Sheep Brain Dissection, Sheep Brain Dissection
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
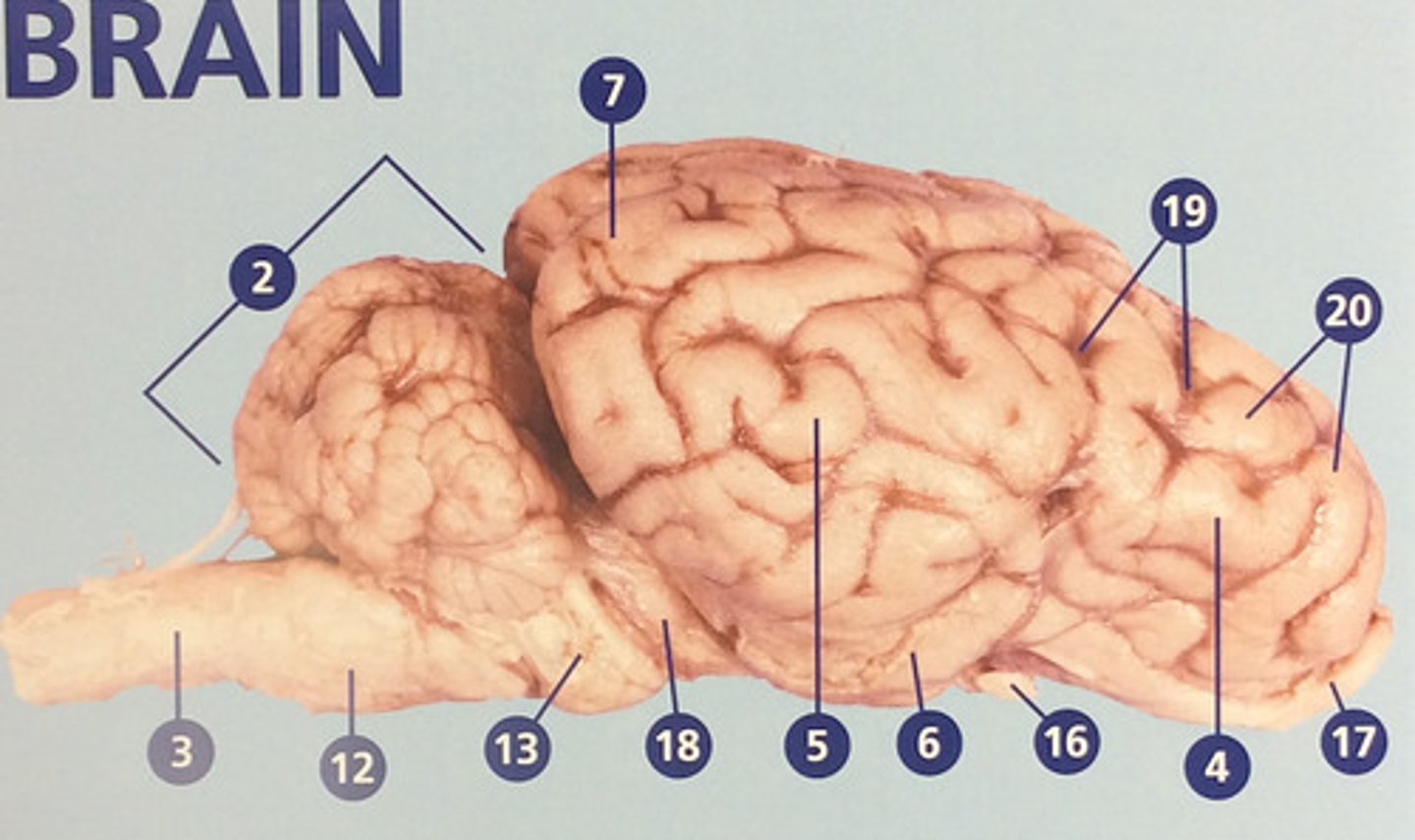
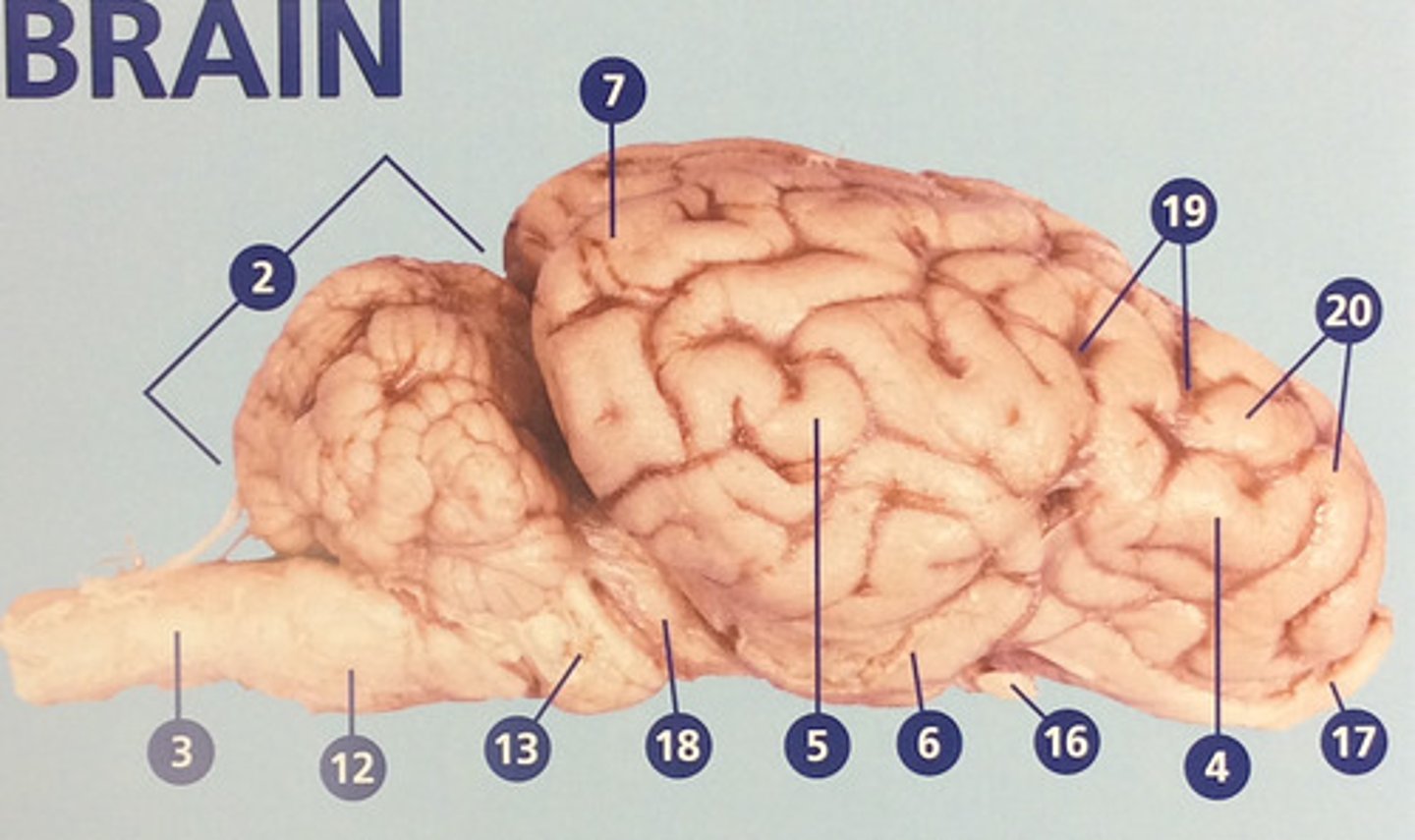
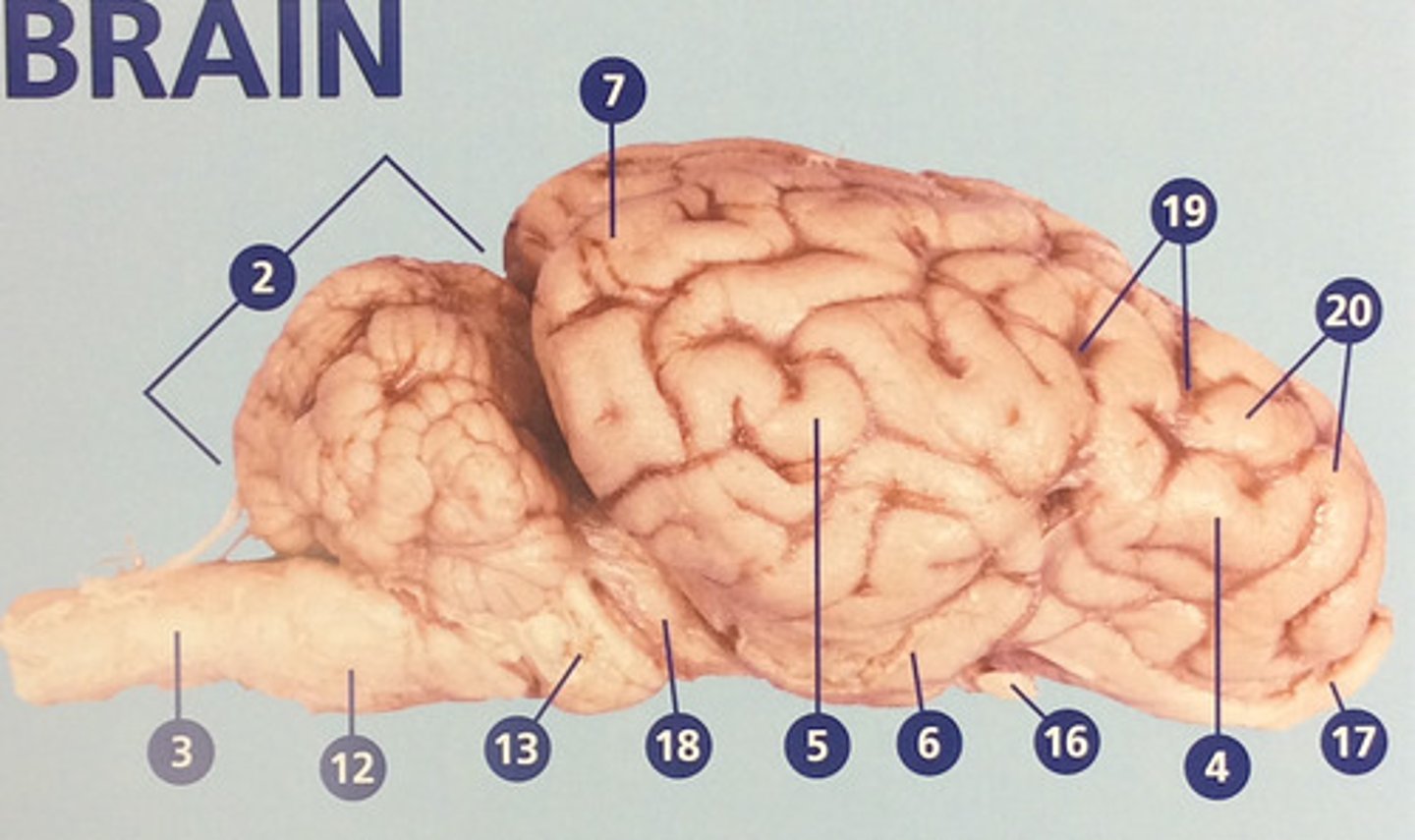
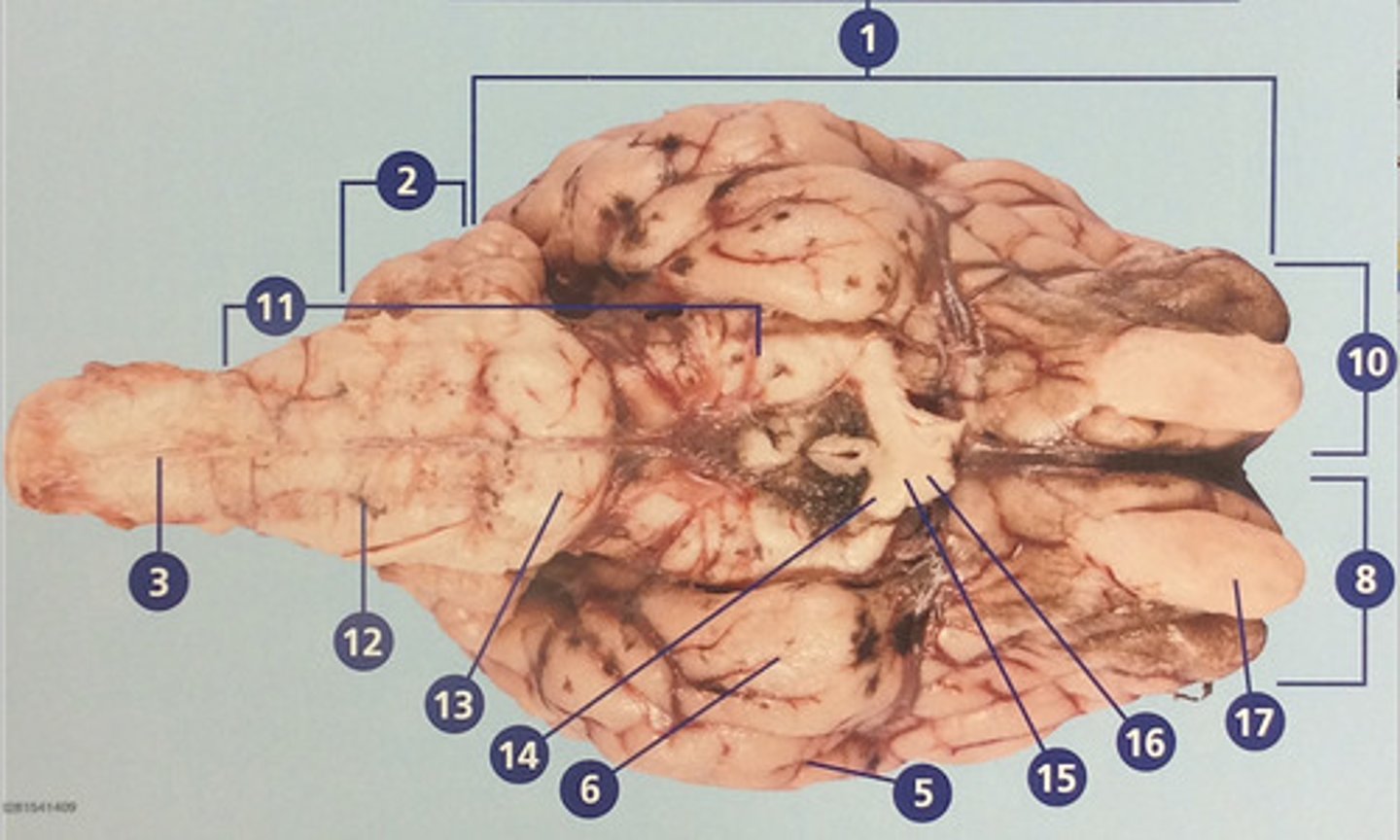
Cerebrum
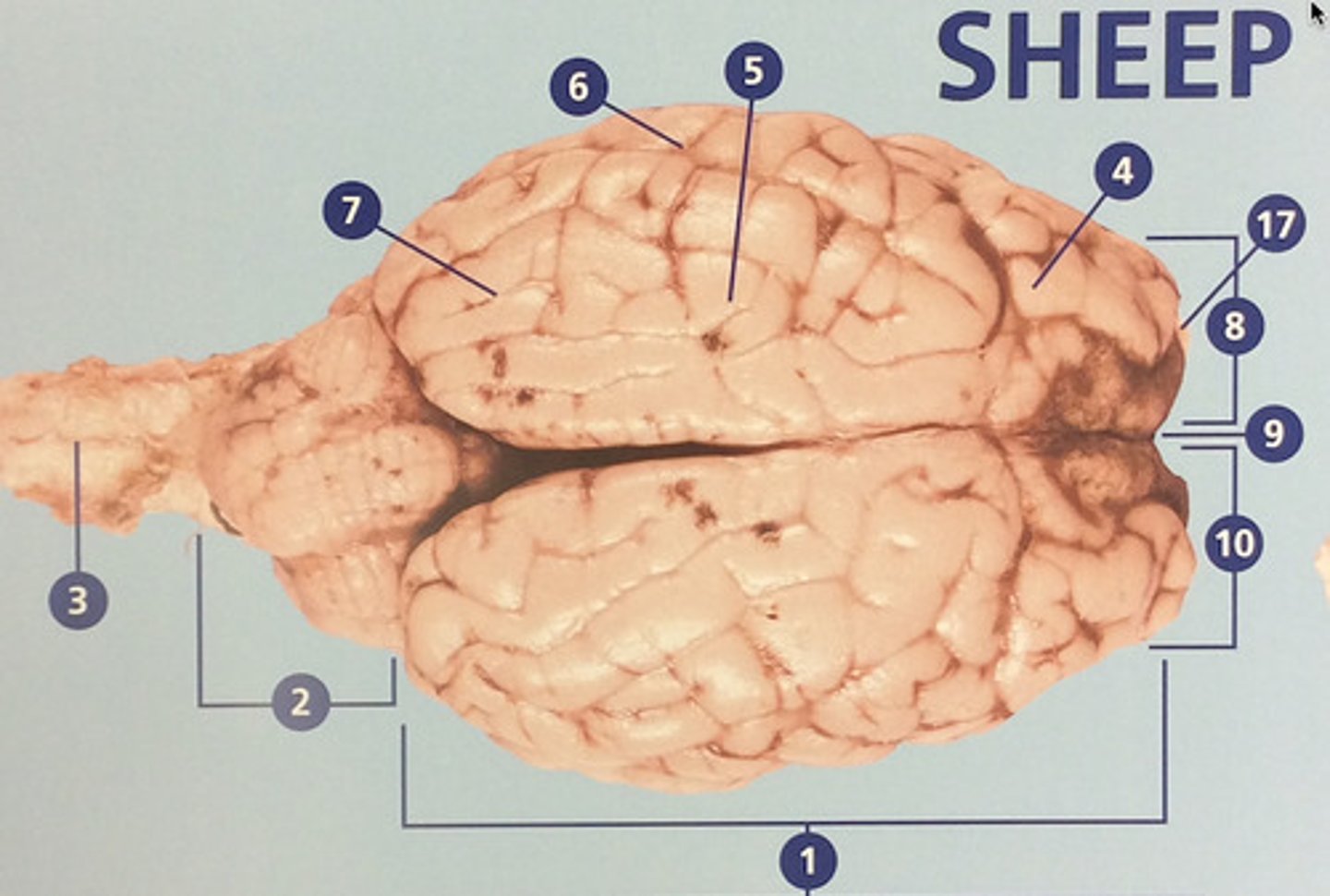
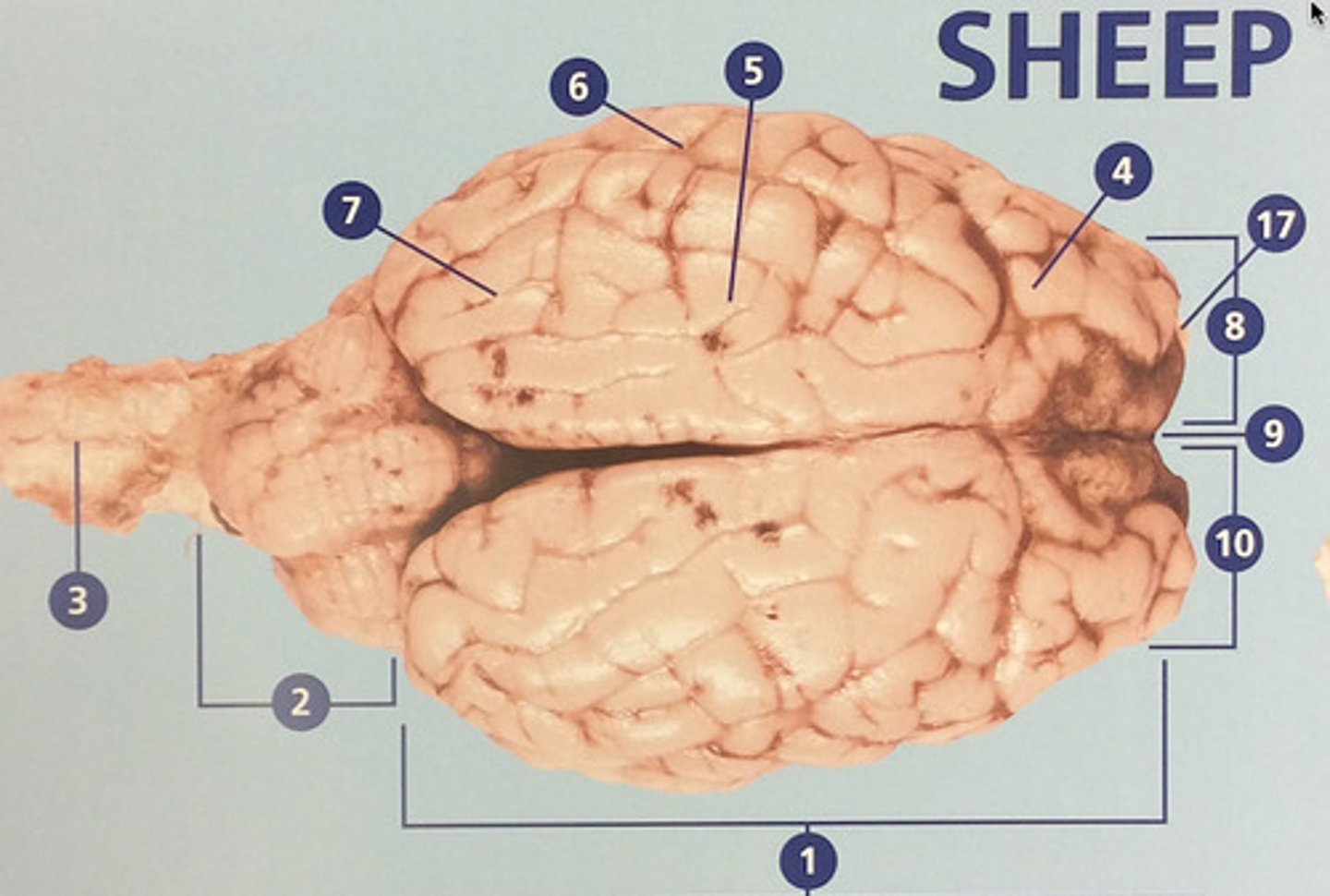
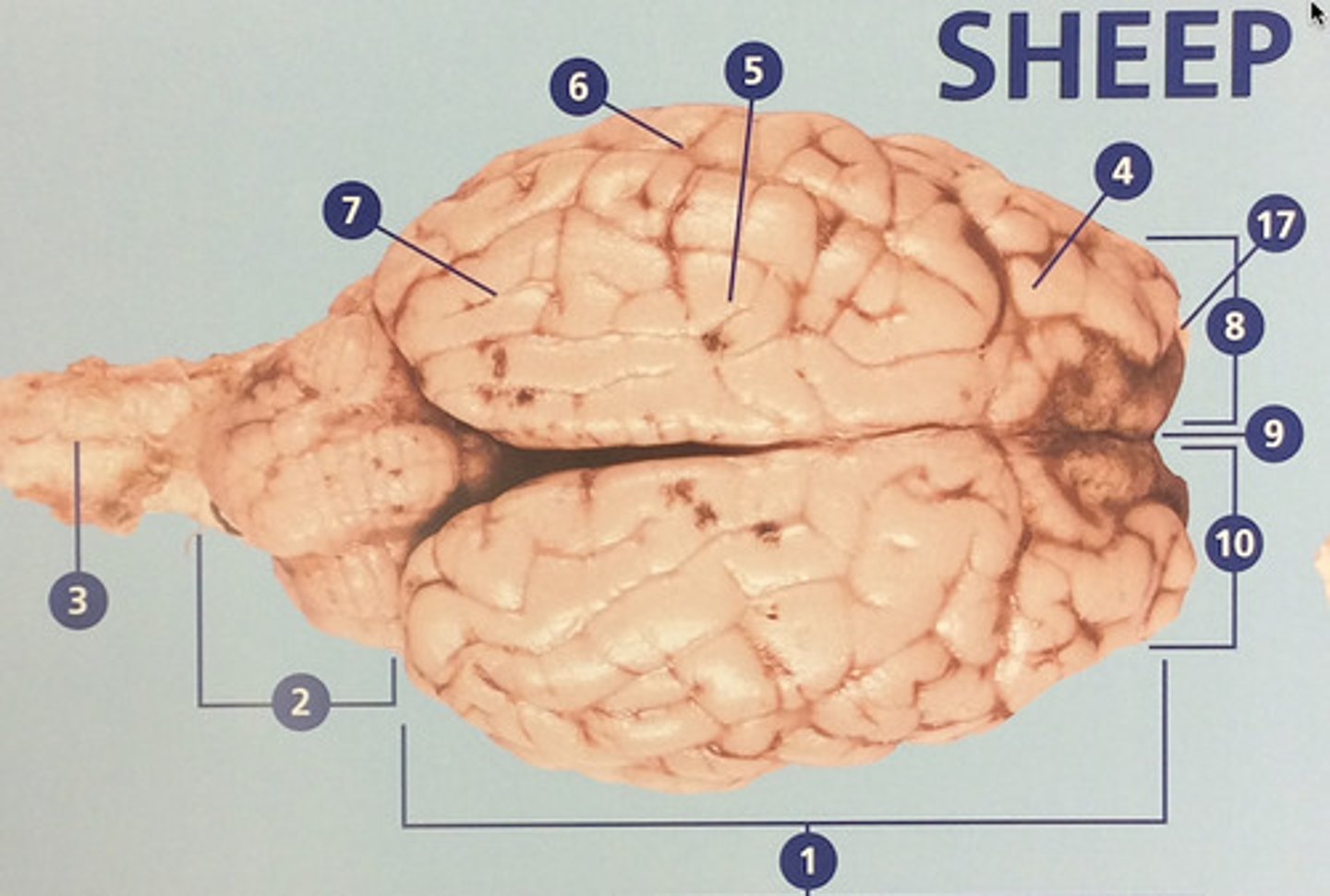
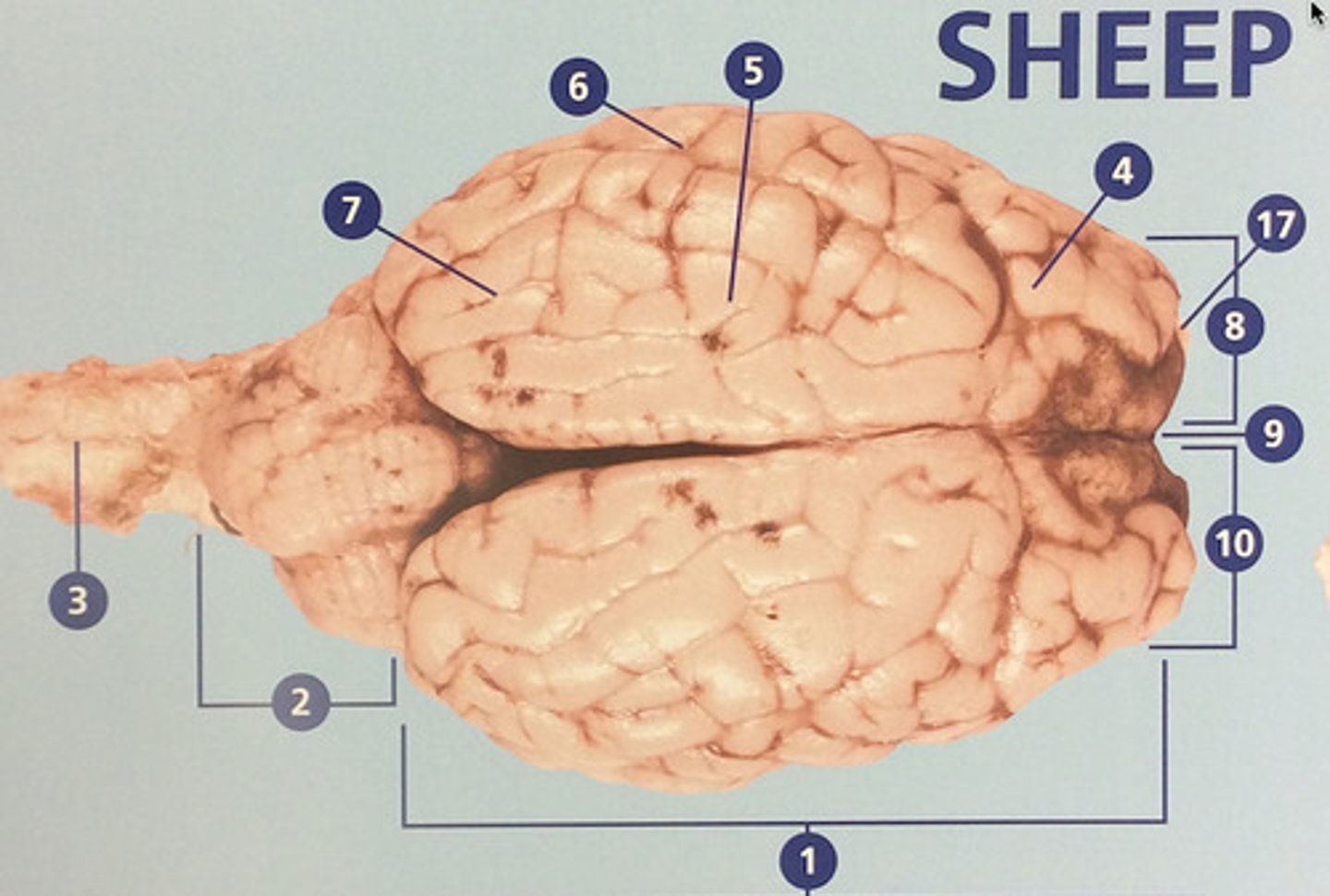
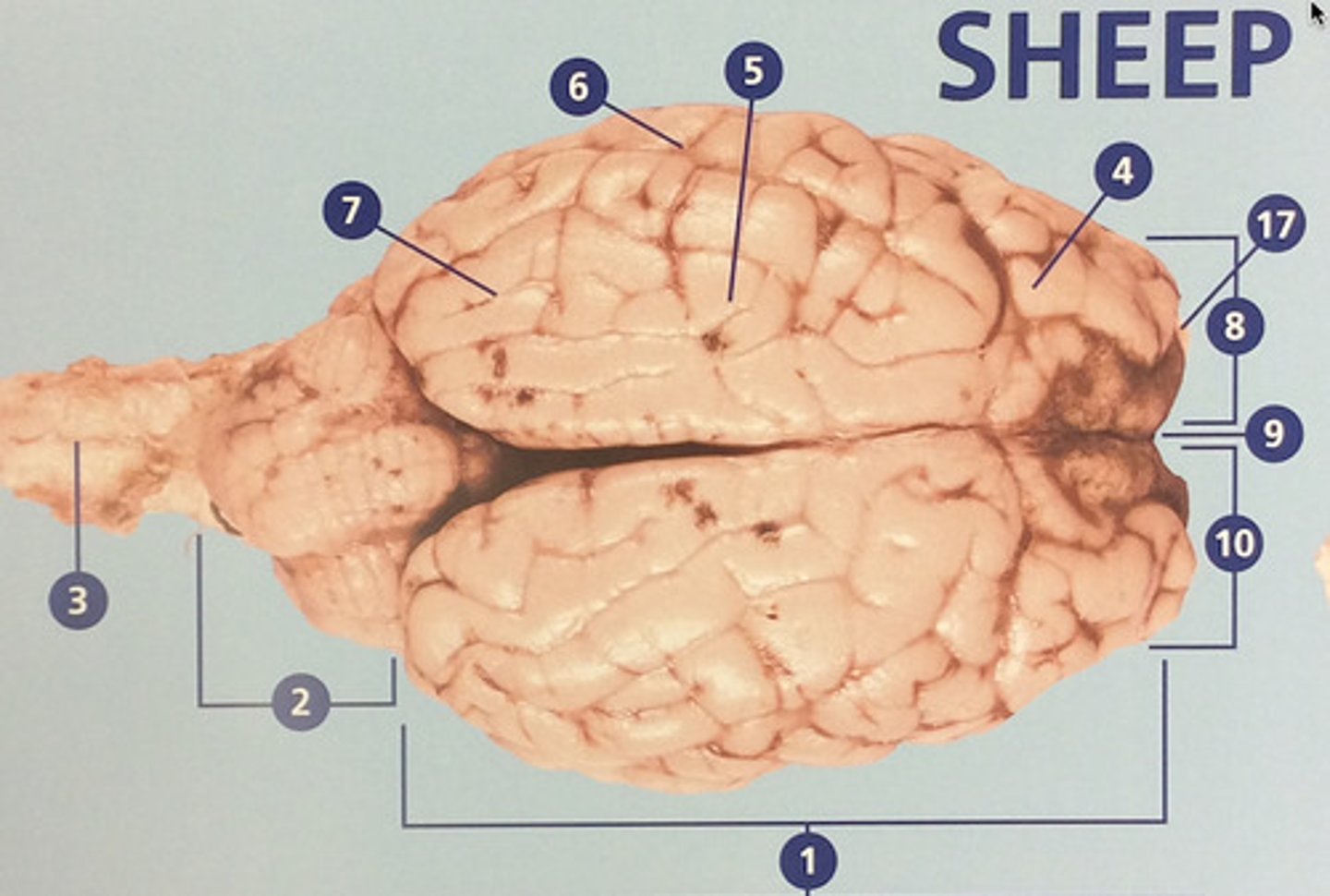
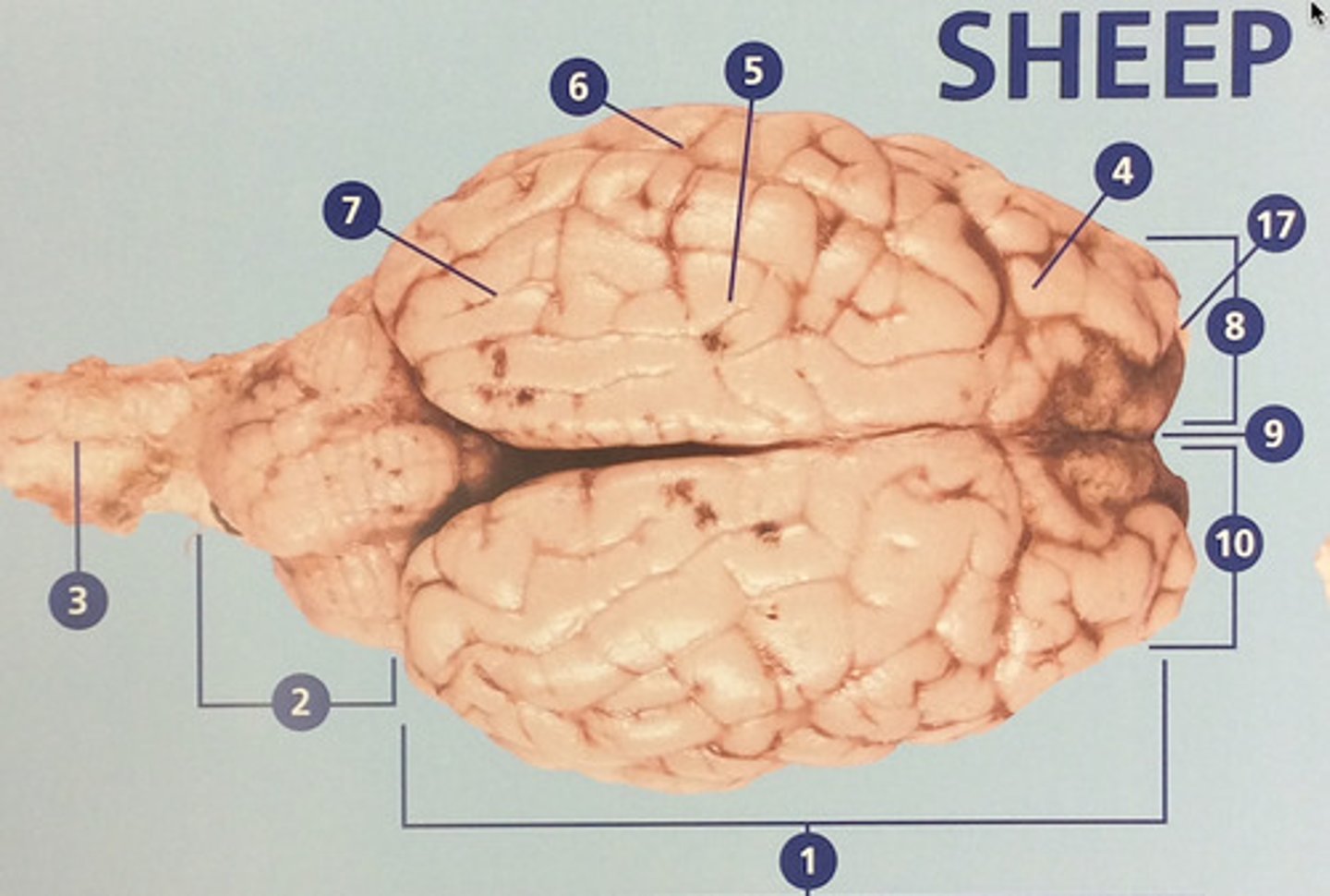
Large, deeply wrinkled region of the brain responsible for conscious experience including perception, emotion, thought, and planning (#1)
Cerebellum
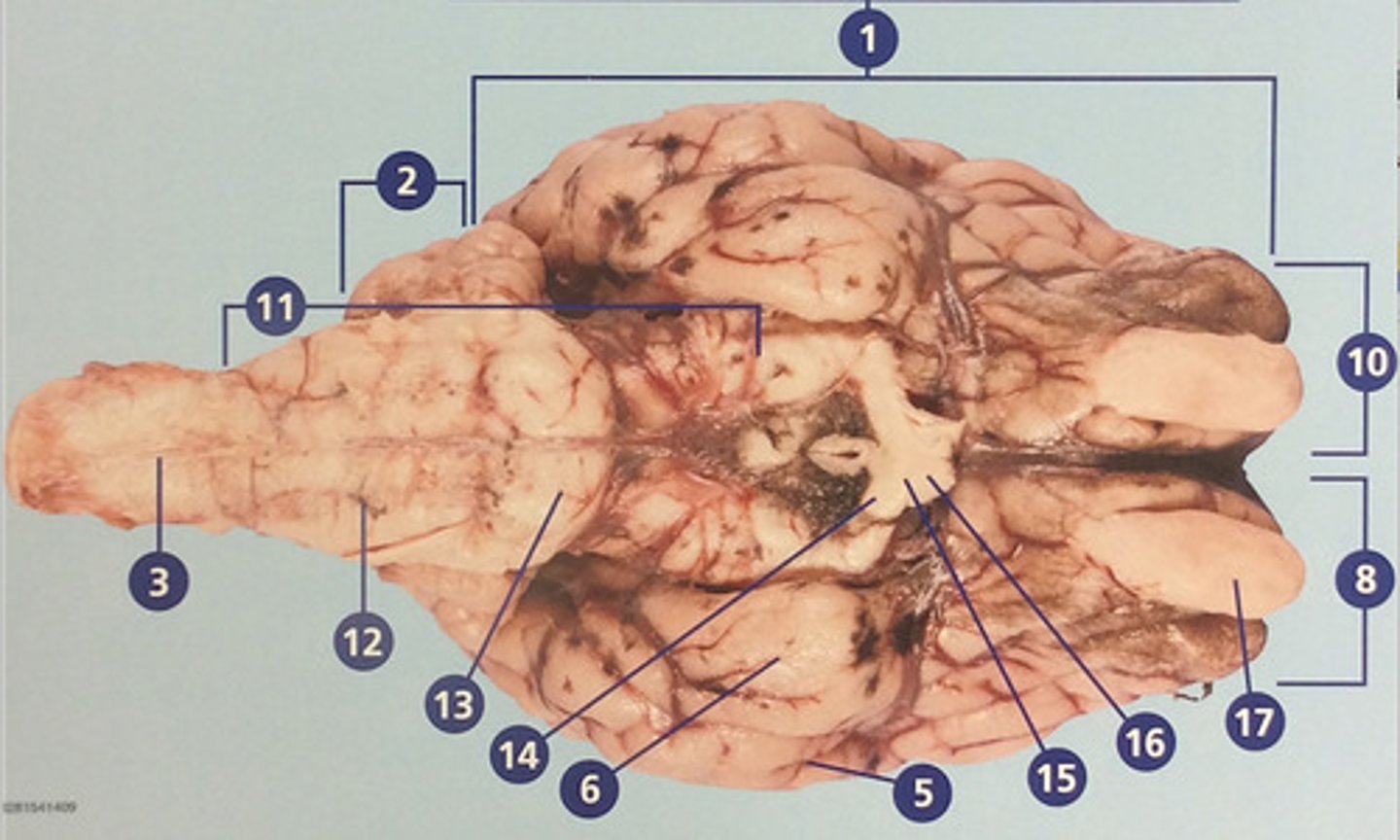
Controls movement, balance, and muscle coordination (#2)
Spinal cord
Bundle of nerve fibers inside the spine that connects the brain to the sensory and motor parts of the body (#3)
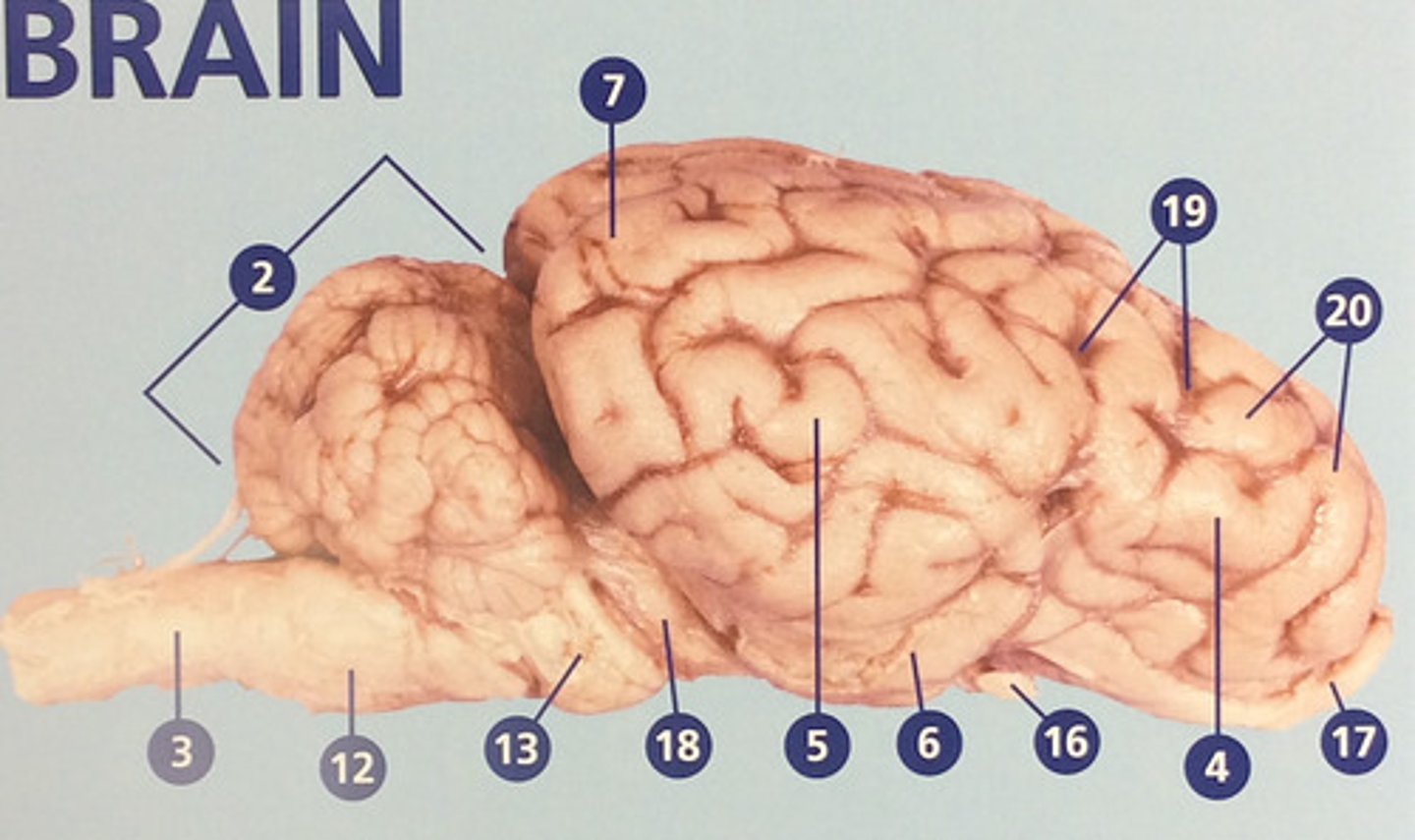
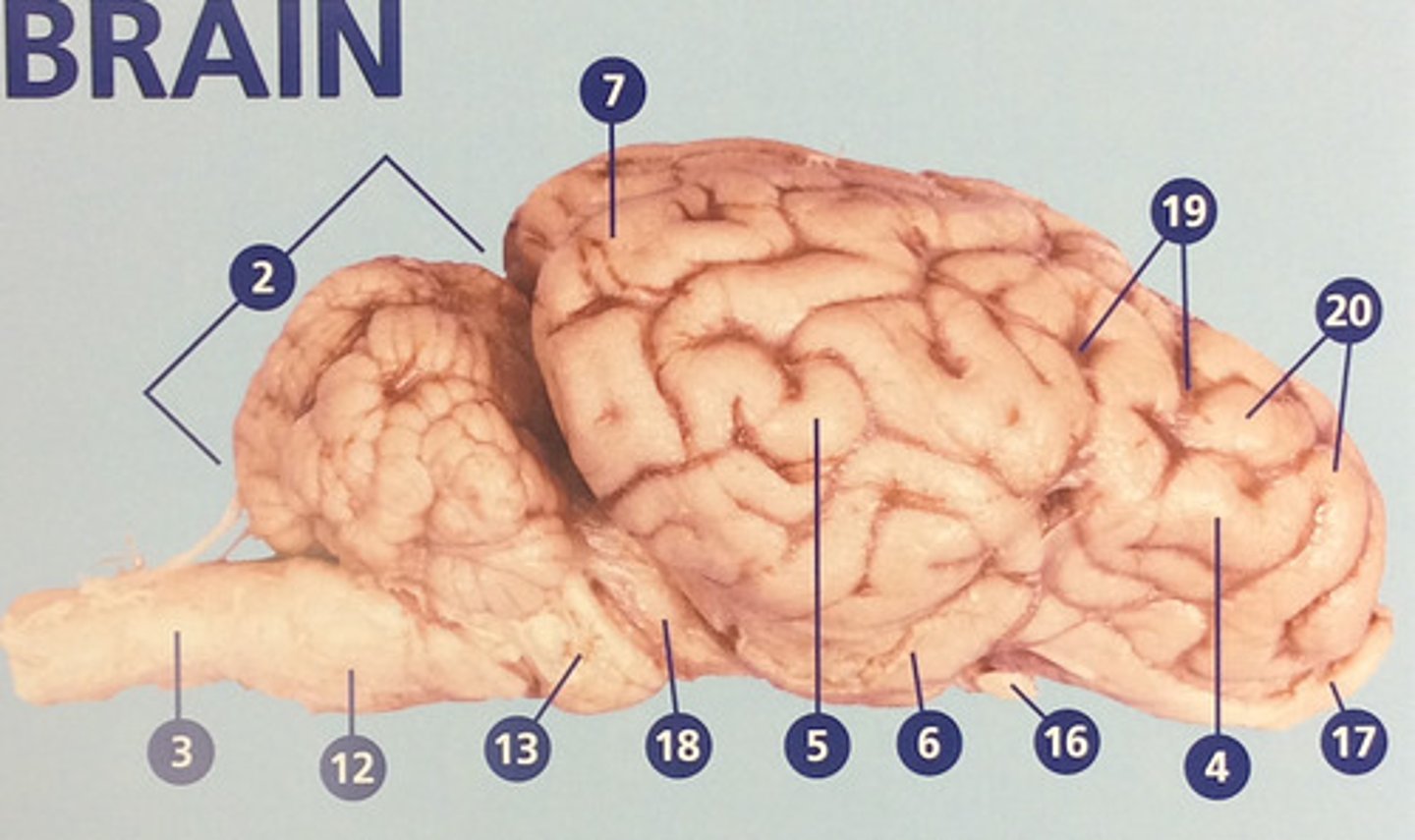
Frontal lobe
Controls cognitive processes such as planning and the inhibition of drives (#4)
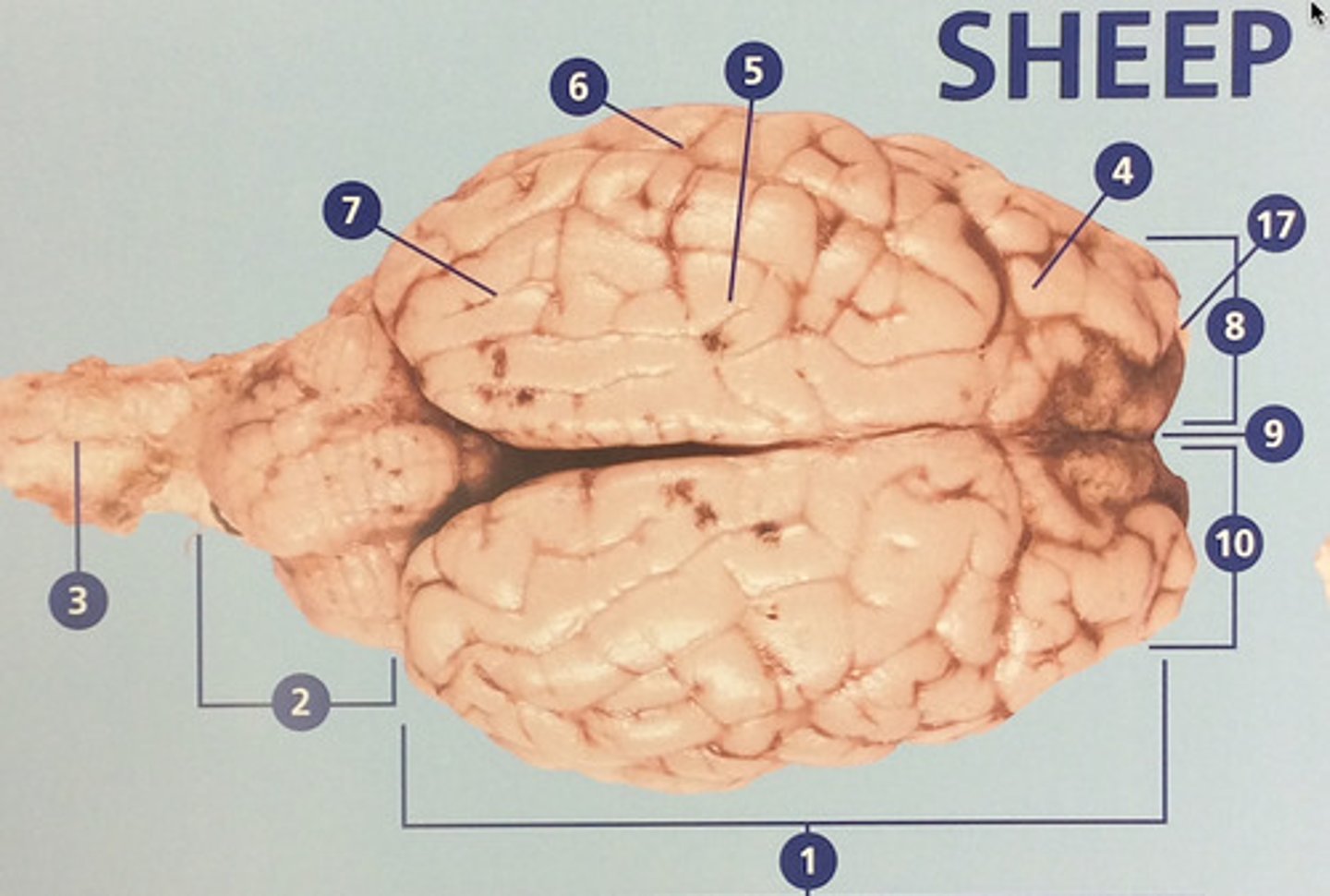
Parietal lobe
Integrates sensory information and functions in spatial perception (#5)
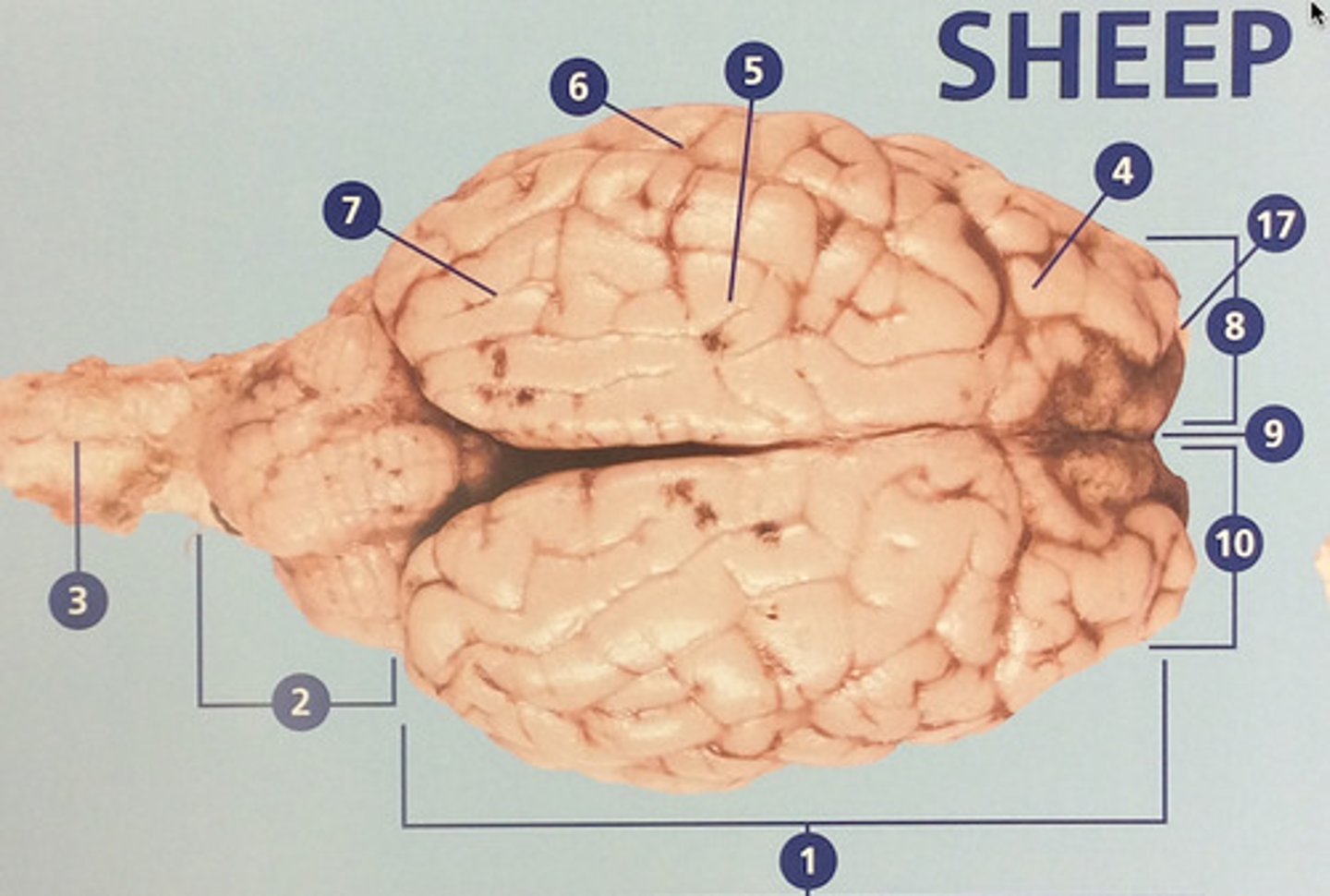
Temporal lobe
Functions in auditory perception and long-term memory (#6)
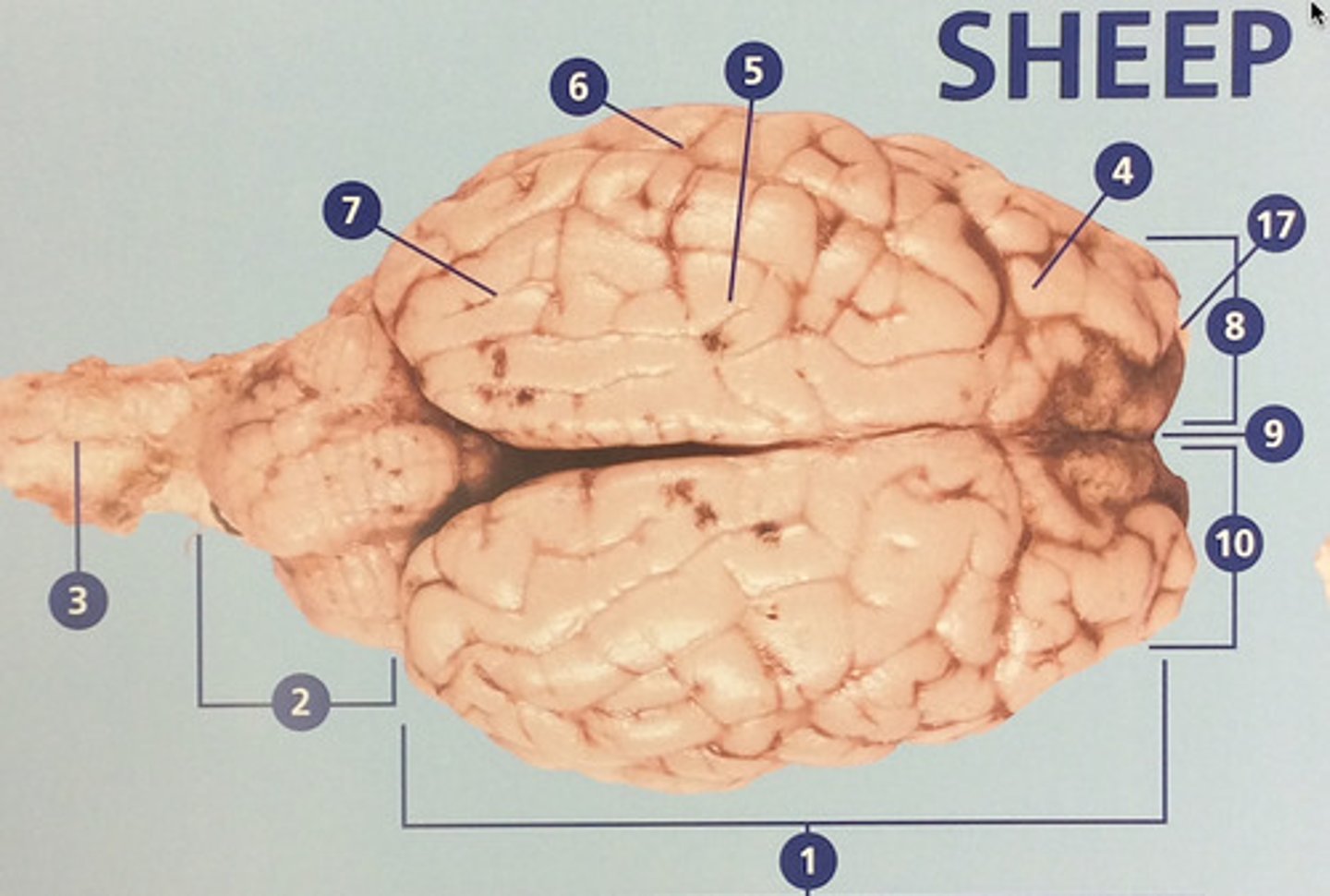
Occipital lobe
Receives sensory information from the eyes (#7)
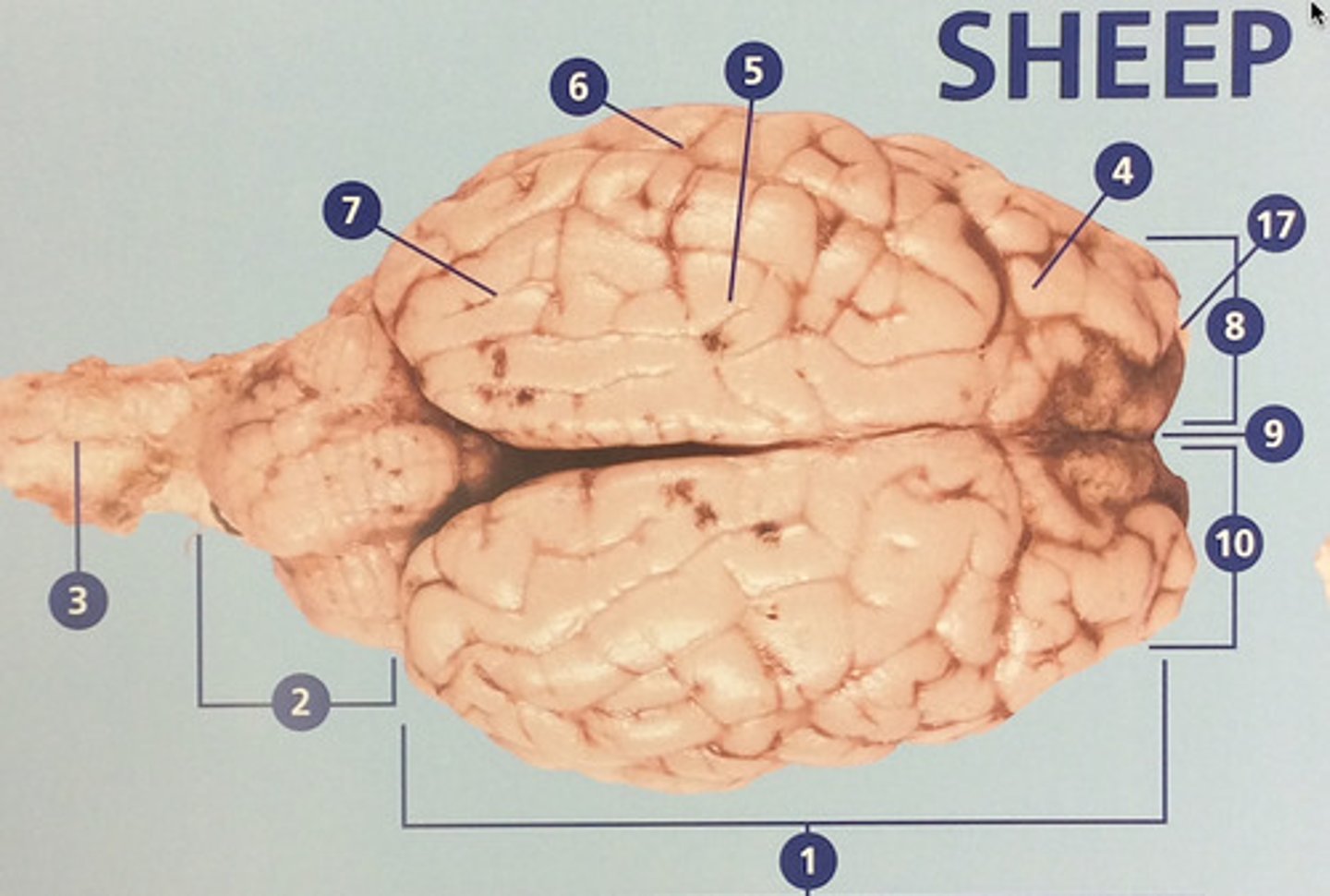
Left hemisphere
The left side of the cerebrum (#8)
Medial longitudinal fissure
Deep groove that separates the right and left hemispheres (#9)
Right hemisphere
The right side of the cerebrum (#10)
Brain stem
Route of information transfer between the forebrain and spinal cord; consists of the medulla, pons, and midbrain (#11)
Medulla oblongata
Brain region that connects to the spinal cord; important in autonomic functions (#12)
Pons
Connection between forebrain, cerebellum, and medulla; important in regulation of sleep and breathing (#13)
Optic tract
Nerves that continue from the optic chiasm to the thalamus, from which visual stimuli and reouted to the visual cortex (#14)
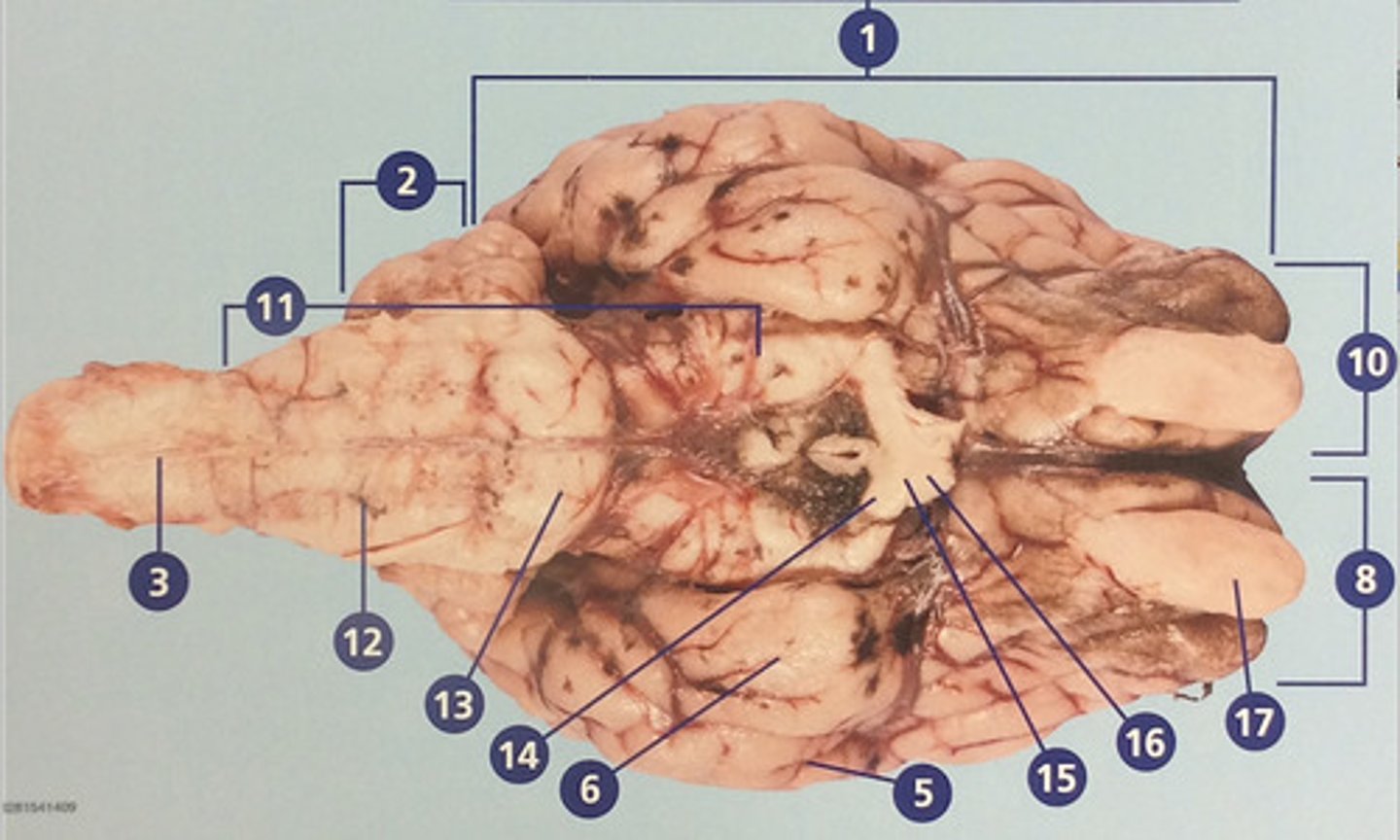
Optic chiasm
Junction at which some fibers from easch optic nerve crisscross, enabling effective binocular vision (#15)
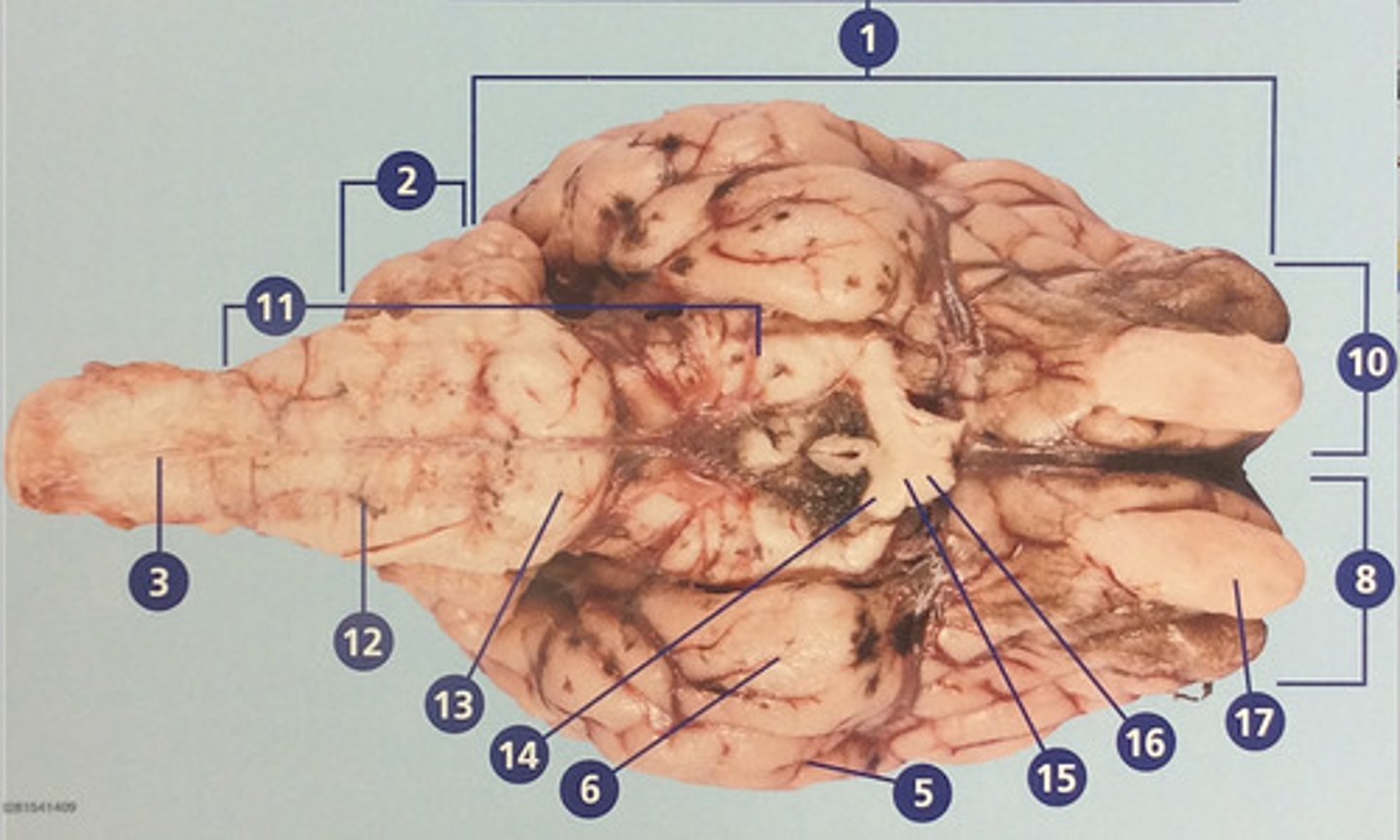
Optic nerve
Connects the retina to the optic chiasm (#16)
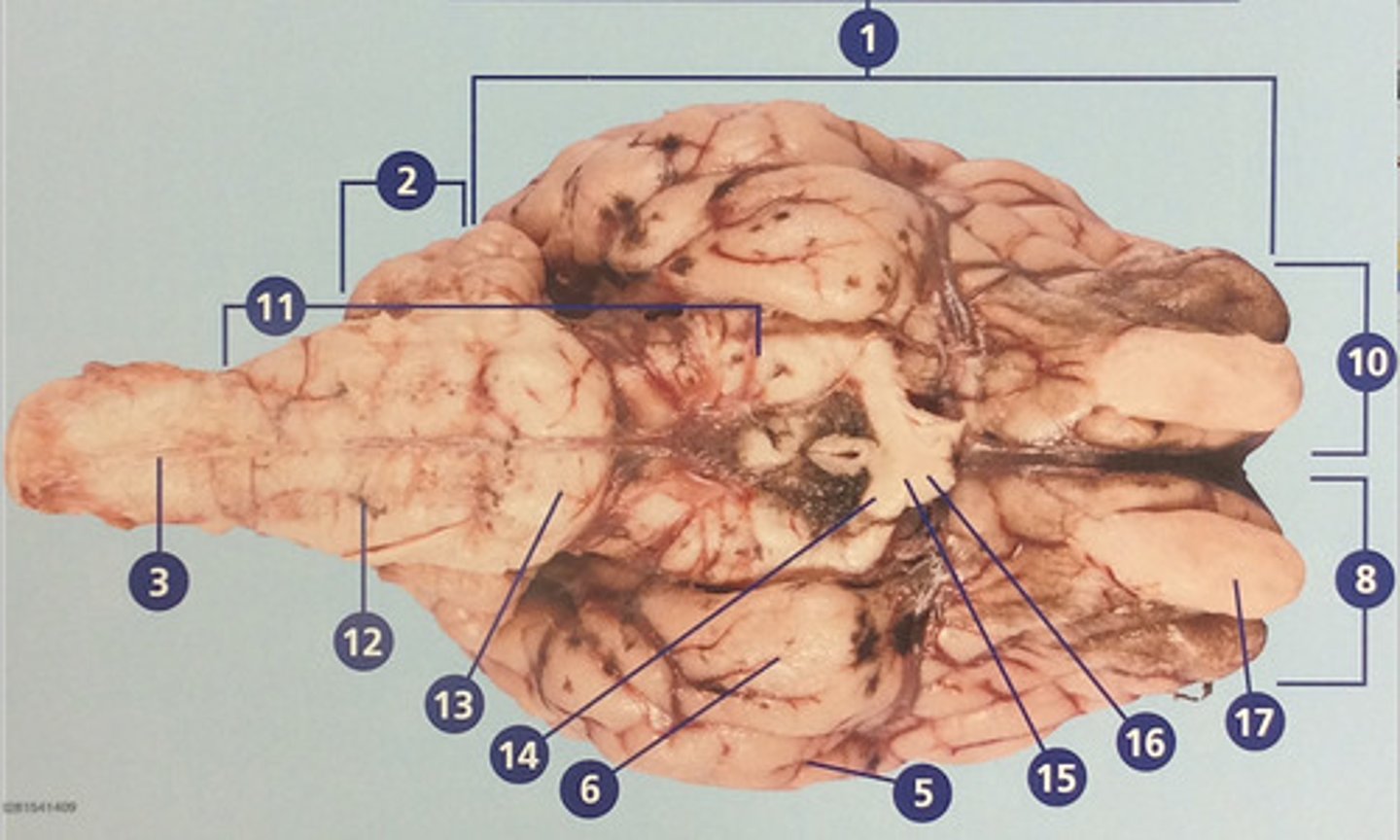
Olfactory bulb
Involved in detection and discrimination of odors (#17)
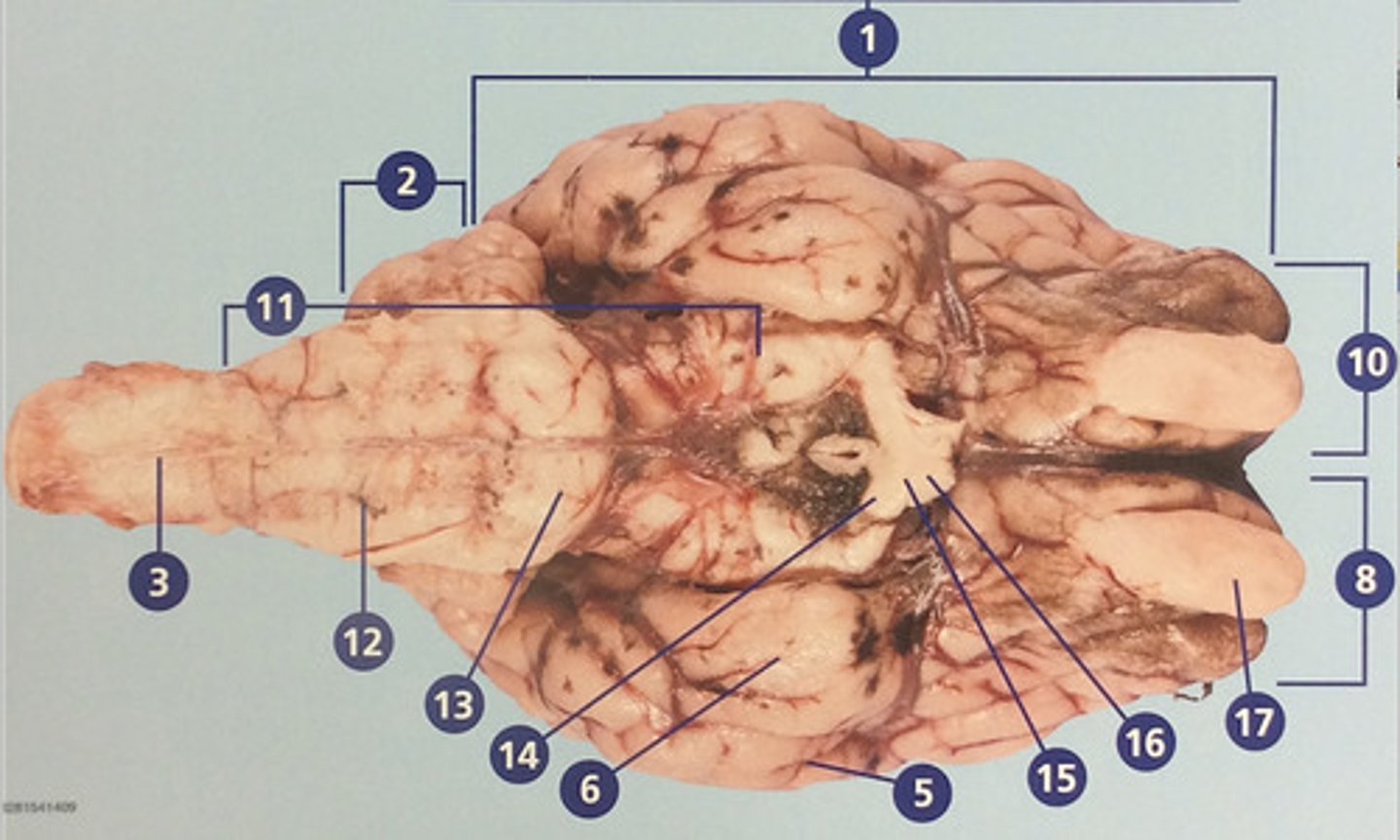
Midbrain
Region connecting the forebrain and hindbrain (#18)
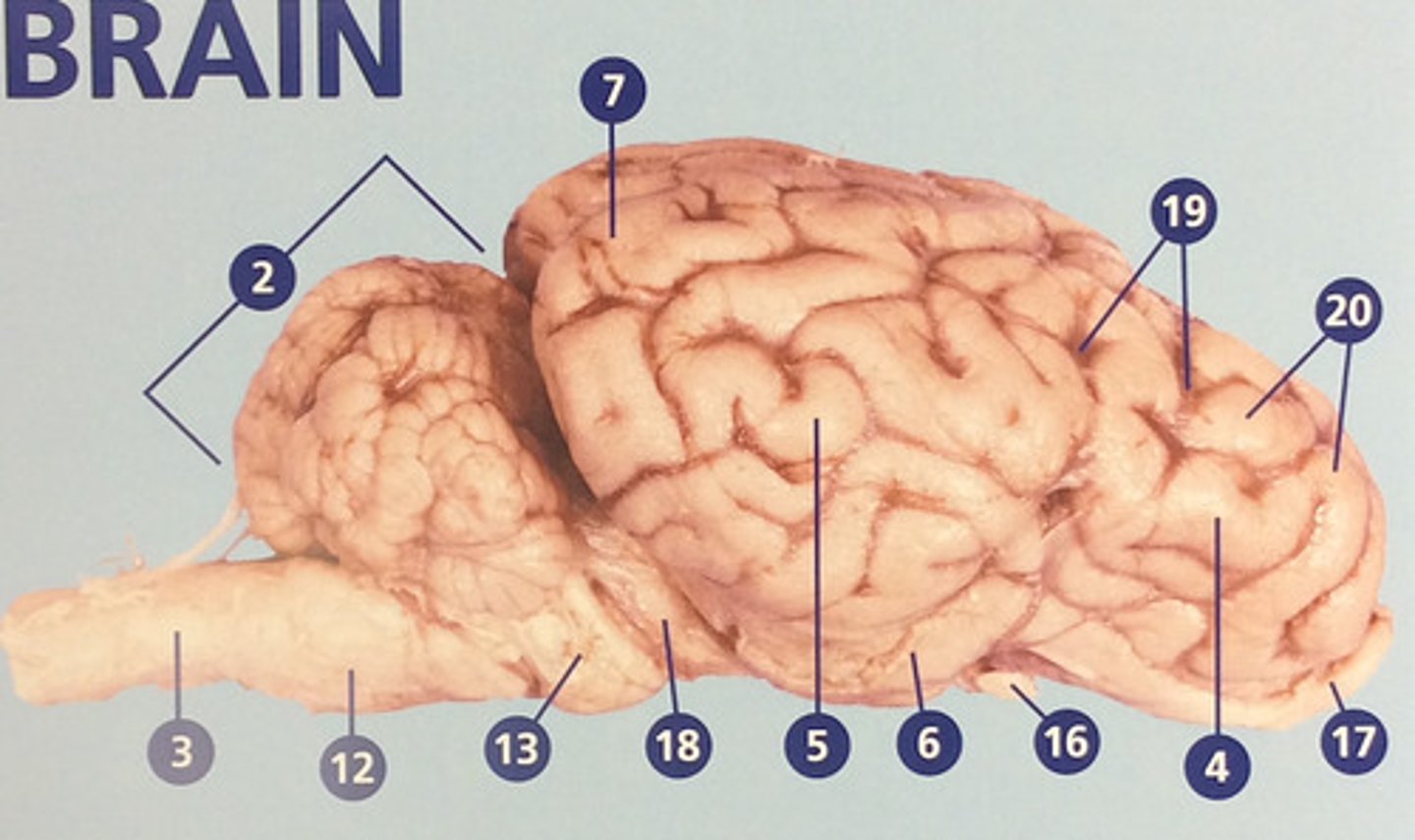
Sulci
Furrows in the folds of the cerebrum (#19)
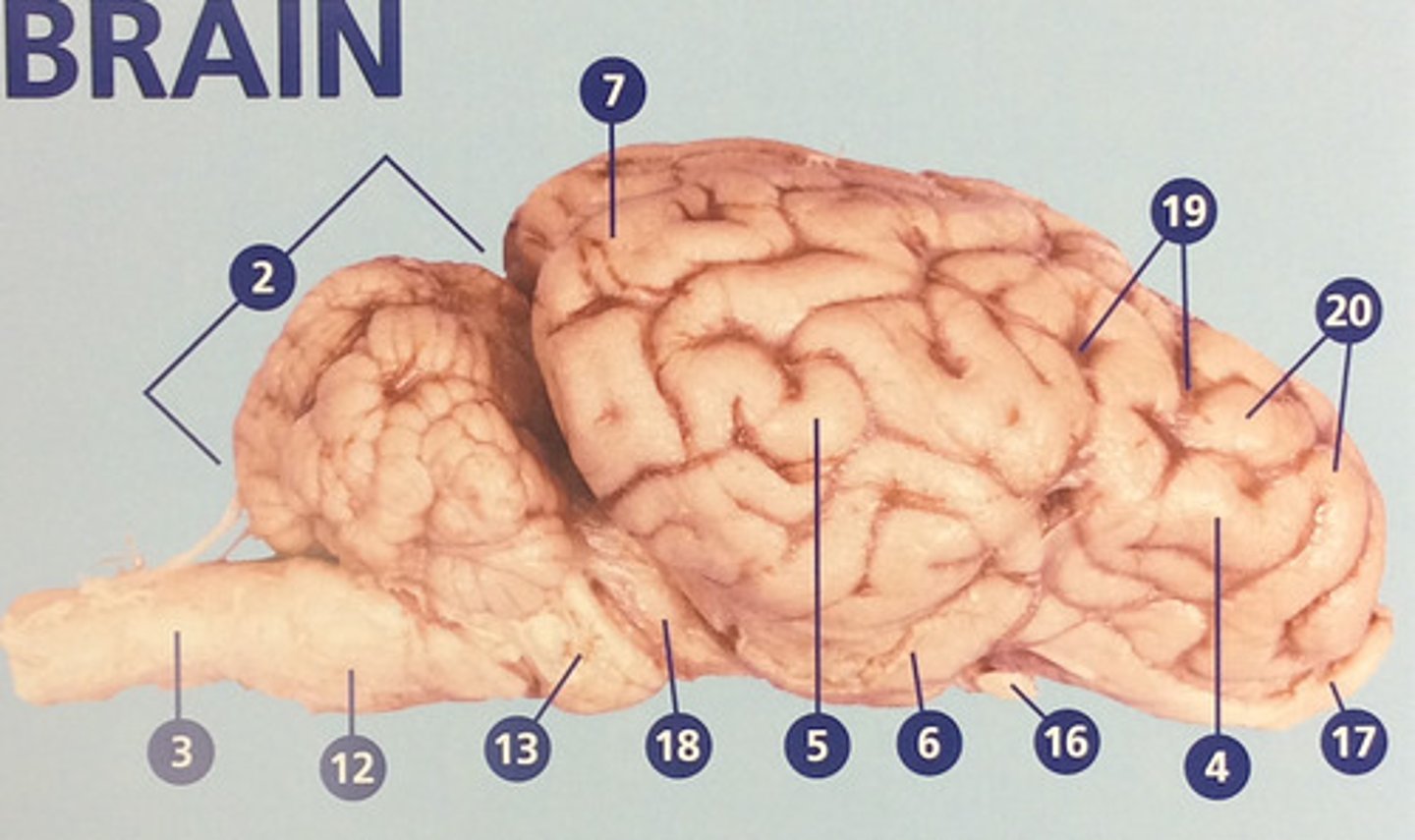
Gyri
Bulges in the folds of the cerebrum (#20)
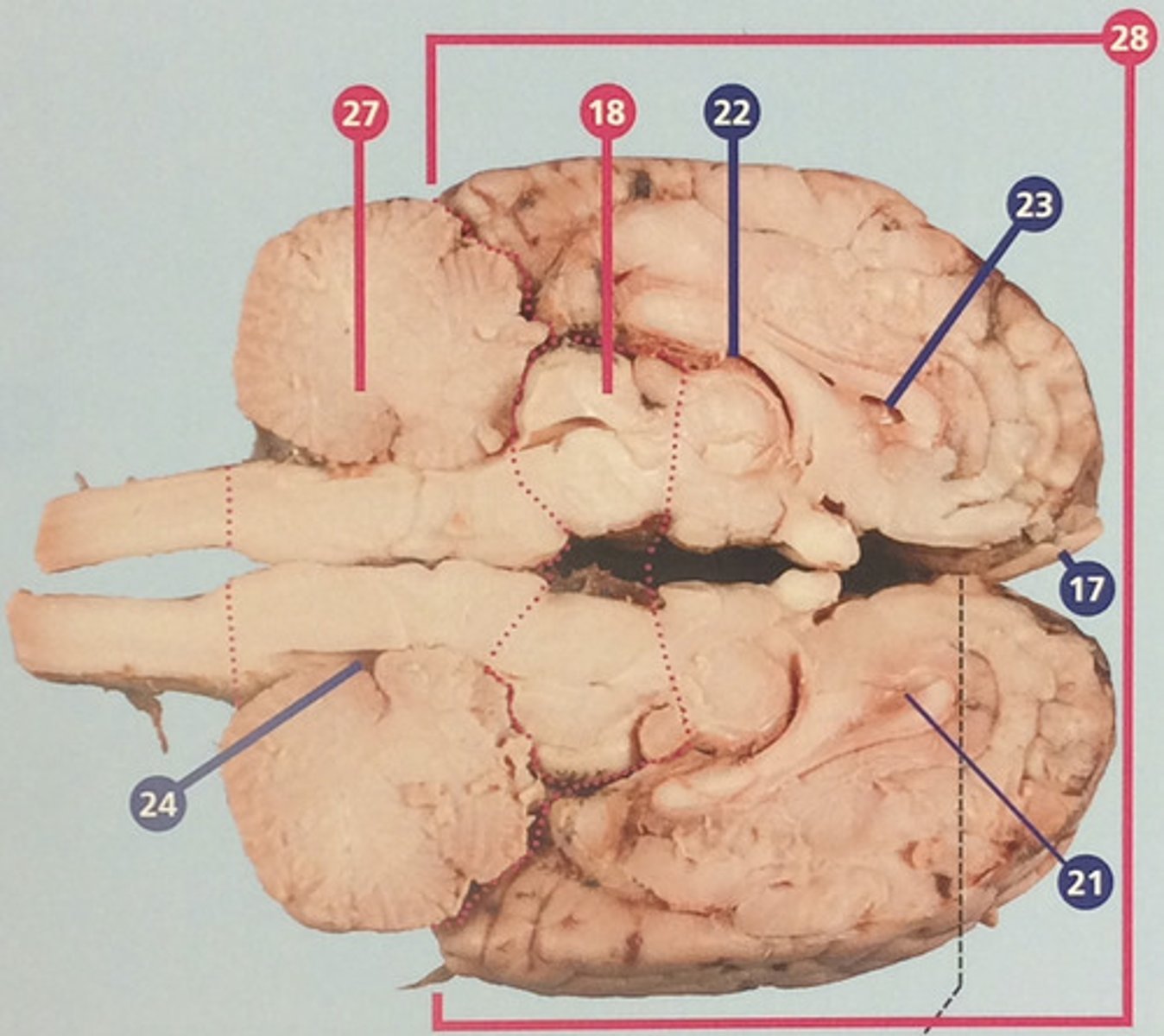
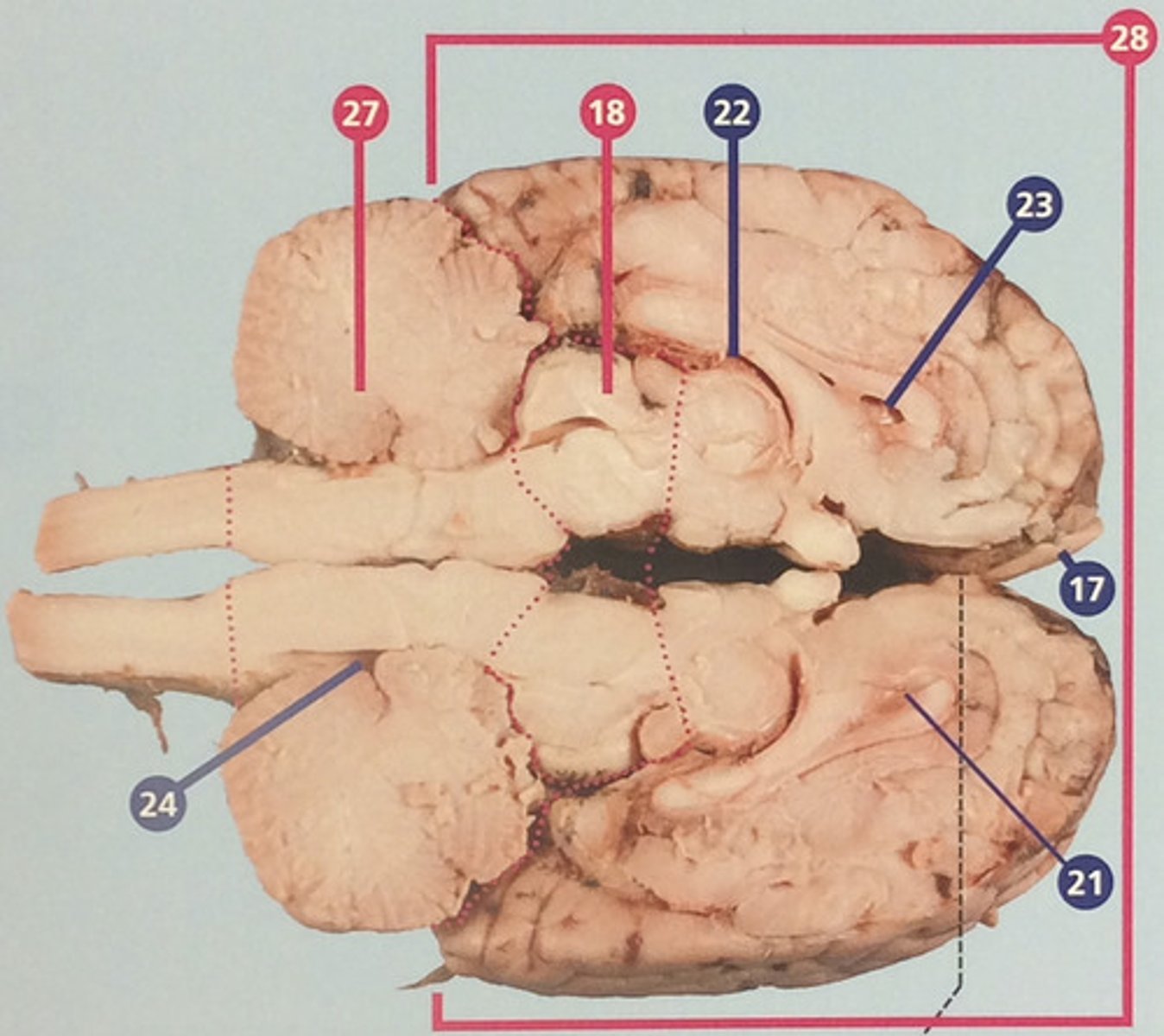
Ventricles
System of cavities and connecting tubes in the brain, including the central canal of the spinal cord; filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which cushions and supports the brain (#22-24)
Arbor vitae
Branching white matter in the cerebellum(#25)
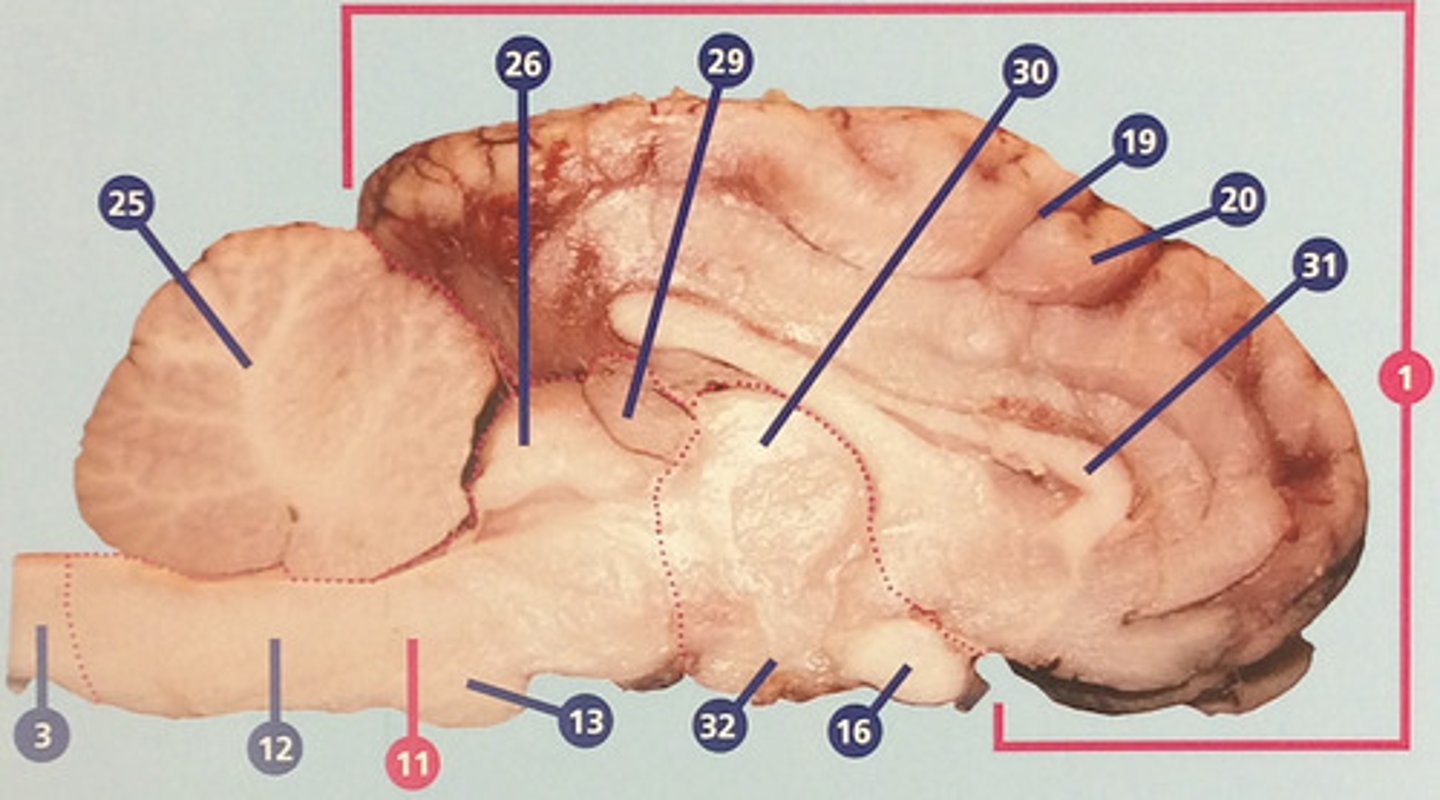
Forebrain
Region consisting of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (#28)
Pineal gland
Endocrine gland that secrets melatonin, which influences circadian rhythms and timing of sexual development (#29)
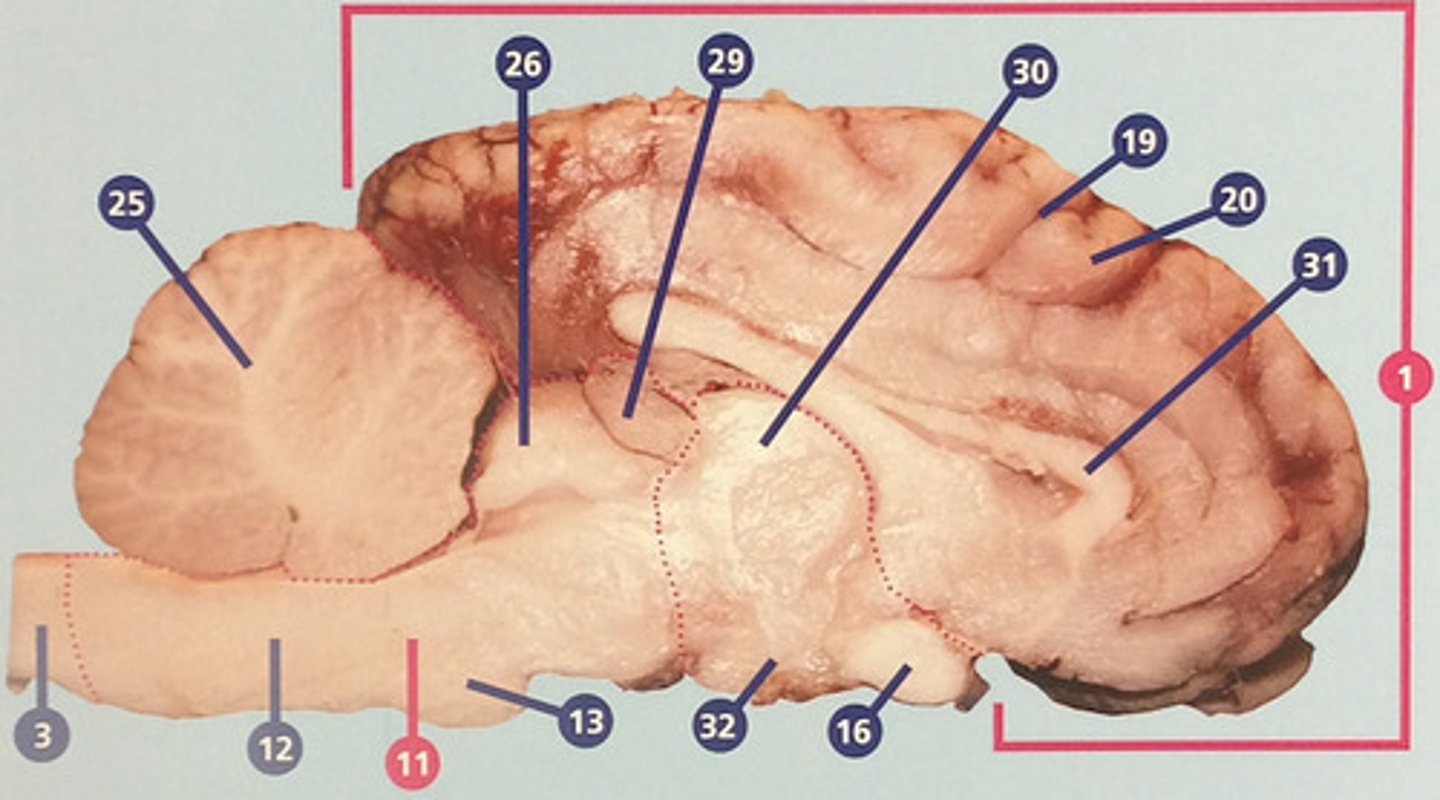
Thalamus
Region between midbrain and cerebral cortex; receives many types of sensory signals and relays them to the cerebral cortex (#30)
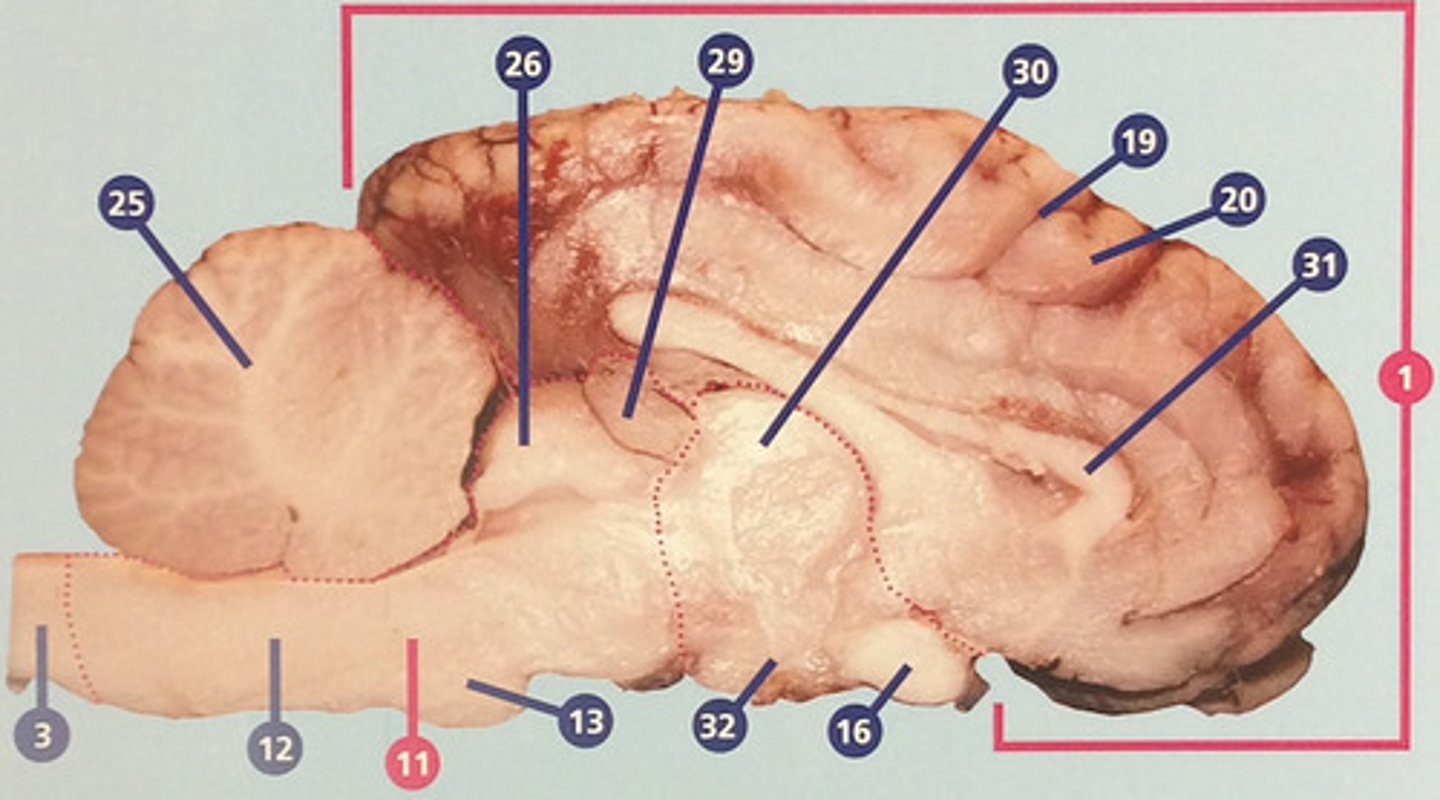
Corpus callosum
Bundle of nerve fibers connecting right and left cerebral hemispheres (#31)
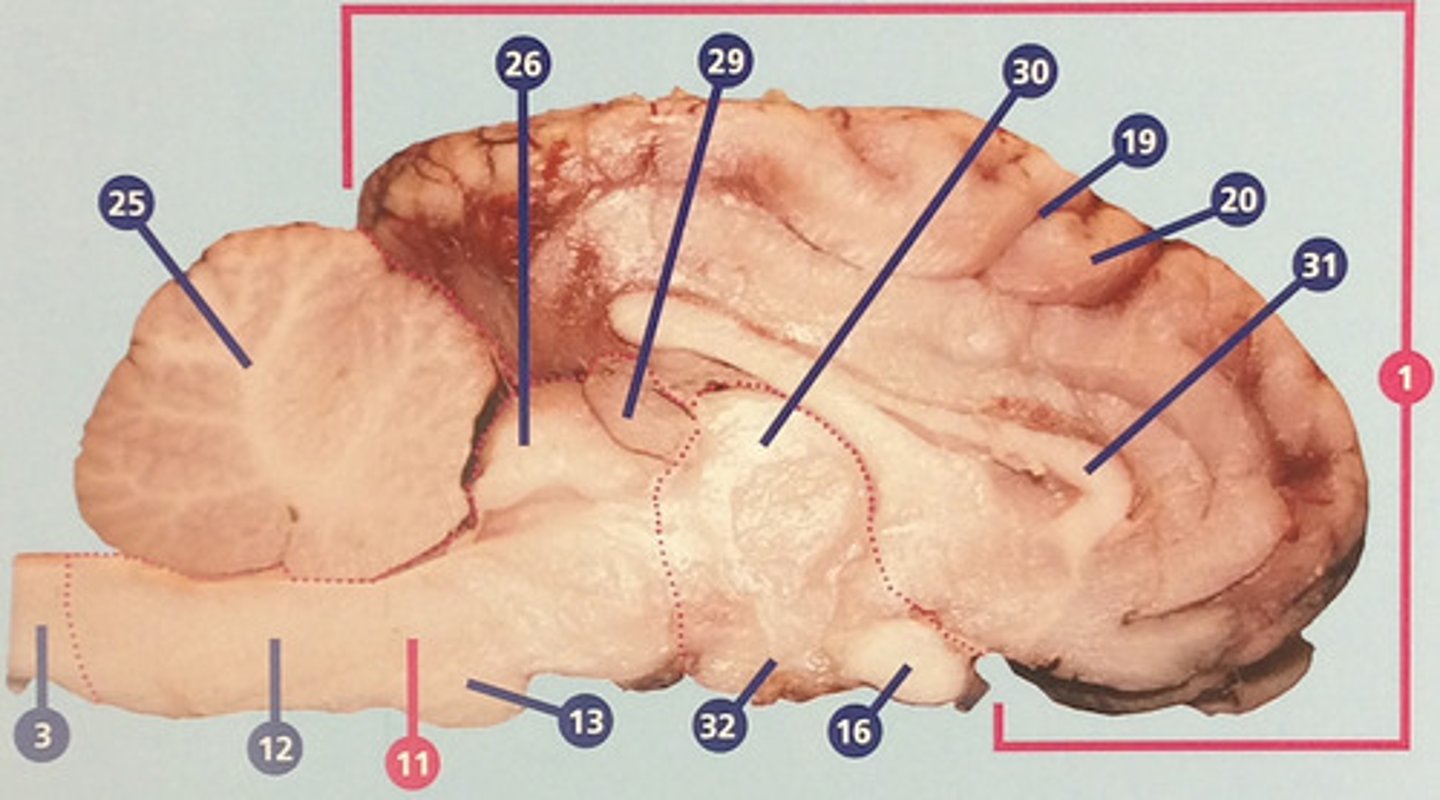
Hypothalamus
Brain structure with many functions including hormone secretion, temperature regulation, and hunger, mood, thirst, and fatigue (#32)
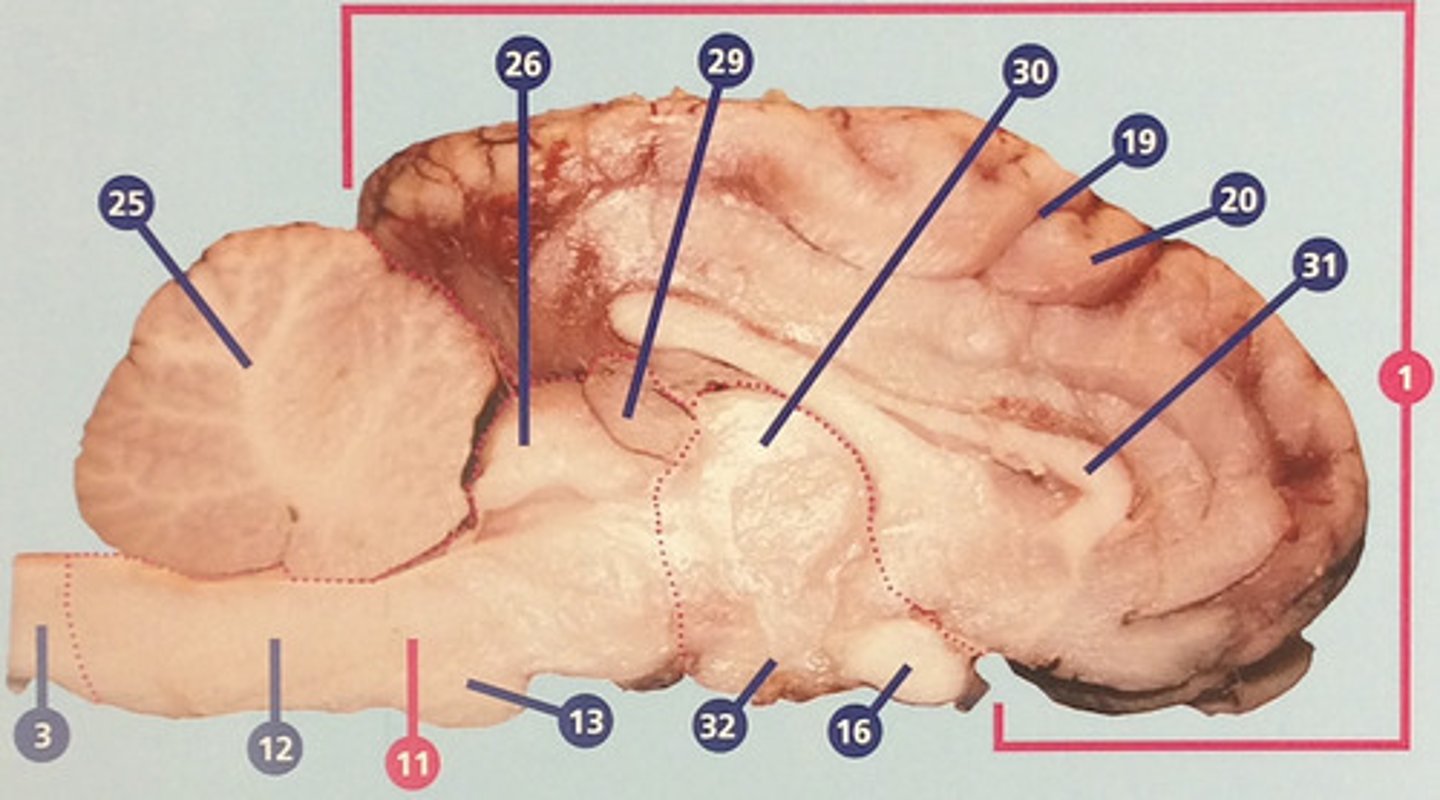
White matter
Portions of the central nervous system made up mainly of myelinated nerve fibers; in the cerebrum, usually surrounded by gray matter (#33)
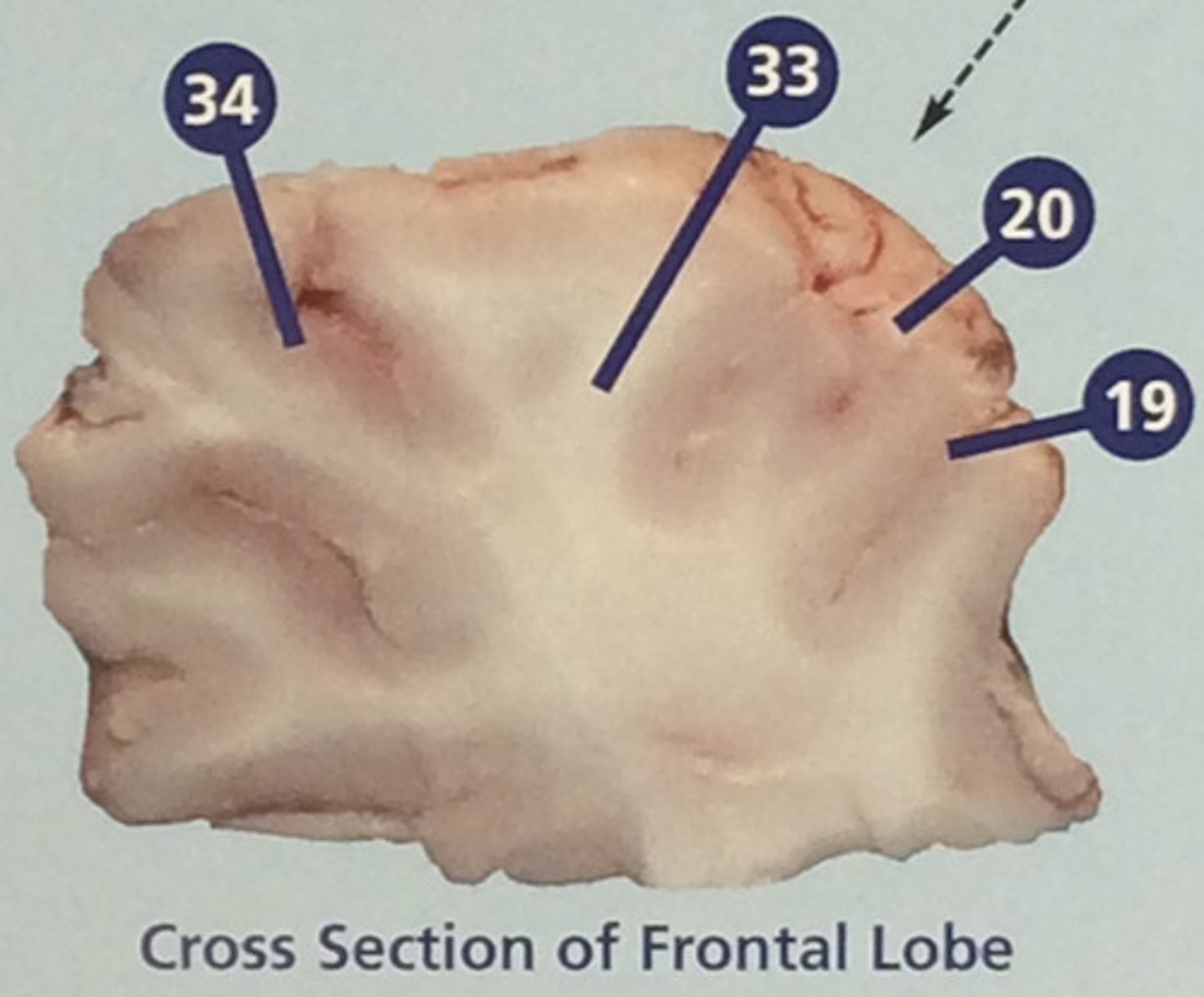
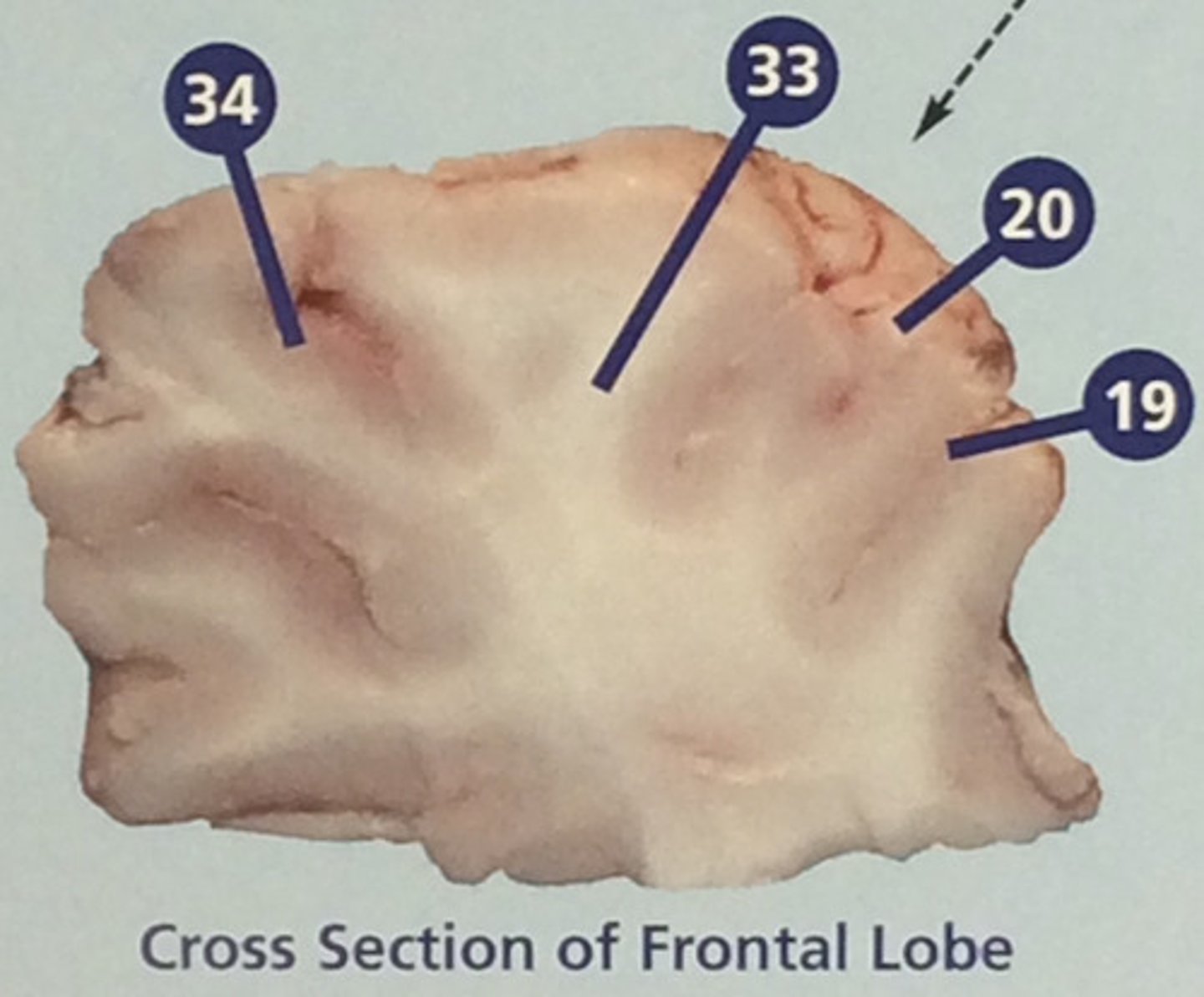
Gray matter
Portions of the central nervous system made up mainly of nerve cell bodies (#34)
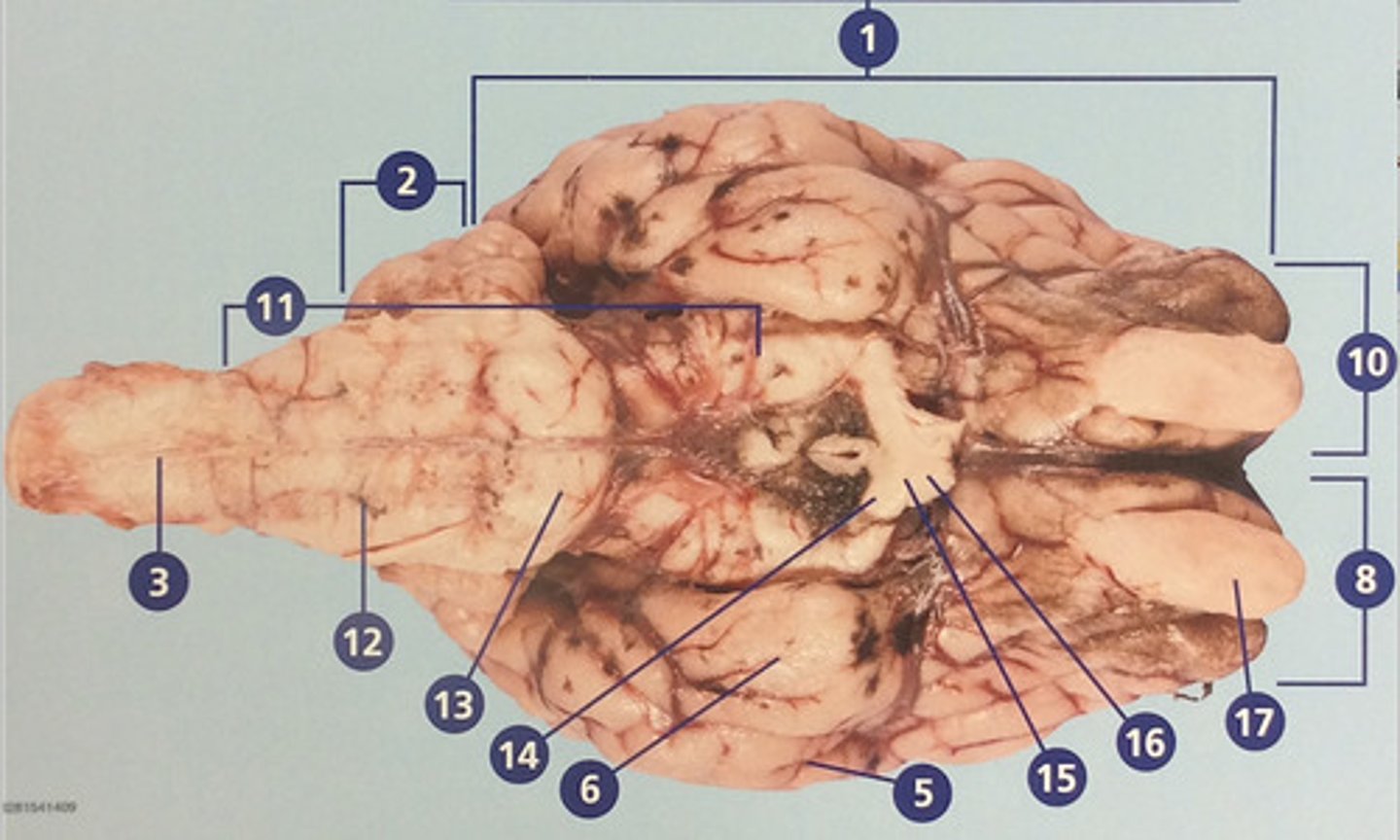
Cerebrum
Large, deeply wrinkled region of the brain responsible for conscious experience including perception, emotion, thought, and planning (#1)
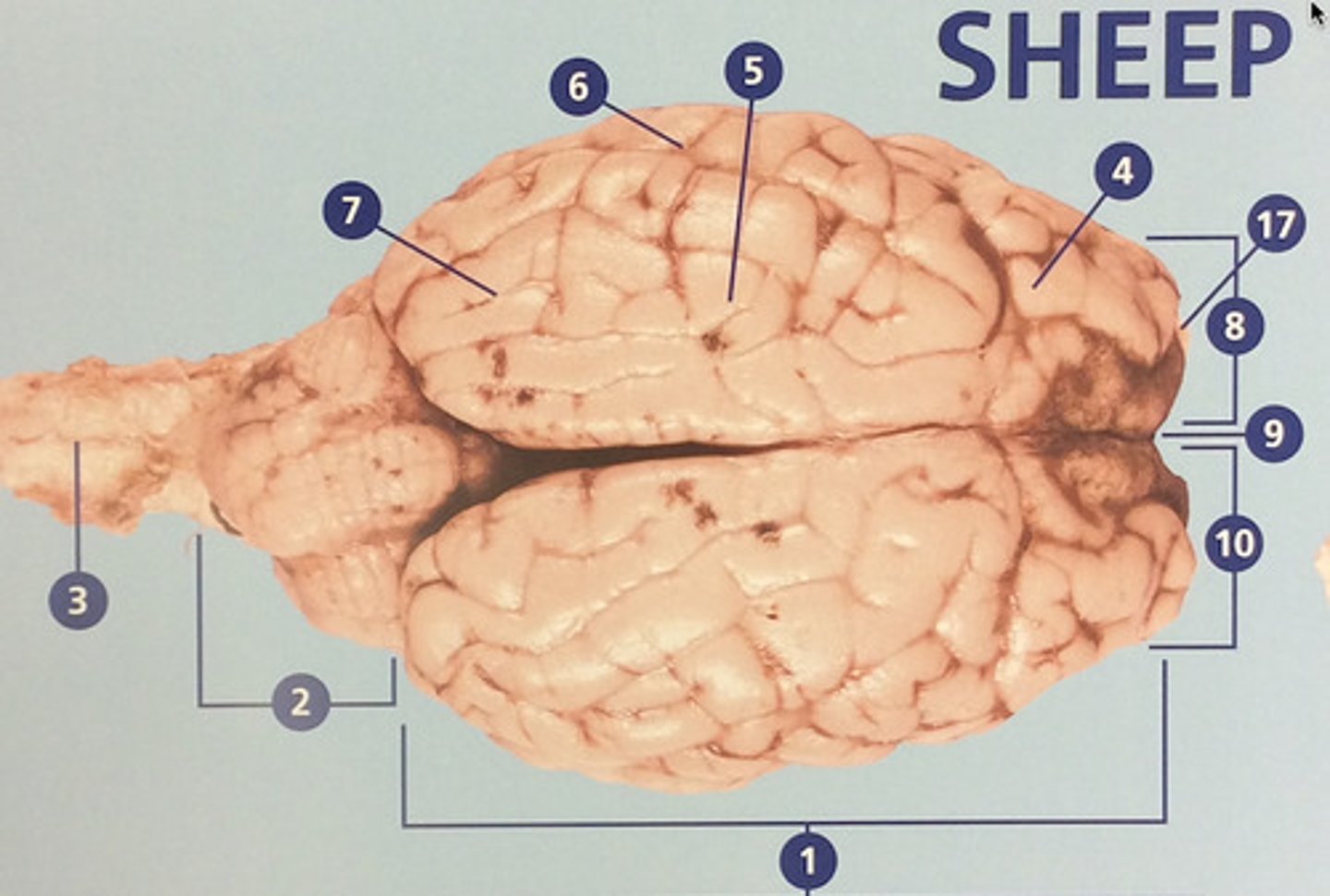
Cerebellum
Controls movement, balance, and muscle coordination (#2)
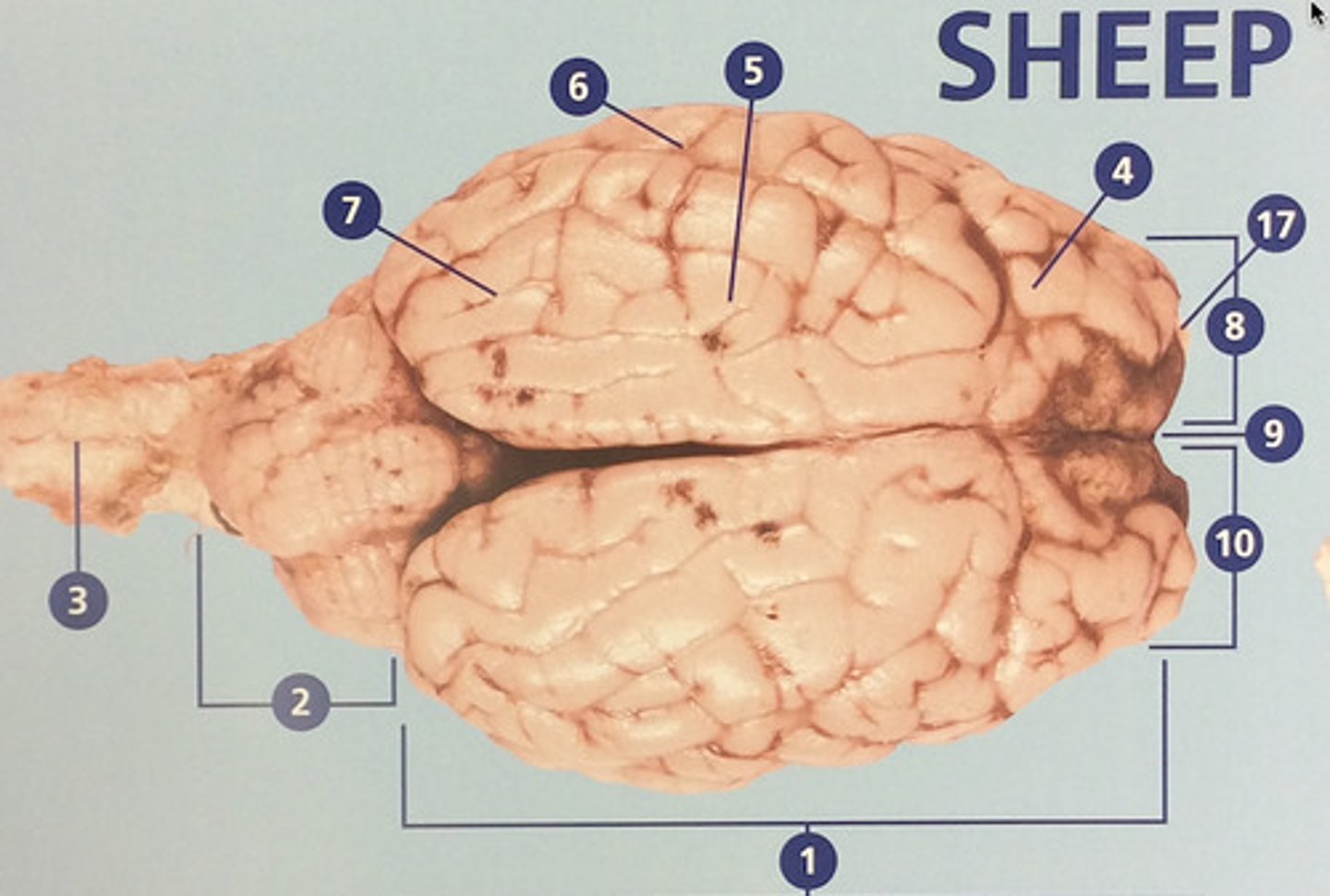
Spinal cord
Bundle of nerve fibers inside the spine that connects the brain to the sensory and motor parts of the body (#3)
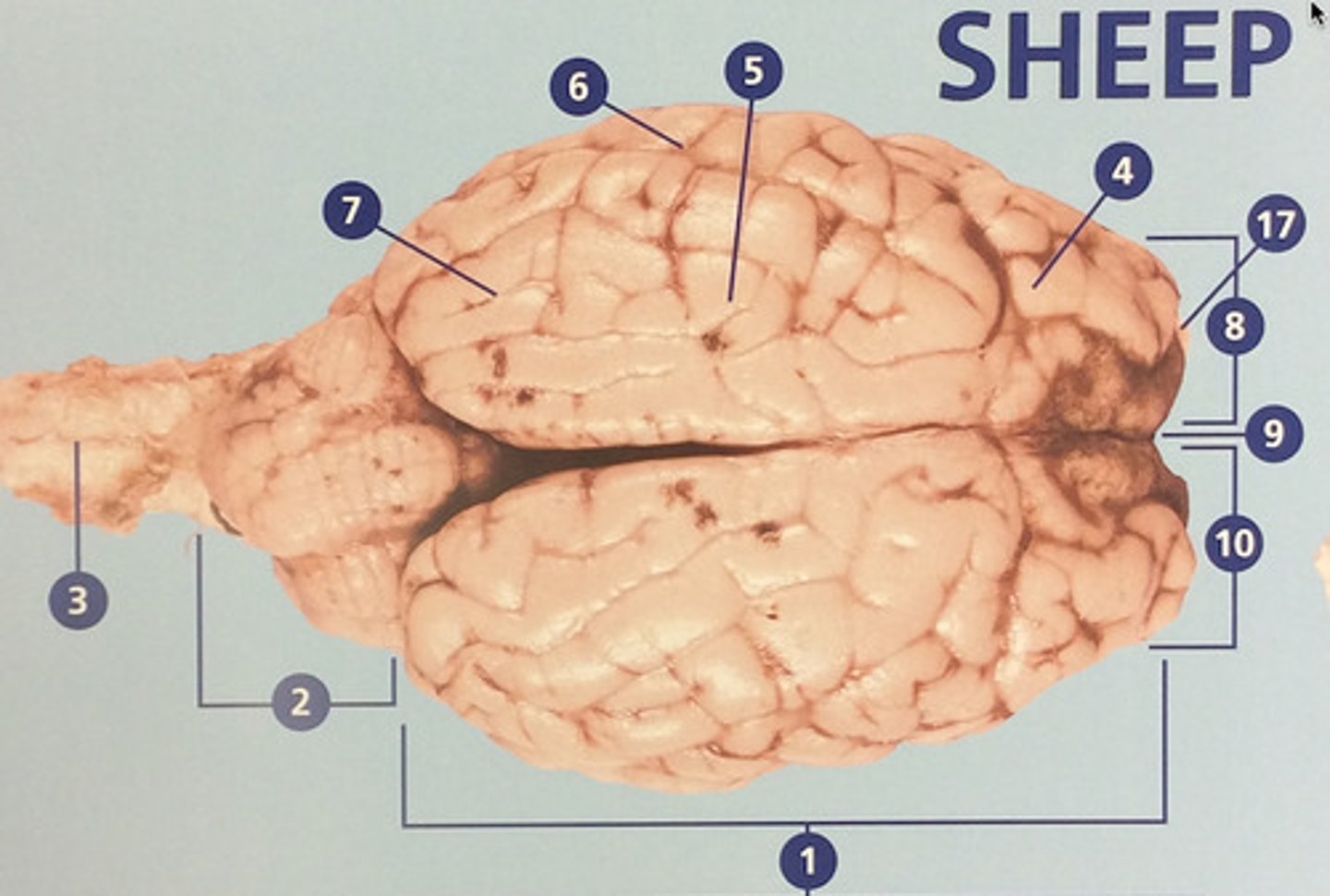
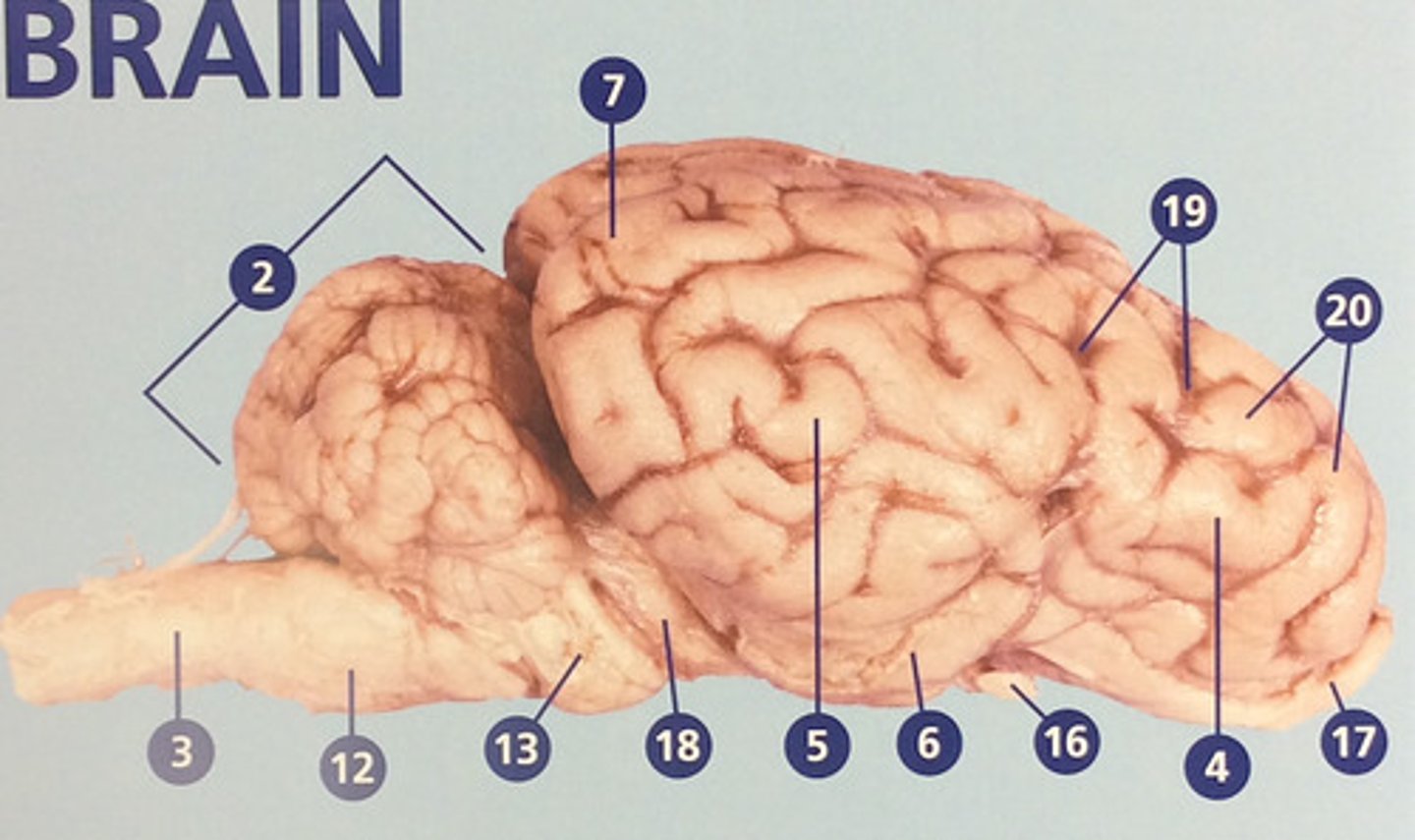
Frontal lobe
Controls cognitive processes such as planning and the inhibition of drives (#4)
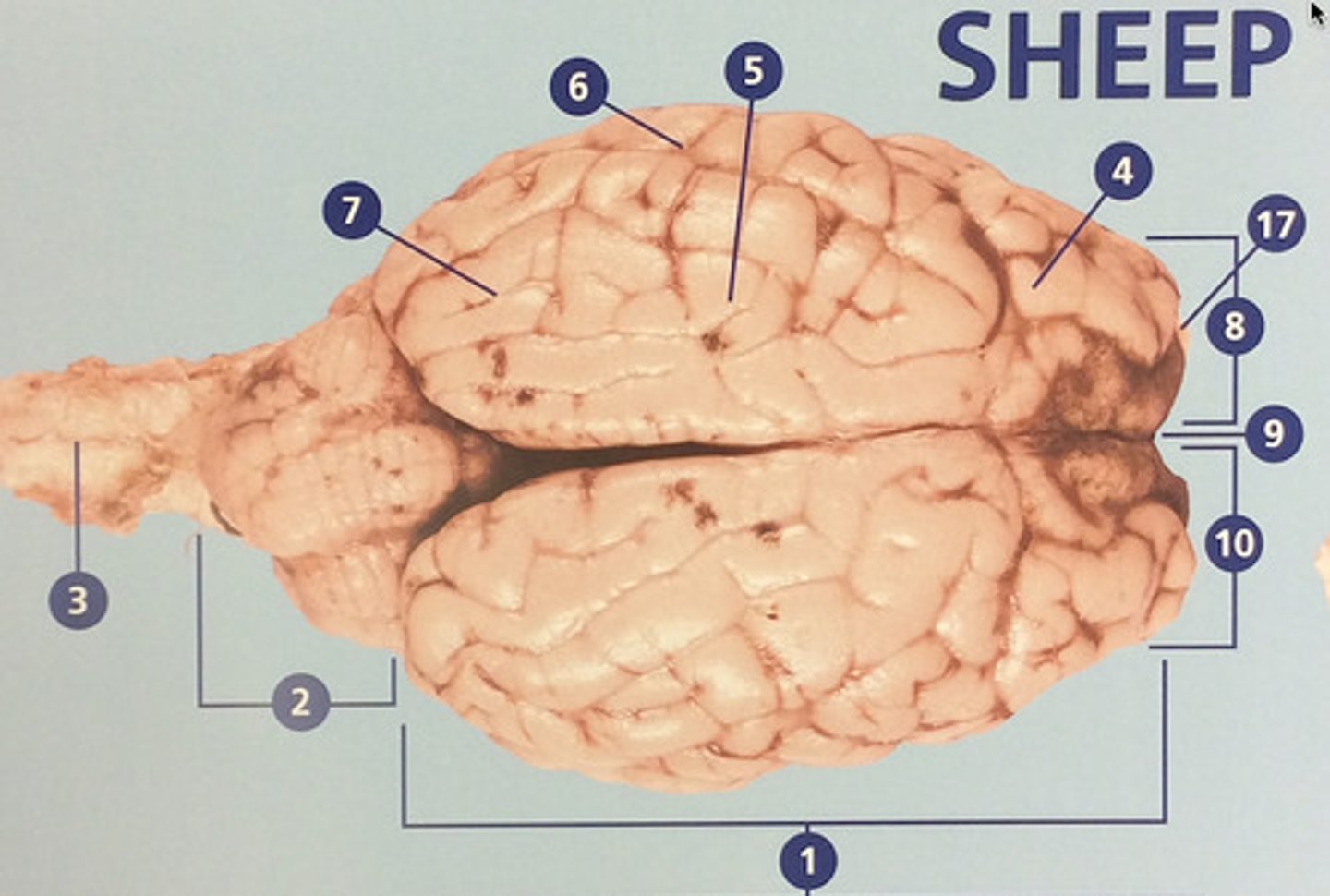
Parietal lobe
Integrates sensory information and functions in spatial perception (#5)
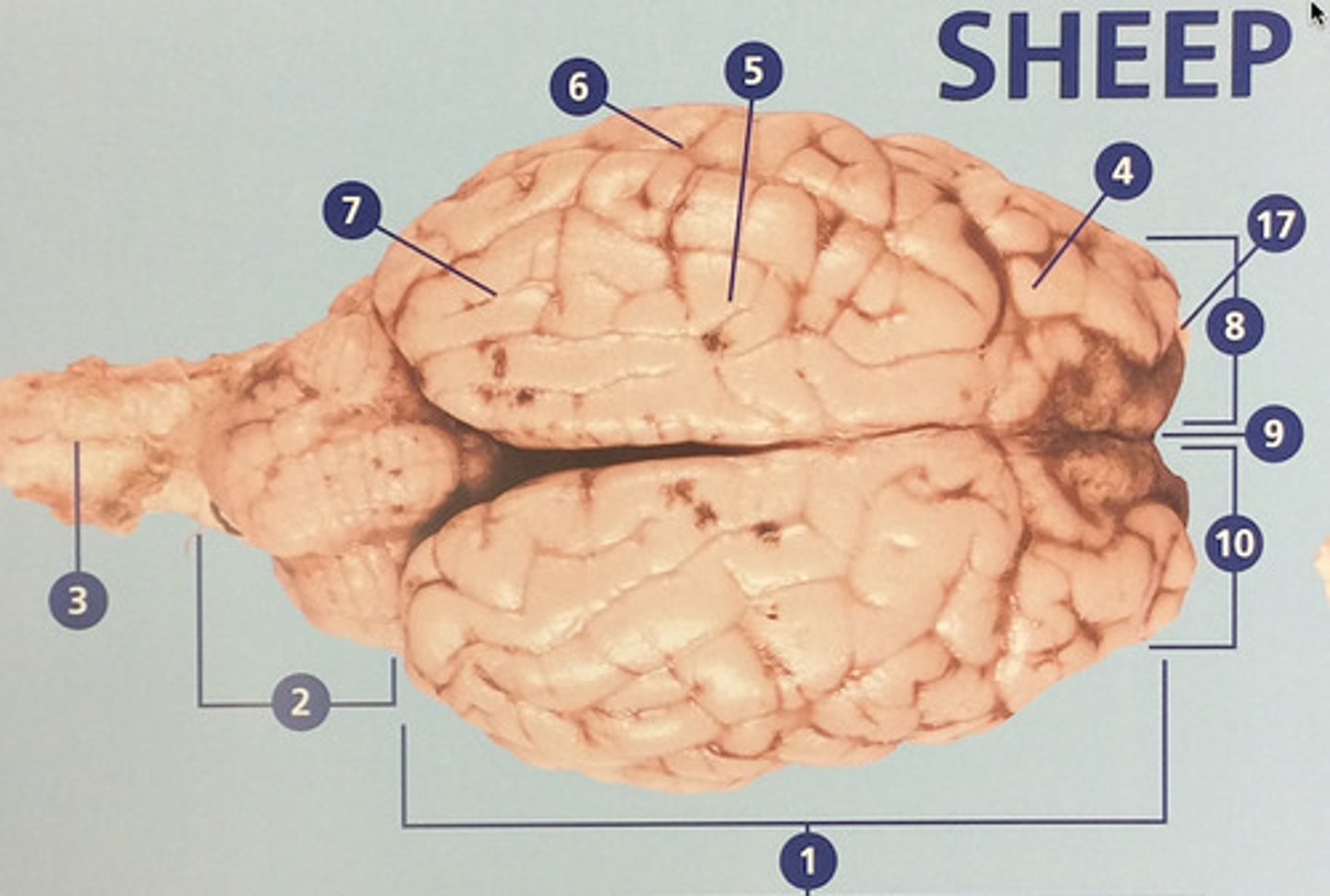
Temporal lobe
Functions in auditory perception and long-term memory (#6)
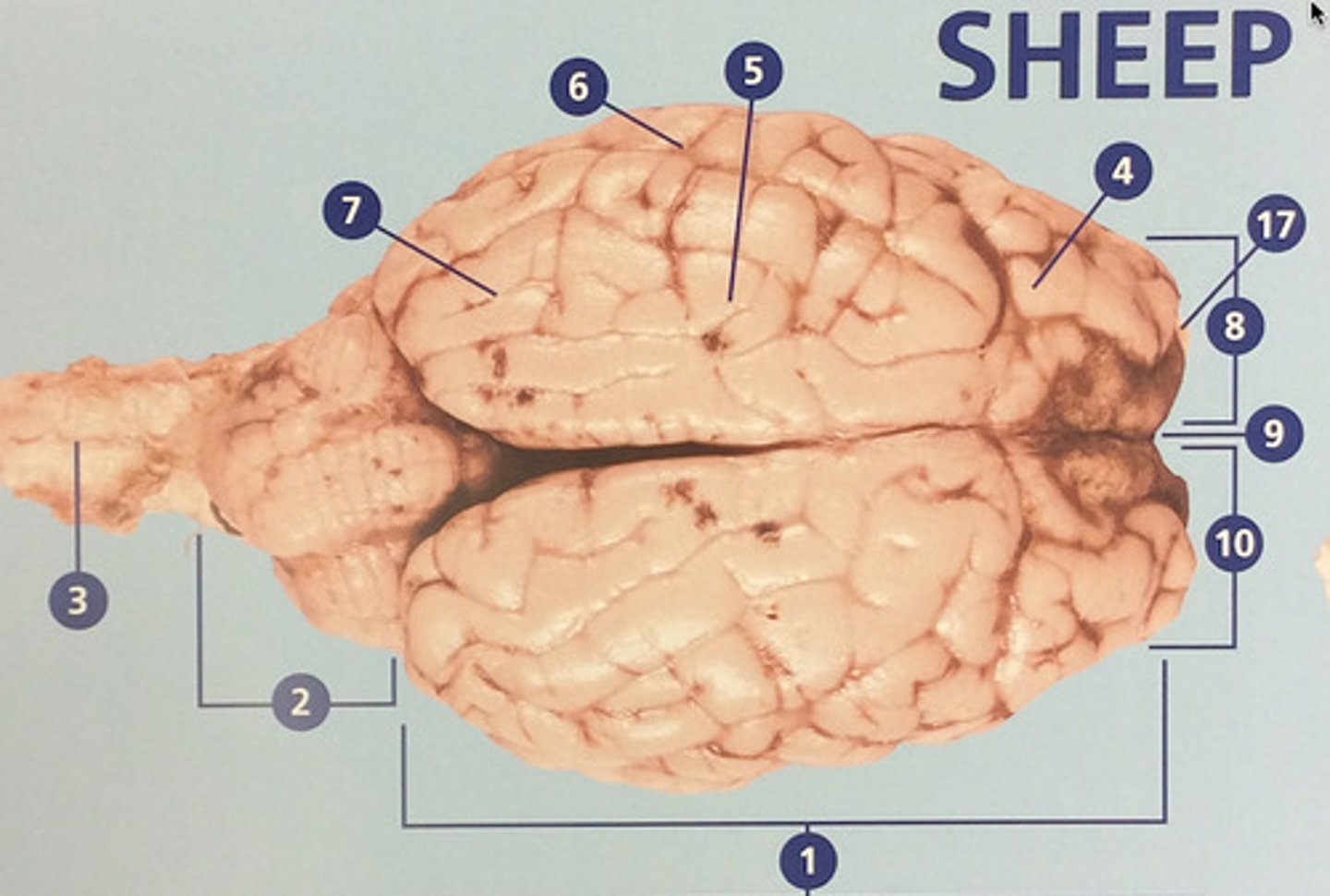
Occipital lobe
Receives sensory information from the eyes (#7)
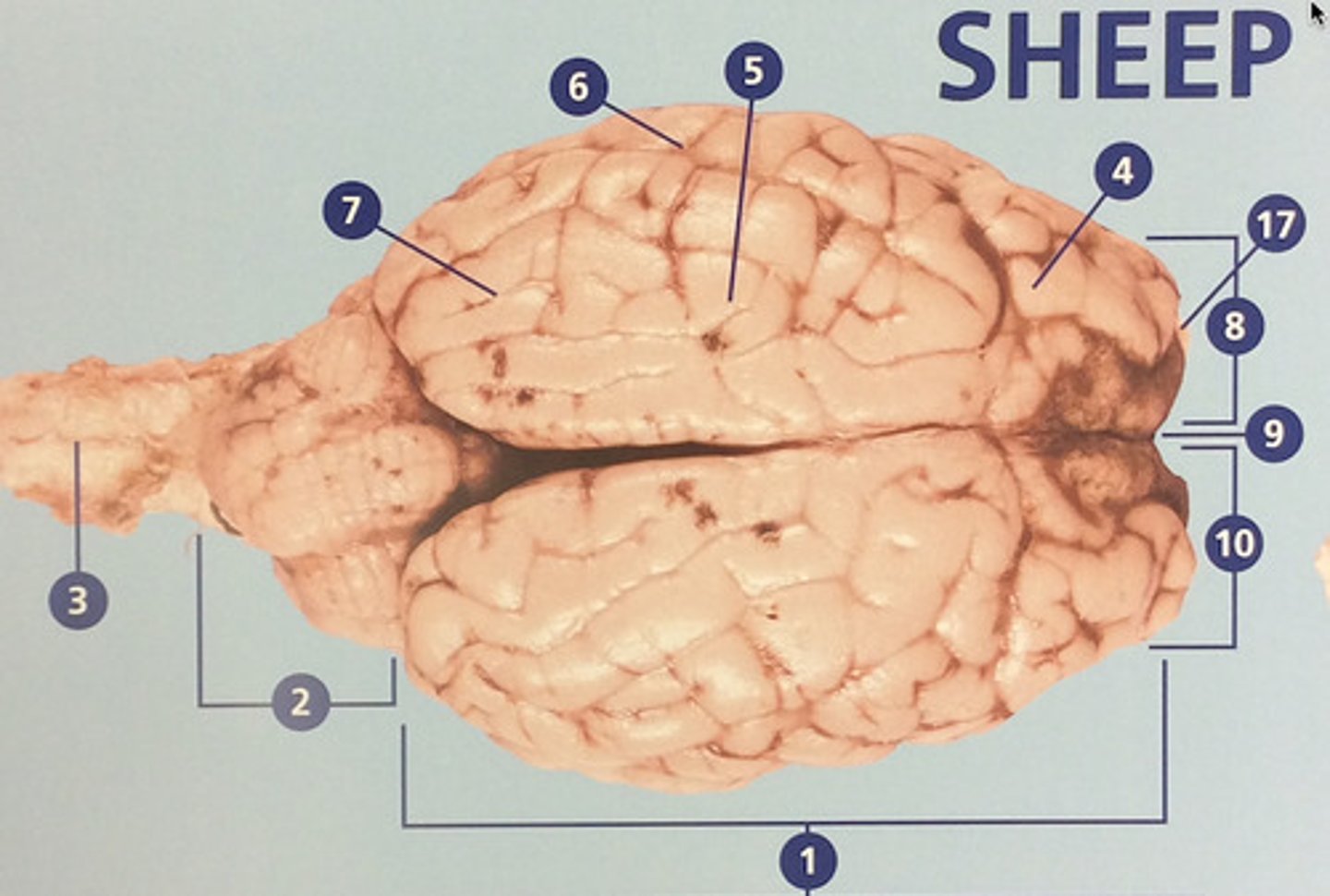
Left hemisphere
The left side of the cerebrum (#8)
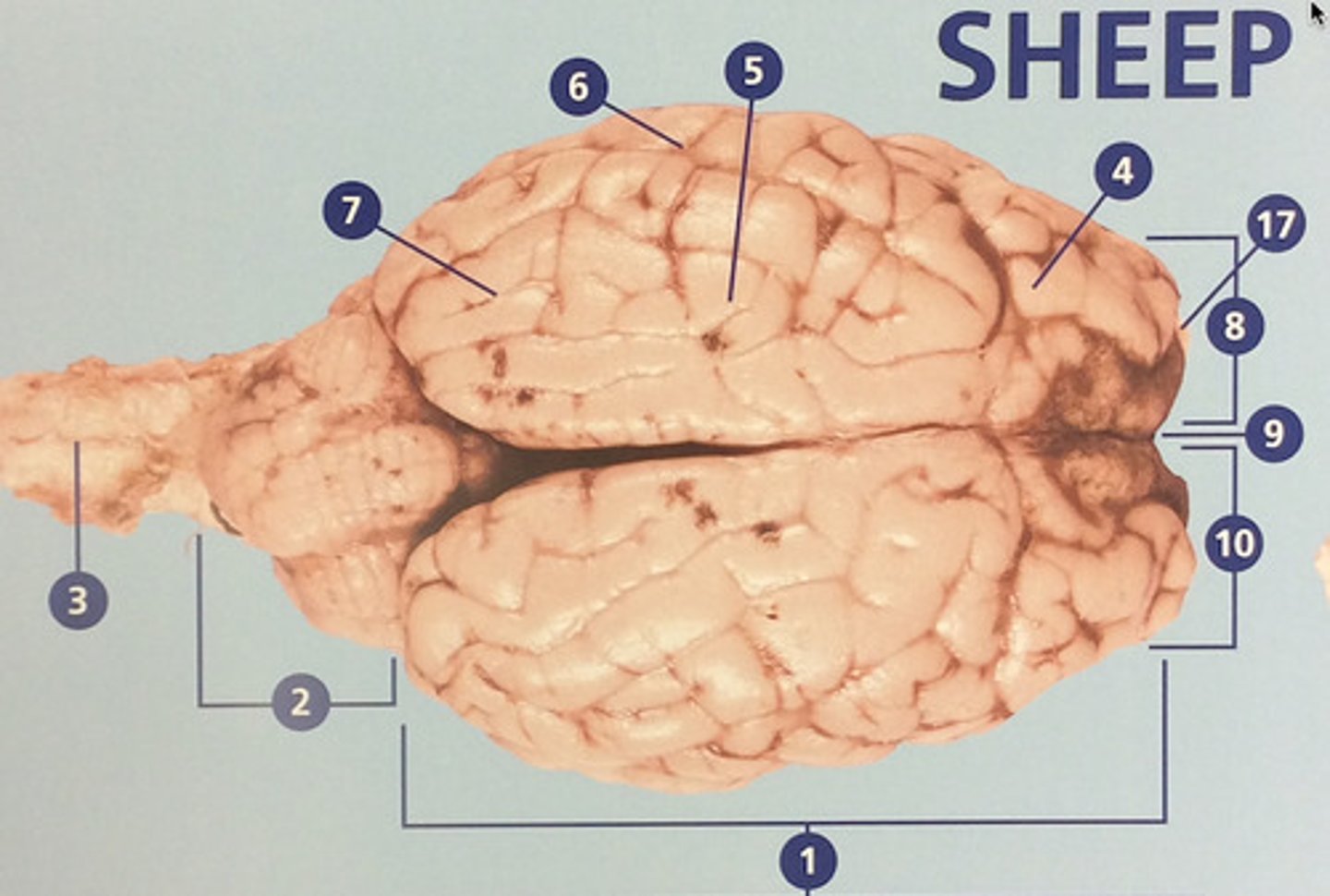
longitudinal fissure
Deep groove that separates the right and left hemispheres (#9)
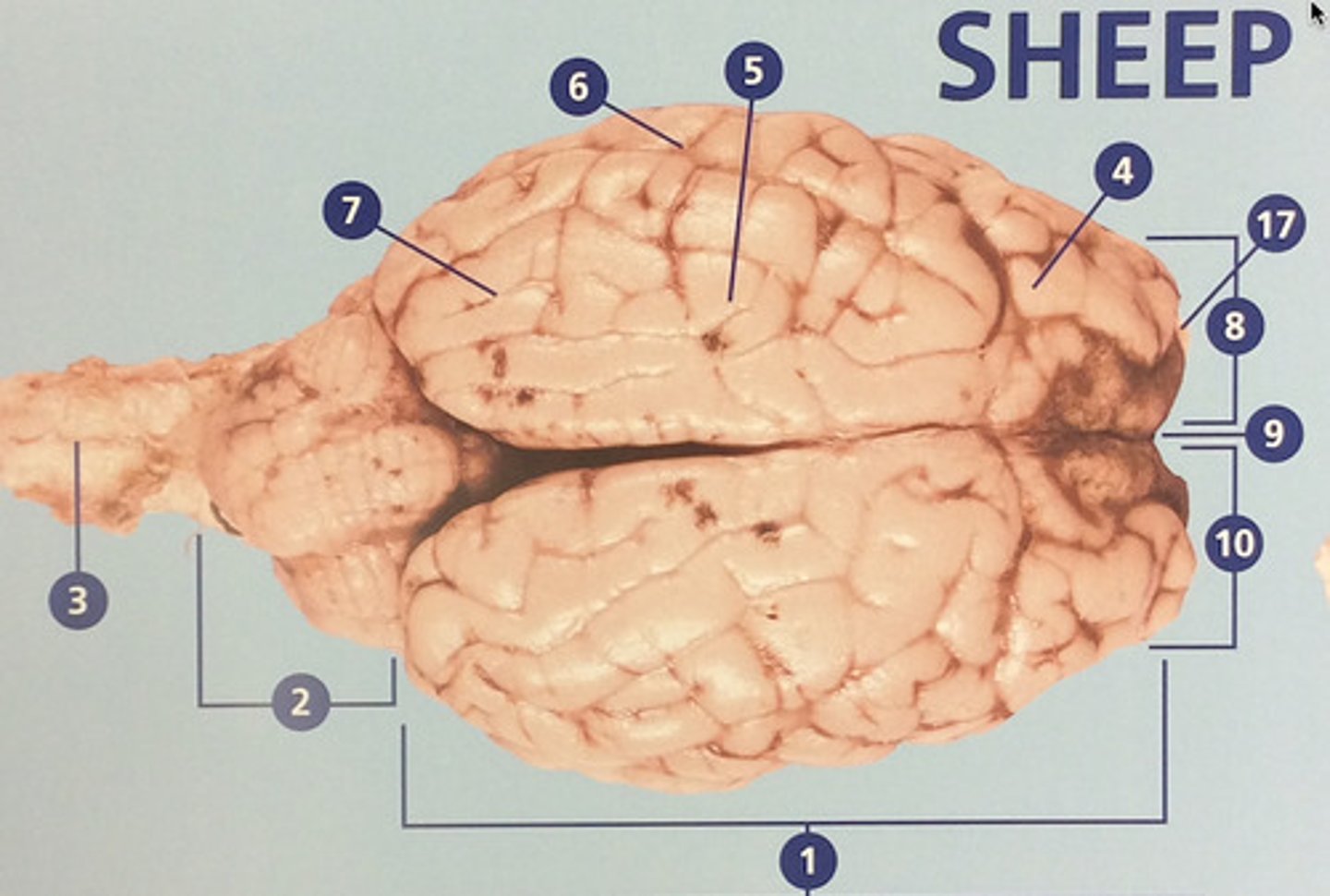
Right hemisphere
The right side of the cerebrum (#10)
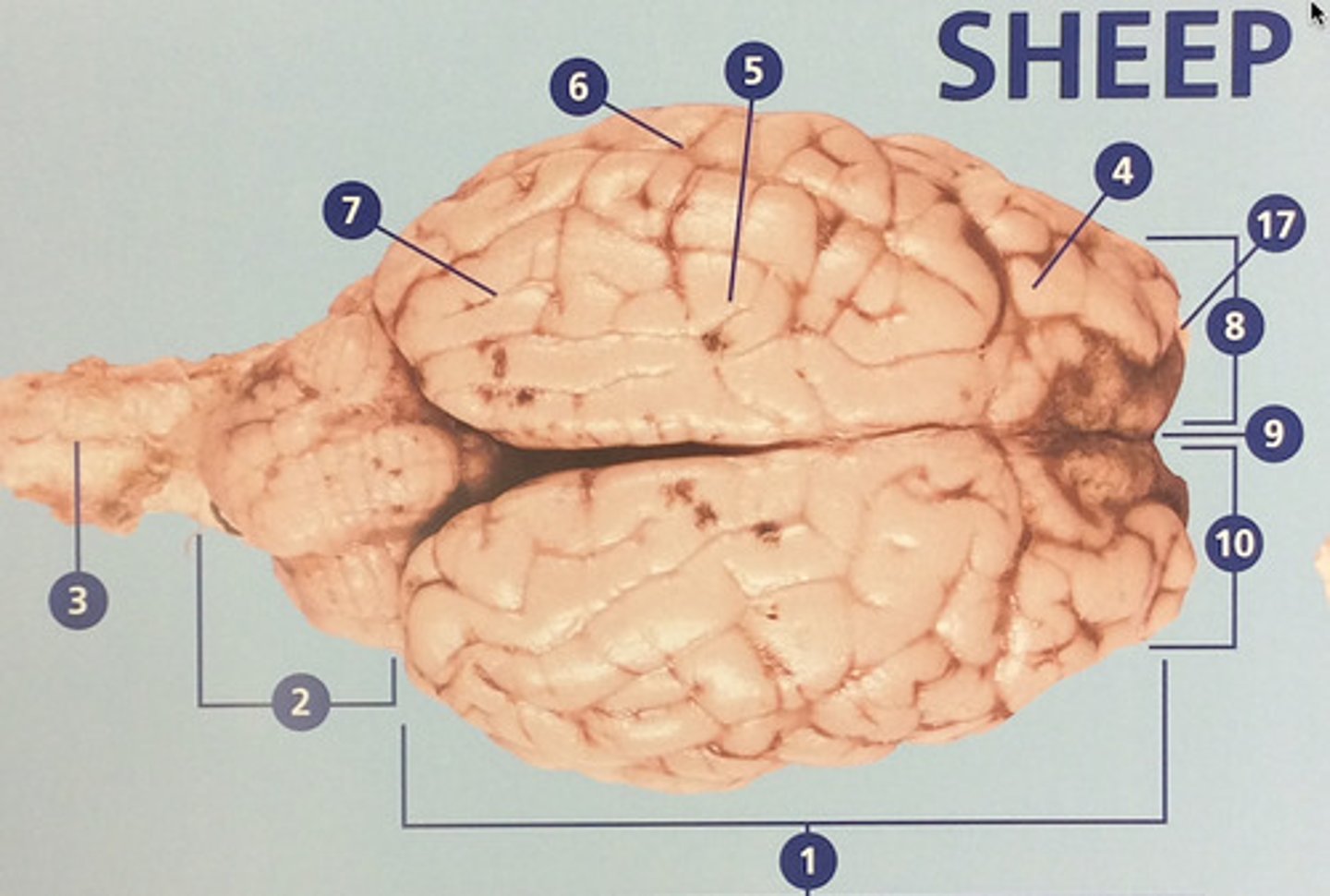
Brain stem
Route of information transfer between the forebrain and spinal cord; consists of the medulla, pons, and midbrain (#11)
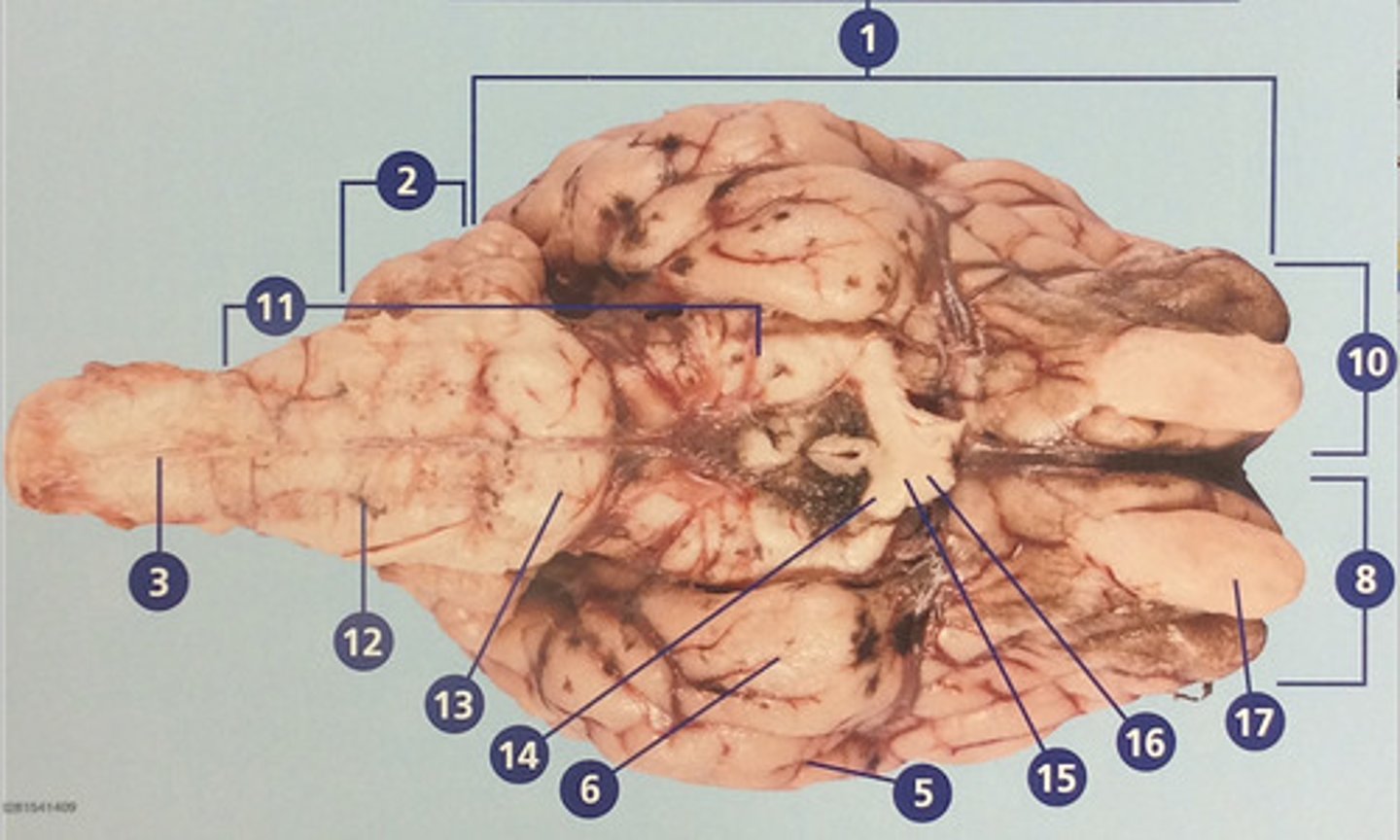
Medulla oblongata
Brain region that connects to the spinal cord; important in autonomic functions (#12)
Pons
Connection between forebrain, cerebellum, and medulla; important in regulation of sleep and breathing (#13)
Optic chiasm
Junction at which some fibers from easch optic nerve crisscross, enabling effective binocular vision (#15)
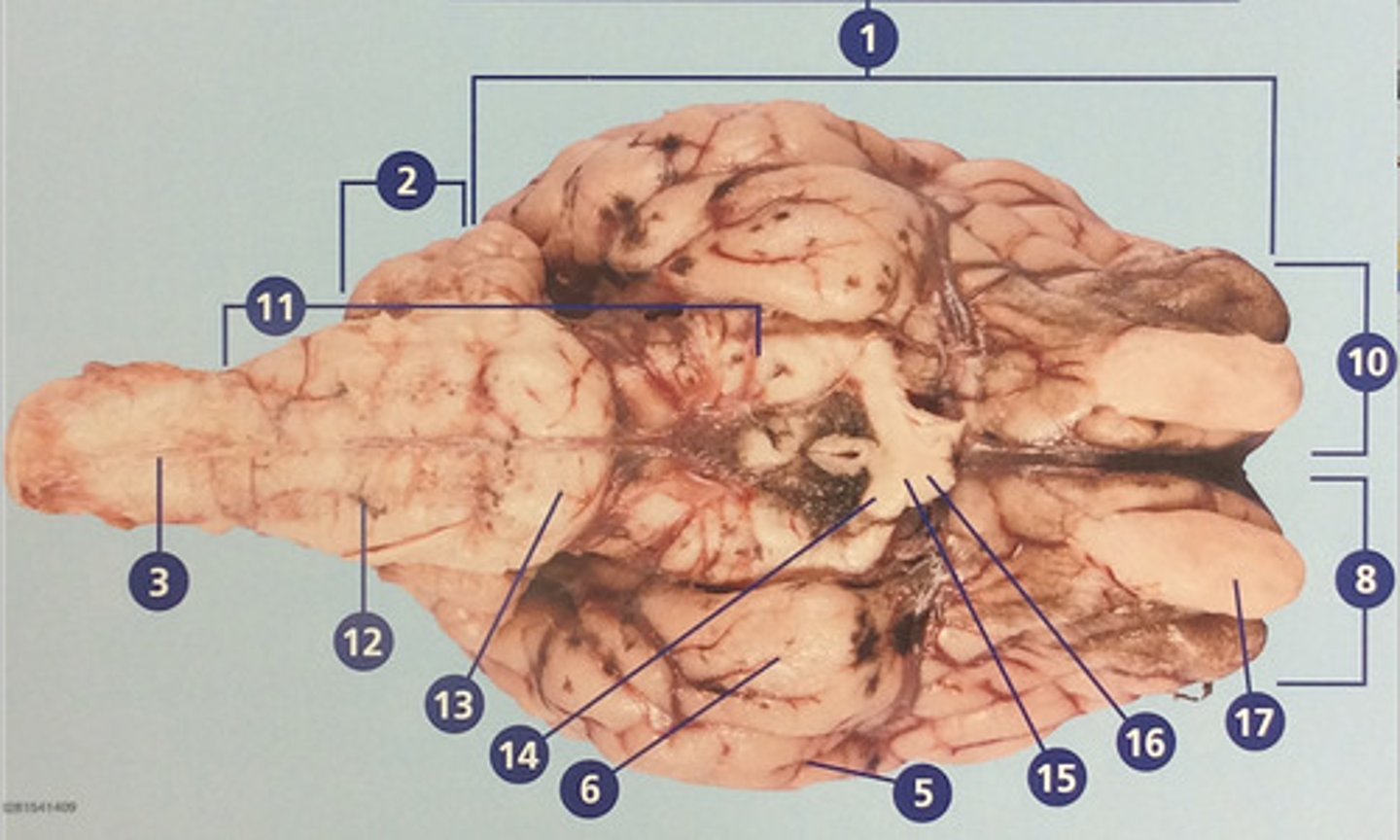
Optic nerve
Connects the retina to the optic chiasm (#16)
Olfactory bulb
Involved in detection and discrimination of odors (#17)
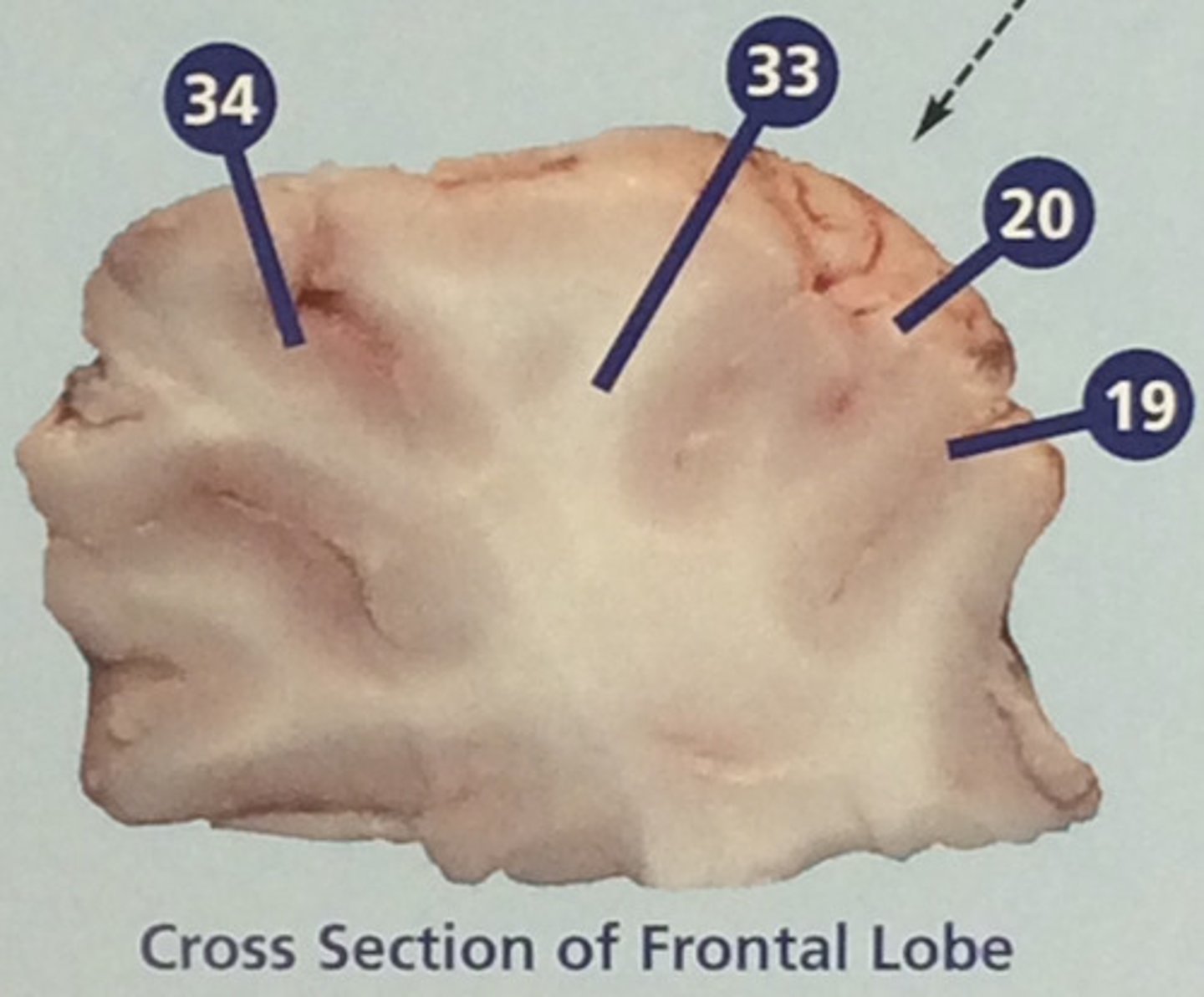
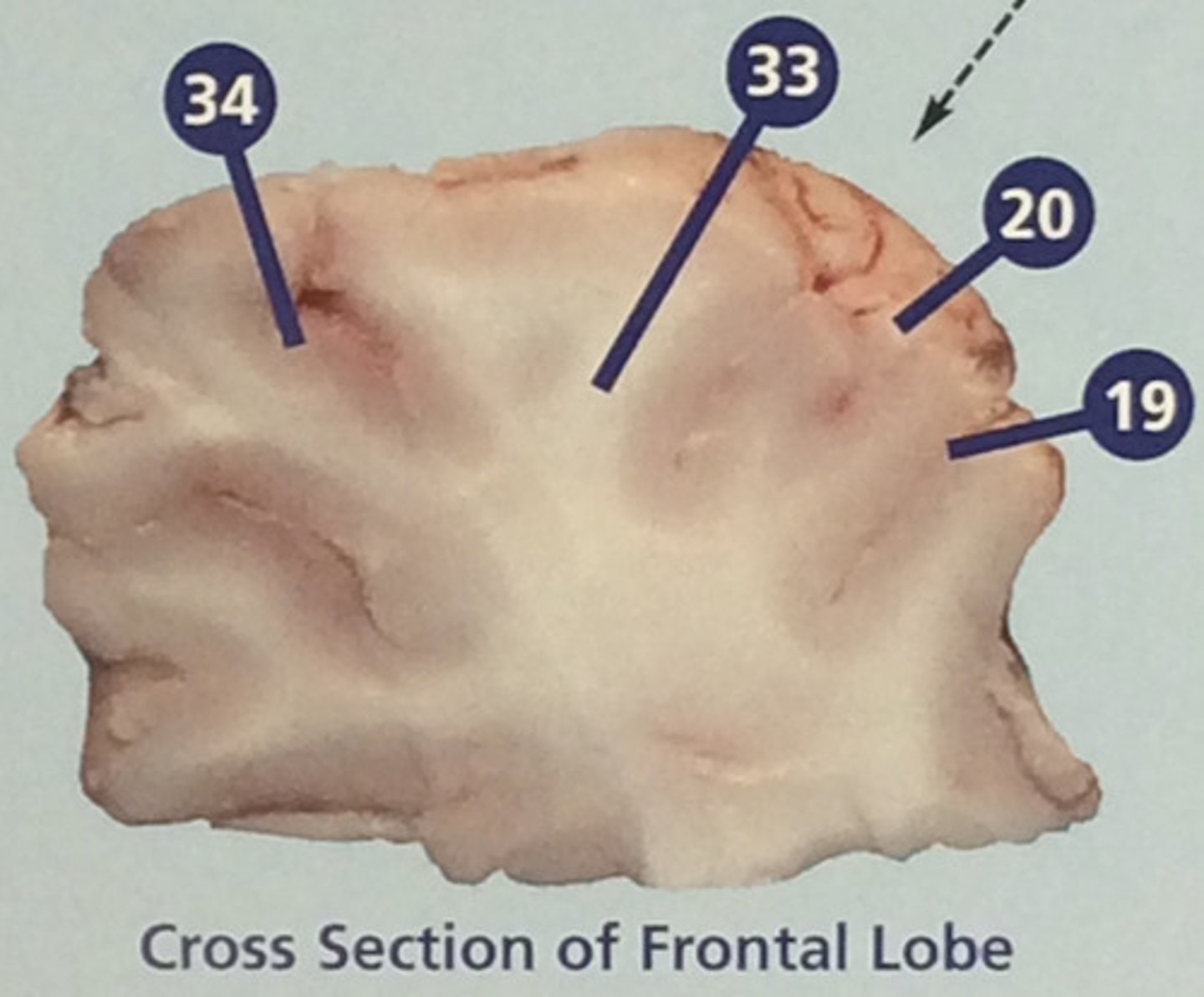
Sulci
Furrows in the folds of the cerebrum (#19)
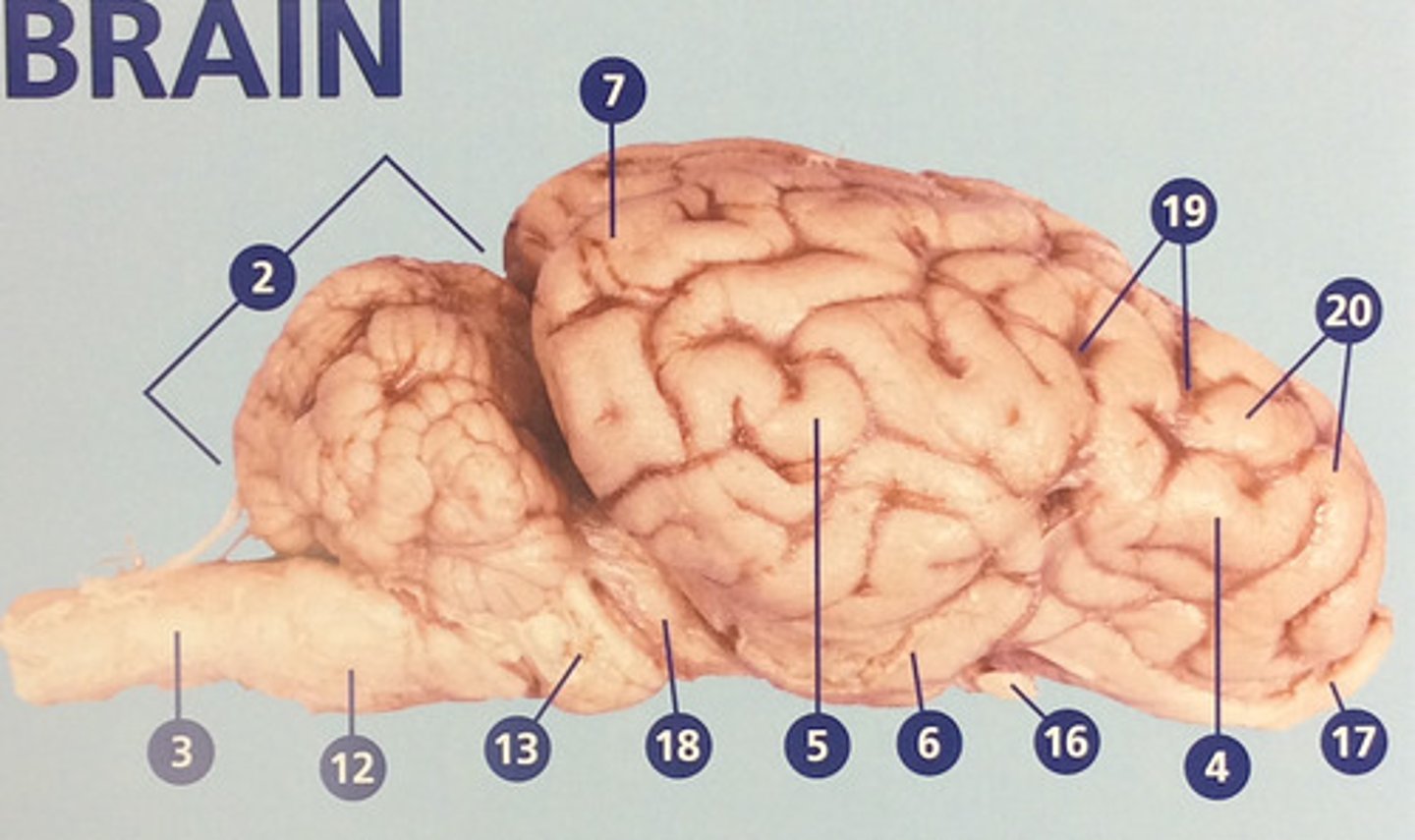
Gyri
Bulges in the folds of the cerebrum (#20)
Arbor vitae
Branching white matter in the cerebellum(#25)
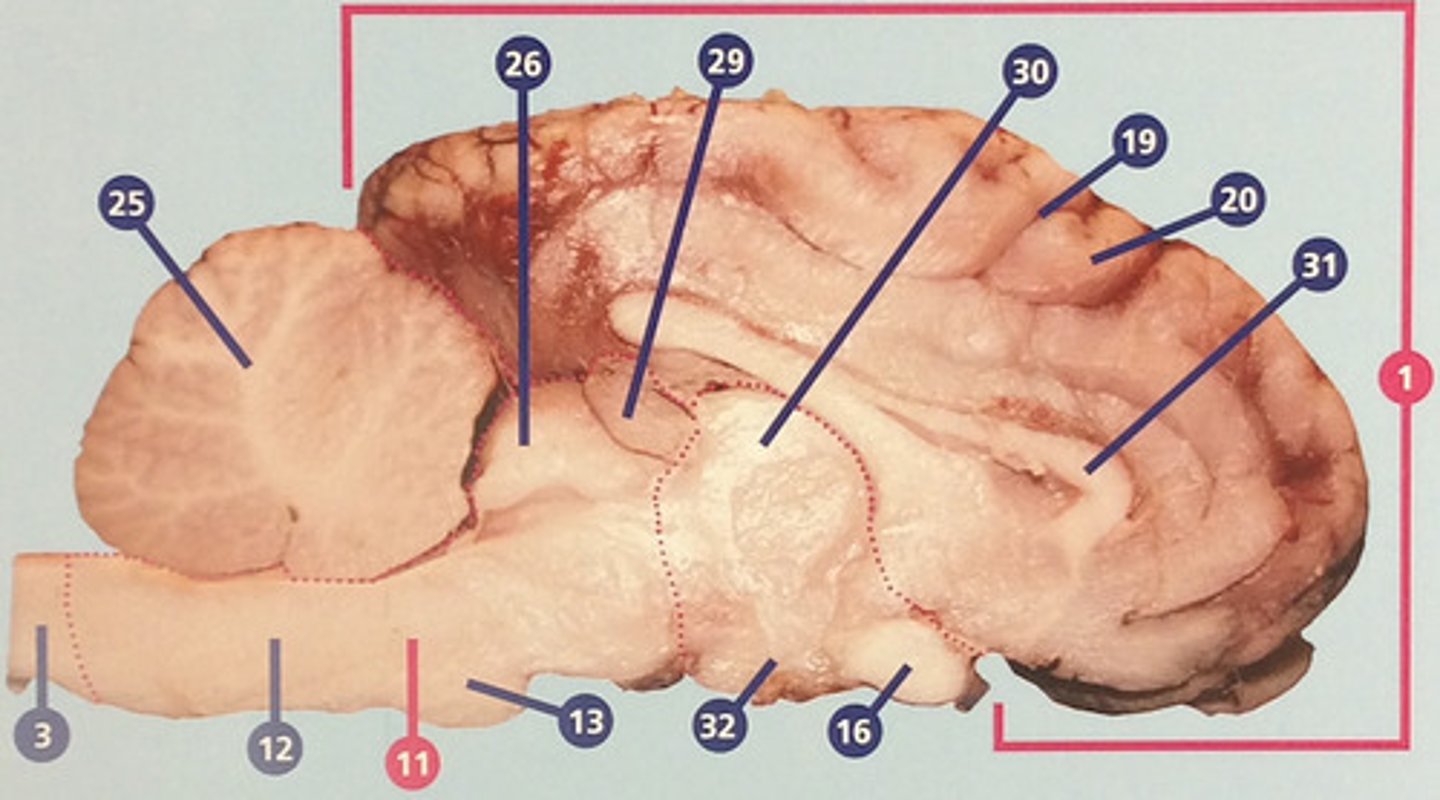
Pineal gland
Endocrine gland that secrets melatonin, which influences circadian rhythms and timing of sexual development (#29)
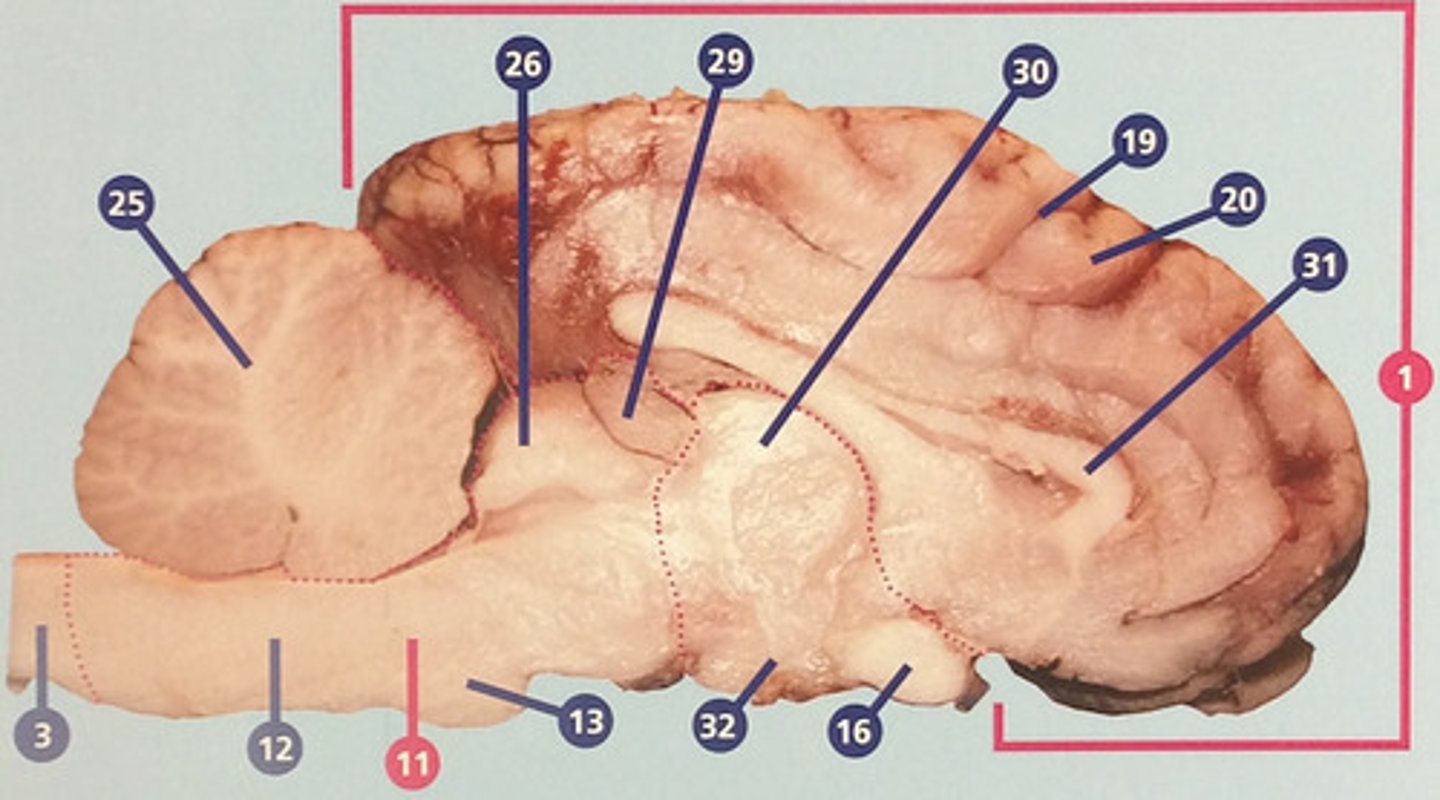
Thalamus
Region between midbrain and cerebral cortex; receives many types of sensory signals and relays them to the cerebral cortex (#30)
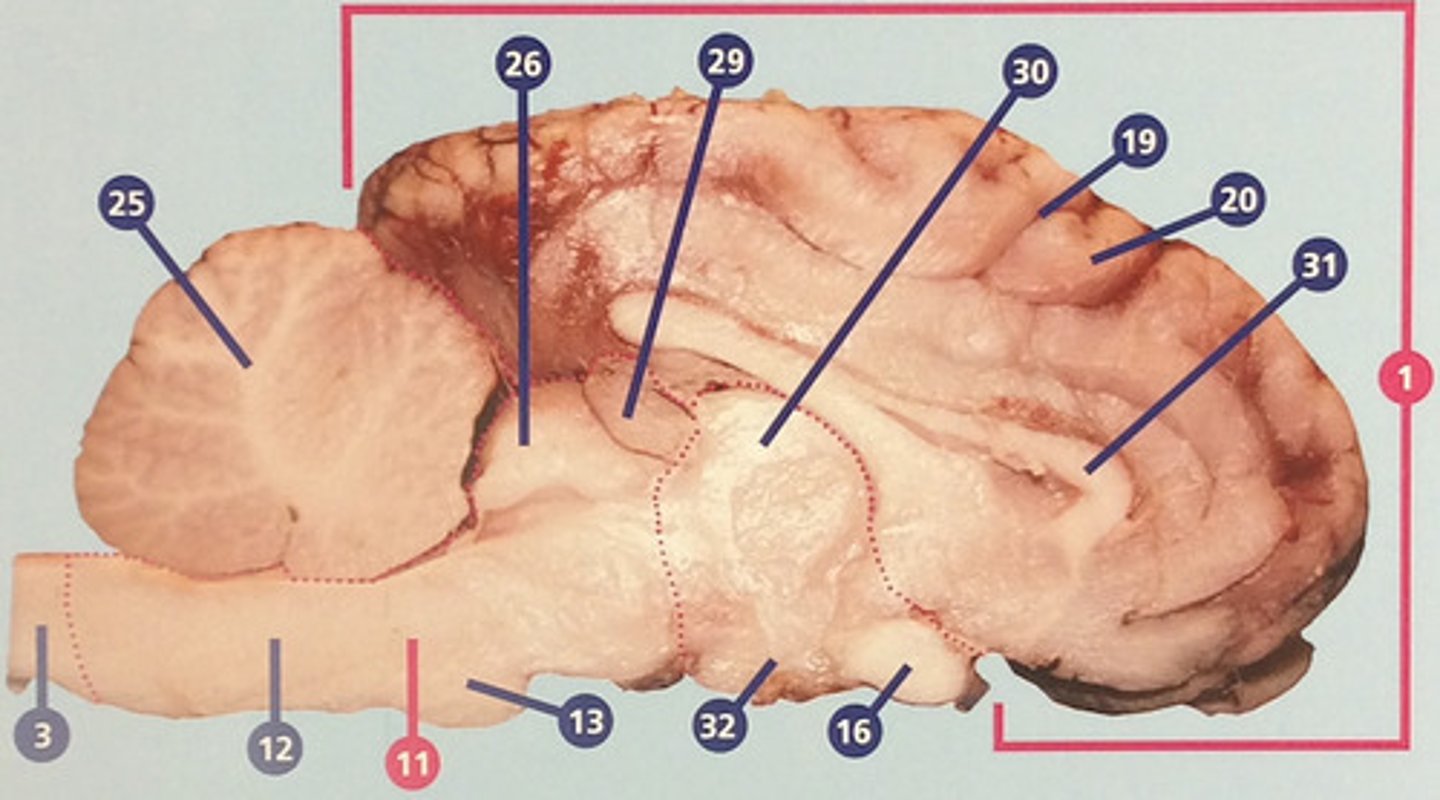
Corpus callosum
Bundle of nerve fibers connecting right and left cerebral hemispheres (#31)
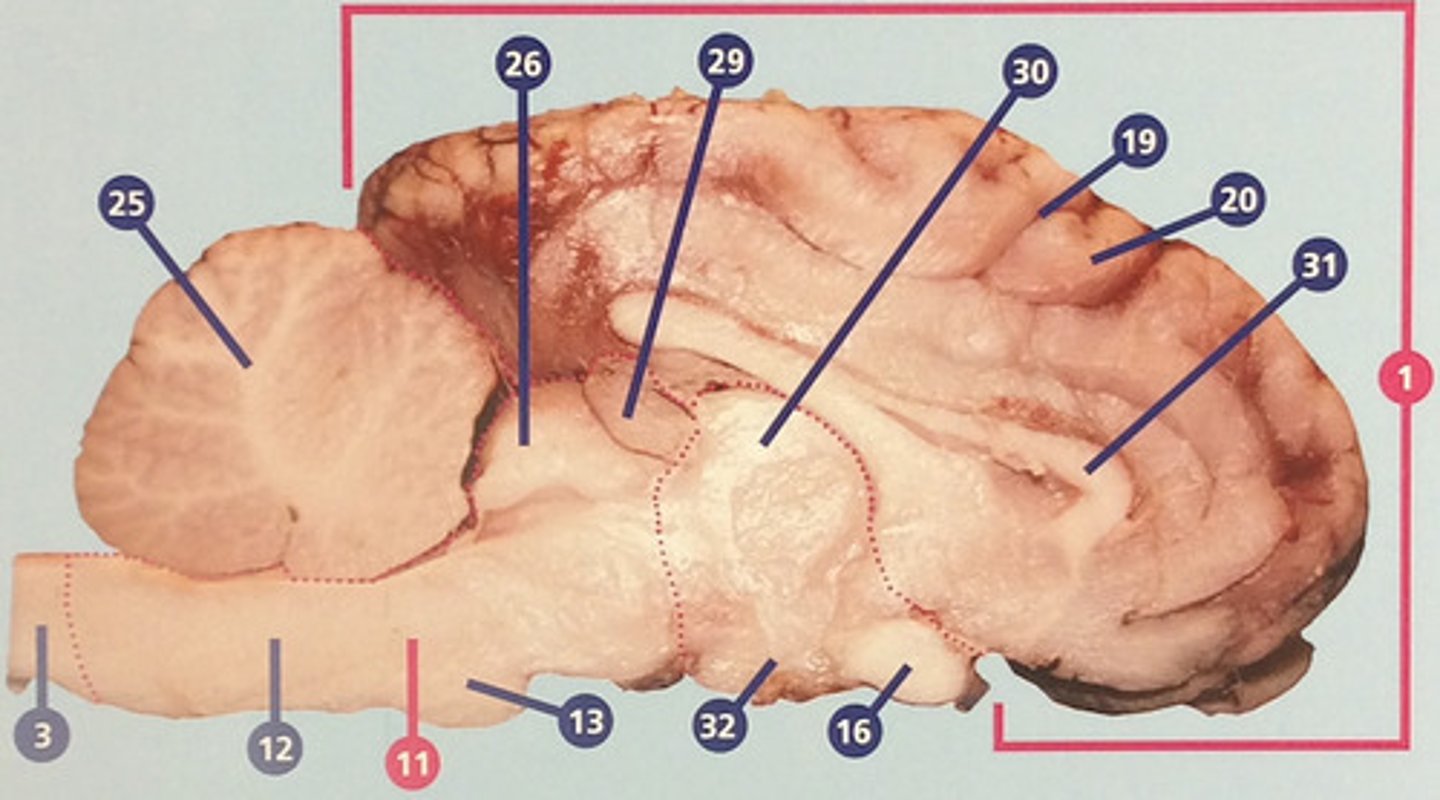
Hypothalamus
Brain structure with many functions including hormone secretion, temperature regulation, and hunger, mood, thirst, and fatigue (#32)
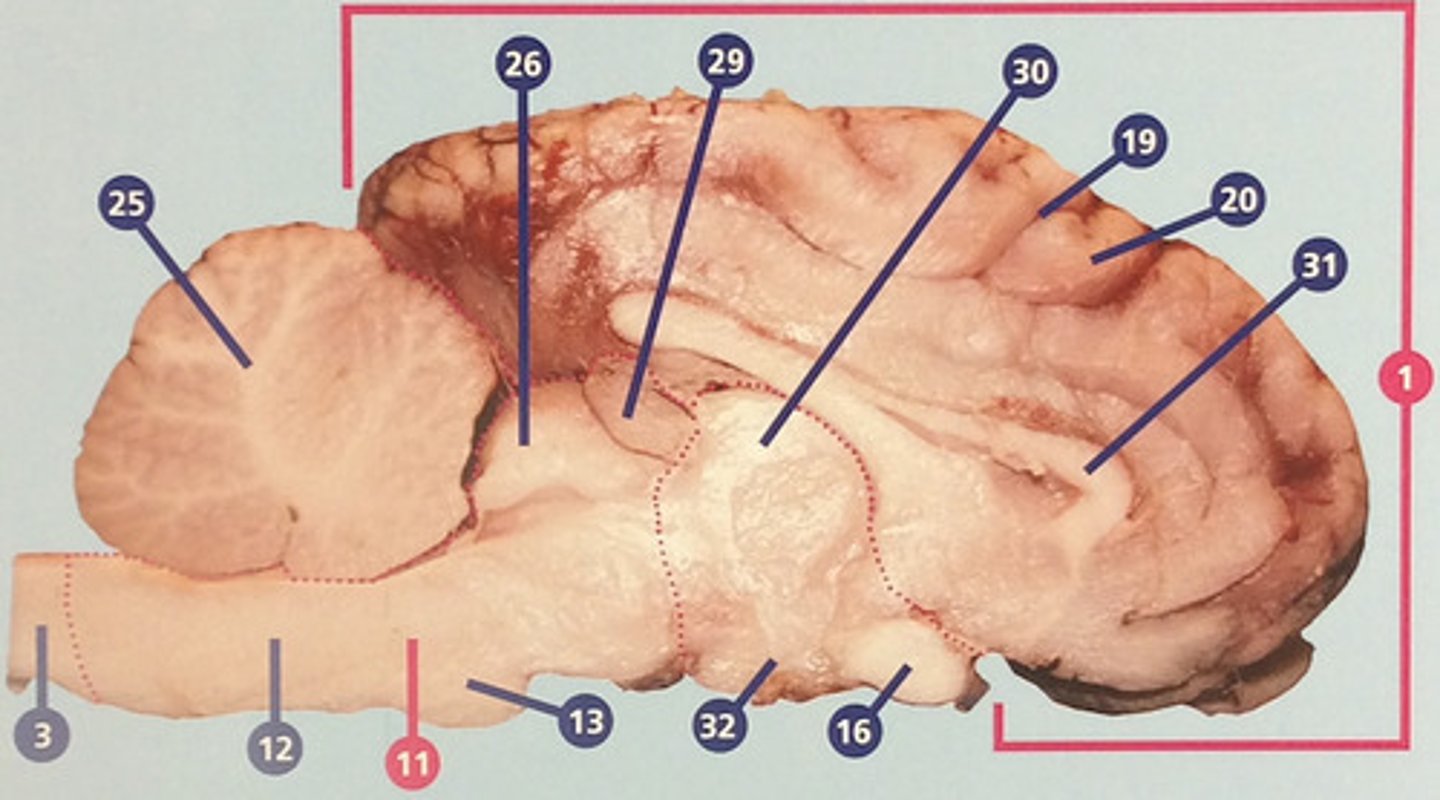
White matter
Portions of the central nervous system made up mainly of myelinated nerve fibers; in the cerebrum, usually surrounded by gray matter (#33)
Gray matter
Portions of the central nervous system made up mainly of nerve cell bodies (#34)
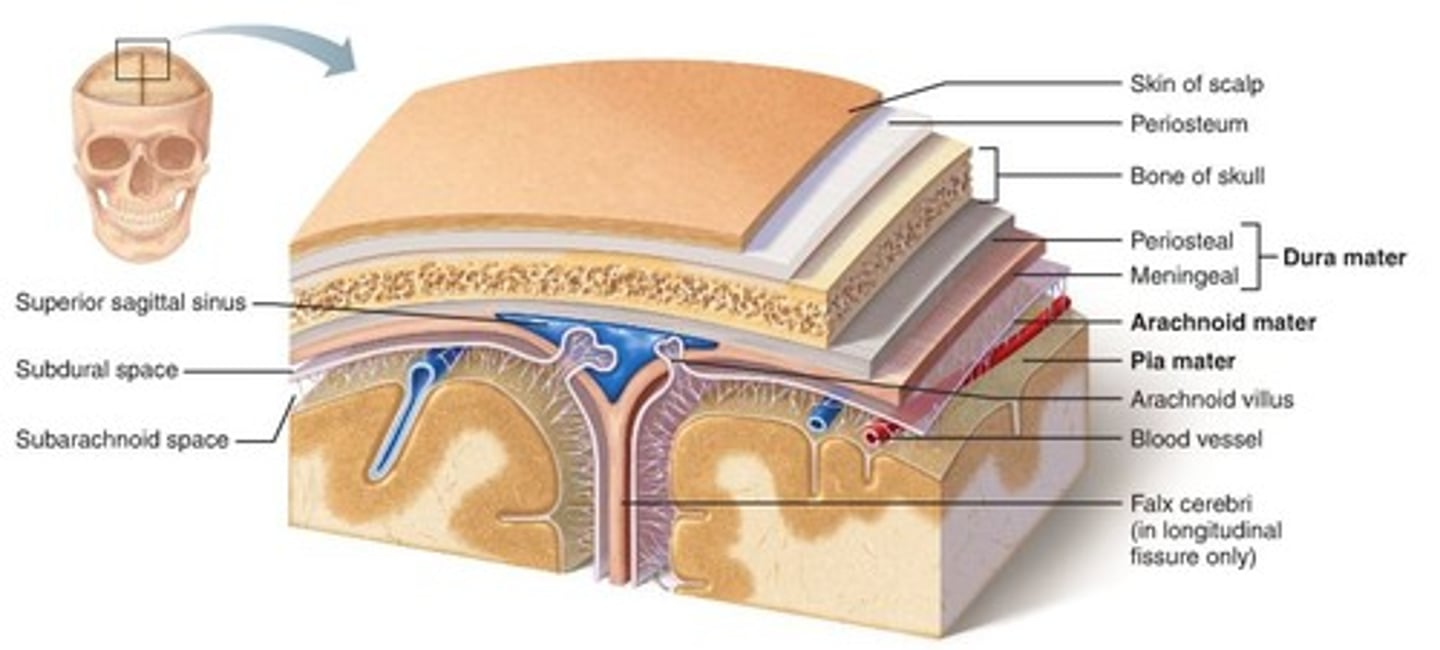
Meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater

lateral ventricle
one of the ventricles located inside the corpus callosum
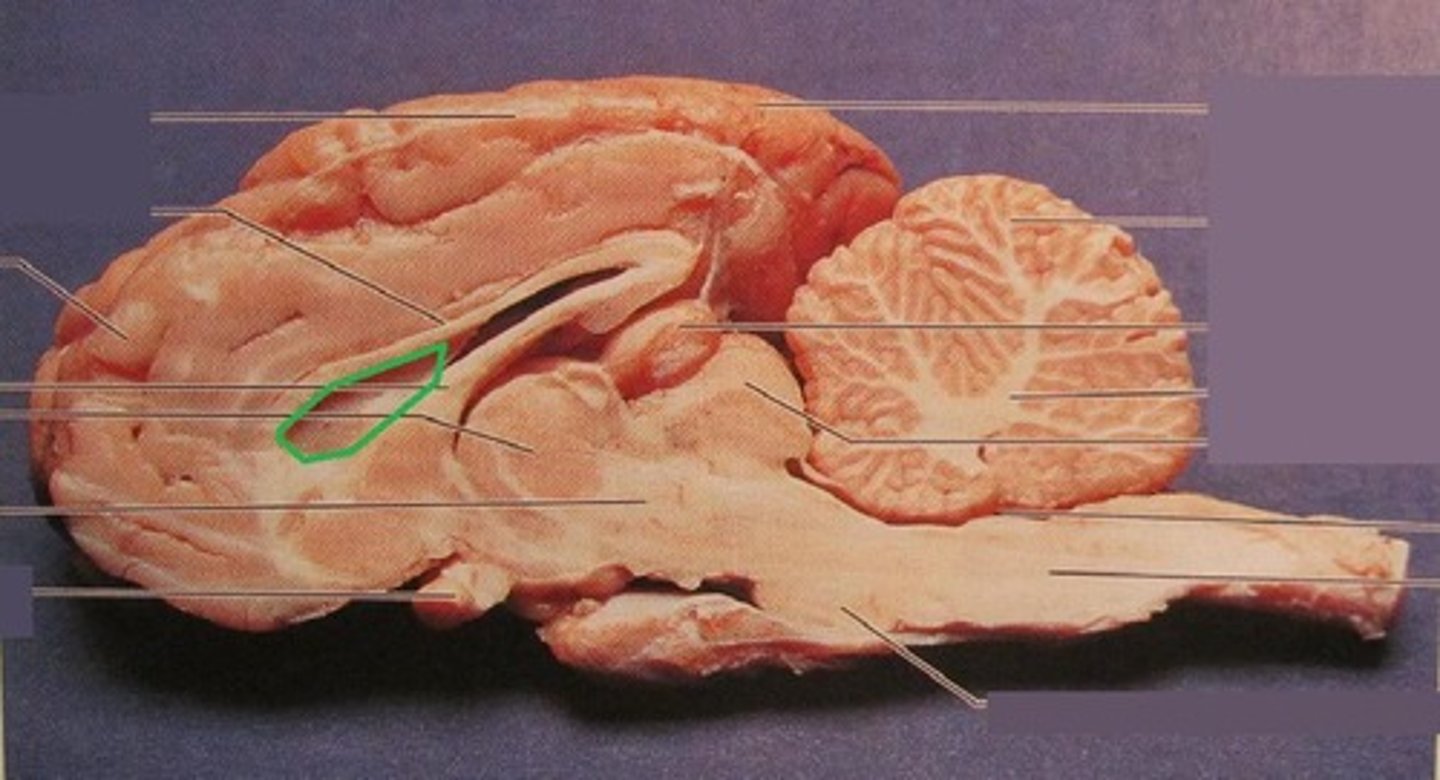
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
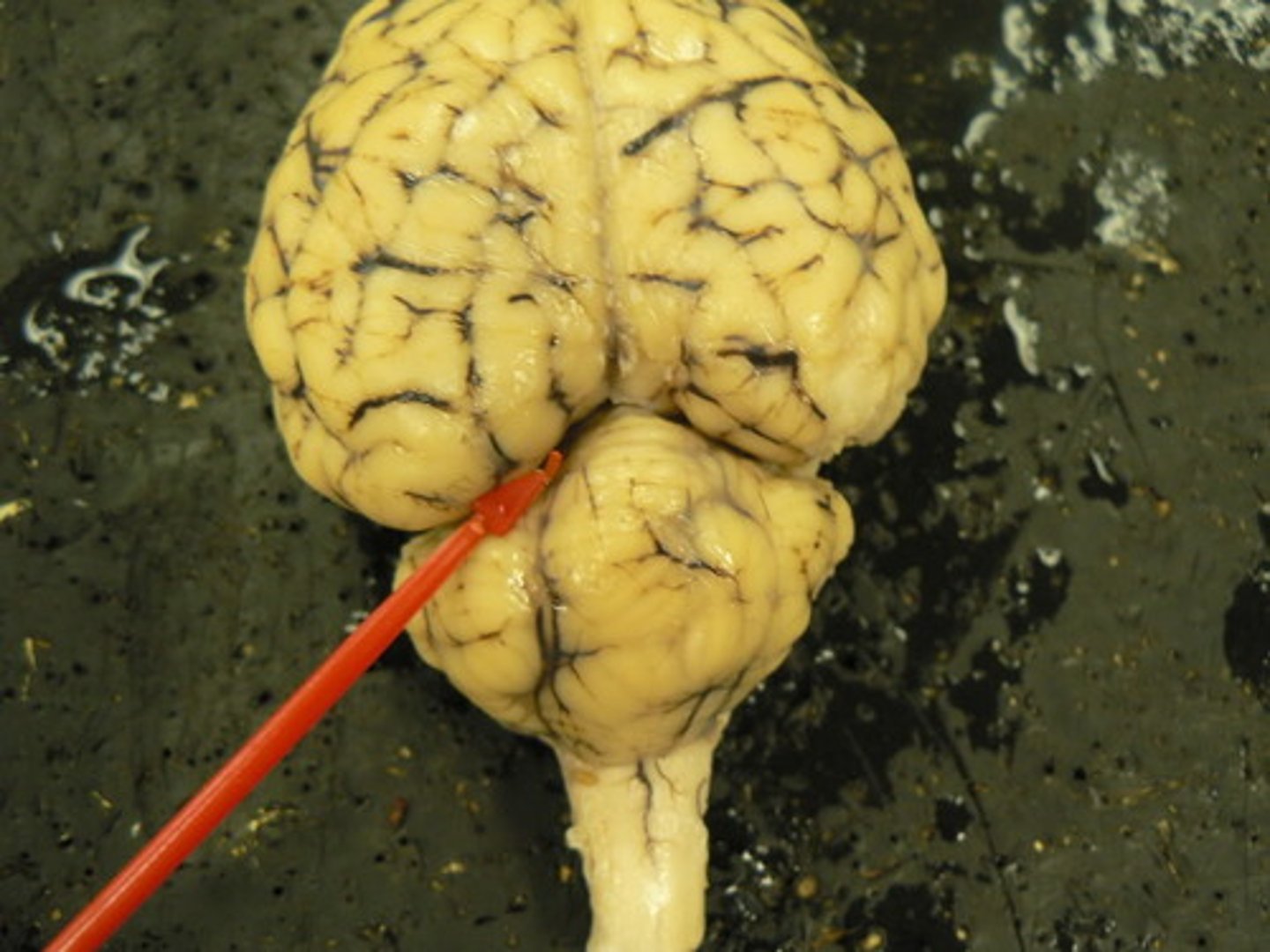
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
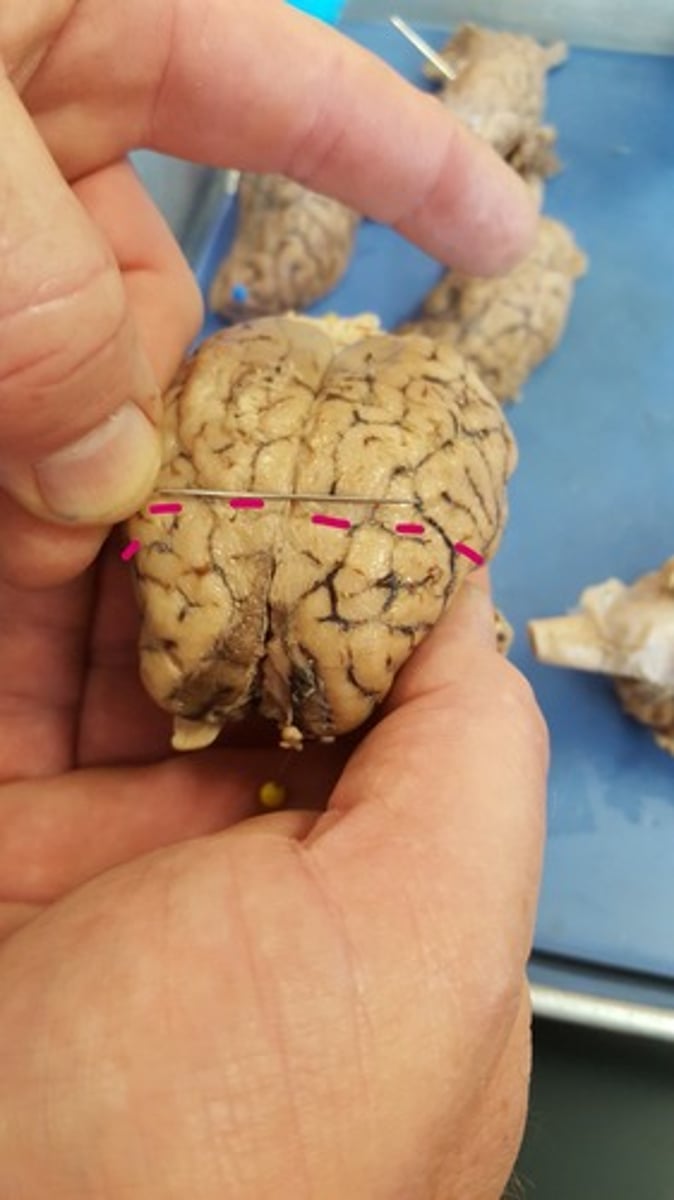
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
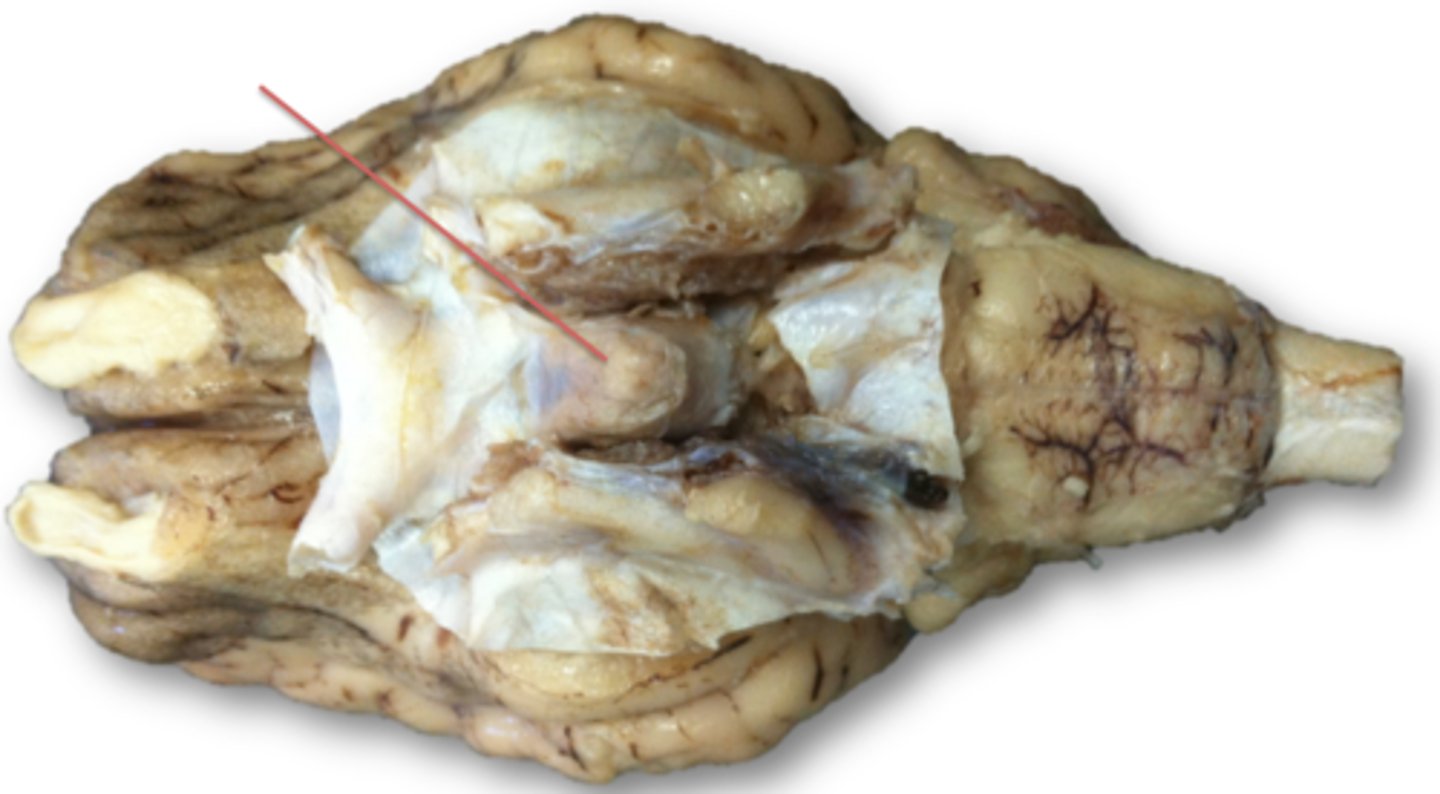
dura mater
outer covering of brain and spinal cord
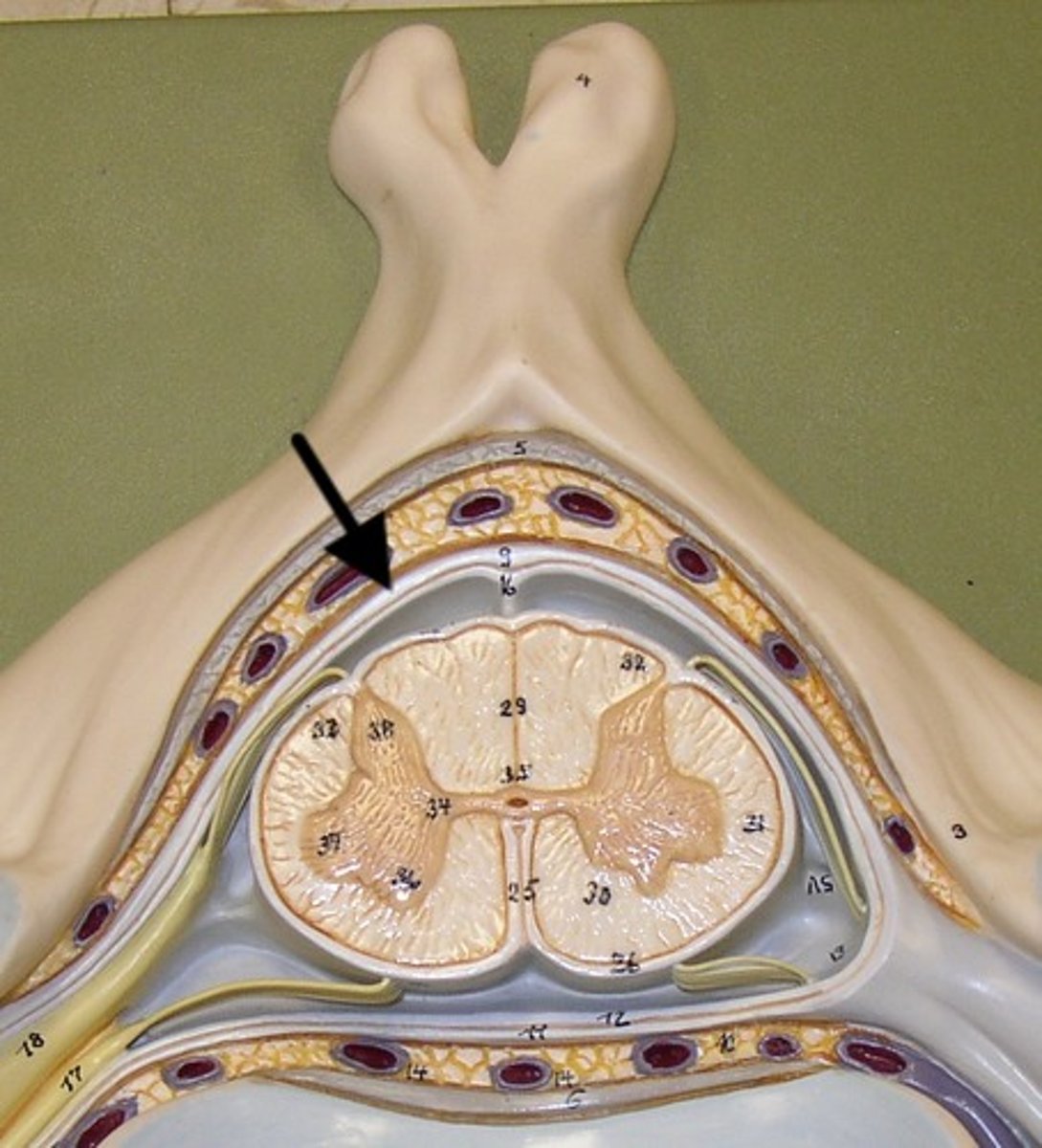
arachnid mater
nonvascular, cobweb-like with reticular and elastic fibers
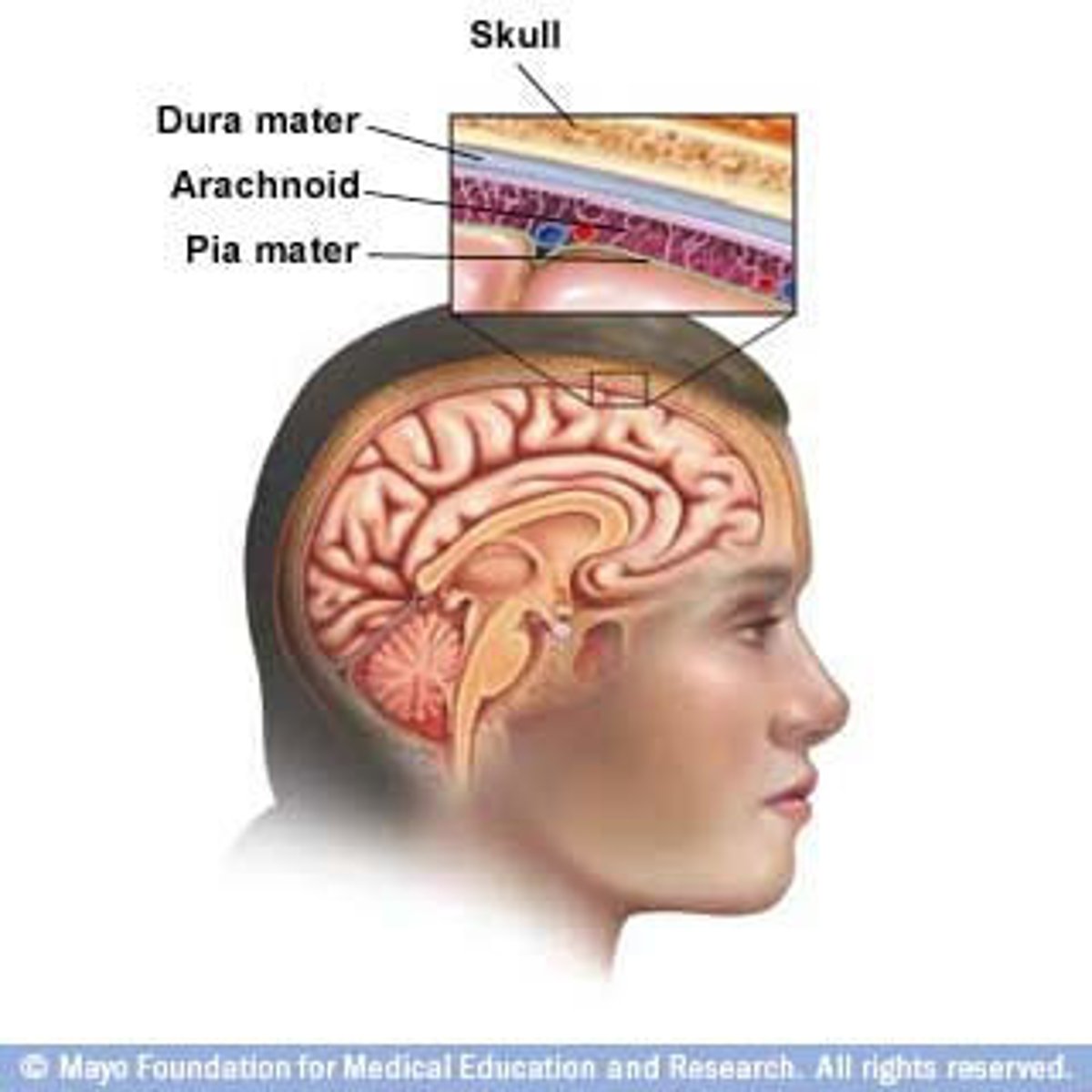
Pia mater
the delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord.