AQA Combined Science - Paper 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
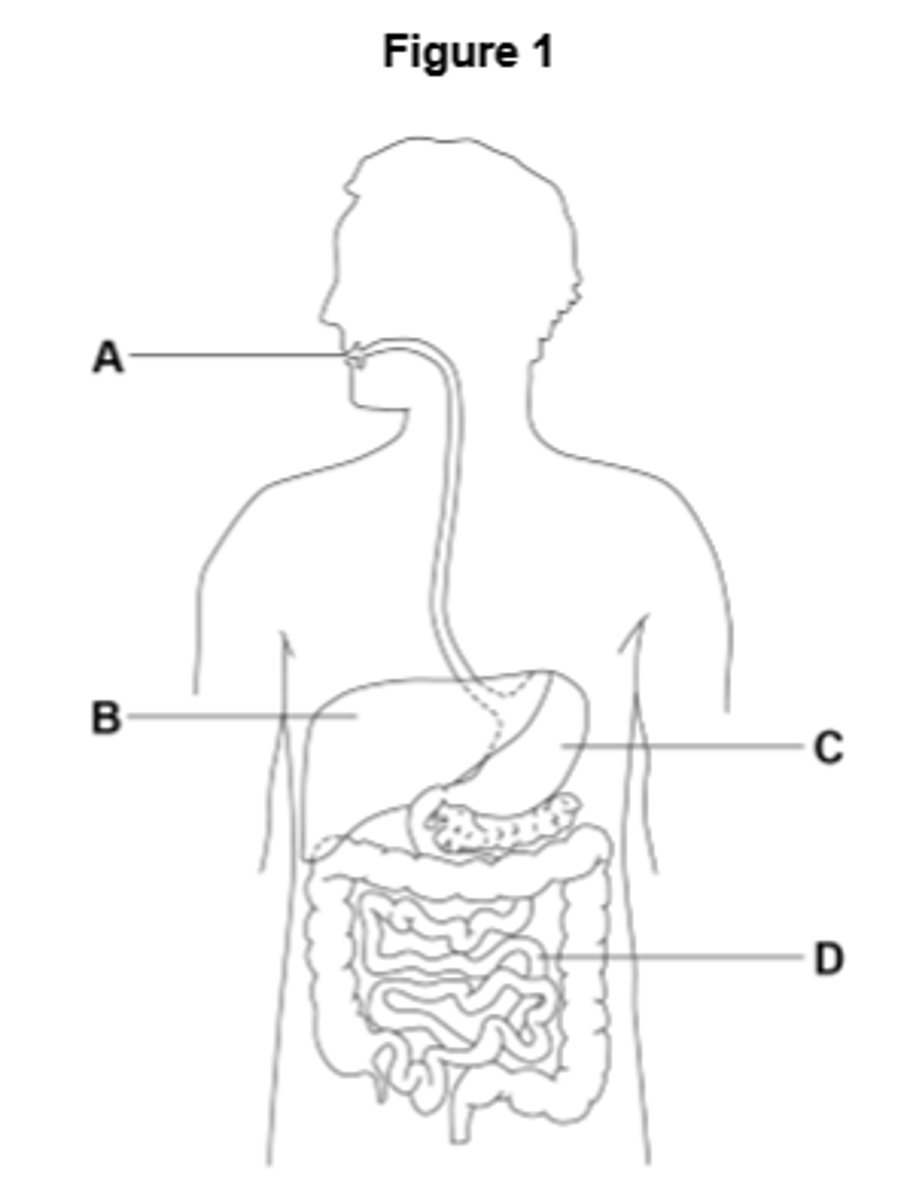
Which Organ is the stomach
C
What is the purpose of the liver?
The liver produces bile for the breakdown of fatty acids (lipids)
What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst (a type of cell that helps to speed up the breakdown of larger molecules. It does not get used up in the reaction.
What pH is the stomach?
pH1 or pH2
Why is the pH of the stomach acidic?
The pH of the stomach is acidic because it is the best condition for the enzymes in the stomach to work.
The stomach produces hydrochloric acid.
How does bile help in the digestion of foods?
It increases the surface area of fats.
What is the result of a positive test for sugar using Benedict's solution?
The Benedict's solution changes colour from Blue to Green or Red.
Green - Little bit of sugar
Red - High levels of sugar.
What is the result of a positive test for protein using Biuret's solution?
The Biuret solution changes from Blue to Purple.
What is the result of a positive test for starch or carbohydrates using iodine?
The iodine changes from orange to black/blue.
Why are starch molecules not absorbed into the blood from the digestive system?
The starch molecules are too large.
The starch molecules are insoluble.
Give one way that the palisade layer is adapted for photosynthesis.
The cells contain a lot of chloroplasts.
Name a factor that affects the rate of diffusion.
A greater difference in concentration, means a greater rate of diffusion.
What type of pathogen causes rose black spot?
Fungus
What type of pathogen is TMV?
Virus
What are toxins?
Various poisonous substances produced by some microorganisms that make us feel ill.
Which of these biological structures are the smallest?
Chromosome
What is active transport?
The movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration. It requires energy.
Which part of the digestive system produces amylase?
Small intestine
What is a maristem?
A meristem is an undifferentiated cell in the tip of the stem and the roots of a plant cell.
What is mitosis?
Cell division that generates new cells for growth and repair. The division of one cell into two genetically identical daughter cells.
What is aerobic respiration?
Release of energy from glucose when oxygen is being used.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is the release of energy from glucose without using oxygen. This produces lactic acid.
What is lactic acid?
Lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration, and is formed when you do not get enough oxygen to your muscles during vigorous exercise.
What is a tissue?
A tissue is a group of similar cells that are working together to perform a job (for example - muscle cells working together to form muscle tissue).
What is the equation for magnification?
Magnification = size of image / size of object
How many micrometers are in 1 mm?
1000 micrometers = 1 mm
Where is meiosis used?
Meiosis happens in reproductive organs to form gametes.
What are gametes?
They are sex cells - Sperm and Egg.
How many chromosomes are in a diploid cell?
46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
How many chromosomes are in a haploid cell?
23 chromosomes
What is the positive test for lipids?
A cloudy emulsion (where the fat and water have separated)
What colour does iodine turn when it detects starch in a food sample?
It goes from orange to blue-black.
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water --light--> glucose + oxygen
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O --light--> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature
What are the main components of blood?
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
What is plasma in the blood?
Yellow liquid that carries blood cells, proteins and dissolved substances around the body
What are platelets in the blood?
They are used to clot the blood and create scabs
What are red blood cells?
Cells that have no nucleus and contain haemoglobin to transport oxygen.
What is haemoglobin?
A large protein that carries oxygen around the body in the red blood cells (oxygen binds to it)
What are white blood cells?
White blood cells are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders.
What are phagocytes?
White blood cells that ingest pathogens like bacteria.
What are lymphocytes?
Type of white blood cell that creates antibodies.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water from a plant.
What are the factors that affect the rate of water loss in a plant (transpiration)?
Humidity (amount of water in the air), the temperature of the environment, and the wind speed.
What is the equation for the gradient of a line on a straight line graph?
Change in y divided by the change in x.
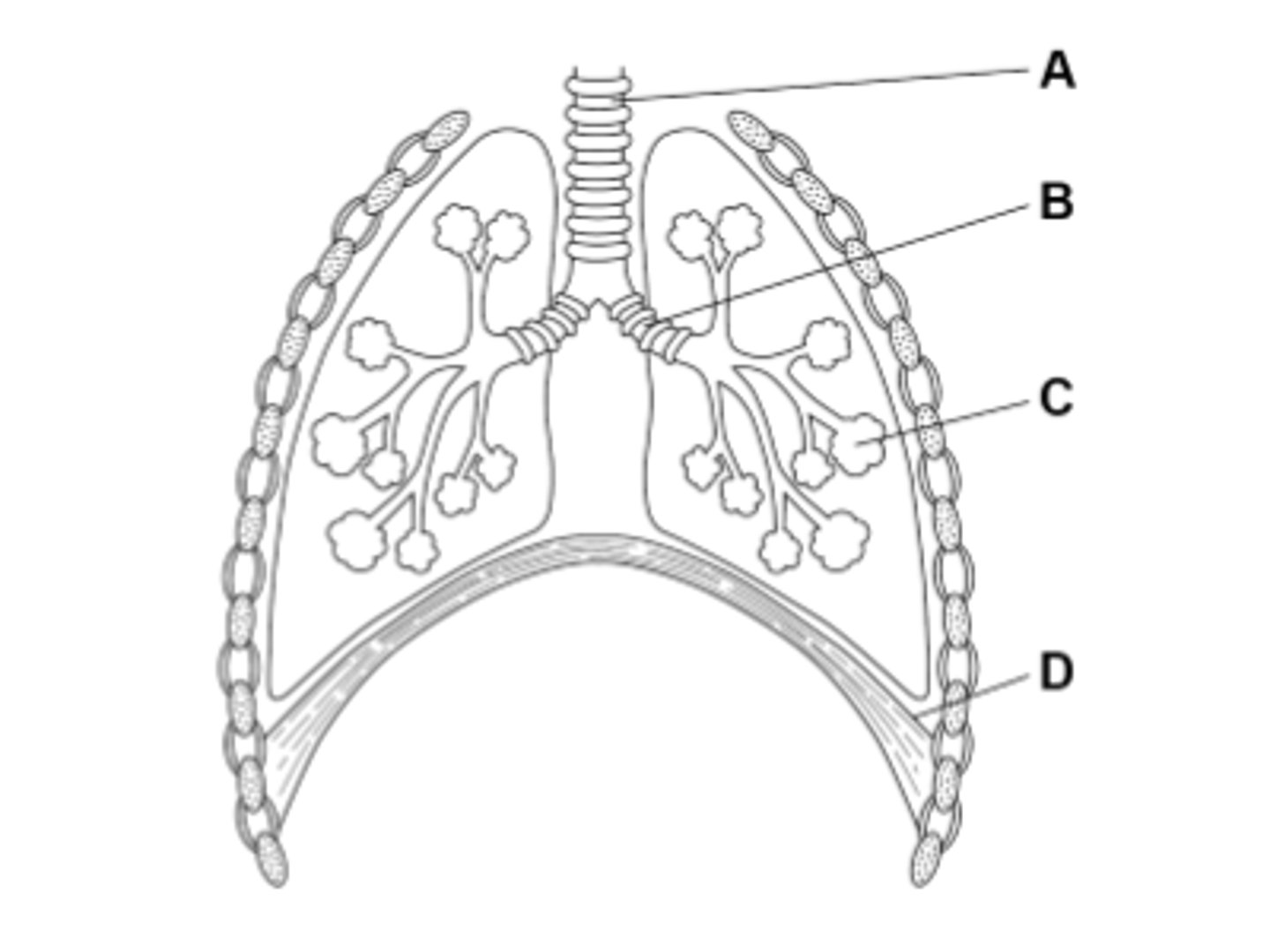
What is A in the diagram?
A is the trachea (windpipe) which supports our neck and windpipe.
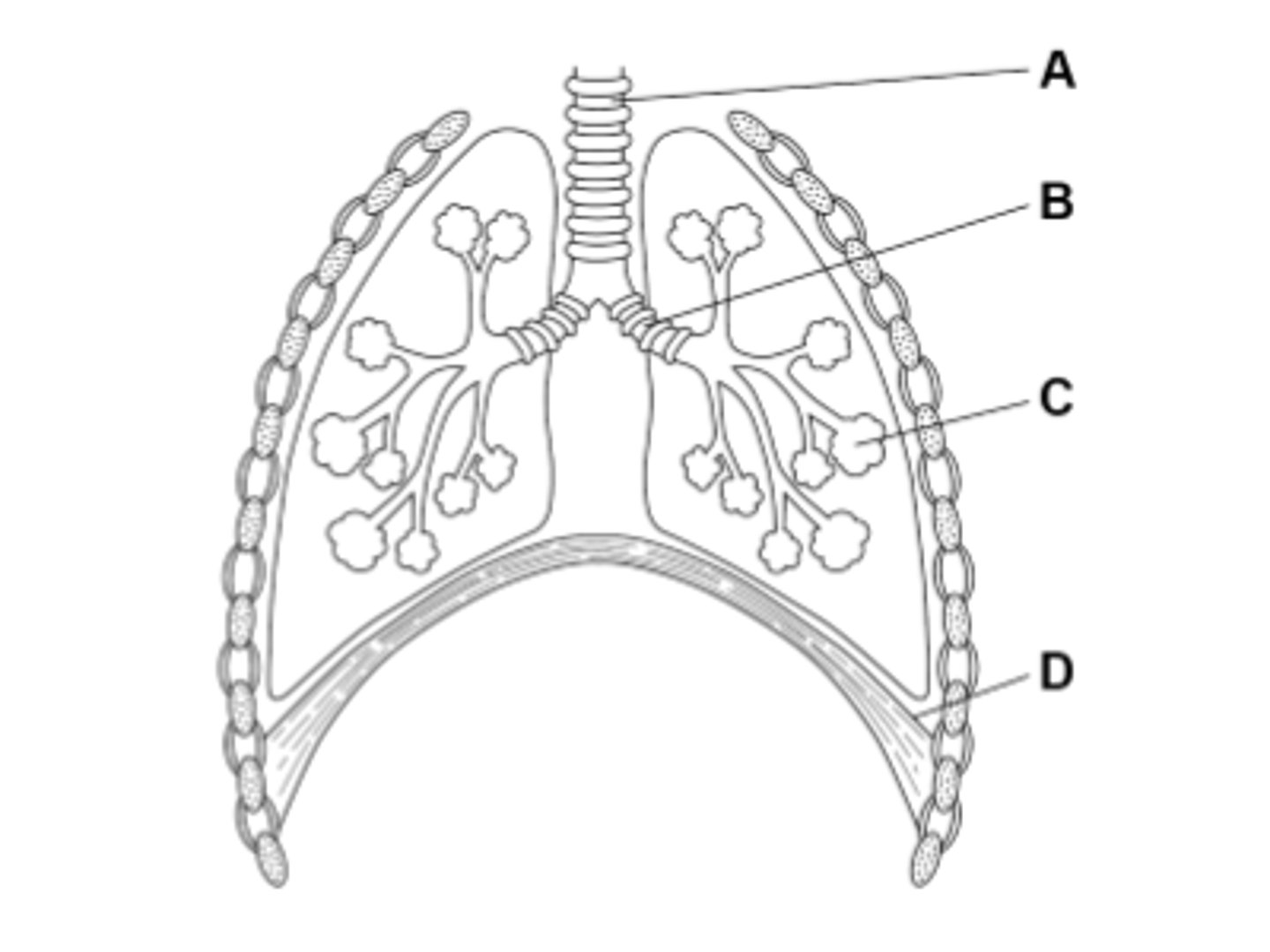
What is B in the diagram?
B is the Bronchus which connects the trachea to the lungs.
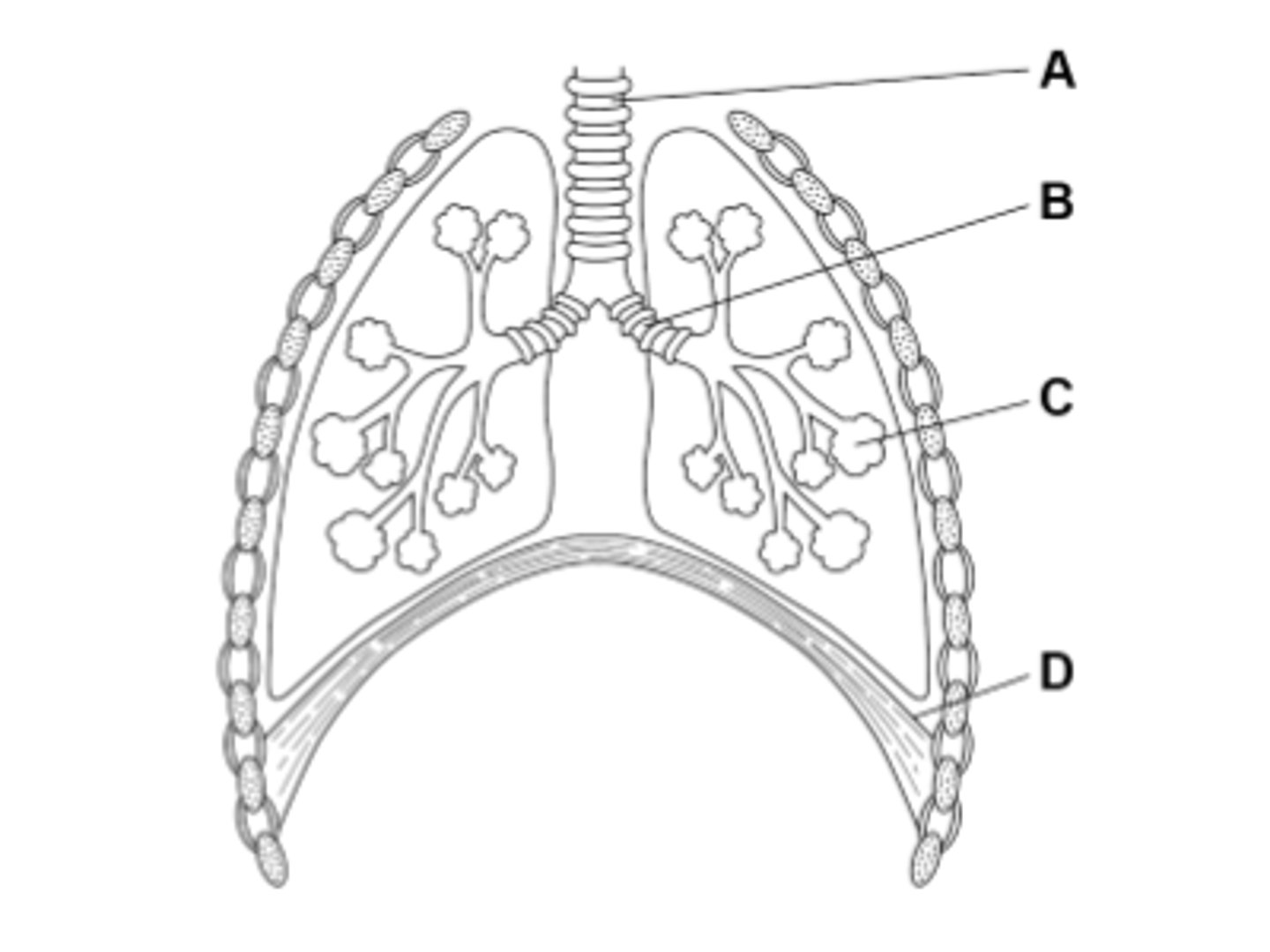
What is C in the diagram?
C is the alveoli which is where gas exchange takes place in the lungs.
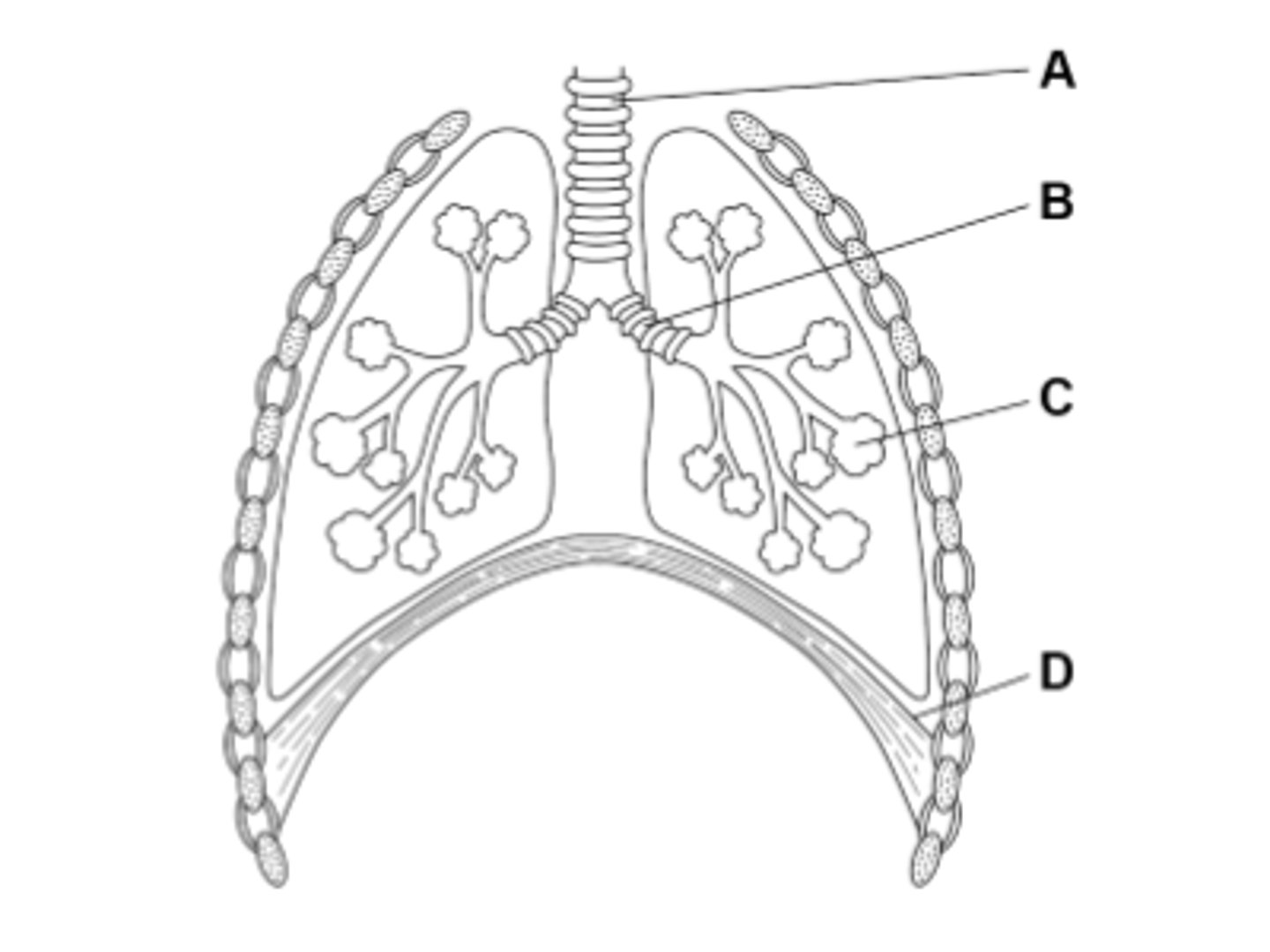
What is D in the diagram?
D is the diaphragm which contracts to cause your lungs to expand and pull air in.
What is a placebo?
A "fake" drug, often a sugar pill to see if improvements are psychological.
Describe how antibodies work.
The antibodies attach to invading cells, and cause them to clump together or destroy them.
Describe how antitoxins work.
They destroy toxins, which cause tissue damage and make us feel unwell.
What is produced in the liver?
Bile.
What is absorbed in the large intestine?
Water.
Where are most food molecules absorbed?
Small intestine
3 multiple choice options
What is a salt?
It is a substance that is produced when a metal takes the place of the hydrogen from an acid.
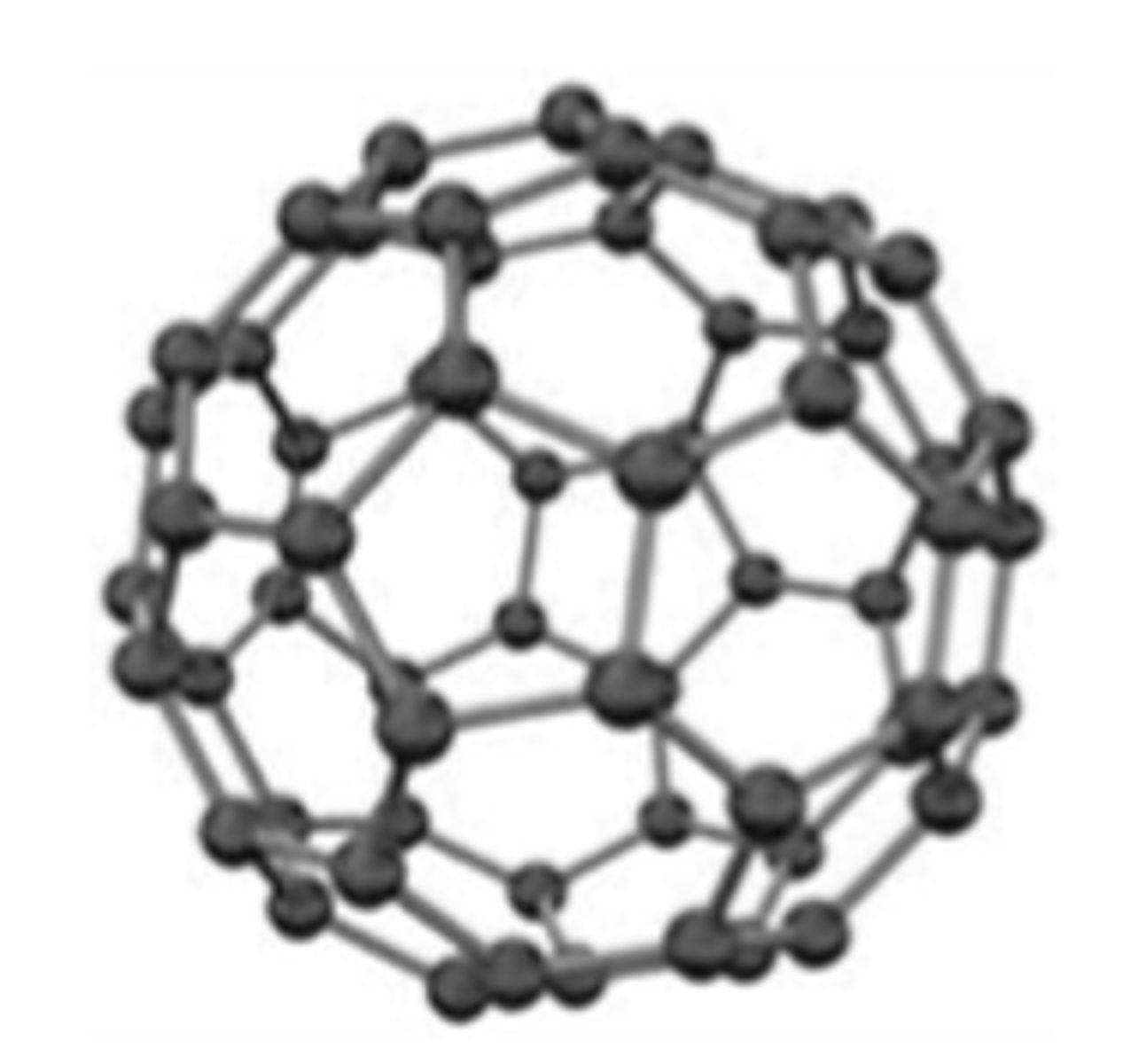
What is the structure of C60?
A fullerene
How many electrons create one covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed when a pair (two) outer electrons are shared between atoms.
What is meant by the term molten?
Molten means a liquid which is hot.
Explain why fluorine is a gas at room temperature.
There are weak forces between atoms.
These weak force require little energy to break them/overcome them.
What acid produces a metal chloride?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
What acid produces a metal nitrate?
Nitric acid (HNO3)
What acid produces a metal sulfate?
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
State one difference in the electronic structure of sodium and chlorine.
They are in different groups in the periodic table, so have different numbers of outer electrons.
State one similarity in the electronic structure of sodium and chlorine.
They are in the same period in the periodic table, so have the same number of outer shells of electrons.
What is cryolite?
A substance added to Aluminium oxide to reduce the energy required to produce Aluminium
Aluminium is produced by electrolysis of a molten mixture - what is in the molten mixture?
The molten mixture contains cryolite and aluminium oxide.
What are the elements in group 8 known as?
The noble gases
What is a limiting factor?
A factor which restricts the rate of a reaction.
Name a limiting factor for photosynthesis.
Temperature
Water
Carbon dioxide concentration
Light intensity
What are the different components of the blood?
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
Plasma
Urea
What is the purpose of red blood cells?
They carry oxygen - Haemoglobin is in red blood cells that binds to oxygen.
What is the purpose of white blood cells?
They help to fight infection.
What is the purpose of the platelets in the blood?
They help to clot and make scabs to prevent infection getting into the body.
What is the purpose of plasma in the blood?
To provide fluid for everything else to dissolve in and move the blood around the body.
What is urea in the blood?
It is made up of waste products and salt which is removed by the kidneys.
What is the phloem?
Carries food from leaves to all other plant cells. Substances can move in two directions in the phloem.
What is the xylem?
A tissue which makes up the stem of a plant. It carries water from the roots of the plant to the leaves.
Water can only travel in one direction.
How is a root hair cell adapted for its function?
It has a large surface area to increase osmosis of water into the cell.
Where are the pacemaker cells found in the heart?
In the right atrium
What is the name of the enzyme that digests starch in the digestive system?
Amylase
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down fats?
Lipase
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down proteins?
Protease
What is a base?
It is an alkali that can dissolve.