Teaching Volume (Capacity II)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Capacity vs volume
Capacity is how much something holds (if filled to the top). The units for capacity are usually L or ml.
Volume can be used to
· refer to capacity i.e. the amount of liquid a container actually holds (usually L and ml)
· refer to the amount of space taken up by a solid object e.g. cube. In this case the unit for volume is centimetre cubes (cm3).
Understanding volume
· Finding volume is similar to finding area in that children must employ the process of constructing composite units (typically cubes), but it is more challenging than area because they are working in three dimensions, and two-dimensional pictures do not show the interior of a solid.
· Visualization skills are invaluable in helping children understand volume. Children must be developmentally ready to visualize the interior of a three-dimensional figure, or think of it in layers, in order to understand volume.
Activity: Understand Volume using sugar cubes
Have child build rectangular prisms with sugar cubes, all the while learning that calculating volume can be as easy as playing with blocks
Activity: Understand Volume using interlocking cubes
To understand why volume is measured in cubic units, students first develop strategies for determining the number of cubes in 3-D arrays.
Volume: Number of cubes in 3-D arrays
Can you see a way to calculate the volume of a cuboid i.e. the number of squares?
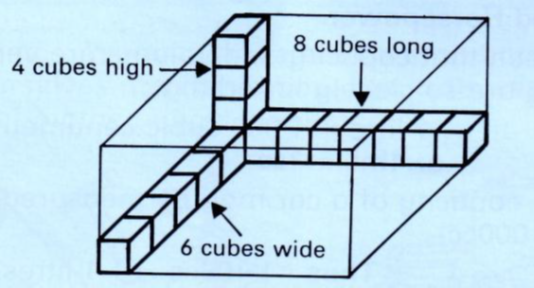
Below, we see a box in the shape of a cuboid showing how it can be filled with cubes.
8 cubes fit along the length
6 cubes fit along the width
4 cubes fit along the height.
We can see that the box contains (8 x 6) cubes in the bottom layer
There are 4 layers altogether.
The total number of cubes required to fill the box is: 8 x 6 x 4 cubes.
In your own time, view the video ‘How many peas fill the classroom?’ available at https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/teaching-volume
Difficulties with volume
• Children in the middle grades have difficulty understanding volume.
• When given a three dimensional solid such as the large cube shown, which is made up of smaller cubes, many children will count the faces of the smaller cube.
• Only 20% of third graders could find the volume of a solid like this, but in fifth grade over half were able to think about the cube in layers and determine the volume as 27 small cubes (Batista & Clements, 1998).
Explorations: relationship between capacity and volume
Investigation 1: Proving 1000ml = 1000 cm cubes (cubic centimetres)
Explore with Dienes
• 1 unit cube (from a set of Base Ten Blocks) is equal to 1 cubic centimeter
• 10 cubic centimeters (represented with a long)
• 100 cubic centimeters (represented with a flat)
• 1,000 cubic centimeters by stacking ten flats on top of each other

The students are able to see how these ten stacked flats fit perfectly into the clear 1,000 mililiter box i.e. 1000cm3 = 1000mL.
Investigation 2: Confirming 1 litre= 1000ml = 1000 cm cubes (cubic centimetres)
Fill the measuring jug to the 1 Litre line. Before pouring the litre of water into the 1,000 ml cube
· Ask children to predict if the water will come up short, overflow or fill the cube perfectly.
· 1 litre of water fills the clear cube to the brim!
· 1 Litre = 1,000mL = 1,000cm3!
Investigation 3: Using the relationship between volume and capacity to find the volume of a solid object (using displacement)
A stone of unknown volume is dropped into the container.
Examine how much the water rose by.
What does this suggest about the volume of the stone?
• 80ml?
• 80cm³

Watch:
Relationship between capacity and volume
Note: 1L= 1000cm3 ( i.e. 1000ml= 1000cm3; 1ml= 1cm3; 400ml= 400cm3)
Recommended Trajectory
1. Introduce the litre as a measurement of volume (before using cubic centimetres and cubic metres)
2. Develop an understanding of the size of a litre and 10 millilitres. (1 millilitre is too small to be appreciated);
3. Estimate and measure using litres and millilitres;
4. Develop an understanding of the size of a cubic metre and a cubic centimetre;
5. Estimate and measure using cubic metres and cubic centimetres.
CAPACITY STATIONS (modify for the class you teach!)
Theme: We are having a birthday party!
Station 1: Volume of different drinking glasses, which will be best to use?
Station 2: Have you enough dips?
Station 3: How much juice do you need to buy?


