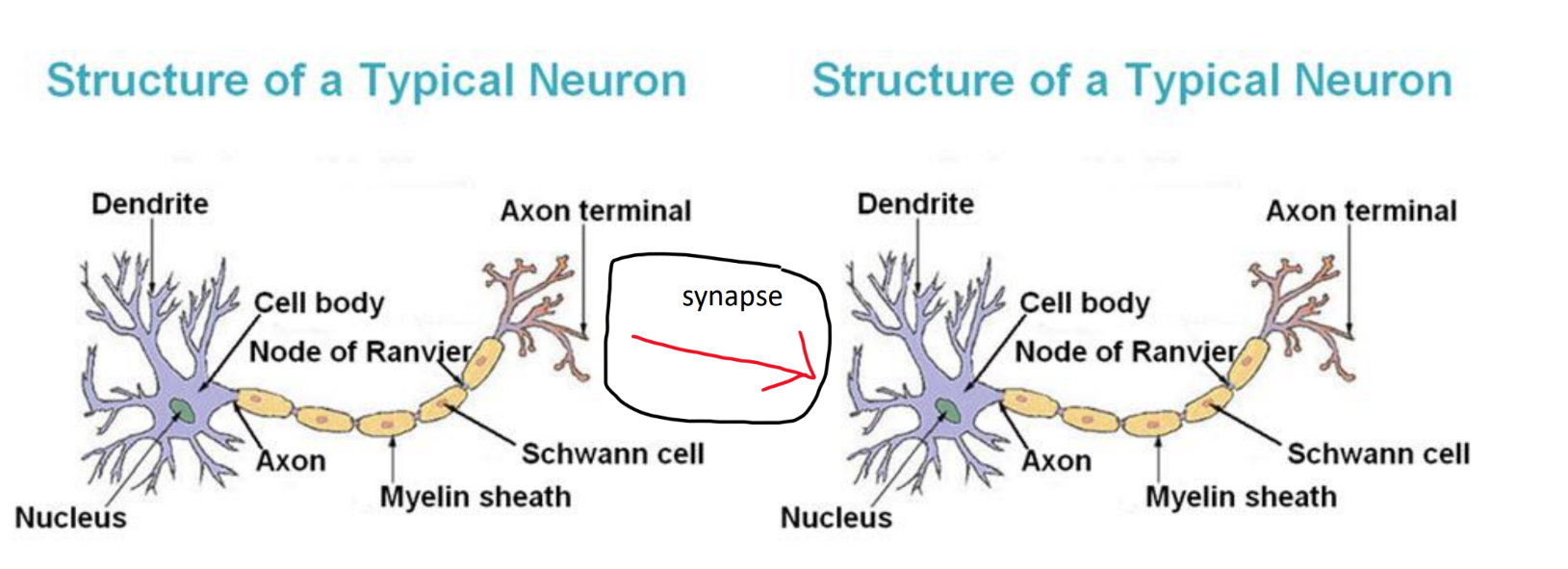
(ant)agonist
agonists mimic neurotransmitters and increase effects
can be drugs or nat prod
drugs → dopamine
endorphins → less pain
morphine → endorphin agonist
dopamine is a dopamine agonist
cocaine is indirect dopamine agonist = blocks reuptake → body produces less → increased tolerance and addiction
antagonists limit neurotransmissions
antipsychotics
scopolamine (motion sick)
antihistamines
caffeine is an adenosine antagonist
tired ib student drinks caffeine → it blocks neurotransmitter called adenosine which regulates tiredness
hard to study cuz ethics, oversimplification
Major Histocompability Complex
section of DNA with genes that create proteins relative to immune system
co-dominant = all allele variants expressed
each allele makes different protein → immune boost
diverser MHC → healthier?
remember wedekind t shirt study
Culture
a set of values beliefs languages rituals traditions etc common stuff shared by a group
surface culture = easily identifiable when compared to other cultures, lang cuisine art
deep culture = need a profound understanding of culture to notice, the submerged part of iceberg
approaches to marriage, concepts of justice etc
have norms that are internal rules/customs/attitudes
norms
internal rules/customs/attitudes of a group
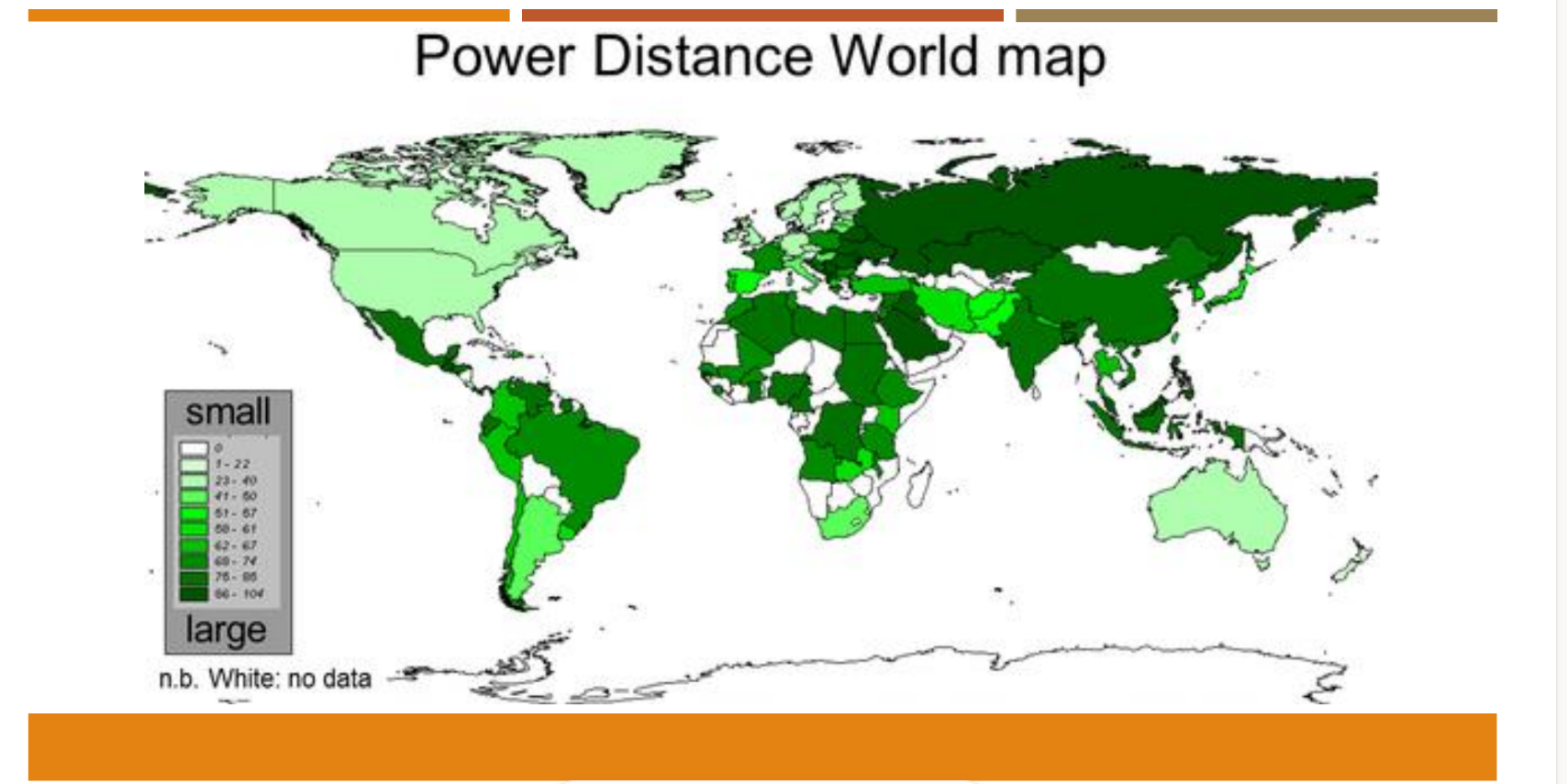
Cultural dimensions - Power distance index
how much a culture respects auth and status
Cultural dimensions - Individualism vs collectivism
how integrated people are to groups [I/we orientation]
![<p>how integrated people are to groups [I/we orientation]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9d4b1de9-7f0f-4b42-afd3-c04086a69178.png)
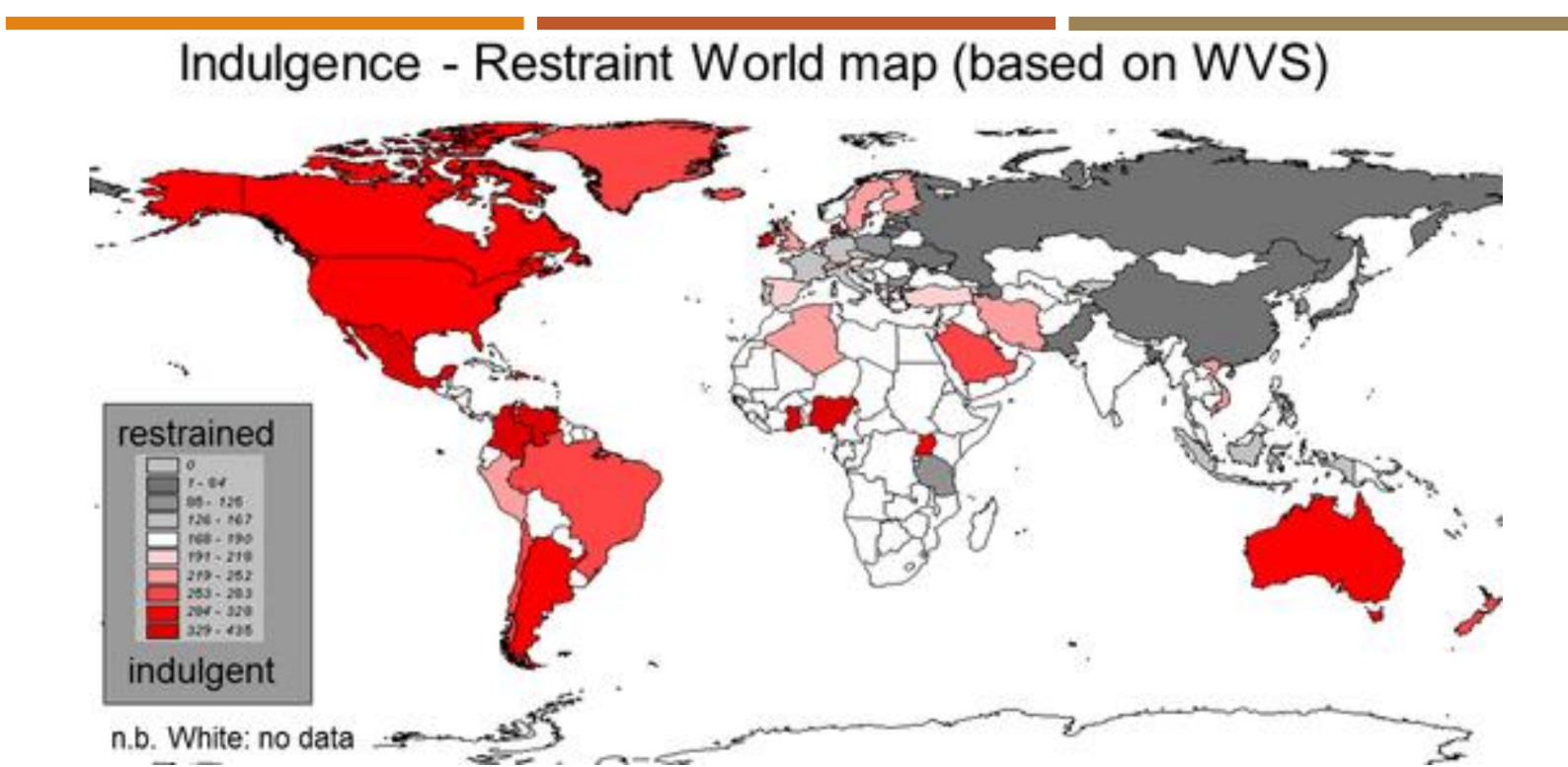
Cultural dimensions - Uncertainty avoidance index
how tolerant for ambiguity a society is
high tolerance = openness to change and not strict rules
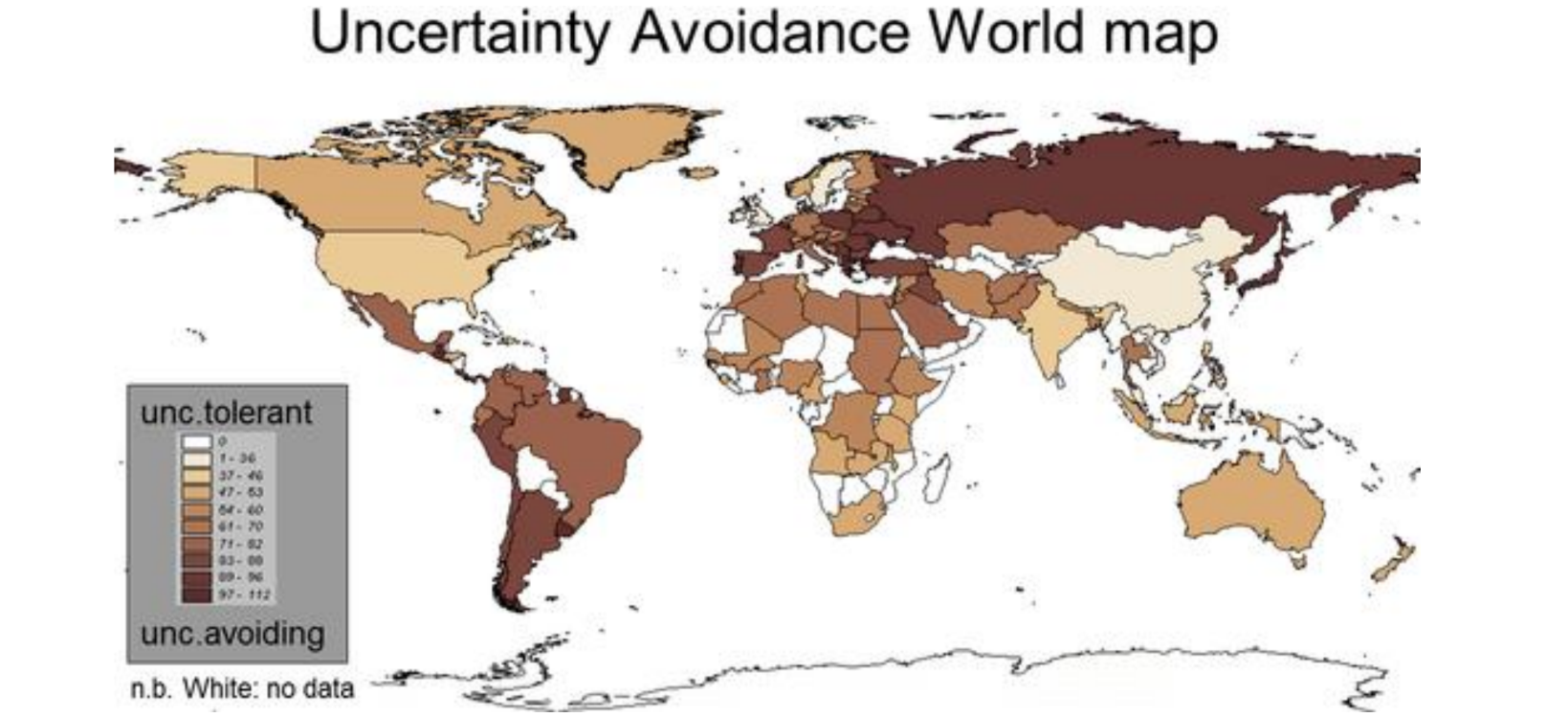
Cultural dimensions - Masculinity and femininity
Masculine = focus på achievement, competition, wealth
Feminine = cooperation relationships QoL
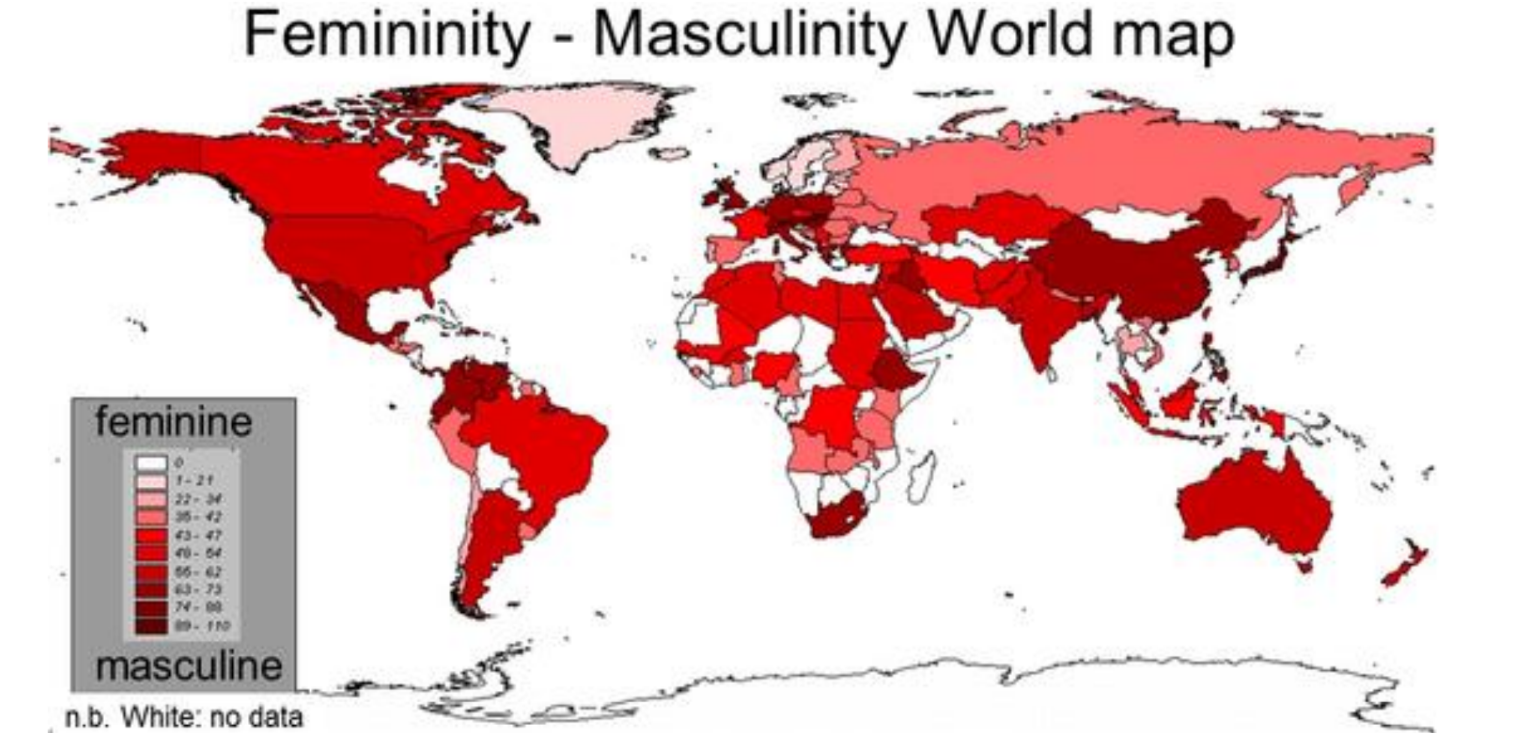
Cultural dimensions - LT vs ST orientaition
Long-term focuses on future, short term keeps traditions, how connected to past and what thinks of future
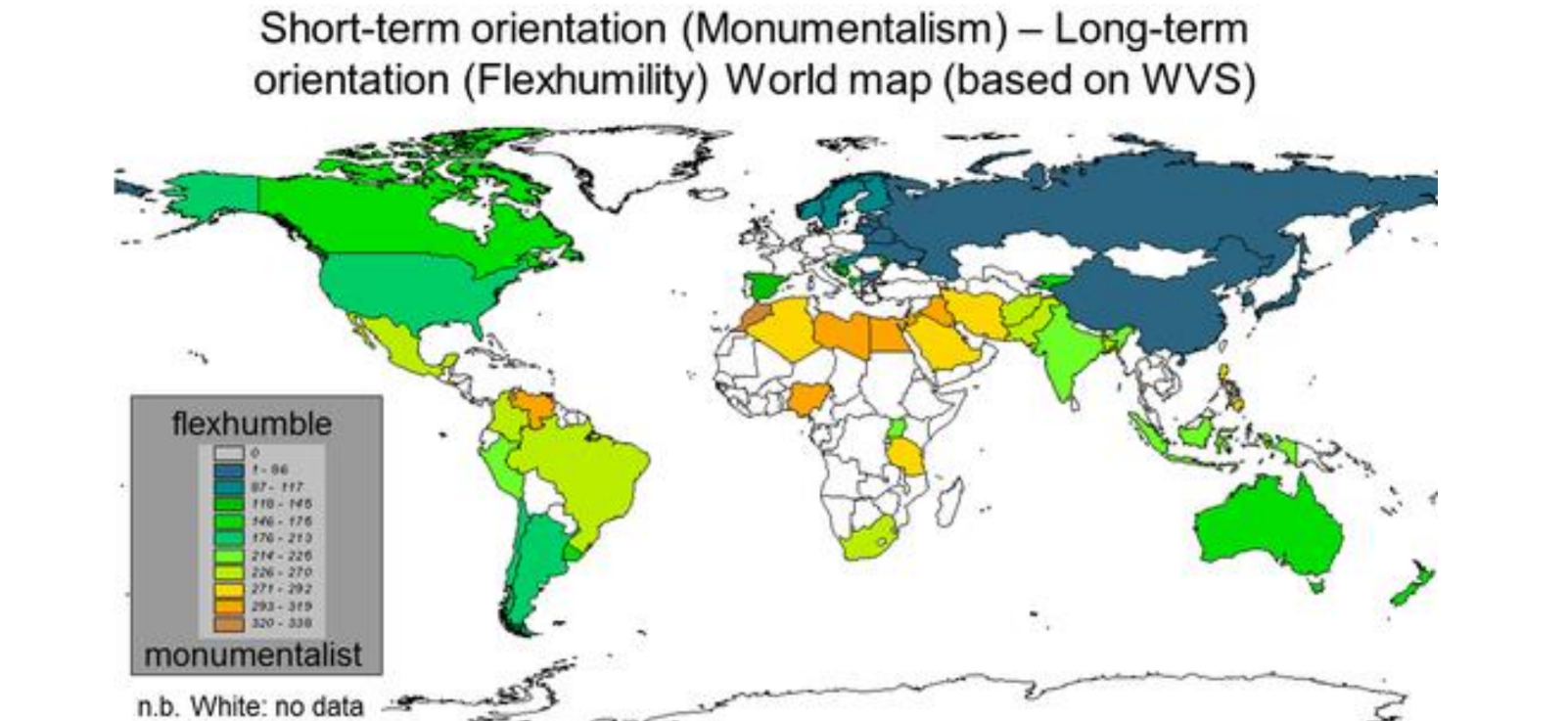
Cultural dimensions - Indulgence vs restraint
indulgence = go out have fun, thinks that has ctrl over life
restraint = strict controlled norms, more fatalistic
Socialization
process of joining a group or society and becuming member
involves interaction with the culture and its representatives
internalization of the cultures norms and what they consider normal
Enculturation
process of learning cultural practices (langs and customs)
tuition
practice
social cognitive theory
Social cognitive theory
“we can learn behaviors by imitating and observing and modeling other people”
vicarious reinforcement → watch and learn, bandura’s bobo doll exp
acculturation
when one with a cultural background moves to another culture and has to learn it
measured with postiive/negative relationship with own and new culture and how much one values keeping the og one
culture shock = when acculturation tension is stressful
acculturation gaps is when kids of immigrants learn new culture, may result in differnet norms at home vs outside
protective factors = bilingualism → low acculturative stress
preference for speaking maj cult language → high risk of something
negative treatment → increased stress
sharing values & beliefs with family lowers it
economic satisfaction lowers too

group dynamics
group interactions, formation, intragroup relationships, tensions
a group
>=2 people who interact (in)directly, hv common interests (values, norms, goals), consider themselves a group
has task-oritented (work) goals and emotional goals (cry)
most have rules and norms
has roles which have expectations of behavior (teacher, the funny person, macbook)
people join them to satisfy needs, reach goals and boost personal identity
Conformity
surroundings influence behavior → we adjust behavior to fit in
dressing like friends
queues
peer pressure
so’s vegan diet
ASCH paradigm
conformity in rules reinforced in groups by reward and punishment

Group cohesion
willingness to belong in group, more positive feelings increases this
social loafing
“oh the other person will do it imma not do shit” happens in groups
norms
behaviors and expectations in a group / rules for behavior
implicit = group does not speak of it
explicit = group does
can be official rules
Social Identity Theory
cohesive groups may develop social identities
categorization (in-group vs out-group), which groups one belongs to
identification - adopting norms and characteristics after joining
comparison - ego boost from social comparison btwn in group and relevant out-groups (sigmas vs betas)
in-group favoritism - in-group successes praised and out-group is belittled (propaganda)
Levine

Motive
reason for behavior
primary/innate = eating for hunger
secondary/learned = craving sweets after
(sub)conscious
motivated actions pleasurable, unmotivated not
ex/in motivations
extrinsic = external factors contribute to motivation (punish/reward) = avoiding punishment
intrinsic = internal factors contribute to motivation (interest, enjoy)= runner’s high or whatever
motivation
behavior dynamics that initiate or sustain or direct or stop actions
basic psychological needs
autonomy = freedom to make decisions, actions etc are authentic
competence = capability and accomplishment feeling
relatedness = being part of something bigger
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
food, water, shelter, warmth → safety, employment, assets → family, friendship, intimacy, belonging → self-worth, accomplishment, confidence → inner fulfilment
cognitions
mental processes related to knowledge and awareness = perceiving, conceiving, remembering, reasoning, judging, imaginging, problem soelving
Dual-process model
divides processing to two models: system 1 and 2 where 1 is intuitive and 2 is rational
cog bias experiments have good results
cause-and-effect
may be simplistic, excludes emotion from dec making
definitions may be unclear
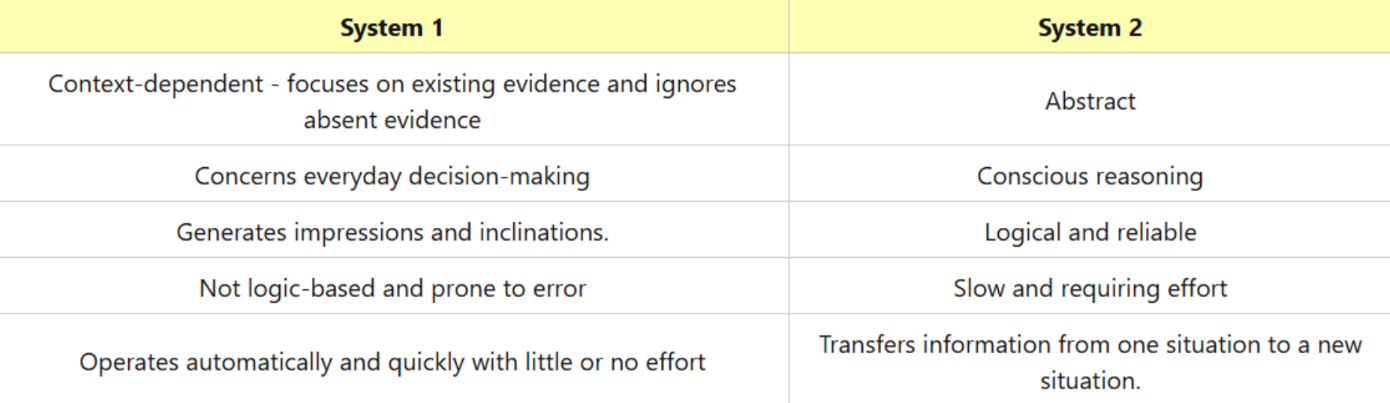
system 1
fast, intuitive and automatic decisions (easy calculations, mooscle memory)
uses heuristics = mental rules of thumb that can guide behavior
amount of thinking is minimized according to cog.psy
hence we use this amap
used more with high cog load = how occupied work memory is
saves mental resources
prone to cog bias

system 2
analytical, complexer, slower, critical (essay writing or making these damn flashcards)
evaluates options and comes to conclusion
used when sys 1 not enough for solution
or for decisions with high significance to individual
cognitive biases
systematic errors in thinking
anchoring bias
overreliance on first info (price tag) (strack and mussweiler 1997)
availability heuristic
most availabel (tiktok) info relied most on
barnum effect
vague descriptions accepted as relevant for personality (horoscopes)
effort heuristic
more effort is seen as higher quality
stereotypes
cog generalizations of characteristics and qualities of members of certain group
often exaggerated and negative
resistant to change even with contradiction
assimilation
new experience challenges schema, integrates new info
accommodation
new experience does not match schema at all, new schema is created
schema congruence
harmony and compatibility = matches existing schema
incongruence = not