ANIML SCI 251, U2.3: Lambing & Neonatal Care
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
what are these signs of?
•bagging up
•hallowing out
•restless behavior
•stopped eating/less interested in hay
•separation from flock
•pawing at the ground
•knickering
•mucus discharged from vulva
•repeatedly lying down and standing back up
•bagging up
•hallowing out
•restless behavior
•stopped eating/less interested in hay
•separation from flock
•pawing at the ground
•knickering
•mucus discharged from vulva
•repeatedly lying down and standing back up
lambings
2
New cards
DEFINITION: when udder develops and becomes firm, approximately 4 weeks before lambing
bagging up
3
New cards
DEFINITION: when the lamb drops into a lower position to allow for delivery approx. 1-2 days before lambing, shows as a sunken loin area
hollowing out
4
New cards
DEFINITION: vocalization, calling out for lambs. done before and after they’re born
knickering
5
New cards
a waterbag indicates that a lamb is coming in approximately ______ minutes
30 minutes
6
New cards
a waterbag should be the color of ______, a darker color/bloody discharge indicates illness
tea
7
New cards
it it normal for a waterbag to rupture? (yes/no)
yes
8
New cards
during a NORMAL birth, 30 minutes after the waterbag you should see:
pair of hooves, head, shoulders, and rest of lamb
9
New cards
what is the ideal position for lambing?
superman
10
New cards
ideally, do lamb’s toes point upwards or downwards?
upwards
11
New cards
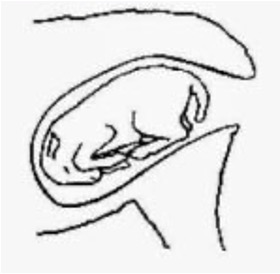
describe this presentation:
breech
12
New cards
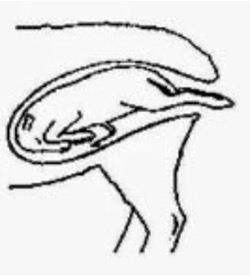
describe this presentation:
backwards
13
New cards
DEFINITION: difficult birth
dystocia
14
New cards
these are examples of what:
•ewe is straining for over half an hour and there’s no sign of a waterbag
•waterbag, but no signs of labor
•active labor for 30+ minutes after waterbag and no sign of a lamb
•no straining, but the ewe appears distressed
•ewe is straining for over half an hour and there’s no sign of a waterbag
•waterbag, but no signs of labor
•active labor for 30+ minutes after waterbag and no sign of a lamb
•no straining, but the ewe appears distressed
dystocias
15
New cards
if progress has stopped, after ______ minutes have passed from contractions, passing waterbags, or appearance of lamb, then call a TA
30 minutes
16
New cards
if the ewe is stressed and running around what should you do?
halter her
17
New cards
list the 4 things needed to assist w/ a dystocia
gloves, OB lube, dystocia bucket, and PPE
18
New cards
DEFINITION: a bucket with plastic bag to line it with warm water and betadine/iodine scrub
dystocia bucket
19
New cards
what is the most important factor to check to see after the lamb is born?
breathing
20
New cards
what do we use to remove fluid from newborn lamb’s nostrils and mouth?
aspirator bulb
21
New cards
list the steps for processing the umbilical cord
clip, dip, strip
22
New cards
what is a lamb’s umbilical cord dipped in?
iodine
23
New cards
where does the lamb receive nutrients from while in utero?
placenta
24
New cards
after lambing, the placenta should be delivered after ______ to ______ hours
2-3 hours
25
New cards
DISEASE:
•cause: placental tags left in the uterus
•clinical signs: fever, stops eating, stops producing milk, bad odor, dark discharge
•treatment: oxytocin at the discretion of a vet
•prevention: minimize stressful events before and during lambing, provide proper supplements
•cause: placental tags left in the uterus
•clinical signs: fever, stops eating, stops producing milk, bad odor, dark discharge
•treatment: oxytocin at the discretion of a vet
•prevention: minimize stressful events before and during lambing, provide proper supplements
retained placenta
26
New cards
DISEASE:
•cause: too cold
•clinical signs: temp below 99 F, hunched posture, hallowed out sides, dehydration,
•treatment: lamb must be warmed (heat lamps, water watter bottles), don’t feed until warmed
•cause: too cold
•clinical signs: temp below 99 F, hunched posture, hallowed out sides, dehydration,
•treatment: lamb must be warmed (heat lamps, water watter bottles), don’t feed until warmed
hypothermia
27
New cards
DISEASE:
•cause: lamb having a difficult time nursing (not standing, mom rejecting lambs) or not enough milk made for all lambs
•clinical signs: cold belly, lethargic
•treatment: tube feed or bottle feed
•cause: lamb having a difficult time nursing (not standing, mom rejecting lambs) or not enough milk made for all lambs
•clinical signs: cold belly, lethargic
•treatment: tube feed or bottle feed
starvation
28
New cards
list the 2 major causes of death in lambs
hypothermia and starvation
29
New cards
DISEASE:
•cause: deficiency of selenium and vitamin E
•clinical signs: abortions, stillborns, miscarriages, retained placenta, and delivering weaker lambs. mild stiffness, pain while walking, hunch posture. cardiac symptoms similar to pneumonia, frothy nasal discharge
•treatment: skeleton symptoms treatable, cardiac symptoms permanent
•prevention: BoSe injection 1-2 days after they’re born
•cause: deficiency of selenium and vitamin E
•clinical signs: abortions, stillborns, miscarriages, retained placenta, and delivering weaker lambs. mild stiffness, pain while walking, hunch posture. cardiac symptoms similar to pneumonia, frothy nasal discharge
•treatment: skeleton symptoms treatable, cardiac symptoms permanent
•prevention: BoSe injection 1-2 days after they’re born
white muscle disease
30
New cards
DISEASE:
•def: low calcium in blood
•cause: lambs fully rely on ewe to provide sufficient calcium, if she isn’t able to provide
•clinical signs: stiff gait, ataxia, salivation, beginning of bloat, and death (if untreated)
•treatment: Ca injection
•def: low calcium in blood
•cause: lambs fully rely on ewe to provide sufficient calcium, if she isn’t able to provide
•clinical signs: stiff gait, ataxia, salivation, beginning of bloat, and death (if untreated)
•treatment: Ca injection
hypocalcemia
31
New cards
DISEASE:
•def: D+
•cause: nutrition deficiencies, infectious agent (bacteria, virus, parasites) like e.coli, crypto, salmonella, and flystrike
•clinical signs D+
•treatment: take temperature, administer anti-D+, electrolytes, and dewormers/antiparasites. Don’t allow to run its course, lamb can become dehydrated
•def: D+
•cause: nutrition deficiencies, infectious agent (bacteria, virus, parasites) like e.coli, crypto, salmonella, and flystrike
•clinical signs D+
•treatment: take temperature, administer anti-D+, electrolytes, and dewormers/antiparasites. Don’t allow to run its course, lamb can become dehydrated
scours
32
New cards
what is the most common and expensive disease that affects newborn ruminants?
scours
33
New cards
DISEASE:
•cause: bacterial infection of multiple joints, entering through castration sites, dirty bedding, or dirty lamb processing tools
•clinical signs: swollen legs, nursing less, infected navel, infected spine, which leads to paralysis of legs
•treatment: antibiotics, if no response, euthanasia
•prevention: clean bedding, ensure proper colostrum, and treat navel w/ iodine
•cause: bacterial infection of multiple joints, entering through castration sites, dirty bedding, or dirty lamb processing tools
•clinical signs: swollen legs, nursing less, infected navel, infected spine, which leads to paralysis of legs
•treatment: antibiotics, if no response, euthanasia
•prevention: clean bedding, ensure proper colostrum, and treat navel w/ iodine
joint/navel ill
34
New cards
list the 3 steps of lamb processing
ear tagging, tail docking, and BoSe injection
35
New cards
what would the first ewe lamb of 2023’s ear tag be?
351
36
New cards
what would the first ram lamb of 2023’s ear tag be
301
37
New cards
ewe lambs are assigned numbers ______ to ______
51-99
38
New cards
ram lambs are assigned numbers ______ to ______
1-49
39
New cards
LAMB PROCESSING:
•pro: decreases risk of fly strike
•con: vaginal/rectal prolapse if tail is docked too short
•pro: decreases risk of fly strike
•con: vaginal/rectal prolapse if tail is docked too short
tail docking
40
New cards
dock the tail after the ______ palpable joint
3rd
41
New cards
what are these signs of?
•ewe spinning around
•kicking at lamb
•ewe spinning around
•kicking at lamb
rejection
42
New cards
these are reasons we may ______:
•mother dies
•ewe has too many lambs
•rejection
•health issues
•poor milk supply
•mother dies
•ewe has too many lambs
•rejection
•health issues
•poor milk supply
foster