Protein Analysis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Methods of protein purification and analysis
• Purification- cell fractination, chromatography, ultrafiltration
• Analysis- spectroscopy, SDS-PAGE, x-ray crystallography
Purpose of protein purification
• Study protein structure, function and interactions
• Essential in understanding disease mechanisms and drugs development
• Biopharmaceutical manufacturing - insulin, growth hormone
Study of proteins
• Control all major cellular functions, important in drug manufacturing
• Must be purified to determine structure and mechanism of action
• Common characteristics- amino acid structure, 3D shape
• Differ in size, shape, net charge, hydrophobicity, stability (resistance to heat), isoelectric point (pH at which they carry no charge)
• Aspirin inhibits COX to prevent prostaglandin formation (inflammation)
Initial considerations in protein purification
• Proteases - enzymes that digest proteins
• Source - bacteria, mammalian cells, biological fluids like blood, saliva, tears
• Can be isolated from original source (native) or expressed via genetic engineering (recombinant)
Cell lysis
• Detergent- physical
• Sonication- sound waves
• Osmotic shock- hypoosmotic solution
• Should leave membrane bound organelles intact, removed by centrifugation, releases proteins from cell
Differential centrifugation
• Centrifugation at increasing speeds to yield pellets of specific organalles
• Low speed - nuclei
• Medium - mitochondria
• High - lysosomes
• Supernatant - soluble target proteins, assay can be performed to identify where it is if not soluble
Column chromatography
• Stationary phase- solid, packed into a column
• Mobile phase- liquid or gas, carries material, flows through column
• Separation based on compounds interaction with stationary phase, large proteins come out first
• Partition chromatography- smaller molecules partition into pores e.g. gel filtration (molecular size)
• Adsorption chromatography- molecules adsorb onto stationary phase e.g. ion exchange (charge), affinity (ligand), hydrophobic interaction
SDS-PAGE
• Used to monitor protein purity
• Denatures protein, separates by mass
• Can resolve many proteins, individual bands can be excised and sequence
• Molecular weight determined by Rf calculation
Hydrodynamic radius
• Effective radius a protein has as it tumbles in solution, if proteins were strictly spherical it would correlate directly with their MW
• Asymetrical proteins may appear larger that spherical proteins of the same MW, elute earlier on a get filtration column
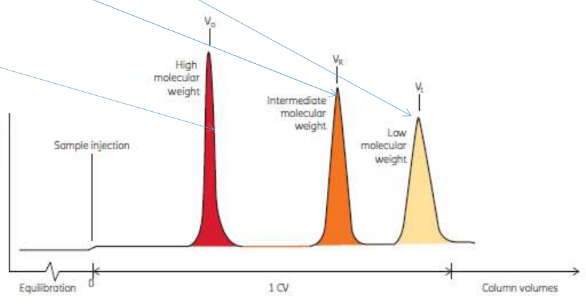
Gel filtration principles
• Filters based on size
• Vo - void volume (outside resin)
• Vi - volume inside resin
• Vt - total column volume (Vi + Vo) (Vg negligable)
• Ve - elution volume
• Kav - partition coefficient (Ve - Vo) / (Vt - Vo), larger proteins closer to 0, smaller closer to 1
• Large proteins elute first, too big to enter pores
Gel filtration procedure and considerations
• Equilibrate column with buffer that will be used in reaction, only one buffer with optimum pH and NaCl added to prevent non-specific electrostatic interactions
• Load concentrated (but less than 50mg/ml) sample onto column, less than 2% of Vt
• Wash continiously with buffer until proteins separate and elute
• Chromatogram will show order of elution
• Only about 10 proteins can be resolved
• Membrane proteins may not behave as expected due to detergents
Gel matrices used and applications of gel filtration
• De-salting - salts can be separated from proteins due to their small size
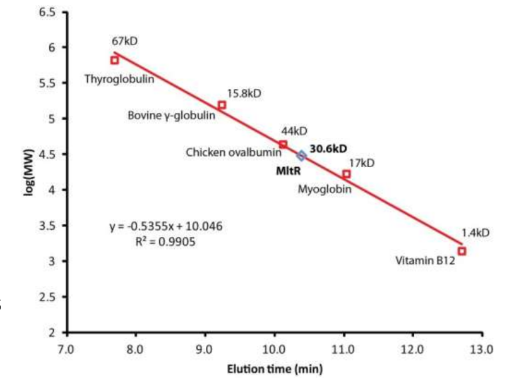
• Estimating molecular weight - load protein standards, plot MW vs elution time or volume and use graph to estimate
• Separating mixture of proteins by MW
• Gel matrices used - agarose (sepharose), dextran (sephadex), polyacrylamide (biogel)
Isoelectric point
• Proteins have surface charges based on amino acid composition (acidic vs basic) and environmental pH
• Isoelectric point - pH at which the net charge is zero
• If the pH is above the pl the protein has a negative charge
• If the pH is below the pl the protein has a positive charge
• Determined by algorithms that compare sum of acidic and basic side chains or isoelectric focusing, proteins migrate through pH gradient and stop where the net charge is 0
Principle of ion exchange chromatography
• Separates proteins based on electrical charge, can separate molecules that differ by just one charged amino acid
• The resin used is charges - cation exchanger is negatively charged and binds positive proteins, anion exchanger opposite
• pH of buffer is adjusted to ensure protein has the charge the resin requires e.g. pH<pl so protein is positively charged
• Elution - altering pH causing the protein to gain or lose charge, increasing NaCl concentration, ions will compete with protein
Myoglobin purification via ion exchange
• Add mince to buffer and strain, pl of 7
• Centrifuge and remove supernatant (myoglobin)
• Equilibrate column with pH 5.6 buffer, myoglobin becomes positively charged and binds to sephadex
• Weak cation exchanger
• Eluted as pH 7.5
• Lysozyme - pl 9.4, pH 8.2, elution at 10.2
What are ion exchange columns made of
• Backbone material - gives structure e.g. polystyrene, agarose
• Functional group (charged) - strong (stays charged over wide pH range) or weak anion or cation exchangers, does not indicate binding ability