Chapter 5 Sections 1, 2, 3 - Science (Abigail Morales)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
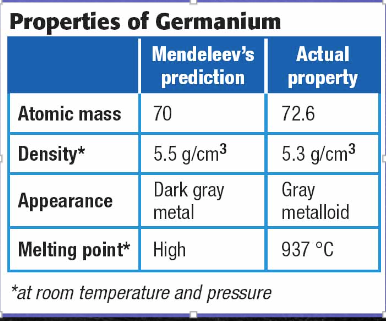
How did Mendeleev arrange the elements in his periodic table?
In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged elements in rows by increasing atomic mass.
What was Mendeleev able to predict?
was able to predict new elements
Why did Mendeleev leave spaces in his table?
He used the spaces to successfully predict the existence and properties of elements not yet discovered.
How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table?
The modern periodic table organizes elements by atomic number. When the elements are arranged in this way, elements that have similar properties appear at regular intervals.
The Periodic Table of the Elements

Do elements become more or less metallic as you move across each period?
less
Period
a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
What do elements in each group have in common?
Similar properties
Group
a vertical column of elements in the periodic table; elements in a group share chemical properties
What are the periodic trends in the periodic table?
The result of electron arrangement
What are chemical properties largely determined by?
The number of valence electrons
What do valence electrons account for?
Similar properties
What is the location of the periodic table related to?
Electron arrangement
Example: Lithium and sodium, in Group 1, each have one valence electron
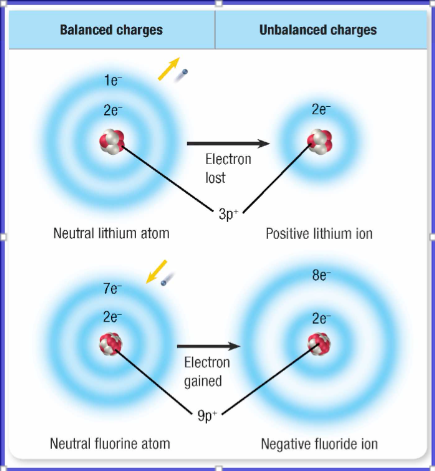
What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons?
If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge.
Are the Group 1 ions positive or negative?
Positive; the single valence electrons is easily removed
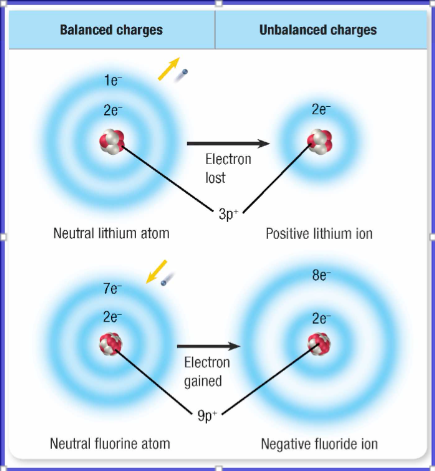
Are Group 17 ions positive or negative?
Negative; the addition of one valence electron fills the outer energy level.
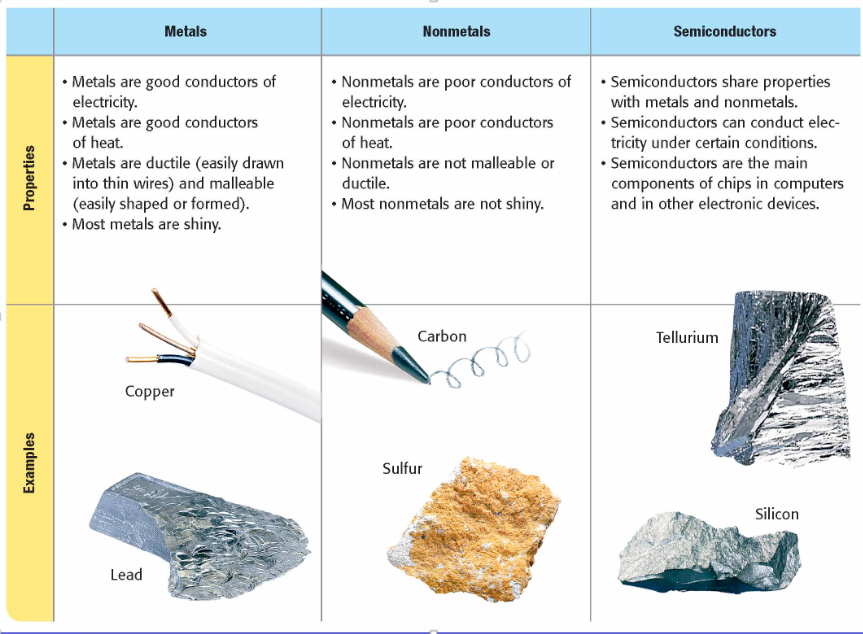
What are the three main categories of elements?
All elements are either metals, nonmetals, or semiconductors.
What do elements in each category have in common?
They have similar properties
Metal
an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well
nonmetal
an element that conducts heat and electricity poorly
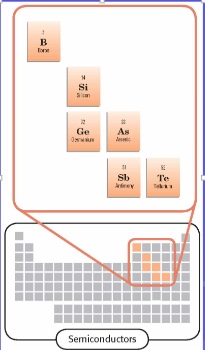
semiconductor (or metalloid)
an element or compound that conducts electric current better than an insulator does but not as well as a conductor does
Examples of metals, nonmetals, and semiconductors
Group 1: Alkali Metals - What metal(s) are contained in this group?
Metal
Group 1: Alkali Metals: How many electrons are in the valence?
1
Group 1: Alkali Metals: How reactive are Alkali Metals?
Very reactive
Group 1: Alkali Metals: What are their shared properties?
Softness, silver in color, shiny, low density
Group 2: Alkali-Earth Metals: What metal(s) are contained in this group?
metal
Group 2: Alkali-Earth Metals: How many electrons are in the valence?
2
Group 2: Alkali-Earth Metals: How reactive are Alkali-Earth Metals?
Very reactive but less than group 1
Group 2: Alkali-Earth Metals: What are their shared properties?
Silver in color, higher density than Alkali Metals
Groups 3-12 Transition Metals: What metal(s) are contained within this group?
metal
Groups 3-12 Transition Metals: How many electrons are in the valence in this group?
1 or 2
Group 3-12 Transition Metals: How reactive are transition metals?
Less reactive than group 2
Group 3-12 Transition Metals: What are their shared properties?
Shiny, good conductors of thermal energy and electricity, higher density than group 1 and 2
Group 17 Halogens: What metal(s) does this group contain?
contains nonmetals
Group 17 Halogens: How many electrons are in the valences of this group?
7
Group 17 Halogens: How reactive is this group?
Very reactive
Group 17 Halogens: What are this group’s shared properties?
Poor conductors of electricity, violent reactions with small Alkali metals to form salt, never in uncombined form in nature
Group 18 Noble Gases: What are the metal(s) within this group?
Nonmetals
Group 18 Noble Gases: How many electrons are in the valence of this group?
8 except Helium
Group 18 Noble Gases: How reactive is this group?
Unreactive
Group 18 Noble Gases: What are this group’s shared properties?
Colorless, Odorless gases at room temp
Semiconductors
Are able to conduct heat and electricity under certain conditions
(Test Question) - How did Mandelev arrange his table?
By mass
(Test Question) - What is each row on the periodic table called?
Periods
(Test Question) - What are columns called on the periodic table?
Groups or families
(Test Question) - What do everything in columns share?
Properties
(Test Question (Short Answer Question)) - Why do jewelers prefer to use metals instead of nonmetals?
Metals are ductile, malleable, and shiny
(Test Question) - As you move to the right do metals become more or less metallic?
Less