General Chemistry (High-Yield)
1/552
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
553 Terms
What is an element?
the PUREST form of a substance that CANNOT be broken down further
What is an atom?
the smallest particle or unit of an element
What is an ion?
a charged atom or molecule, formed by adding or removing electrons
What is a molecule?
a single structure made up of two or more atoms (same or different atoms)
What is a compound?
a structure made up of two more DIFFERENT elements
What is the relationship between molecules and compounds?
all compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds
What is homogeneous mixture?
a mixture that is UNIFORM in composition and appears the same throughout (aka solutions)
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
a mixture that is NOT UNIFORM in composition
What type of mixture is a solution?
a homogeneous mixture
What type of mixture is a mixed coffee?
a homogeneous mixture
What type of mixture is a salad?
a heterogenous mixture
What is matter?
anything that takes up space and has mass
What are the phases of matter?
solids
liquids
gasses
plasma
What is a solid?
a phase of matter that is rigid and has a definite space
What is a liquid?
a phase of matter that flows and takes the shape of its container
What is a gas?
a phase of matter that takes the shape and volume of its container
What is plasma?
a phase of matter that exists in a gaseous state and contains electrically charged particles (at very high temperatures)
What is mass?
a measure of the amount of matter in an object (same on all planets)
What is weight?
the force that gravity exerts on an object (different on all planets)
How is weight represented mathematically?
w=mg
What is the Law of Conservation of Matter?
a scientific law that states matter cannot be created or destroyed
What are physical properties?
properties that DO NOT alter the composition of a substance
What is a physical change?
a change that DOES NOT alter the chemical composition of a substance
What are chemical properties?
properties that alter the composition of a substance
What is a chemical change?
a change that results in alteration to a substance’s chemical composition
What types of properties are density, color, and melting point?
physical properties
What types of properties are separating a mixture, flammability, toxicity, and reactivity?
chemical properties?
What is an intensive property?
a physical property that DOES NOT depend on the amount of substance present
What is an extensive property?
a physical property that depends on the amount of substance present
What are intensive properties used for?
identification of a substance
What are extensive properties used for?
quantification
Are density, temperature, and melting point intensive or extensive properties?
intensive properties
Are mass and volume intensive or extensive properties?
extensive properties
What are SI Units?
standardized units used in chemistry and science
What is the SI unit for length?
meter (m)
What is the SI unit for time?
second (s)
What is the SI unit for temperature?
kelvin (K)
What is the SI unit for amount of substance?
mole (mol)
What is the SI unit for electric current?
ampere (amp)
What is the SI unit for luminous intensity?
candela (Cd)
What is the SI unit for mass?
kilogram (kg)
How do convert from one unit to another?
using dimensional analysis
What is dimensional analysis?
a process used to convert from one set of units to another
What is the general formula for dimensional analysis?
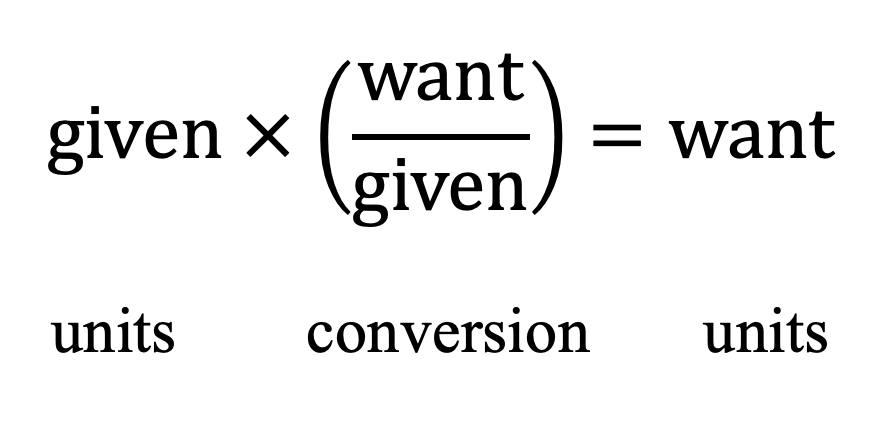
What is the formula for calculating density?

What does the prefix milli (m) indicate?
103 (1,000 in 1 base unit)
What does the prefix micro (μ) indicate?
106 (1,000,000 in 1 base unit)
What does the prefix nano (n) indicate?
109 (1,000,000,000 in 1 base unit)
What does the prefix kilo (k) indicate?
103 (1,000 base units)
What are significant figures?
meaningful digits that follow specific rules
What are the significant figures rules?
ALL nonzero numbers are significant
zeros in the MIDDLE of nonzero numbers are significant
zeros AFTER the decimal are significant
zeros and coefficients in SCIENTIFIC NOTATION are significant
LEADING or BEGINNING zeros are NOT significant
zeros in a LARGE NUMBER without a decimal are NOT significant
What is the significant figure rule for adding or subtracting?
the answer should be the least amount of decimal places (relative to the calculation)
What is the significant figure rule for multiplication and division?
the answer should be the least amount of significant figures (relative to the calculation)
What is accuracy?
how close a measurement is to reality
What is precision?
how close a series of measurements are to each other
What is percent error?
the difference between calculation (theory) and reality (actual yield)
What is formula for calculating percent error?
![% error = [ (actual - theoretical) / theoretical ] x 100](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fe840440-21f2-4cd4-a20c-c8b5689160fa.png)
What is a spectrophotometer?
a laboratory device used to measure a solution’s concentration (via light absorption)
What is a separatory funnel?
a laboratory device used to extract (separate) components of a heterogeneous mixture by solubility (polar vs. nonpolar)
What is a condensor?
a laboratory device used during distillation (purification), which separates homogeneous liquids (mixtures of different boiling points)
What is a Buchner Funnel?
a laboratory device used during vacuum filtration to isolate (separate) a solid product (via filter paper)
What is a centrifuge?
a laboratory device used isolate (separate) compounds in a heterogenous mixture from each other, based on densities (via spinning)
What is a beaker?
laboratory glassware used for stirring, mixing, and heating solutions
What is a erlenmeyer flask?
laboratory glassware used for transferring or mixing liquids for a reaction
What is a graduated cylinder?
laboratory glassware used to transfer liquids and for general measurements (variable accuracy)
What is a burrette?
laboratory glassware used to transfer precise amounts of liquids during titrations (usually by 0.1 mL increments)
What is a volumetric flask?
laboratory glassware used as a container for liquids with known, accurate amounts or creating mixtures to known volumes
What is a volumetric pipette?
a laboratory device used to measure VERY ACCURATE liquid volumes
Are beakers and erlenmeyer flasks used to measure accurate volumes?
no
What is the best method to measure accurate liquid volumes?
using a volumetric pipette
How does one accurately determine (read) the volume of a liquid?
reading the line at the bottom of the meniscus of a liquid
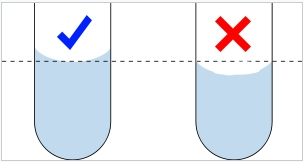
What is parallax error?
a measurement error from failure to properly determine (read) a liquid volume when a meniscus is present
How is pH measured in the laboratory?
pH strips
pH probe (device)
How is pH measured using a pH strip?
a dab of solution is applied to the strip, and the color of the strip determines the pH
How is pH measured using a pH probe?
a pH probe is calibrated with a buffer solution (usually at pH 4 and 10)
dipped into the unknown pH solution
rinsed with deionized water between measurements
dabbed dry with Kimwipes™ to prevent reading errors
How are solids weighed (mass measured) in the laboratory?
a weigh boat is tared or pre-weighed
reagent (solid) is poured into another paper or boat and transferred to the measured paper or boat to weigh
Can you ever place a measuring spoon into a reagent bottle?
no
What are monatomic elements?
elements that can exist in a single-atom form
What are diatomic elements?
elements that CAN’T exist as a monatomic element, and two atoms of the element must be bonded to each other
What are the 7 diatomic elements?
hydrogen (H)
nitrogen (N)
oxygen (O)
fluorine (F)
chlorine (Cl)
bromine (Br)
iodine (I)
Do most elements exist as monatomic or diatomic elements?
monatomic elements
What are allotropes?
molecules with different formulas whose atoms are all of the same element
What is a prime example of an allotrope?
O2 (molecular oxygen) and O3 (ozone)
What are ionic compounds?
a compound comprised of a metal and a nonmetal bonded together via ionic bonds
What is the one compound (exception) that is ionic even though there are no metals in it?
NH4Cl
What are ionic bonds?
bonds that involve one atom (typically the metal) giving up electrons to the other (typically the nonmetal)
How are ionic compounds named?
name the metal
write the metal’s oxidation state as a roman numeral in parentheses (unless there is an exception)
name the nonmetal using an “ide” ending
When naming ionic compounds, which metals do not require their oxidation state to be written out in parentheses?
column I metals (+1)
column II metals (+2)
Al (+3)
Zn (+2)
Cd (+2)
Ag (+1)
What are polyatomic ions?
ions made up of multiple atoms, which are held together by covalent bonds, but as a whole, they are capable of forming ionic bonds with other molecules
What are molecular compounds?
a compound comprised of two or more nonmetals bonded together via covalent bonds
What is another name of molecular compounds?
covalent compounds
What is the general formula for naming molecular compounds?
AxBy
How are molecular compounds named?
assign the appropriate numerical prefix to the first element (skip this step if x = 1)
name the first element by its regular name on the periodic table
assign the appropriate numerical prefix to the second element
name the second element (nonmetal) using an “ide” ending
What is the general definition of an acid?
proton (H+) donors
What is the general definition of a base?
proton (H+) acceptors
What are binary acids?
acids that follow the formula: H-one other element
What are oxyacids?
acids that follow the formula: Hx-middle atomy-Oz
How are binary acids named?
use the prefix “hydro” and insert the name of the second atom, replacing the “ine” with the ending “ic acid”
How are oxyacids named?
based on the number of oxygen atoms
How are oxyacids with 0-2 oxygen atoms named?
use the prefix “hypo” + replace the ending of the middle atom with “ous acid”