3.1 - GDP, national income and business cycle
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
national income
country's total economic output and income, measured as the value of goods and services produced within a specific period
gross domestic product GDP
market value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a time period
nominal GDP
measures a country's economic output
NOT YET ADJUSTED IN INFLATION
circular flow of income
how money moves through an economy, showing the
interactions between households and firms
in the production and consumption of goods and services.
expenditure approach to calculating nominal GDP
adding up total spending on the nation's final goods and services during a specified period.
nGDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
income approach to calculating nominal GDP
adding all incomes earned by factors of production in a nation
nGDP = wages + rents + interest from capital + profit
output approach in calculation nominal GDP
nGDP (measurement the total value of goods and services produced in a country during a specific period)
gross national income GNI
the total income earned by a country's people and businesses, even if it was earned outside the country
nominal vs real values
nominal → not yet adjusted
real → adjusted to inflation
total vs per capita values
total → the whole value
per capita → value of country’s GDP/ GNI divided by its population
advantages of per capita values
differences between population sizes while total doesn’t
accounts for population growth
useful as a summary measure the standard of living in a country
purchasing power parity PPP
a conversion factor
indicates the relative value of currencies based on the cost of ‘basket of goods’ and services, allowing for more accurate economic comparisons between nations.
purpose of PPP
to compare economic productivity and standards of living across countries
by adjusting for differences in price levels.
calculating nGDP
nGDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
calculating nGNI
nGNI = nGDP + net income from abroad
calulating rGDP
rGDP = nGDP of a year x (price level of base year)
rGDP = (nGDP/ price deflator) x 100
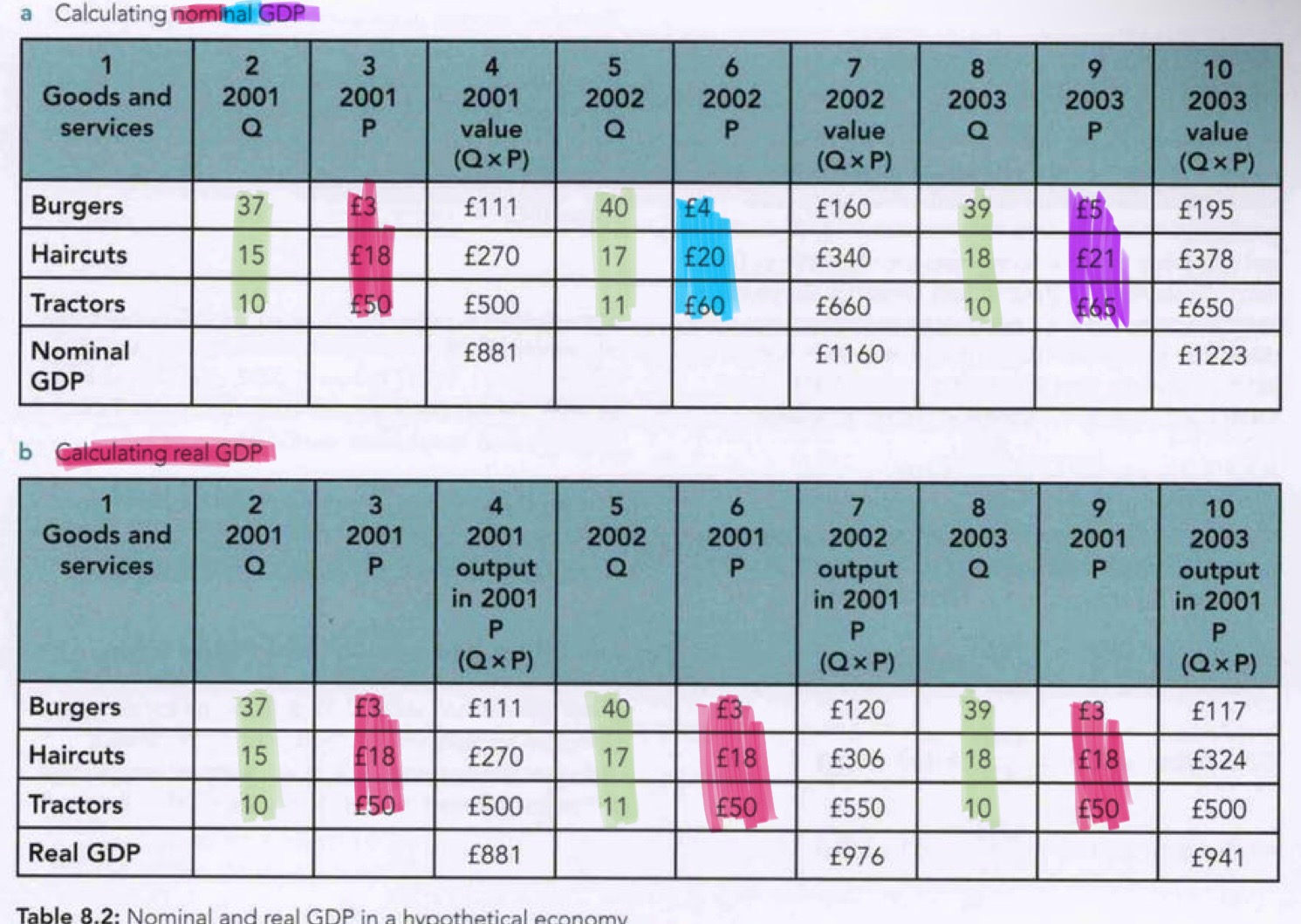
GDP deflator
price index used to convert nGDP to rGDP
GDP deflator = (nominal GDP / real GDP) x 100
base year value
100
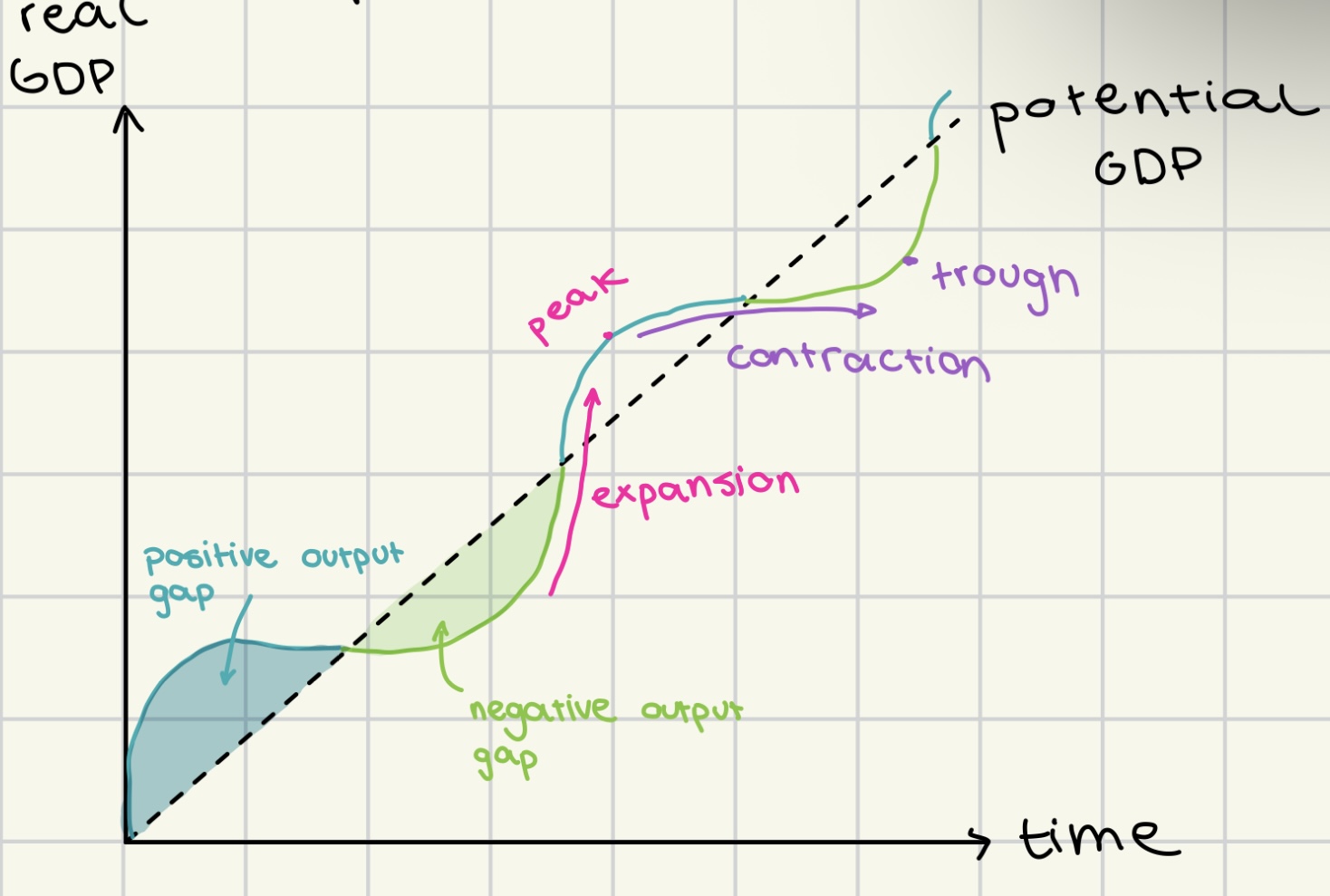
business cycle
shows the short term fluctuations in the growth in the growth of rGDP
alternating periods of expansions and contractions
business cycle graph and assumptions
peak
high rates of economic growth
high inflation
low unemployment
high confidence in market
positive output gap
through
negative economic growth
low inflation
high unemployment
low confidence in market
negative output gap
national income statistics
data that measures a country's economic performance, including GDP, GNI, GNP
national income statistics purpose
making comparisons between countries
wealth
standard of living
provide insight into effectiveness of government policies
insight into economic performance
limitations of using GDP data to compare living standards between countries
lack of information on inequality
no information on quality of goods/services
doesn’t include unpaid/voluntary work/ black markets
GDP would be higher if recorded
doesn’t consider differences in hours worked
doesn’t include the time taken to produce
doesn’t account for environmental factors
gives no reliable comparison of actual standards of living
alternative measures of well-being
OECD better life index
11 variables (education, safety, housing etc.)
happy planet index
measures sustainable wellbeing with 3 factors
(wellbeing x life expectancy)/ ecological footprint
happiness index
10 areas of personal life (health, social support etc.)