Lymphatic System and Immune Response
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terms and concepts related to the lymphatic system and immune response.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
function of lymphatic system
maintenance of fluid balance
returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels
lymphoid organs and tissues
provides strucural basis of immune system
house phagocytic cells and lymphocytes
structure of organs and tissues
spleen, thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes, other lymphoid tissues
lymphatic vessels
return interstitial fluid and leaked plasma proteins back to blood
once interstitial fluid enters lymphatics it is called
lymph
lymph flows toward the heart through a
one-way system
lymphatic capillaries
very permeable
absent from bones, teeth, bone marrow and central nervous system
pathogens travel throughout body through lymphatics
lymph
comparable to blood plasma
has wbc
chyle
lymph formed in the digestive system that is rich in triglycerides (fat) ad looks milky white
lymphatic ducts
empties lymph into venous circulation at the junction of internal jugular and subclavian veins
right lymphatic duct
drains right upper arm and right side of the head and thorax
lymph is propelled by
milking action of skeletal muscle
pressure changes in thorax during breathing
pulsation of nearby arteries
contractions of smooth muscle in walls of lymphatics
valves to prevent backflow
lymphocytes
main warriors of immune system that arise in red bone marrow
lymphocytes mature into what two main varieties
t cells and b cells
lymphocytes function
protects against antigens like bacteria, toxins, viruses, cancer, mismatched rbcs
macrophages
phagocytize (eat) foreign substances; help activate t cells
dendritic cells
capture antigens and deliver them to lymph nodes; activate t cells
reticular cells
produce reticular fiber stroma that supports other cells in lymphoid organs
lymph nodes
principal lymphoid organs of the body that are embedded in connective tissue
common causes of swollen cervical lymph nodes
bronchitis, common cold, ear infections, scalp infections, strep throat, tonsillitis, ear/nose/throat/mouth infection
area where lymph nodes can be felt
groin, armpit, behind the ears, back of the head, sides of the neck, under the jaw/chin
lymph nodes functions
filter lymph by macrophages destroying microorganisms and debris
it activates the immune system; lymphocytes activated and mount attack against antigens
structure of a lymph node
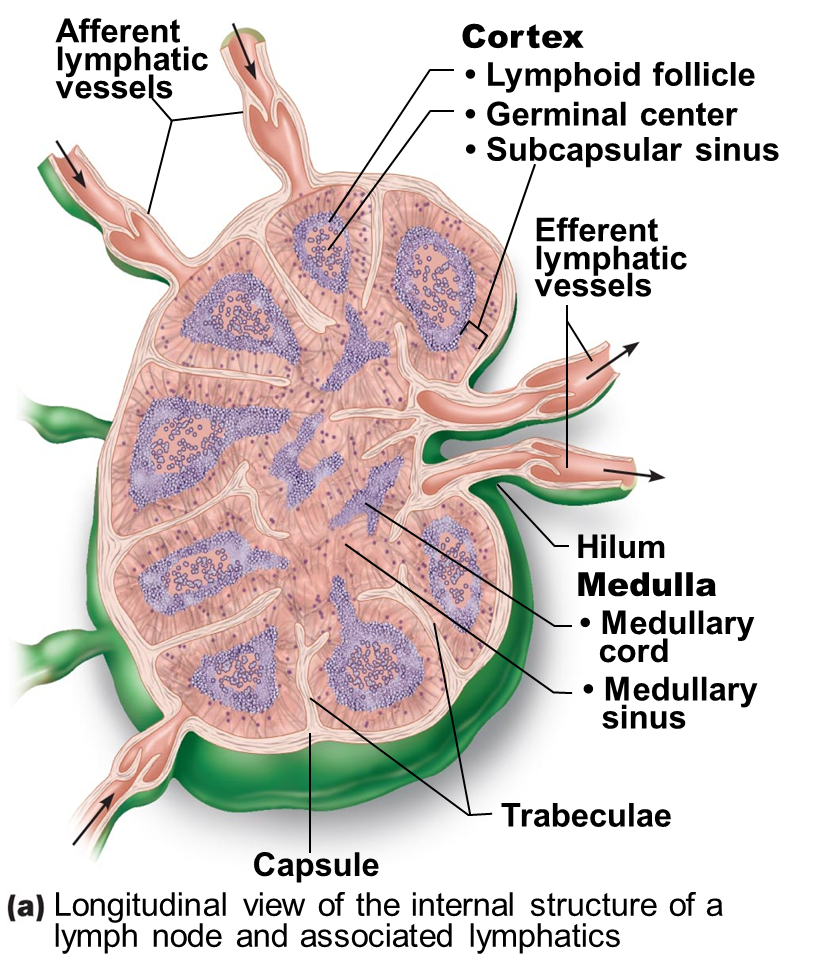
largest lymphoid organ
spleen
functions of spleen
site of lymphocyte proliferation
cleanses blood of aged cells/platelets
stores breakdown products of rbc
white pulp area of the spleen is
around central arteries
red pulp area of the spleen is
in venous sinuses and splenic cords
Thymus
maturation area for t-cells
increases in size and most active during childhood
thymic lobules
contain outer cortex and inner medulla
largest collections of Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
are found in tonsils, appendix, Peyer’s patches (lymphoid follicles)
Mucosa-associated Lymphoid tissue (MALT)
lymphoid tissue in mucous membrane throughout the body that protects from pathogens trying to enter the body
simplest lymphoid organ
tonsils
tonsils
contain follicles with gerinal cneters
not fully encapsulated
tonsils have overlying epithelium that invaginates forming what
tonsillar crypts that tray/destroy bacteria and allows immune cells to build memory for pathogens
appendix
serves as a haven for useful bacteria
blind-ended tube connected to the cecum
Peyer’s patches and appendix
generate “memory” lymphocytes
destroy bacteria
3
there are ___ times as many cells from bacteria, archaea, etc living in you than you can cell (which is about 10 trillion)
immunity
resistance to disease (immune = free)
innate defense system in nonspecific
surface barriers: skin. mucosa
internal defenses: anti-microbial proteins, phagocytes, inflammation
adaptive defense system is specific but slow
humoral immunity: b-cells
cellular immunity: t-cells
innate defense
mechanical surface barriers that ward off invading pathogens
chemical surface barriers
protective chemicals inhibit/destroy microorganisms
defensins
antimicrobial peptides and inhibit their growth
internal defenses (specifically cells and chemicals)
necessary if microorganisms invade deeper tissue
phagocytes, natural killer (NK), antimicrobial proteins, fever, inflammatory response
phagocytes include
neutrophils and macrophages
Neutrophils
most abundant WBC, but die fighting
macrophages
develop from monocytes and are the chief phagocytic cells
phagolysosome
when phagosome fuses with lysosome
mechanisms of phagocytosis
phagocyte must adhere to particle
cytoplasmic extensions bind to/engulf particle in vesicle called phagosome
inflammatory response
triggered whenever body tissues injured
prevents spread of damaging agents
disposes of cell debris and pathogens
alerts adaptive immune system
sets the stage for repair
cardinal signs of acute inflammation
redness, heat, swelling, pain, impairment of function
what are the chemical signals released by damaged cells
kinins, prostaglandins (PGs), and complement
aspirin
relives some of the effects of pain, fever, and blood clotting
kinins, prostaglandins (PGs), and complement
dilate arterioles (hyperemia)
make capillaries leaky (so wbc can get out)
many attract leukocytes to area