oral radiology ch 1-3 extended
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
radiology
is the science or study of radiation as used in medicine
a branch of medical science that deals with the use of x-rays, radioactive substances, and other forms of radiant energy in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
radiograph
a photographic image produced on film or computer by the passage of x-rays through teeth and related structures
why are dental images important in dentistry?
radiographs (images) enable diagnosis
dental images enable the dental professional to identify many conditions that may otherwise go undetected and to see conditions that cannot be identified clinically
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
roentgen was experimenting with vacuum tubes and fluorescent screen when he discovered an unknown glow
print of his wife’s hand was the first known image taken with x-ray technology

C.Edmund Kells
introduced the paralleling technique in 1896
was the first to use radiographs in the dental practice
radiation
a form of energy carried by waves or a stream of particles
the emission and propagation of energy through space or a substance in the form of waves/particles
capable of producing ions by removing or adding an electron to an atom
x-radiation
a high-energy radiation produced by the collision of a beam of electrons with a metal target in a x-ray tube
x-ray
a beam of energy that has the power to penetrate substances and record image shadows on receptors
dental radiograph
a photographic image produced on a receptor by the passage of x-rays through teeth and related structures
radiography
the art and science of making radiographs by the exposure of a receptor to x-rays
dental radiography
the production of radiographs by the exposure of a receptor to x-ray
dental radiographer
any person who positions, exposes, and processes dental x-ray image receptors
image
a picture or likeness of an object
image receptor
a recording medium; examples include x-ray film, phosphor plate, or digital sensor
imaging, dental:
the creation of digital, print, or film representations of anatomic structures for the purpose of diagnosis
Coolidge
developed first x ray tube
Fitzgerald
went on to improve long-cone paralleling technique
McCormack
used paralleling technique in practical dental radiography
Morton
exposed first dental radiograph in the united states (living patient)
Price
introduced bisecting tehnique
Raper
wrote first dental text; introduced bite-wing tecchnique
Rollins
wrote first paper on the danger of x-radiation
Walkhoff
exposed first dental radiograph
in which shell do electrons have the greatest binding energy?
k shell
what type of electrical charge does the electron carry?
negative
which terms describes two or more atoms that are joined by chemical bonds
molecule
which statement describes ionization
is the production of ions, or the process of converting an atom into ions.
ions are known as atoms that have undergone the process of losing or gaining electrons, therefore becoming electrically unbalanced
which is not a type of particle radiation
nucleons
which term describes the process by which unstable atoms undergo spontaneous disintegration in an effort to attain a more balanced nuclear state
radioactivity
which is not a type of electromagnetic radiation
electron
which statement is incorrect?
wavelength is the distance between waves
which statement is incorrect
x-rays travel at the speed of sound (they actually travel at the speed of light)
which statement is correct
x-rays have more energy than visible light does
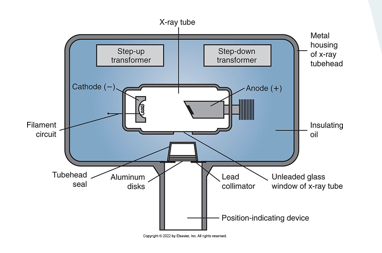
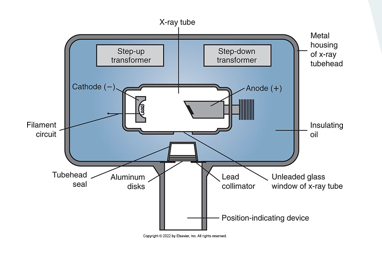
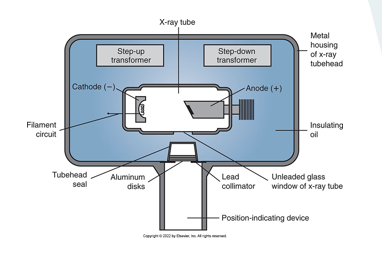
be able to identify and label x-ray tube
step up transformer
step down transformer
cathode
anode
aluminum disk
tubehead seal
position indicating device
unleaded glass
insulating oil
metal sealing
lead collimator window
which regulates the flow of electrical current to the filament of the x-ray tube?
low-voltage circuit
which is used to increase the voltage in the high voltage circuit?
step up transformer
which does not occur when the high voltage circuit is activated
x-rays travel from filament to target
which is the location where x rays are produced
positive anode
which is the location where thermionic emission occurs
negative cathode
which accounts for 70% of all the x-ray energy produced at the anode?
general radiation
which occurs only at 70 kV or higher and accounts for a very small part of x-rays produced in the dental x-ray machine?
characteristic radiation
which describes primary radiation?
radiation that exits the tubehead
which describes scatter radiation
radiation that has been deflected from its path by interaction with matter
which type of scatter occurs most often with dental x-rays?
compton
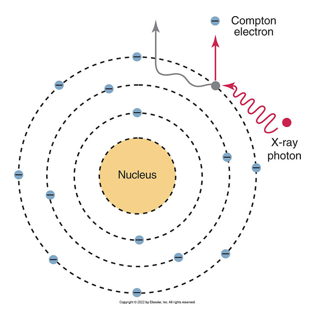
Known at the “binding energy” of an electron
electrons are maintained in their orbits by electrostatic force between positive nucleus and negative electrons
the closer the electron shell is to the nucleus, the stronger the bind will be
radioactivity
is the process by which certain unstable atoms or elements undergo spontaneous disintegration or decay
the dental profession does not deal with radioactivity
cathode
(-) CATNAP
supplies the electrons necessary to generate x-rays
cathode rays are streams of high-speed electrons that originate in an x-ray tube
tungsten filament produces electrons when heated
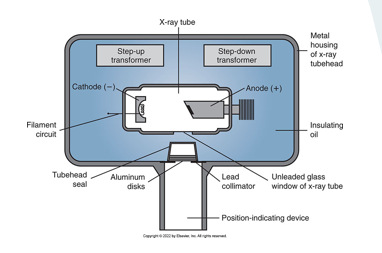
insulating oil
surrounds x-ray tube and transformers, prevents overheating
anode
(+) CATNAP
consists of a wafer-thin tungsten plate embedded in a solid copper rod
converts electrons into x-ray photons
early production of dental x-rays
electricity from the wall outlet supplies the power to generate x-rays
the current is directed to the filament circuit and step-down transformer in the tubehead
the filament circuit uses 3-5 volts to heat the tungsten filament in the cathode
thermionic emission occurs, and the release of electrons
electrons stay in an electron cloud until the high-voltage circuit is activated
primary radiation
the penetrating x-ray beam that is produced at the target of the anode
what is produced and comes out of PID
secondary radiation
x-radiation created when the primary beam interacts with matter
is what is not used from the primary radiation and hits outside of the target
scatter radiation
a form of secondary radiation, the result of an x-ray that gas been deflected from its path by an interaction with matter
scattered radiation is when the radiation is deflected off of something
compton scatter
ionization takes place and x-rays have been made, but the x-ray photon loses energy and focuses in a different direction. does not help in taking a useful radiograph
the ejected electron is termed a Compton electron
free radical formation
occurs when x-ray photons are absorbed by water within a cell
the free radicals combine to form toxins that damage cells
ONLY creates a toxin when it interacts with water via ionization
indirect theory
x-ray photons are absorbed within the cell and cause the
radiosensitive organs
lymphoid tissue
bone marrow
testes
intestines
radioresistant organs
salivary glands
kidney
liver
critical organ
an organ that, if damaged, diminishes the quality of a person’s life
critical organs exposed during dental radiographic procedures include
skin
thyroid gland
lens of the eye
bone marrow
somatic cells
are all of the cells in the body except reproductive cells
the latent period in radiation biology is in the time between
exposure to x-radiation and clinical symptoms
a free radical
combine with molecules to form toxins
direct radiation injury occurs when
x-ray photons hit critical targets within a cell
indirect radiation occurs when
x-ray photons are absorbed and form toxins
which relationship describes the response of tissues to radiation?
linear, nonthreshold
which statement is incorrect?
long-term effects are seen with small amounts of radiation absorbed in a long period
radiation injuries that are not seen in the person irradiated but that occur in future generations are termed
genetic effects
what is most susceptible to ionizing radiation
small lymphocyte
The sensitivity of tissues to radiation is determined by:
mitotic activity, cell differentation, and cell metabolisim
Which of the following is considered radioresistant?
Mature bone cells
An organ that, if damaged, diminishes the quality of an individual's life is termed a:
critical organ
The traditional unit for measuring x-ray exposure in air is termed:
the roentgen
what is the greatest contributor to artificial radiation exposure
medical radiation
the amount of radiation exposure an individual receives varies depending on:
film speed, collimation, technique, exposure factors