Enteric methane
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Rumen functioning
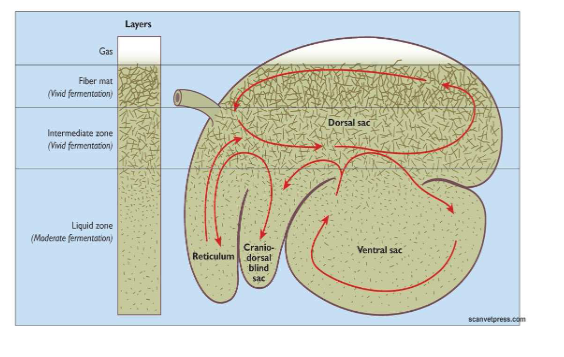
rumen anatomy and digesta content
layers
gas
fiber mat - vivid fermantion
intermated zone - vivid fermantion
liquid zone - moderate fermatnion
dutch dairy cow eats on average per day
55 kilo roughage
75% grass
25% corn
5 kg of concentrate
100 liters of water
100 grams of vitamens and minerals
Fate of nutrients in the rumen
can end up as microbes, SCVFA, or feed
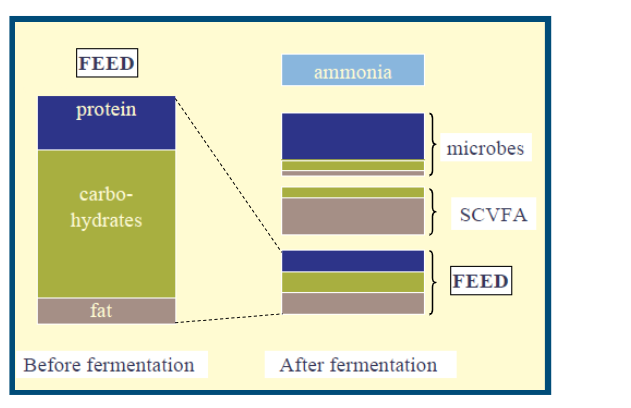
methane production - how it works in the rumen
cellulose, strach and sugars
pyruvate
acetate
Enteric fermentation
Digestive process
carbohydrates are broken down to VFA under anaerobic conditions
CH4 is produced as by-product
In the rumen we find the following
protozoa
bacteria
fung
archeae live fry or in symbiosis with protozoa
methane production - possible interventions
inhbit methanogens direct or indirect via protozoa
alternative H2 sinks like NO3/SO3
Complete inhibition
redirect fermentation to propionate formation by modulation of bacteria
acetate, butyrate, propionate
Nutritional strategies to reduce GHG emissions from ruminats
improve feed efficiencye, roughage quality, concentrates
lipid supplements to diets
feed additives (modify rumen microbiota, defaunation
feed additives (alternative hydrogen sinks)
novel feed sources
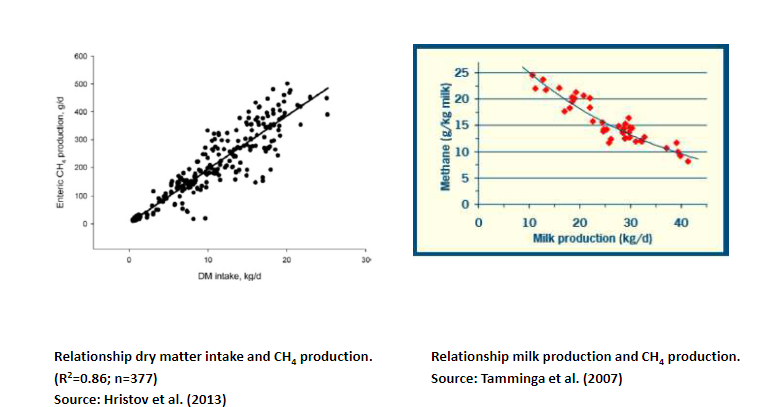
methane production - intake and milk production
positive relationship dry matter intake and CH4 production
negative relationsship milk production and CH4 production
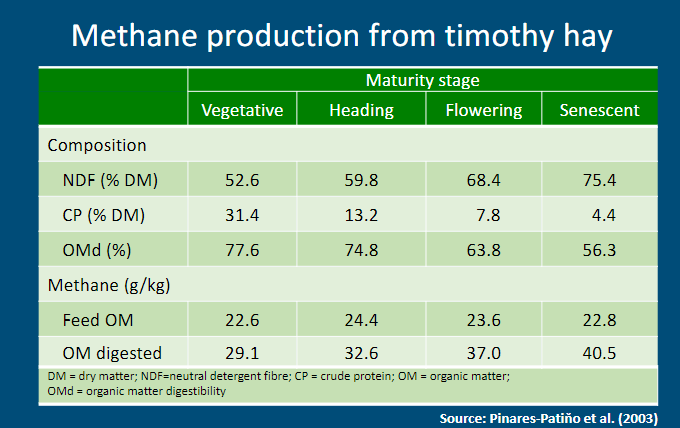
Effect of plant physiological stage
see picture
Effect of concentrates
methane production roughage cs concentrate
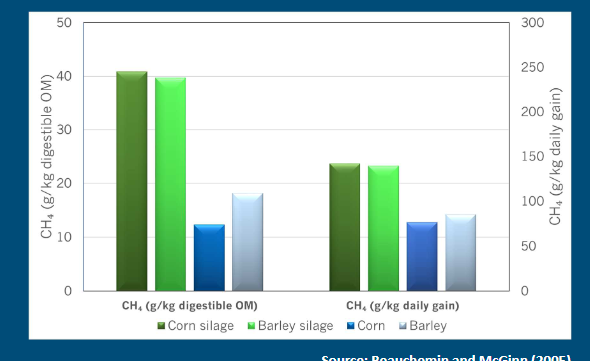
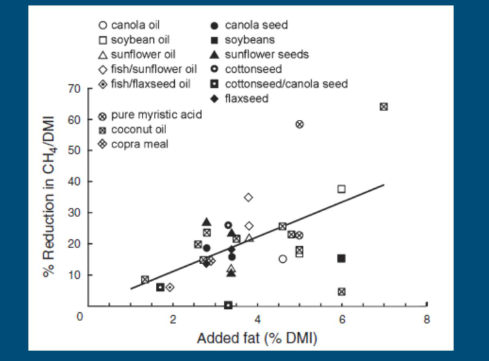
effect of lipid supplementation to diets
pisitive relatonsih
more fat, higher the percentate of reduction CH4
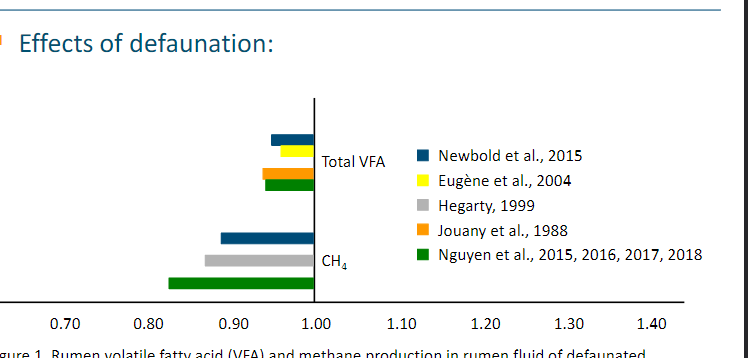
Methane production: feed additive
see picture
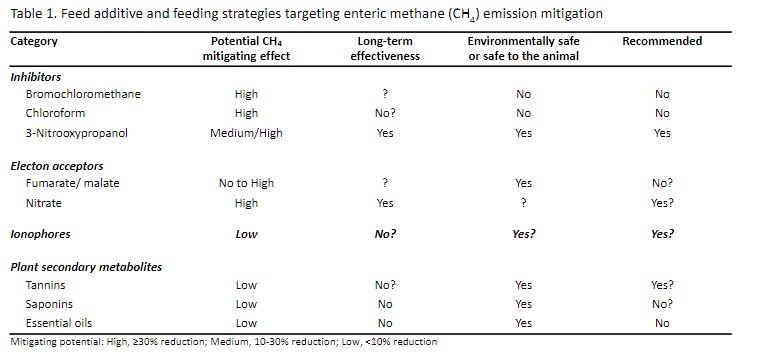
feed additivesL nutritional stragegies
an overview
see picture
seaweed
asparogopsis taxiformis
feeding cows seaweed could reduce their methane emissions by more than 80
effective component is CHBR3 bromoform
3-nop 3-nitrooxypropanol
can save co2a
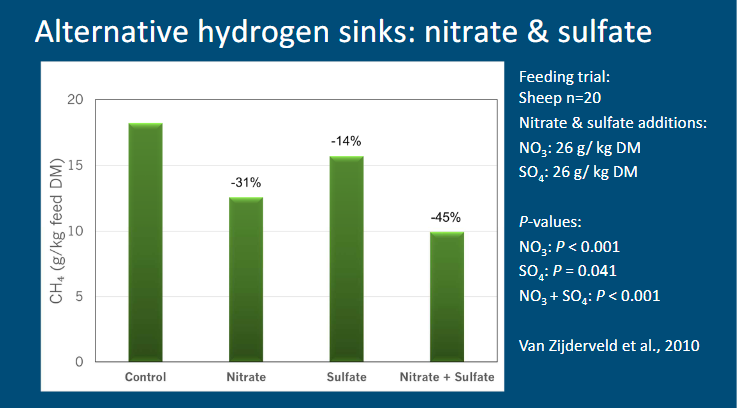
lternative hydrogen sink nitrate and sulfate
see picture
role of tannins in relation to methane mitigation
two functional groups
condensed tannins
regarded being beneficial
prodelphinidinds (PD) and procyanidins (PC)
hydrolysable tannins
regardes as being harmful
gallotannins and ellagitannins
wheat straw
abundant agricultural by-product with a worldwide prduction of 529 million tons annually
lignin
can only be degraded in the presence of oxygen
bonds between ligning and carbohydrates have to be broken
different methods to unseal the cell walls
only some fungi can degrade lignin