1.2 Cell Structure
1/30
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does an animal cell that a plant cell does not?
Centrioles
What does a plant cell that an animal cell does not?
Chloroplast
Cellulose cell wall
Permanent vacuole
Animal and plant cells diagrams
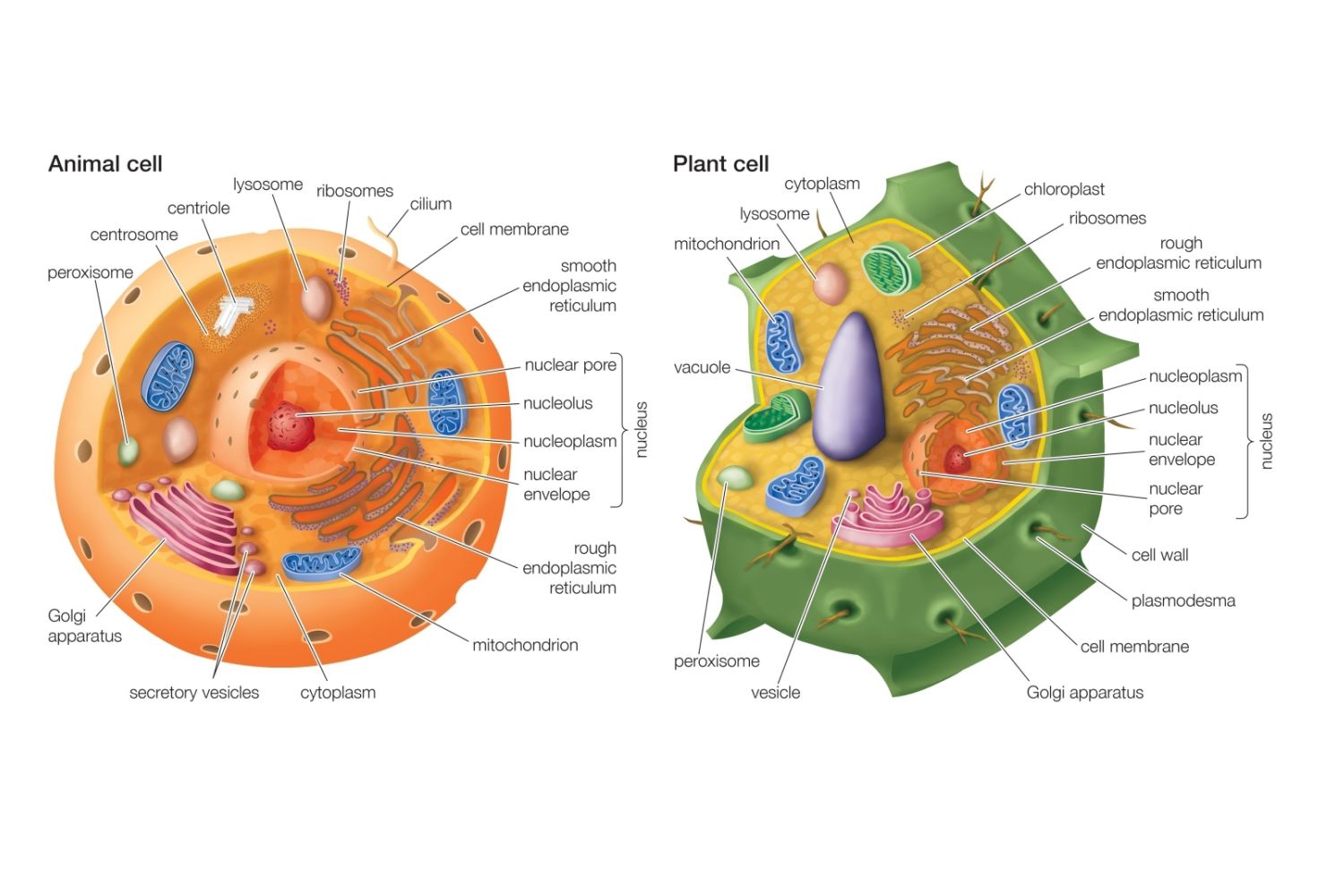
Nucleus
contains genetic material
controls all activity of cell
Chromatin - nucleus
dispersed genetic material
Nucleolus - nucleus
makes rRNA
Nuclear pores - nucleus
allows material to move in and out
Nuclear membrane - nucleus
double layered and continuous with endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
network of membranes forming interconnected sacs called cisternae
originates from outer membrane of nucleus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes attached
protein synthesis occurs
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesises lipids
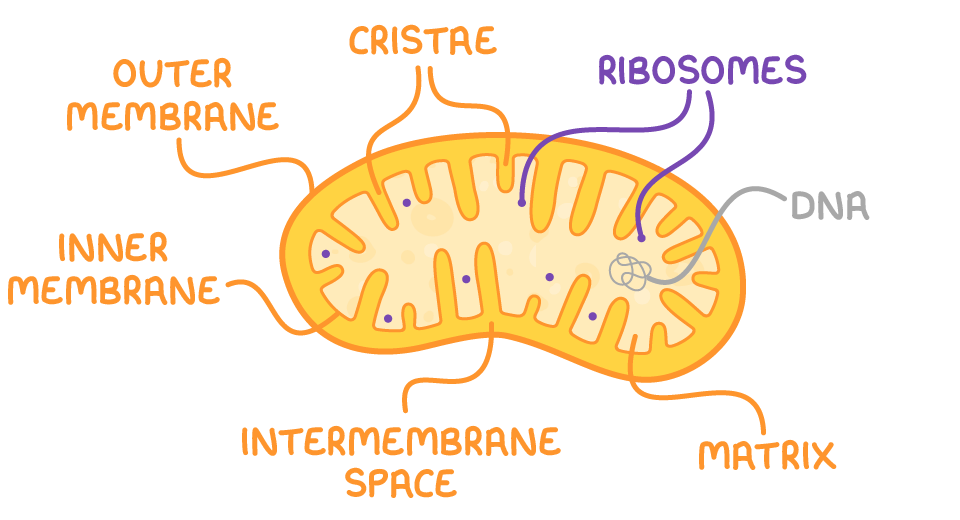
Mitochondria
convert potential energy into ATP during aerobic respiration
Ribosome
made up of large and small subunit
involved in protein synthesis
70s ribosome in prokaryotes
80s ribosome in eukaryote
Golgi body
formed by vesciles
modifies and packages proteins
forms lysosomes
secretes carbohydrates
produces secreting enzymes
Lysosome
from the golgi body
contains enzymes
destroys and digests worn out material
Centrioles
only animal cells
found outside nucleus in centrosome
forms spindle fibres for cell divison
Vacuole in plant cells
large and permanent
storage
surrounded by tonoplast
Vacuole in animal cells
small and temporary
Cell wall
only plant cells
prevent osmotic bursting
give cell strength and support
Plasmadesmarta
links plant cells together
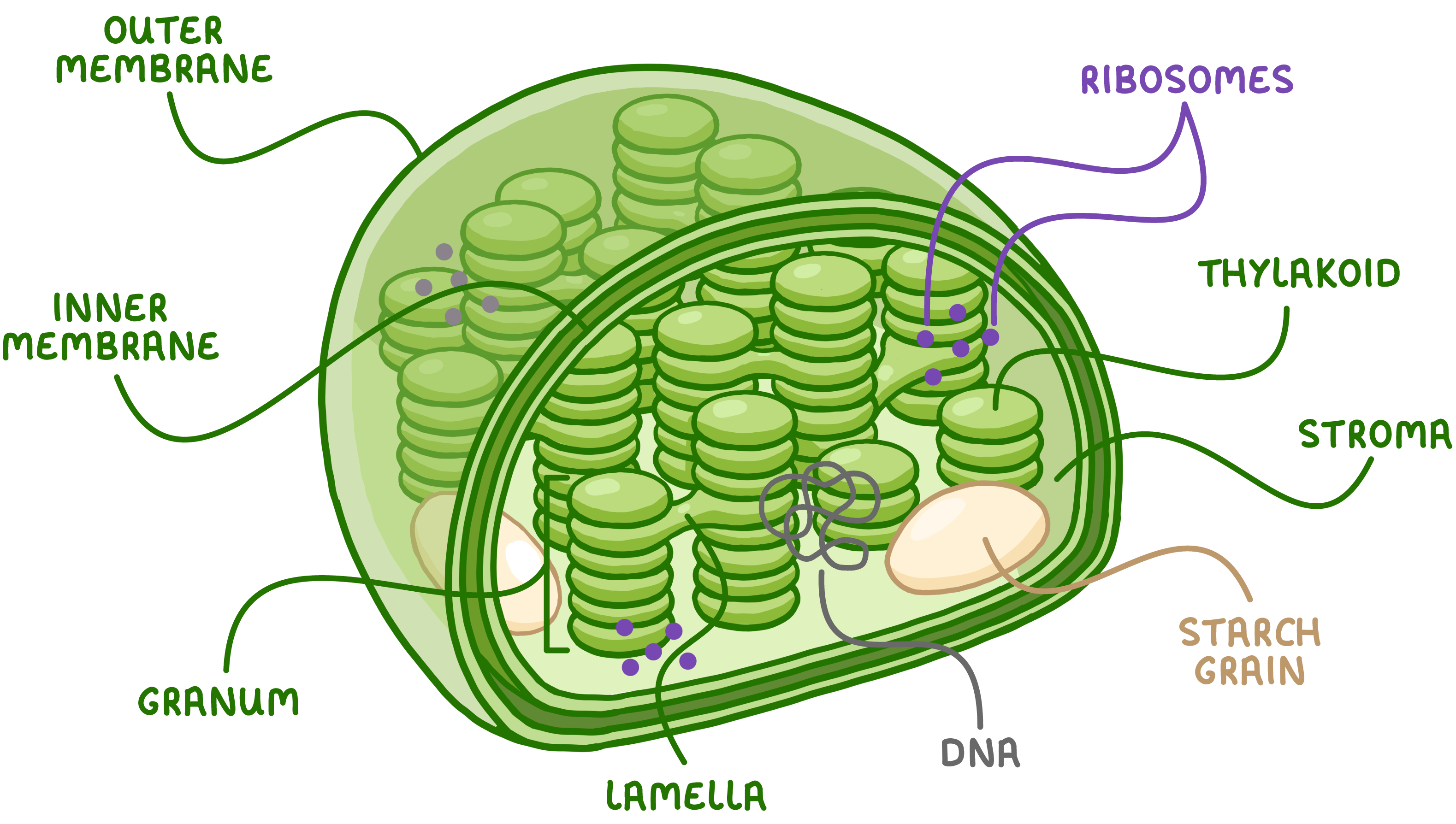
Chloroplast
only plant cells
contains chlorphyll for photosynthesis
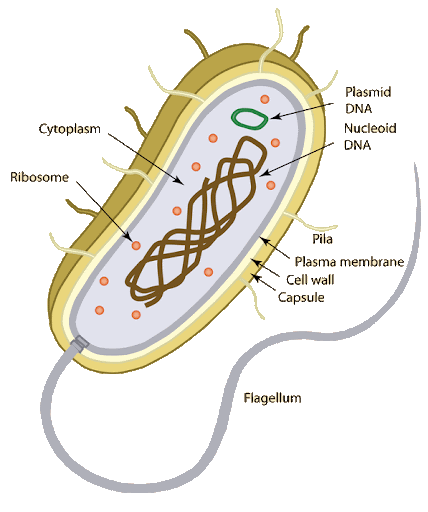
Prokaryotes
found in bacteria
no membrane-bound organelles
DNA lies free in cytoplasm
no nuclear membrane or ER
small ribosomes (70s)
Eukaryotes
plant/animal/fungi/protoctist
membrane bound organelles
DNA in chromosomes
distinct nucleus
large ribosomes (80s)
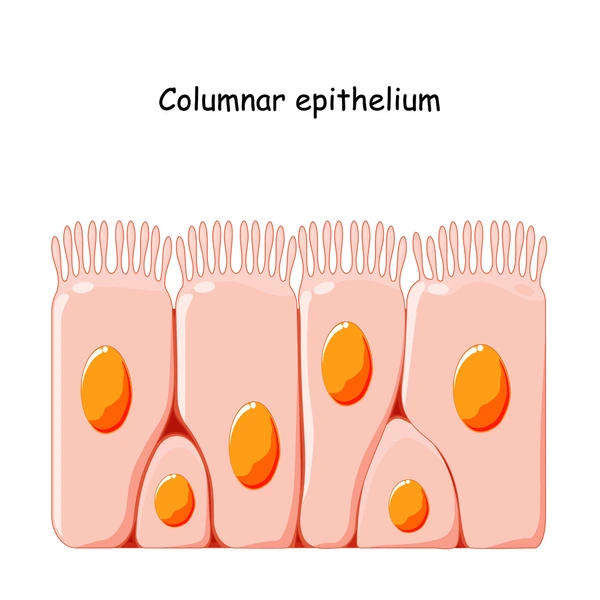
Ciliated columnar epithelium
transport substances e.g. mucus in bronchi
cilia move and sweep substances
columnal
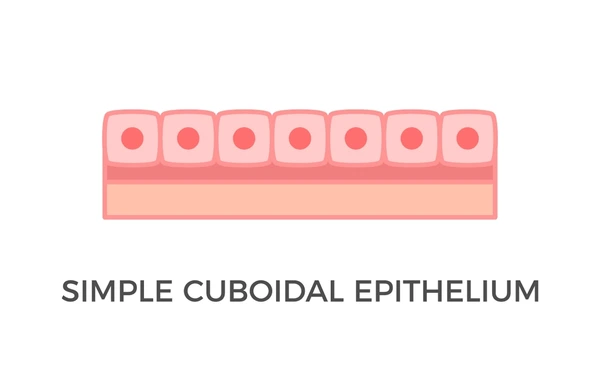
Cubodial epithelium
lines the kidney tubules and small intestine
cubed
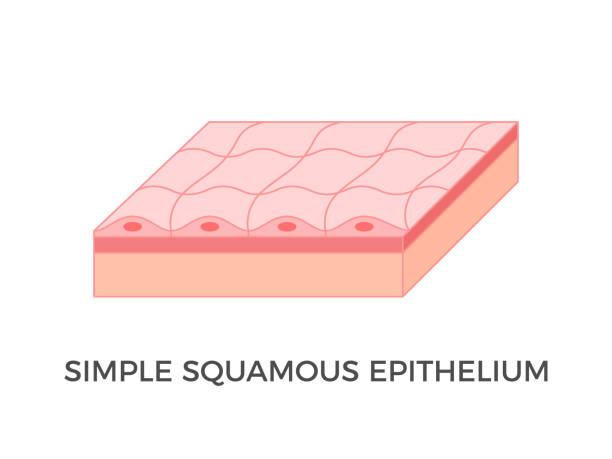
Squamous epithelium
flattened cells
form walls of alveoli and bowmans capsule
Striated/skeletal muscle
attached to bones
bands of long fibres
voluntary muscle tissue
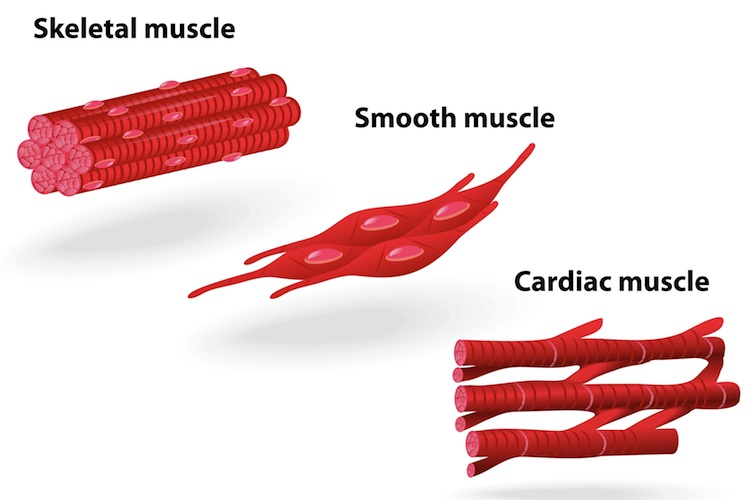
Smooth muscle
individual spindle shapes cells
contract rhythmically
skin/digestive/respiratory systems
incoluntary muscles
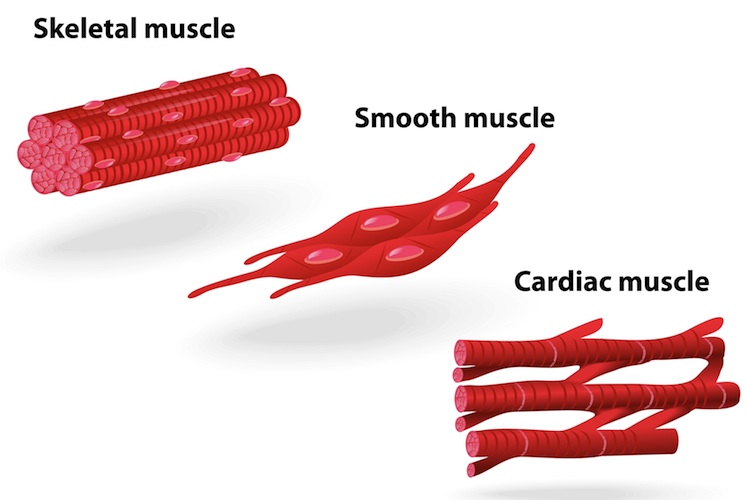
Cardiac muscle
found in heart
contract rhythmically
do not tire out
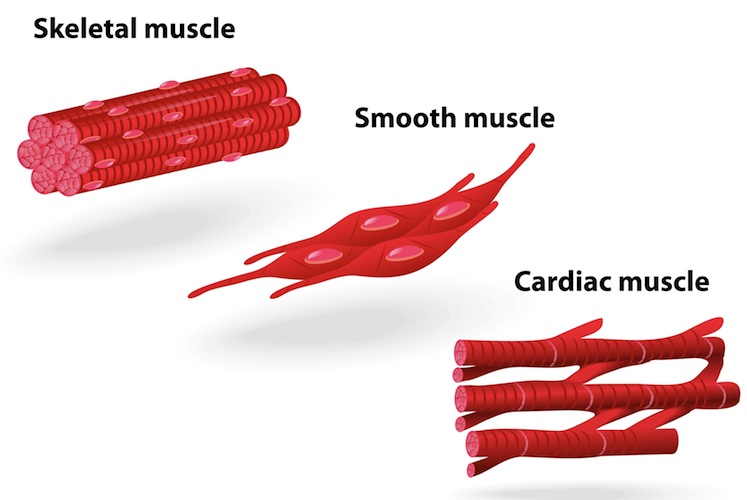
Connective tissues
connect, support or separate tissues and organs
elastic and collagen fibres
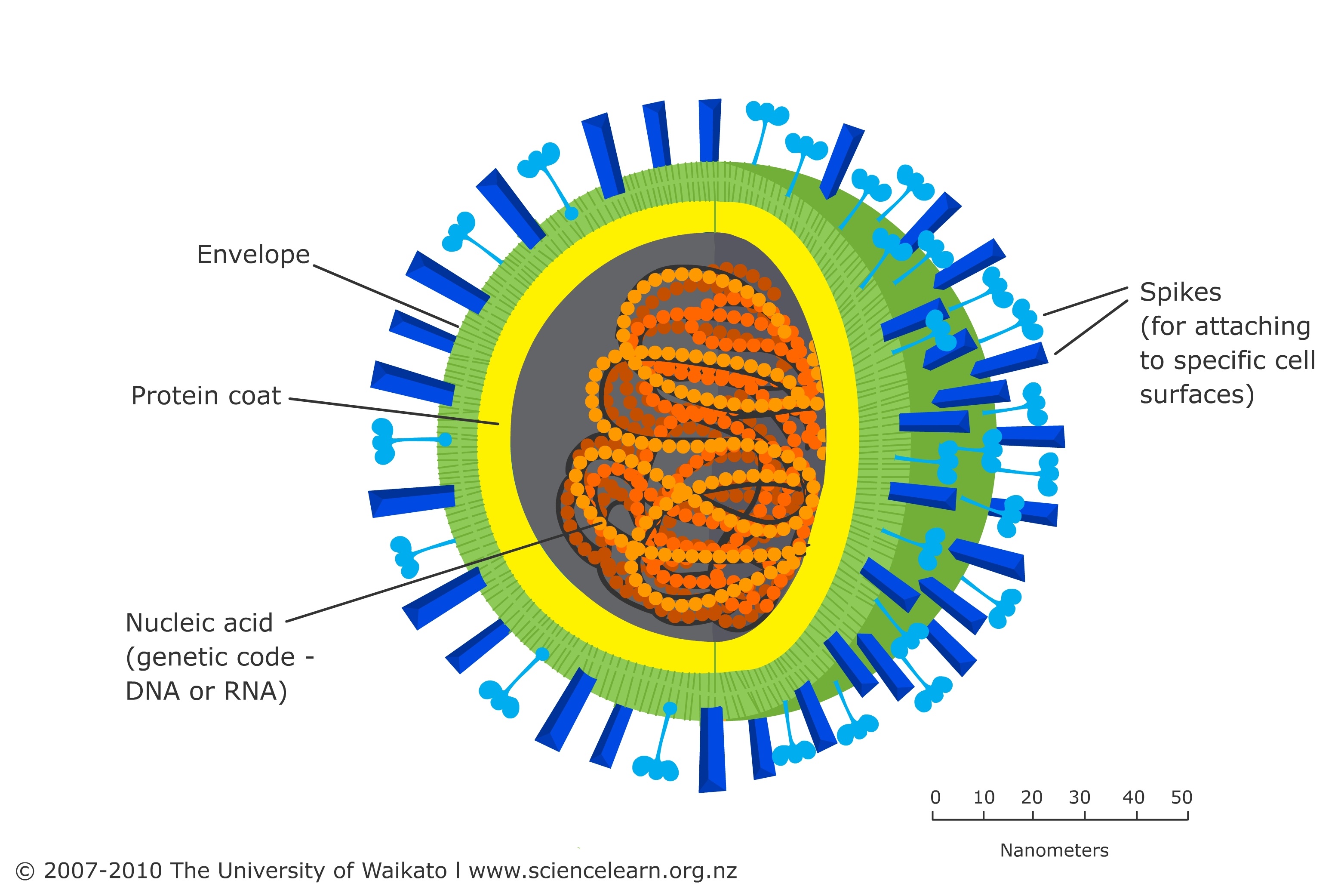
Virus structure