Lecture 24: High-Performing Teams (11/18)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reading: H&M Chapter 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Collaboration has increased over the past 2 decades. How much has it increased by?
50% or more
When people work together to finish a job, such as building a house, the job will probably:
A. Get finished faster
B. Take longer to finish
C. Not get done
This is a question from a fourth grade standardized test in Ohio. The “correct” answer if you are fourth grader in Ohio is A. But, Richard Hackman uses this example in the beginning of his book Leading Teams to make the point that research evidence would suggest that B or C is actually just as, if not more, likely)
What are the common causes of team failure
Underutilization of information & expertise:
perceived obstacles to voicing dissenting opinions
Failure to discover “who knows what” within the team
Corrosive Dynamics
Inadequate trust, cohesion, and shared identity that undermines communication and collaboration
Team Stagnation
Tendency to persist with existing, outdated routines rather than to learn and adapt over time
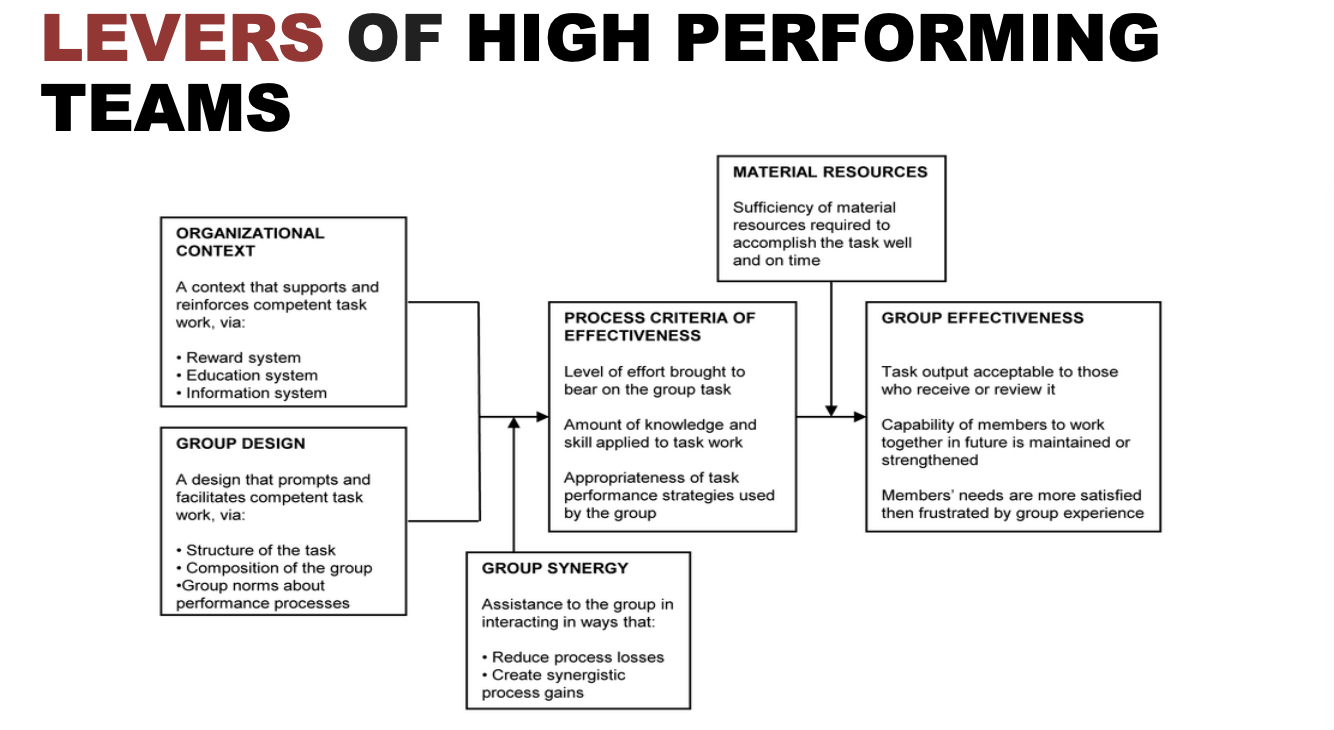
What are the levers of high performing teams?
Team performance depends on:
organizational context
group design
group strategy
process criteria of effectiveness
material resources
→ group effectiveness
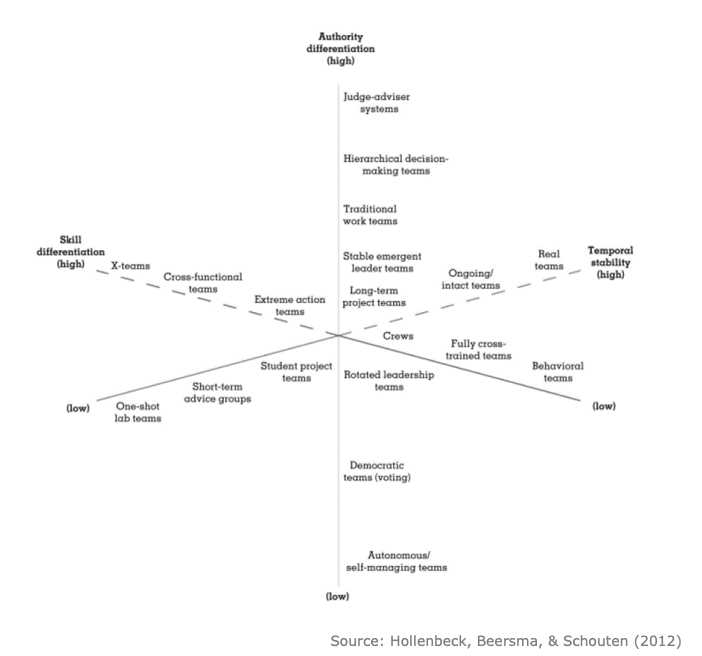
What is a work team? Describe the diagram from Kozlowski & Bell (2003)
Work teams:
Are composed of 2 or more individuals
Who exist to perform organizationally relevant tasks
Share one or more common goals
Exhibit task interdependencies
Diagram:
The diagram places different kinds of teams on three key dimensions:
Authority differentiation (vertical axis)
Skill differentiation (diagonal axis from left to right)
Temporal stability (horizontal axis) → length of teams
What are the key enabling conditions for high-performing teams
Compelling Direction
• High performing teams have explicit goals, which are clear, challenging, and consequential
Strong Structure
• High performing teams have the right mix and number of members, perform meaningful tasks, and establish clear norms
Supportive Context
• High performing teams have a reward system that reinforces good performance, an information system that provides access to necessary data, an educational system that offers training and development, and access to the material resources (e.g., funding, technological assistance) required to do the job
Shared Mindset
• In high performing teams, members have a strong common identity and a shared understanding of the task and one another
What are the 5 factors that Google’s Project Aristotle found to have the biggest impact on team success?
Psychological Safety – team members feel safe to take risks and be vulnerable in front of one another
Dependability – team members get things done on time and meet Google’s high bar for excellence
Structure & Clarity – team members have clear roles, plans, and goals
Meaning – work is personally important to team members
Impact – team members think their work matters and creates change
In the case of hospital teams the Edmondson (1996) studied, what did he hypothesize about the teams where adverse drug events (ADEs) would be lower
Better nurse managers
Higher quality interpersonal processes
Greater perceived performance
Which of the following do you think might best explain these counterintuitive findings (for the case of hospital teams)
A. Teams that perceived themselves as high performers became complacent
B. Teams with strong nurse managers failed to take personal responsibility
C. Teams with a poor manager and interpersonal processes covered up their mistakes
D. Teams with strong interpersonal processes engaged in groupthink
C. Teams with a poor manager and interpersonal processes covered up their mistakes
What is psychological safety?
A team climate characterized by interpersonal trust and mutual respect where people feel comfortable speaking up and being themselves
What are ways leadership can foster psychological safety?
Demonstrate engagement
Model curiosity and ask lots of questions
Offer input, be interactive, and show you’re listening
Be inclusive in decision making
Frame work as a learning problem, not an execution problem
Encourage others to speak up and offer their input, opinions, and feedback
Don’t interrupt or allow interruptions
Show confidence without appearing inflexible
Acknowledge your own fallibility
Invite the team to challenge your perspective and push back
What is Tuckman’s Stage Model for team development?
Forming:
Unclear objectives, roles and responsibilities
Confusion
Storming
• Members vie for influence
• Conflict
Norming
• Members reconcile differences and develop norms to guide subsequent interaction
• Consensus
Performing
• Group energy is channeled into the task
• Confidence
Adjourning
• Task termination, disengagement, and disbanding of the team
• Closure
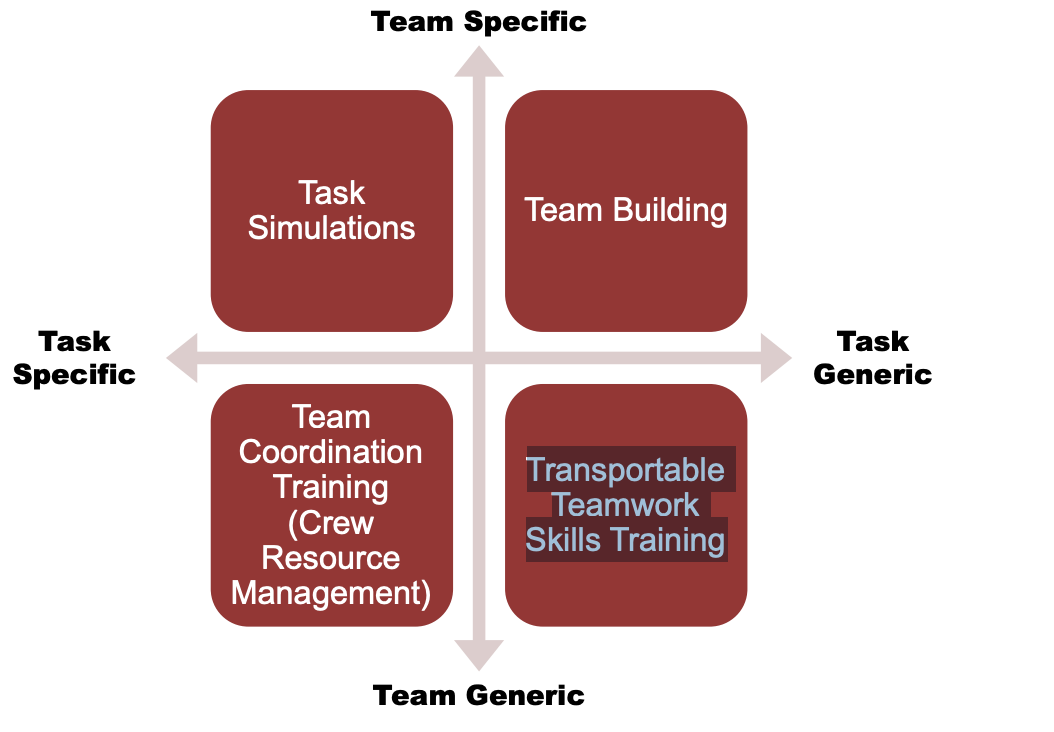
What are various team training approaches?
Task simulations
Team building
Team Coordination Training (Crew Resource Management)
Transportable Teamwork Skills Training
Task specific team training focuses on developing skills that are related to specific tasks
Task generic team training focuses on developing skills that generalize across different tasks
Team specific team training focuses on developing an intact team
Team generic team training focuses on developing individuals to work across different teams