Elasticity and Hooke’s law
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Elastic equilibrium position
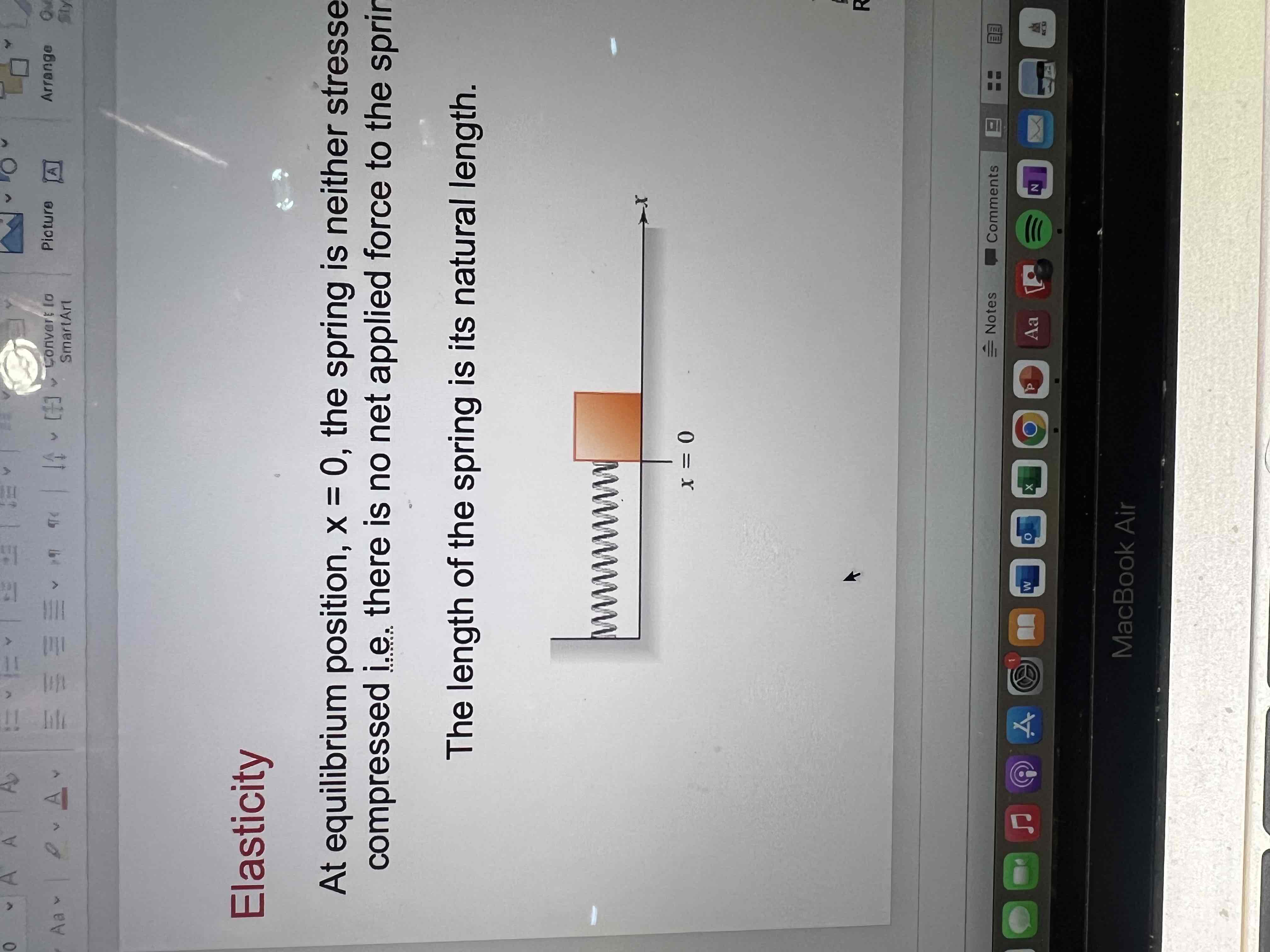
At equilibrium position, x=0, the spring is neither stressed or compressed ie there is no net applied force to the spring
The length of the spring is its natural length
Elasticity
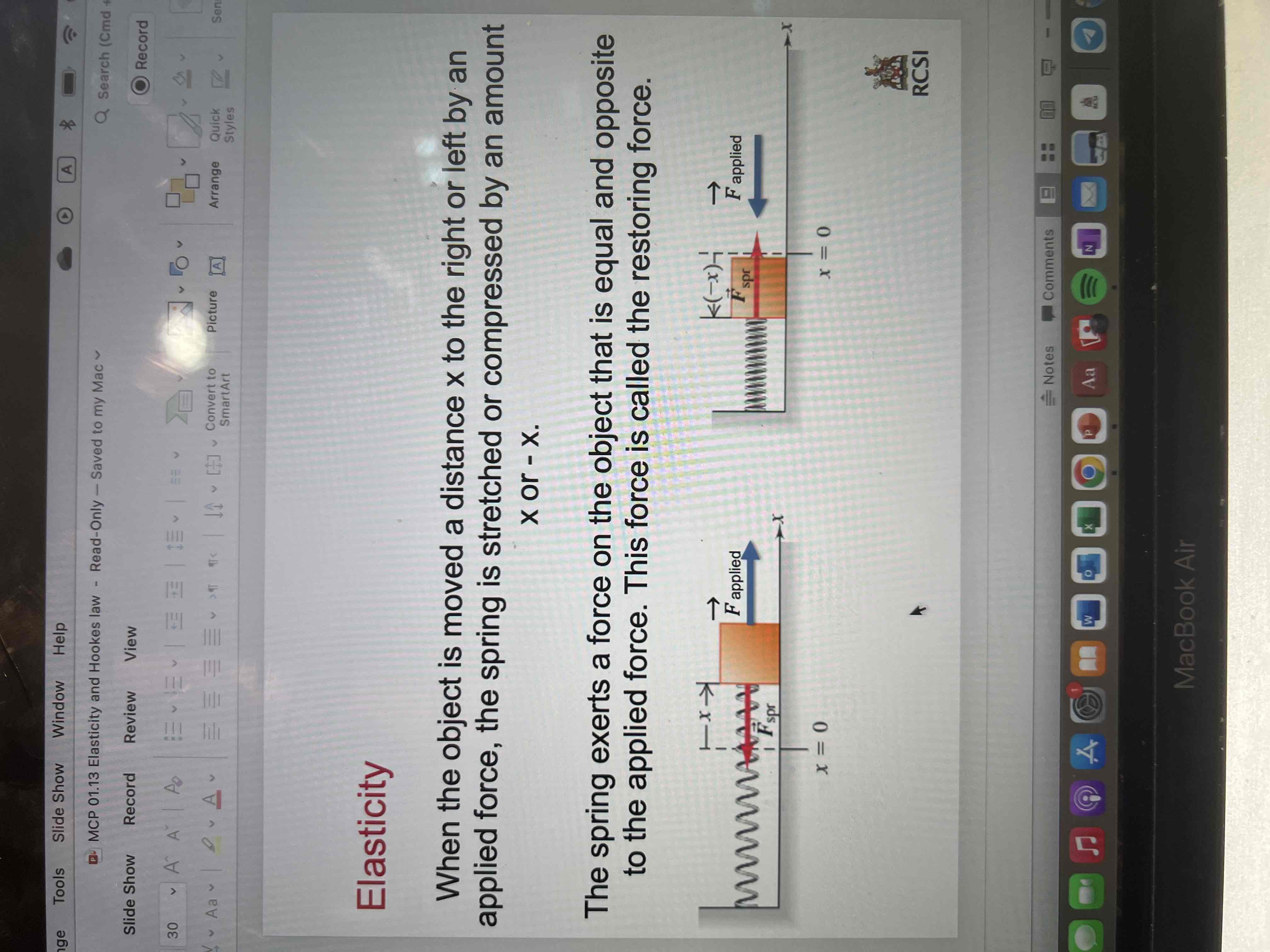
When the object is moved a distance x to the right or left by an applied force, the spring is stretched or compressed by an amount x or -x.
The spring exerts a force on the object that is equal and opposite to the applied force. This force is called the restoring force.
Restoring force
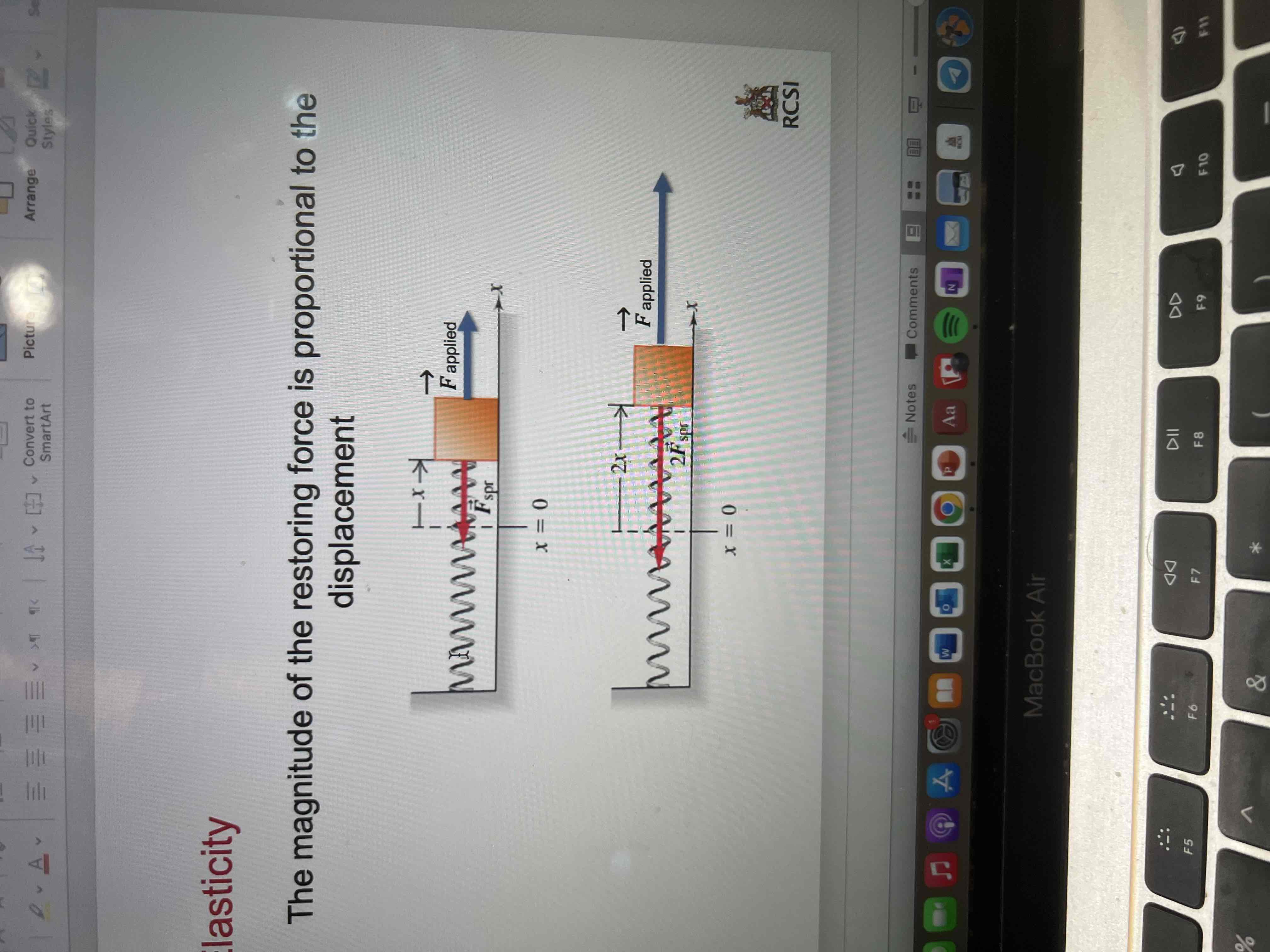
The magnitude of the restoring force is proportional to the displacement
Hooke’s Law
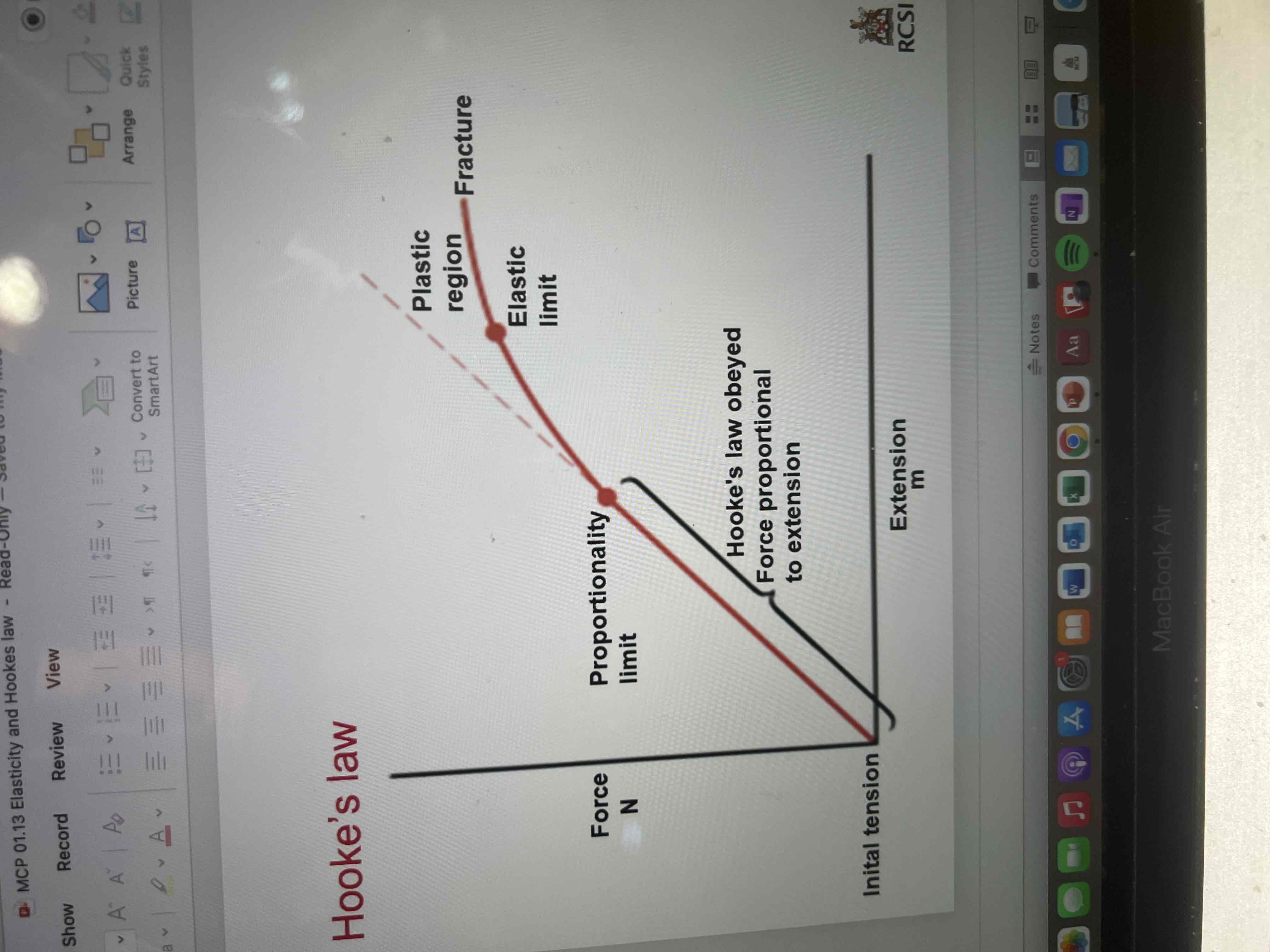
States that when an object is bent, stretched or compressed by a displacement s, the restoring force F is directly proportional to the displacement, provided the elastic limit is not exceeded.
F directly proportional to -s
F=-ks
(-) ensures that the displacement and restoring force are always in opposite directions.
(Ignore the sign for calculations)
Hooke’s law constant k
k is the spring constant and has units Nm^-1 and is a measure of the stiffness of a spring
k is a very stiff spring that requires a large force for a little deformation
k is a weak spring that requires only a small force for the same deformation
Elastic limit
The maximum force that a material can withstand before permanent deformation
All materials have an elastic limit beyond which it’s original shape can never be recovered.
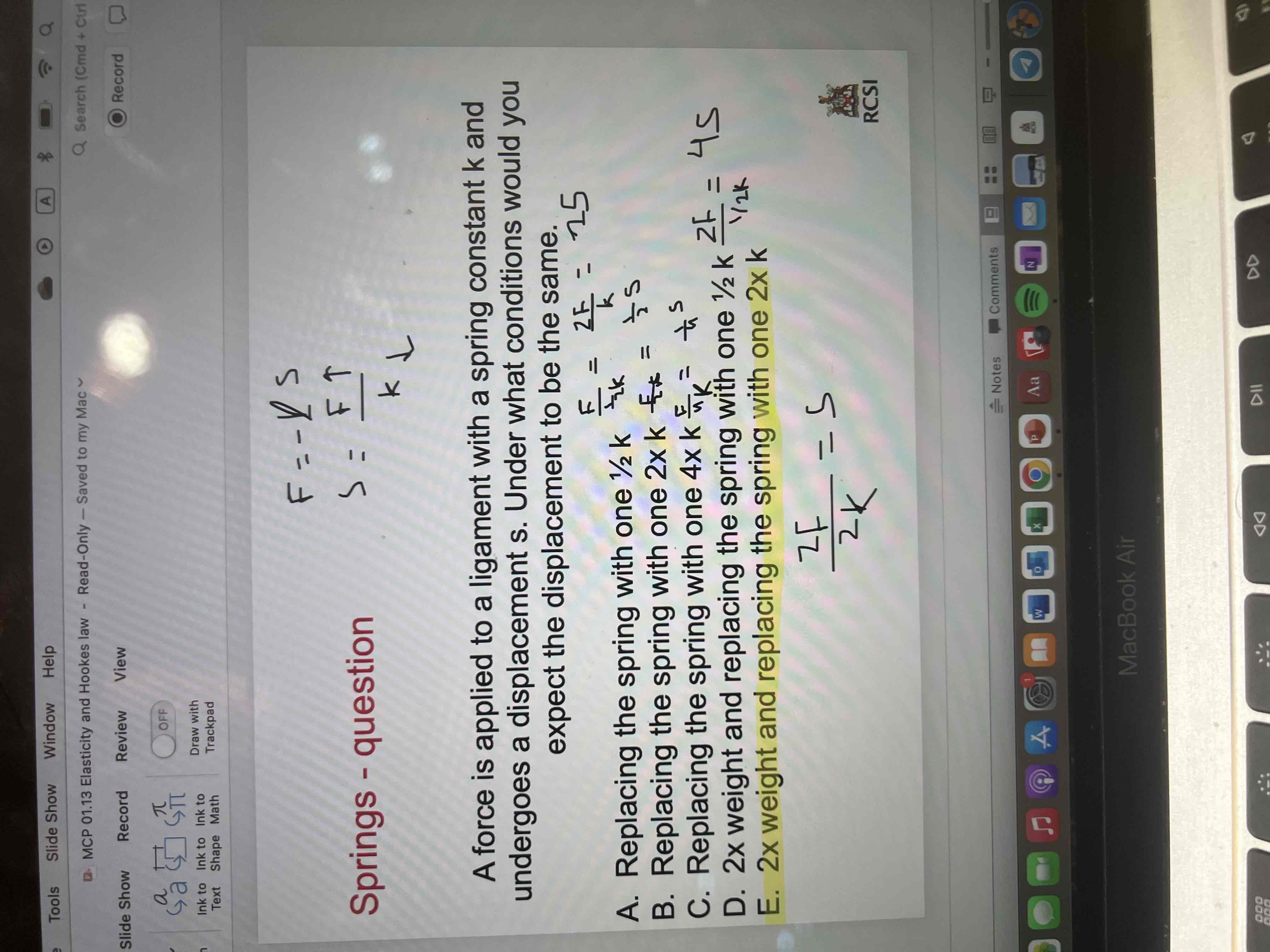
Springs question
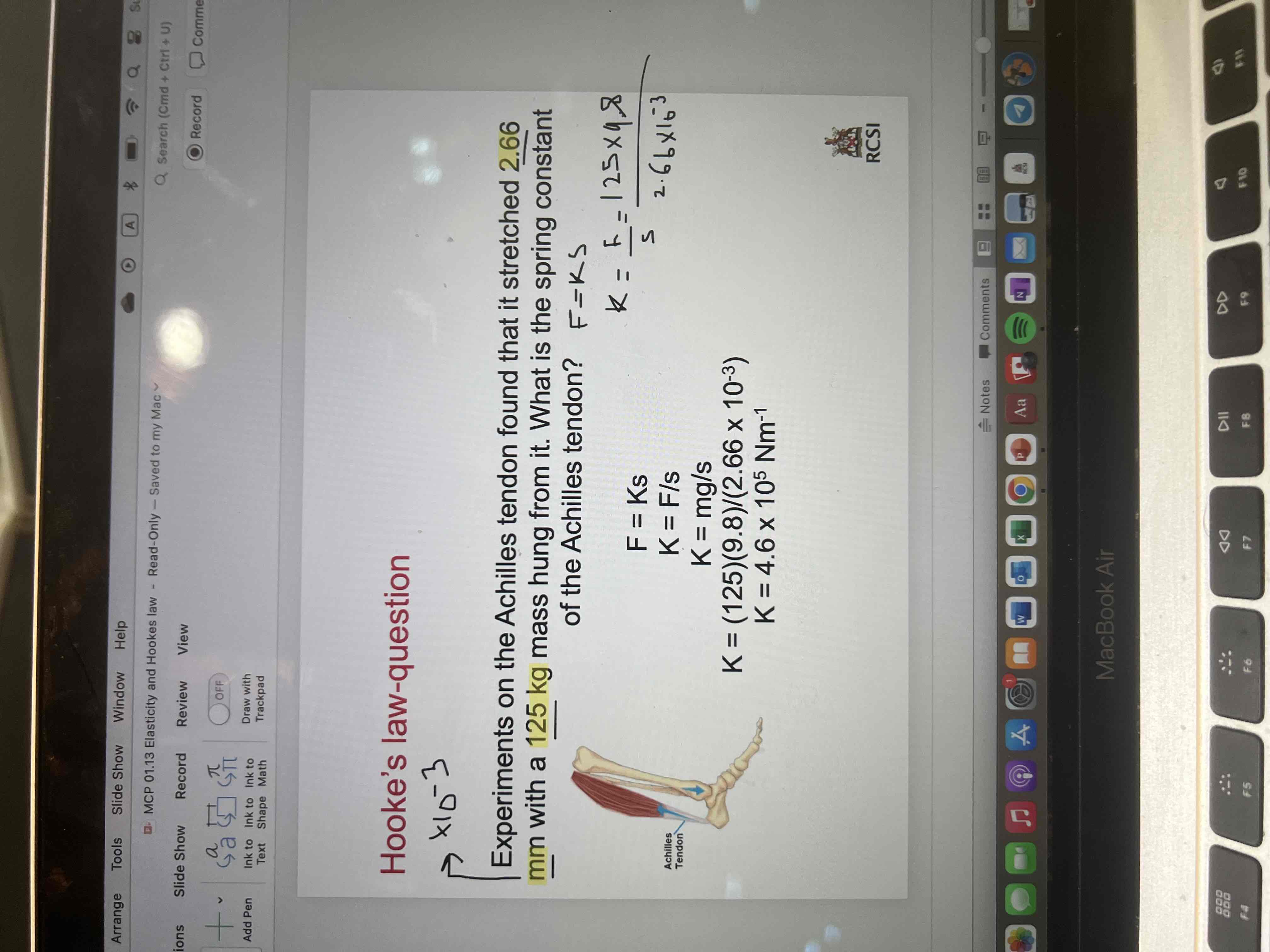
Hooke’s law question 1
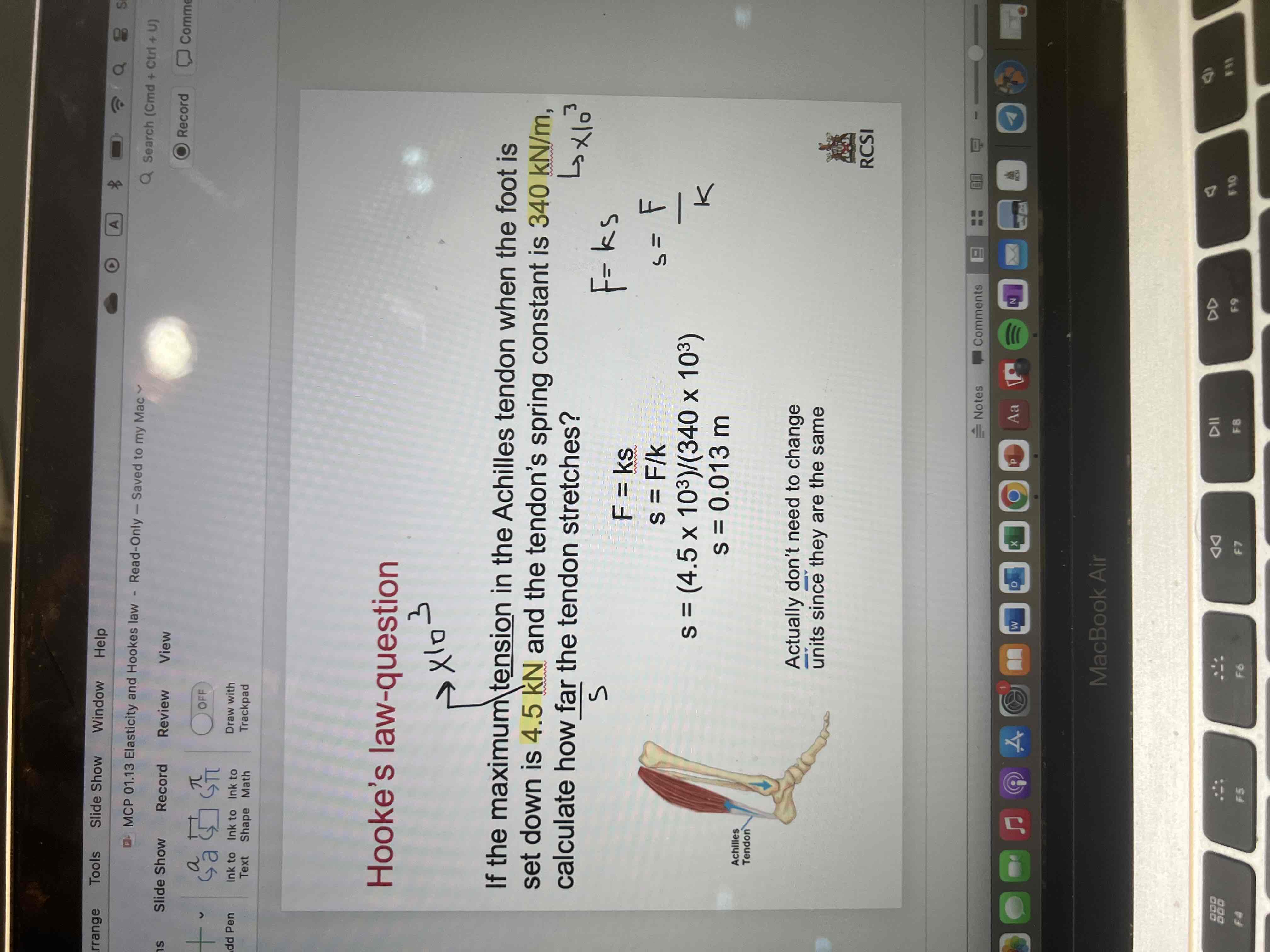
Hooke’s law question 2
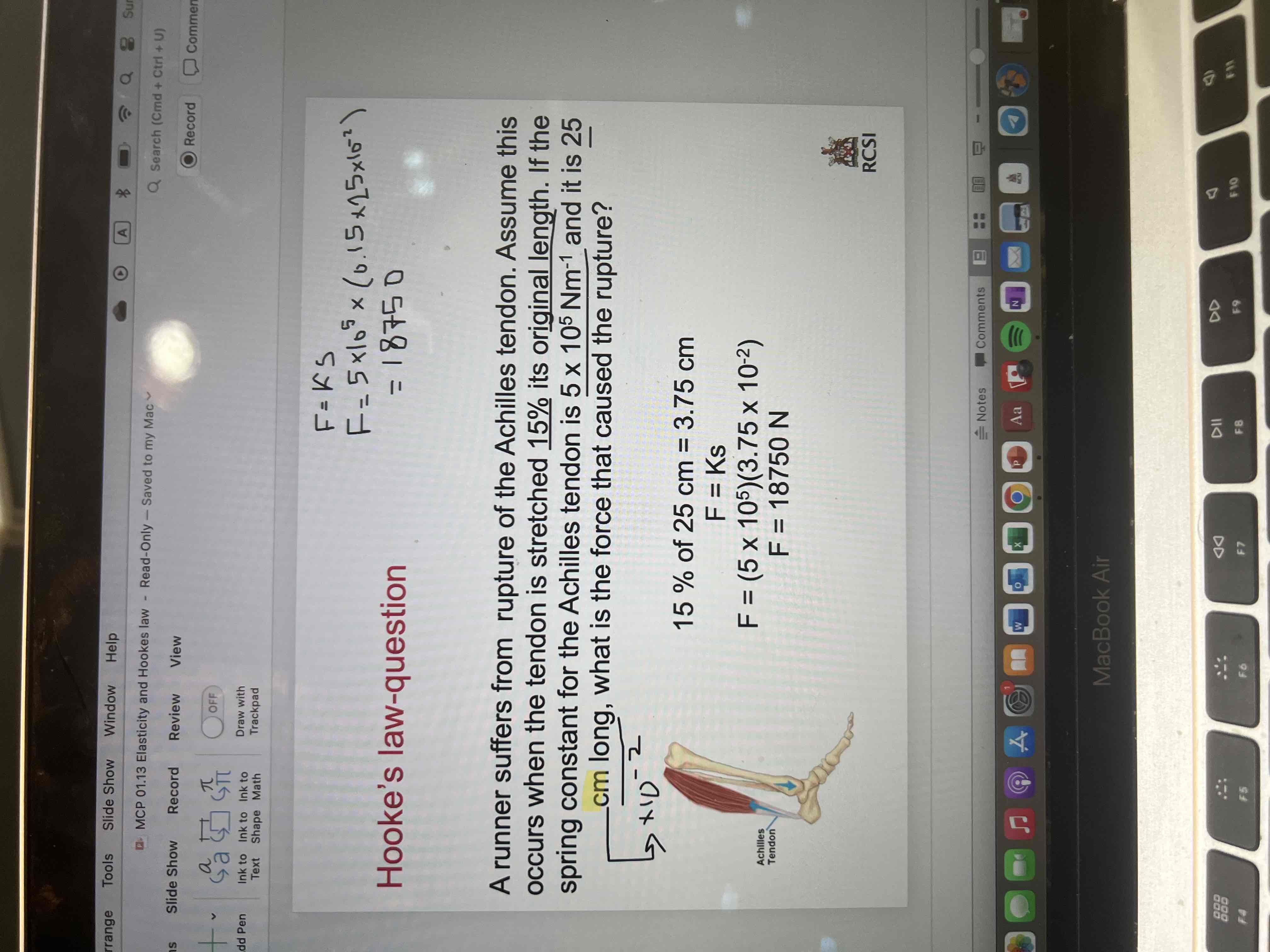
Hooke’s law question 3
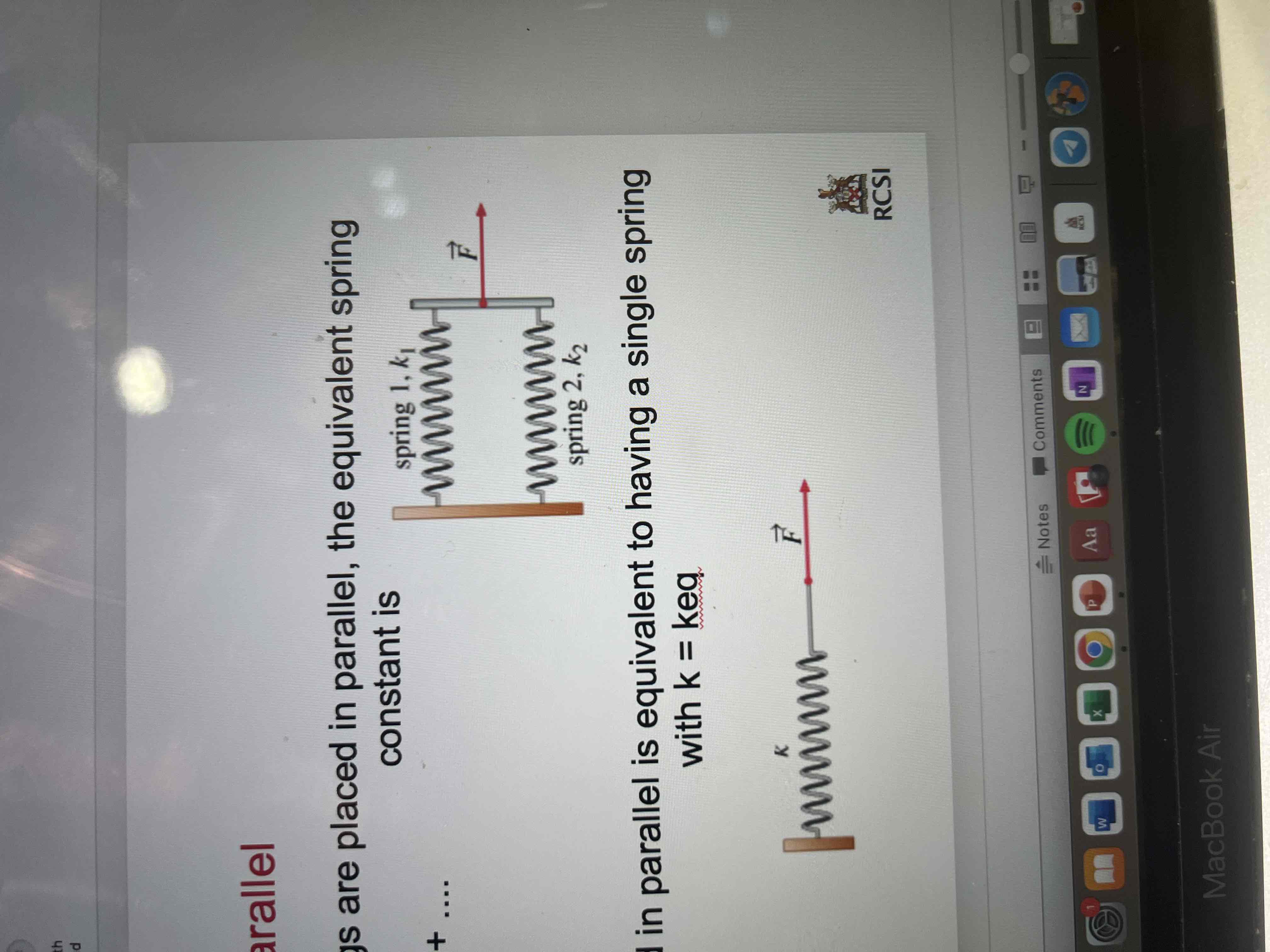
Springs in parallel circuit
The equivalent sprint constant is keq= k1 + k2
Springs placed in parallel is equivalent to having a single spring with k=keq
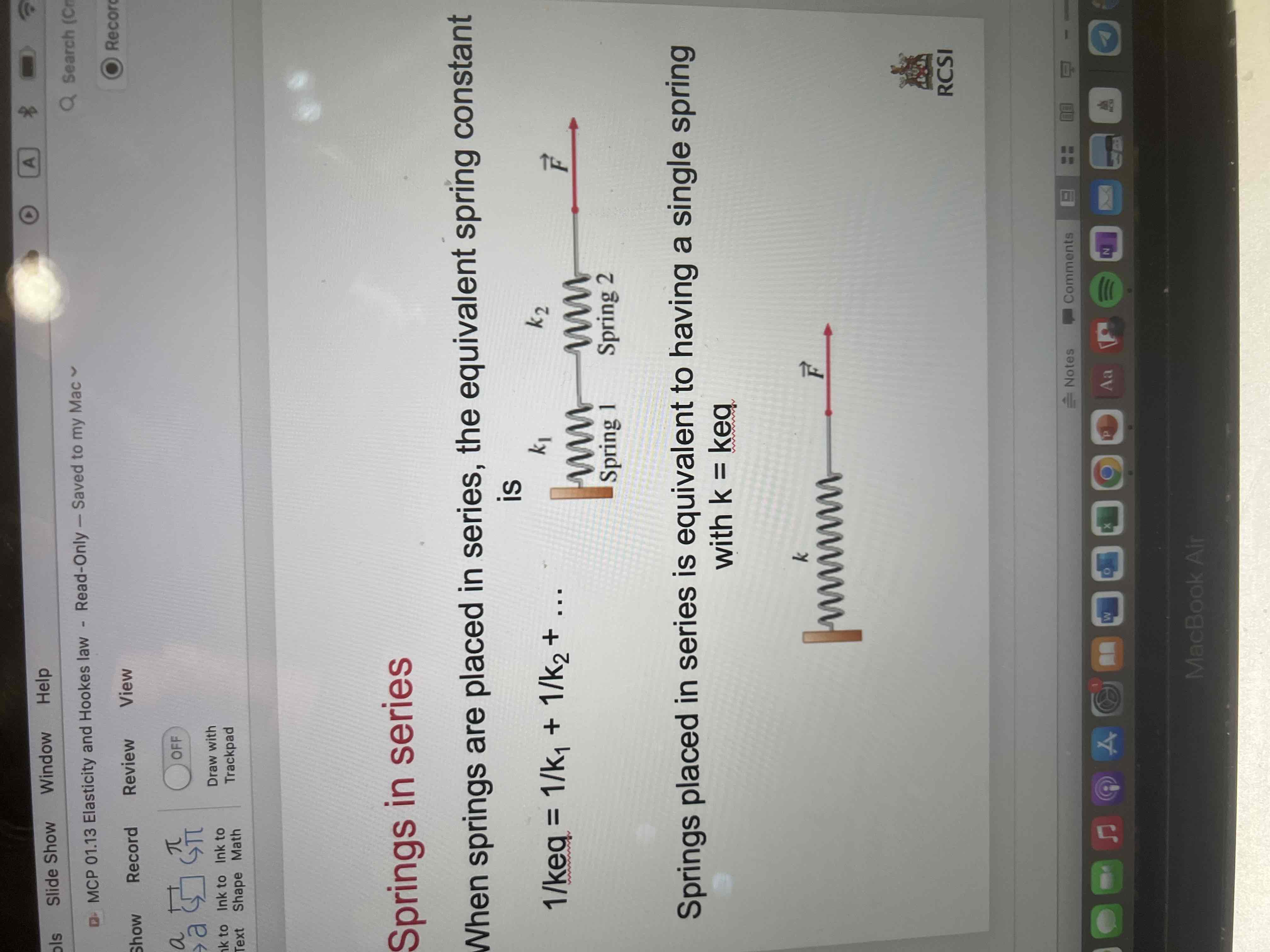
Springs in series circuit
The equivalent spring constant is 1/keq= 1/k1 + 1/k2
Springs places in series is equivalent to having a single spring with k=keq
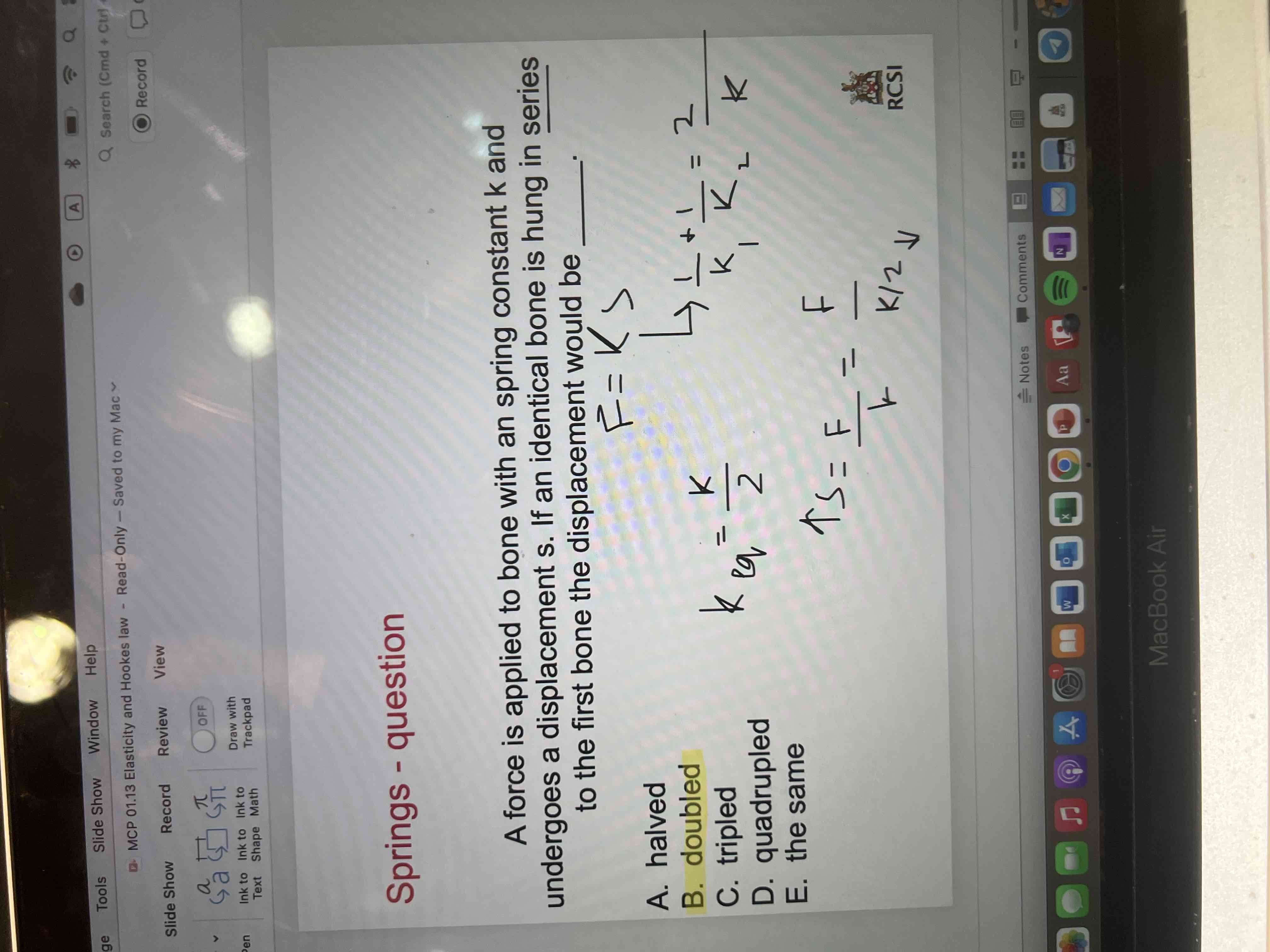
Springs question 2
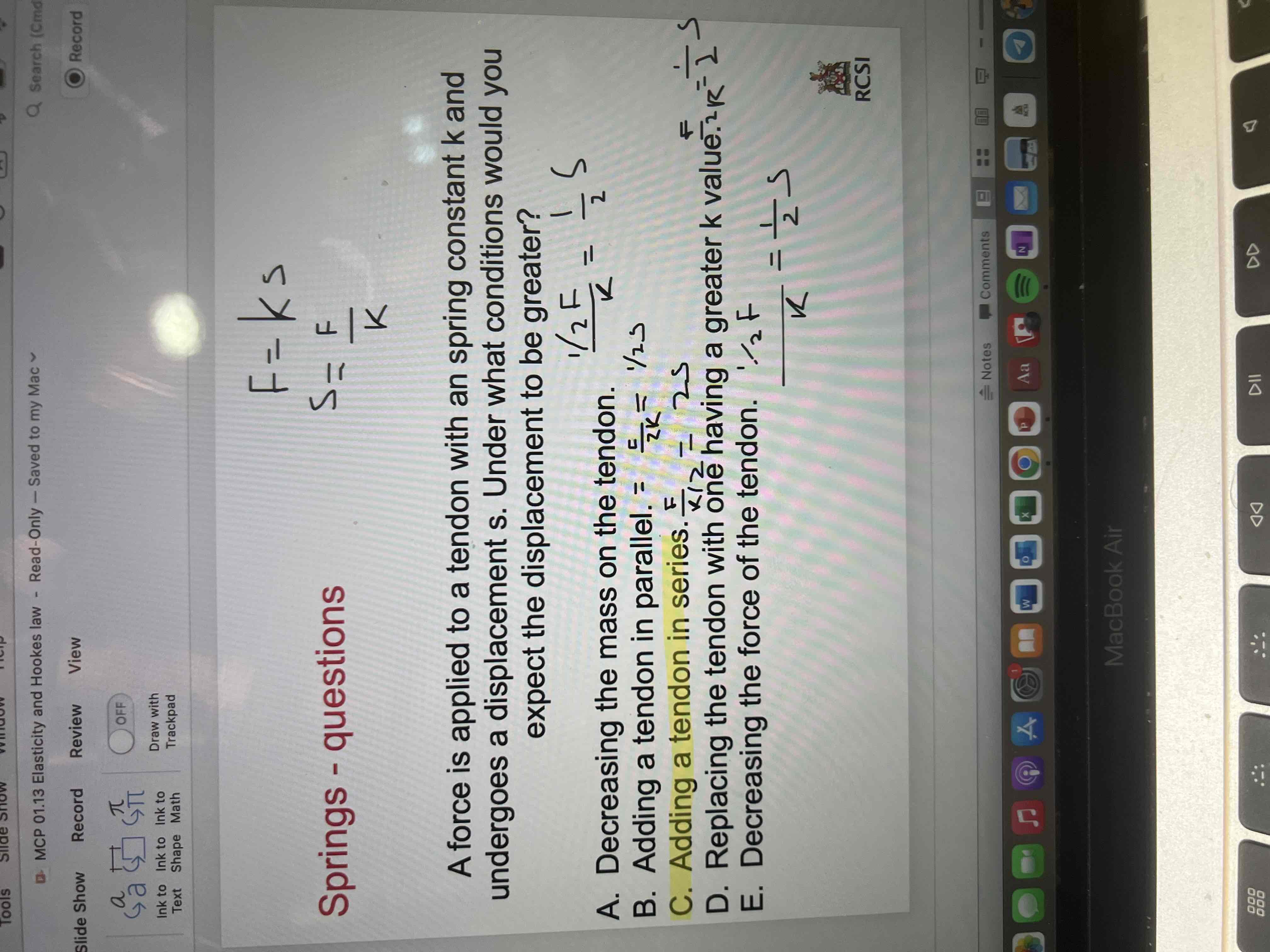
Springs question 3
Bungee jumping
